一.I/O多路转接之epolI


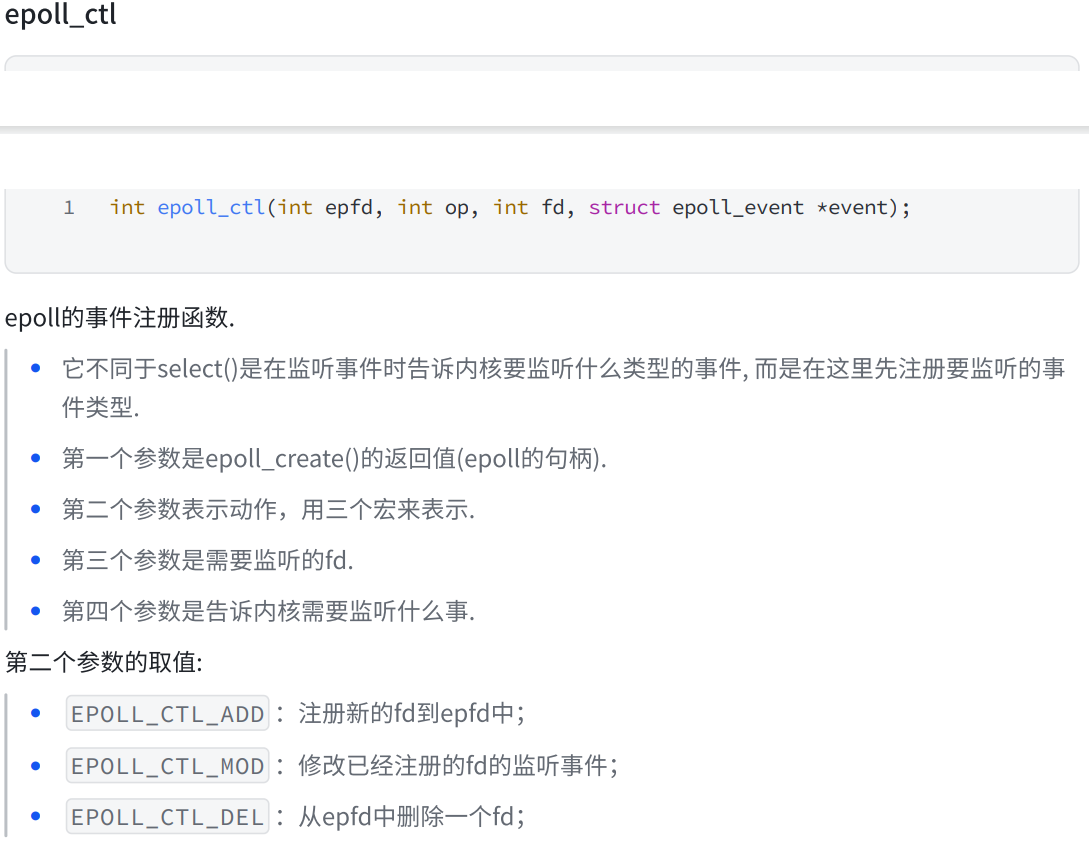


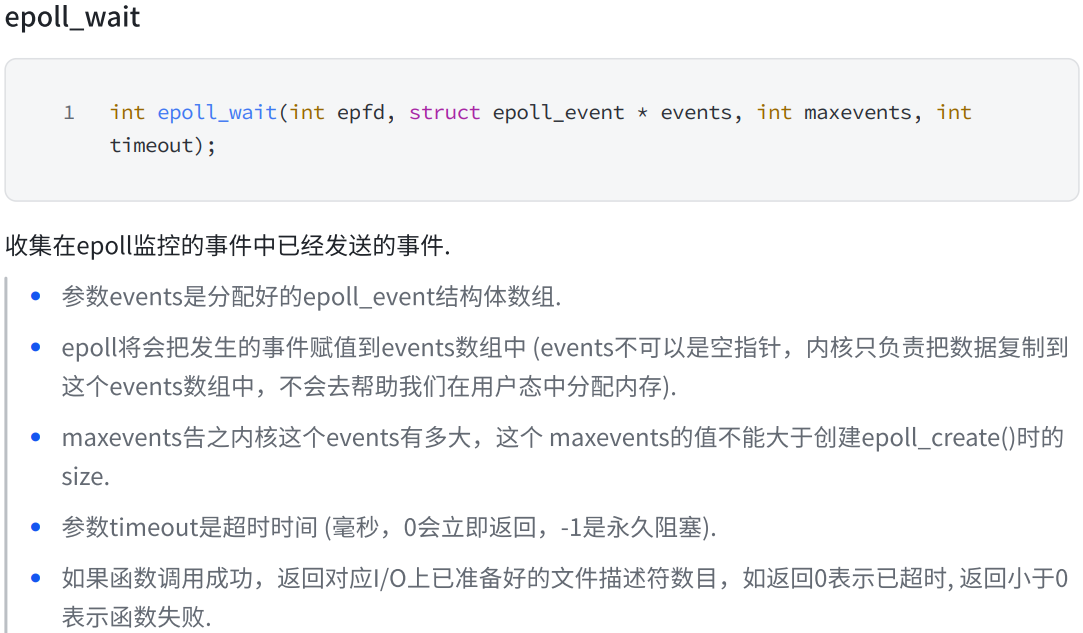
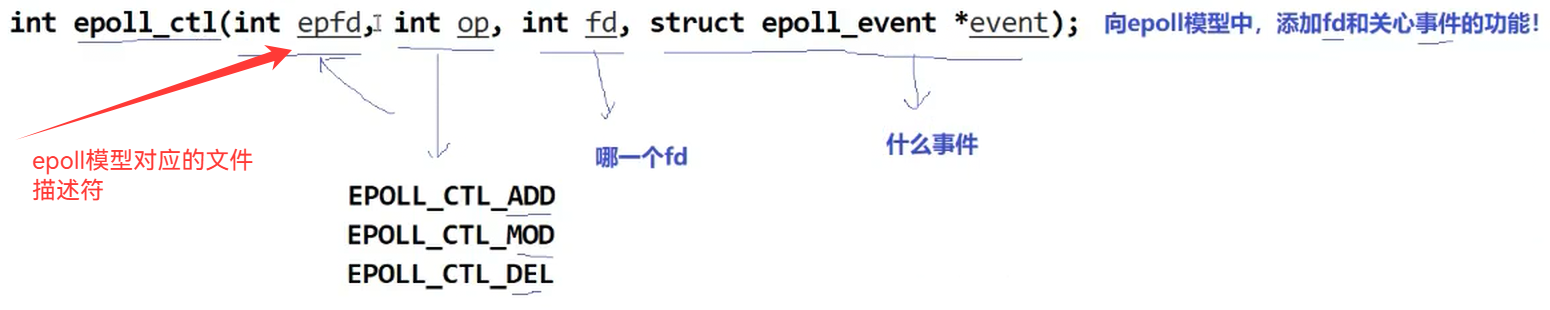
二.epoll接口详解



![]()


这些事件也是宏定义,和poll也是差不多的
三.epoll的原理 & 接口重弹
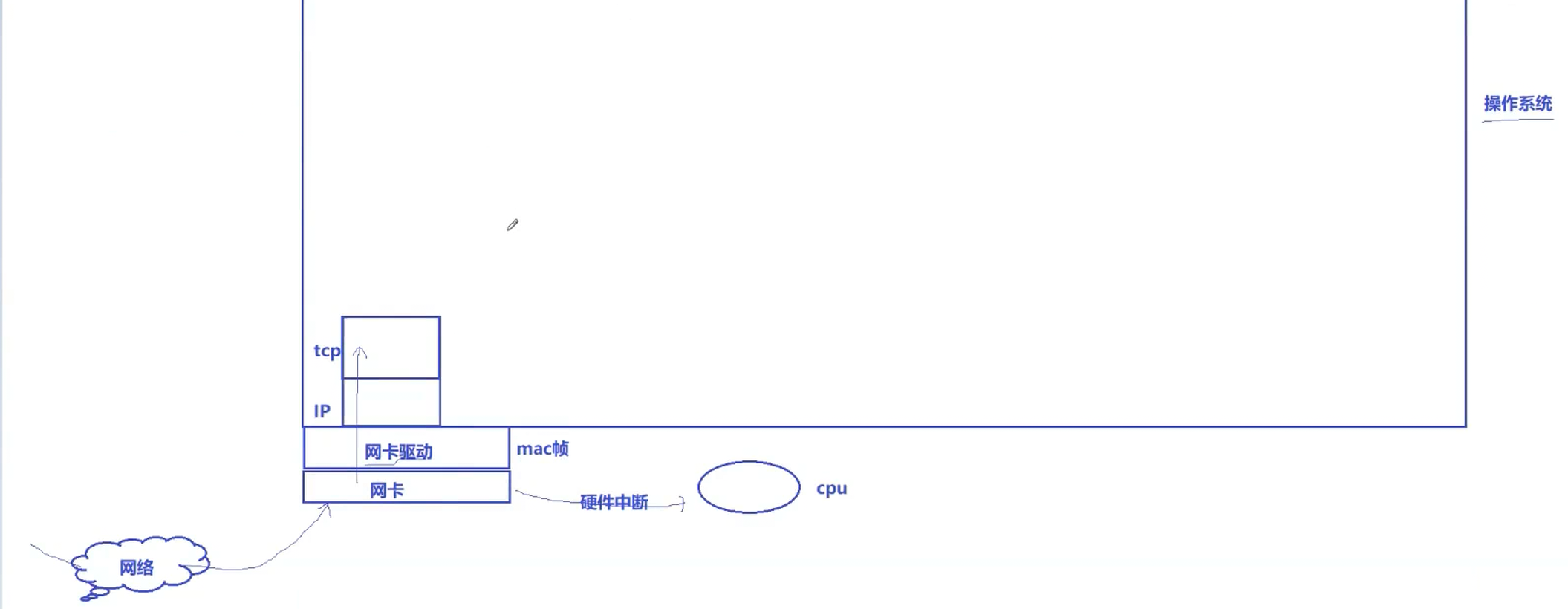
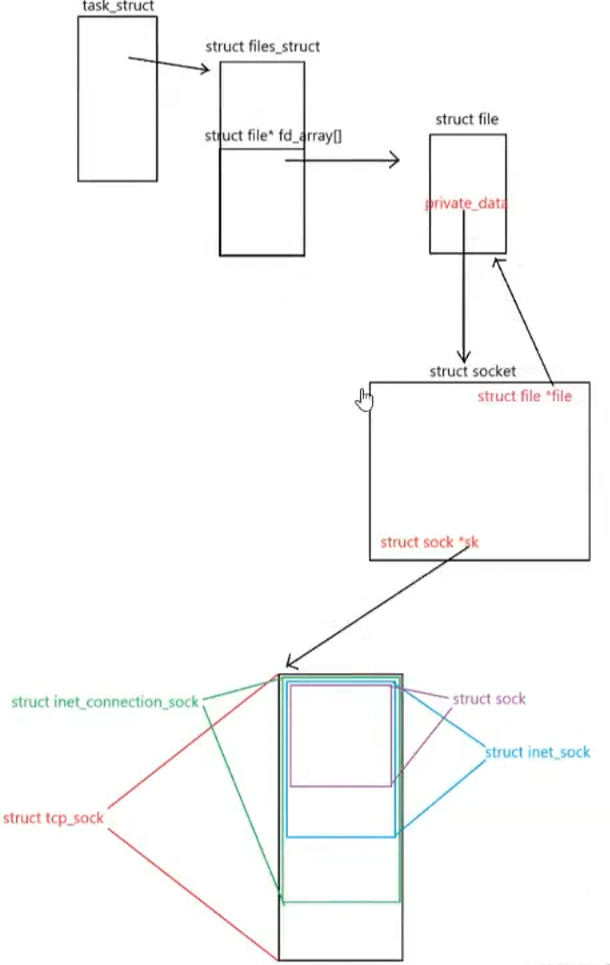
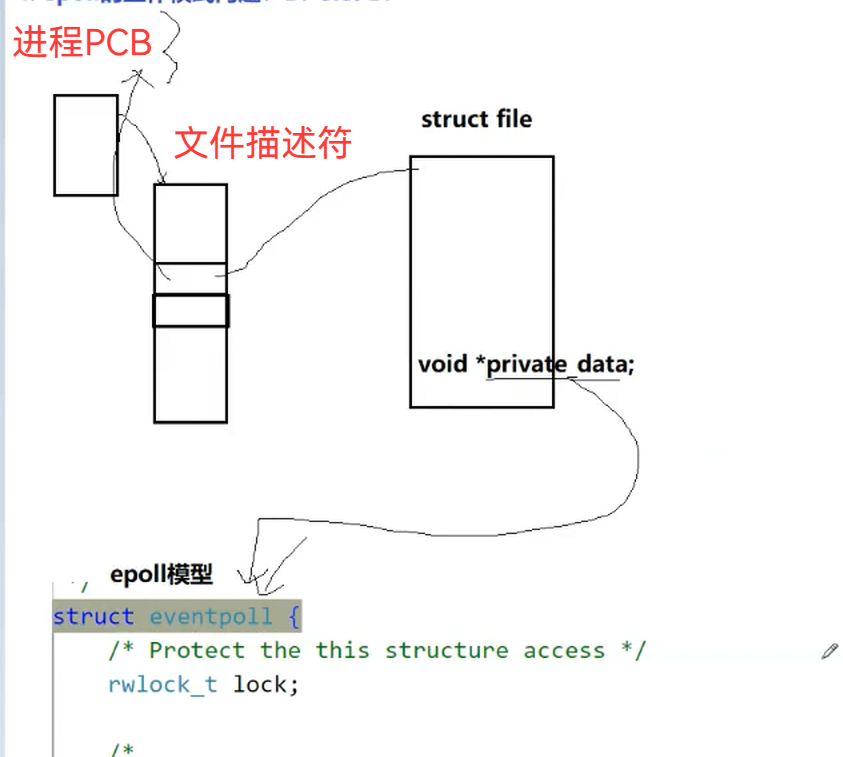
我们要指向对应的tcp_sock结构,因为sock是结构体的第一个成员,所以我们可以进行强转
这个sock,inet_sock等都是一套继承体系

UDP和TCP的区别就是UDP没有对应的inet_connection_sock(链接管理相关)
在上层都叫我们对应的sock,下层进行了封装

select会将我们对应的文件描述符表进行遍历,发现有对应的信息就向上返回(但是这样效率太低了)
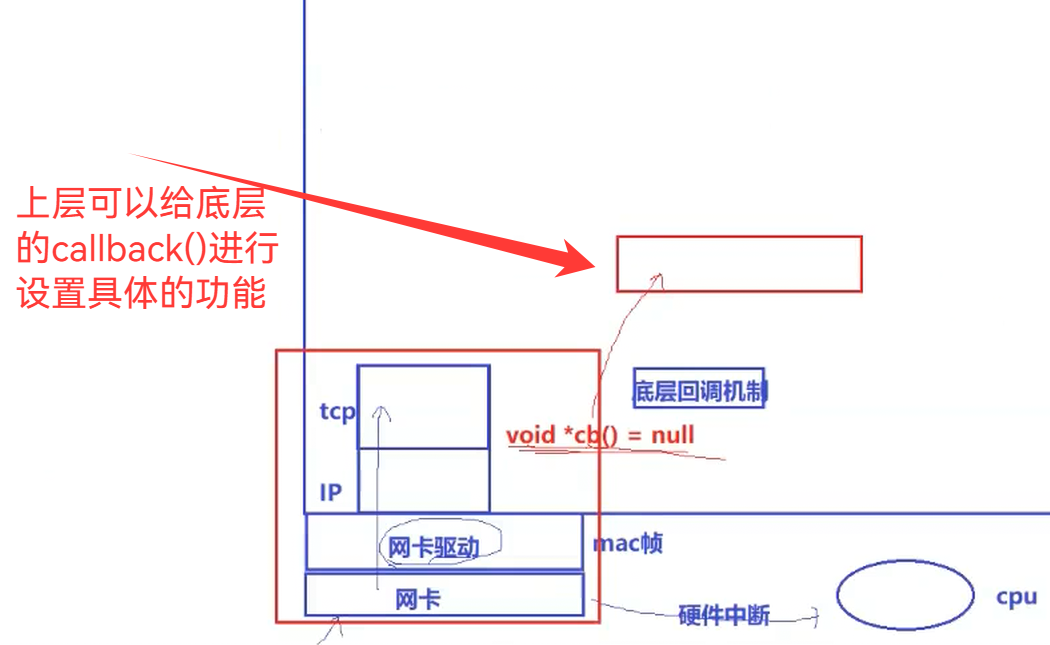
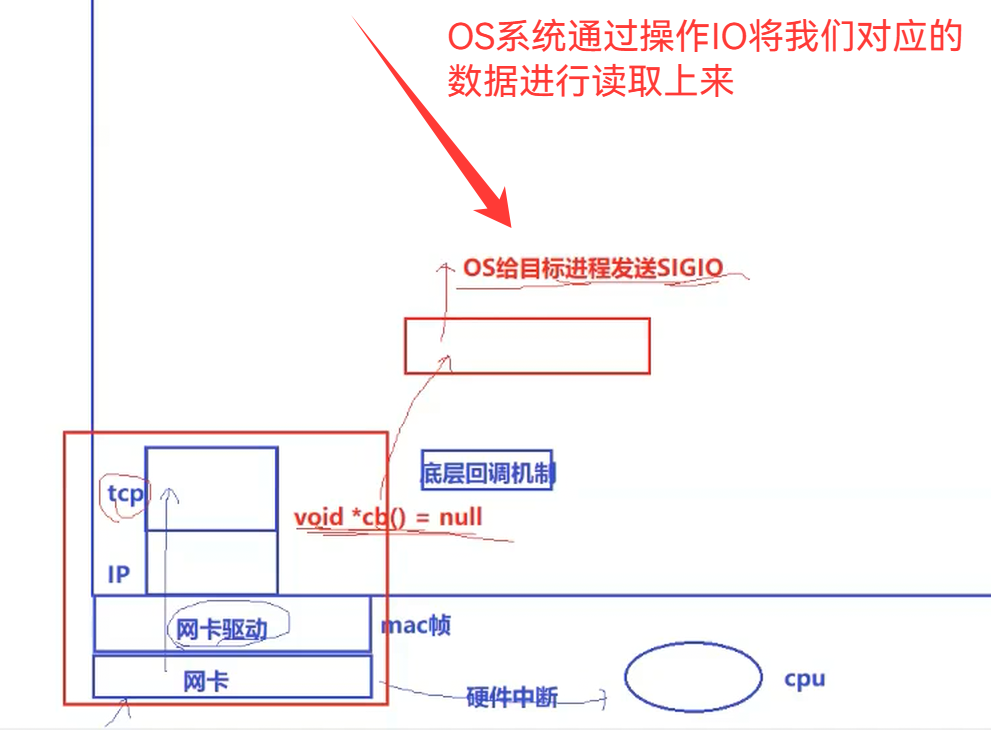
但是这里不是我们对应的select的实现机制(信号驱动式IO的原理)
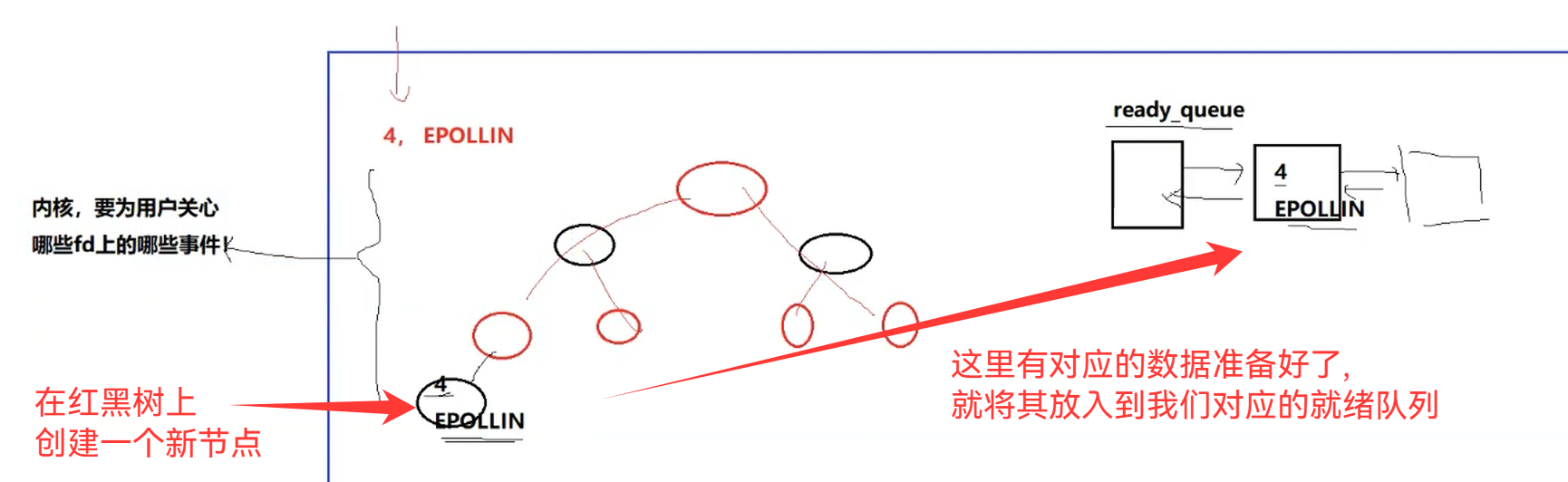
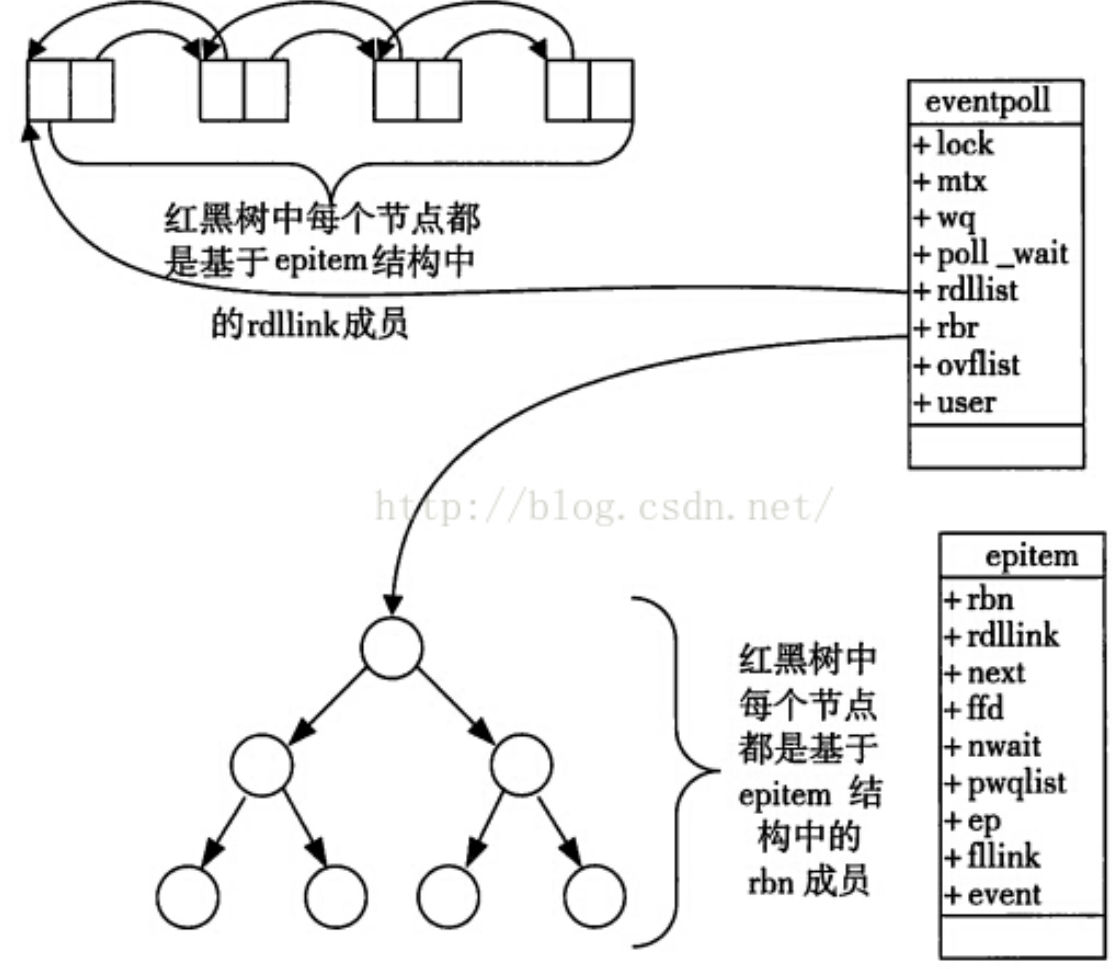
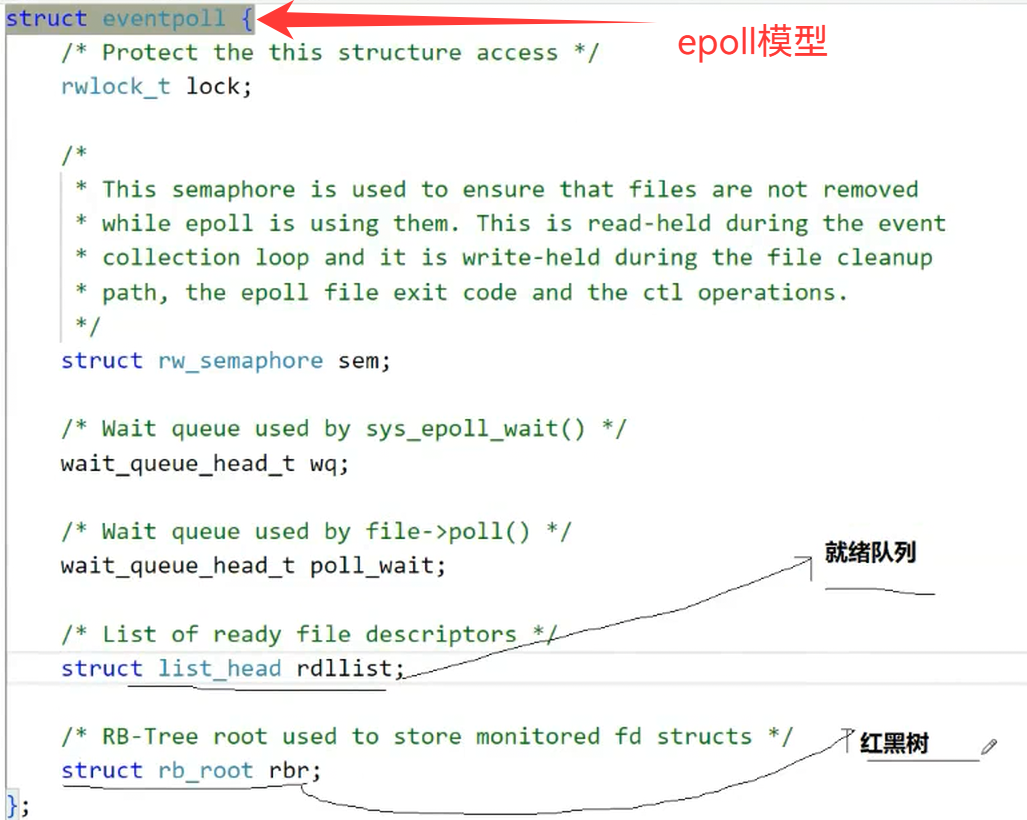
一个节点代表,一个文件描述符和用户要关心的该文件描述符的所有事件

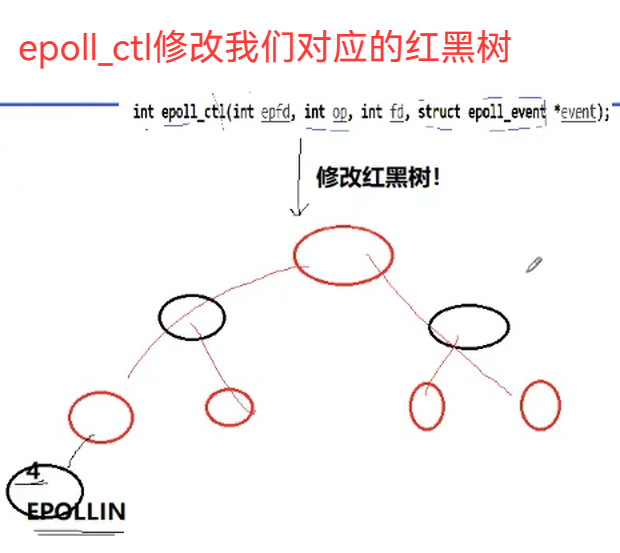
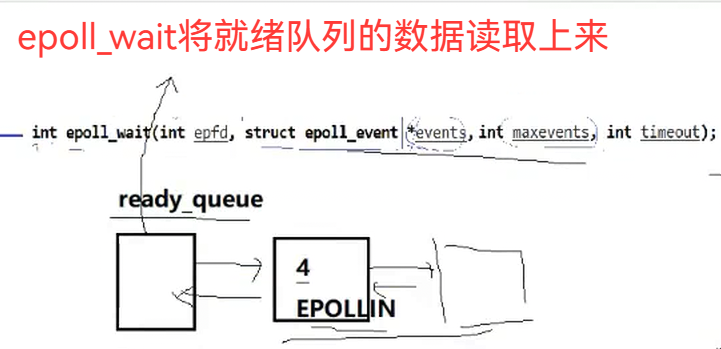
那我们怎么知道红黑树该节点已经就绪了呢?
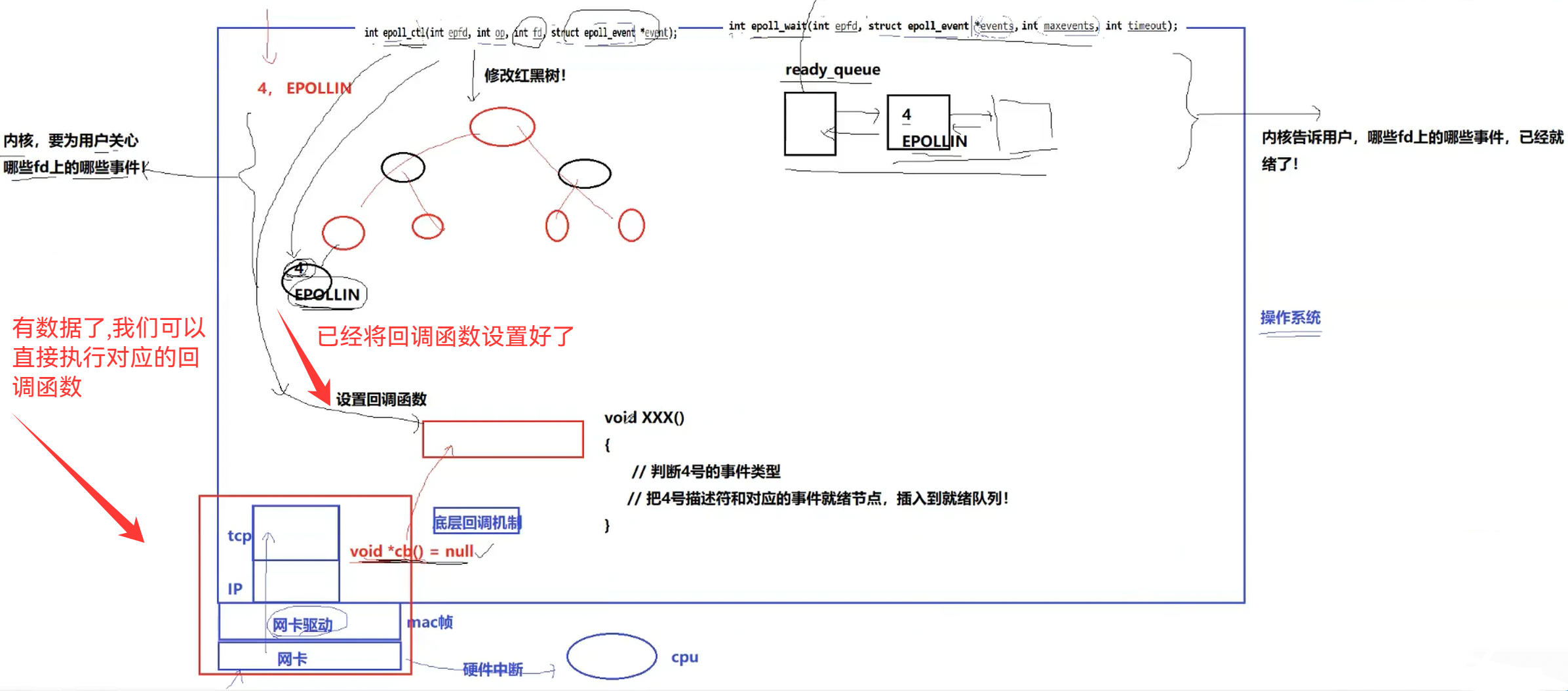
整体的这一套就叫做我们的epoll模型(宏观模型)



只要移动指针就能实现对应的将节点信息移动到就绪队列中

所以后续我们操作对应的epoll模型就是对文件描述符进行操作

四.epoll代码编写

#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <memory>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include "Log.hpp"
#include "Socket.hpp"
using namespace SocketModule;
using namespace LogModule;
const int gdefaultfd = -1;
// 最开始的时候,我们的服务器,只有一个文件描述符
class EpollServer
{
static const int revs_num = 64;
public:
EpollServer(int port) : _port(port),
_listen_socket(std::make_unique<TcpSocket>()),
_isrunning(false),
_epfd(gdefaultfd)
{
}
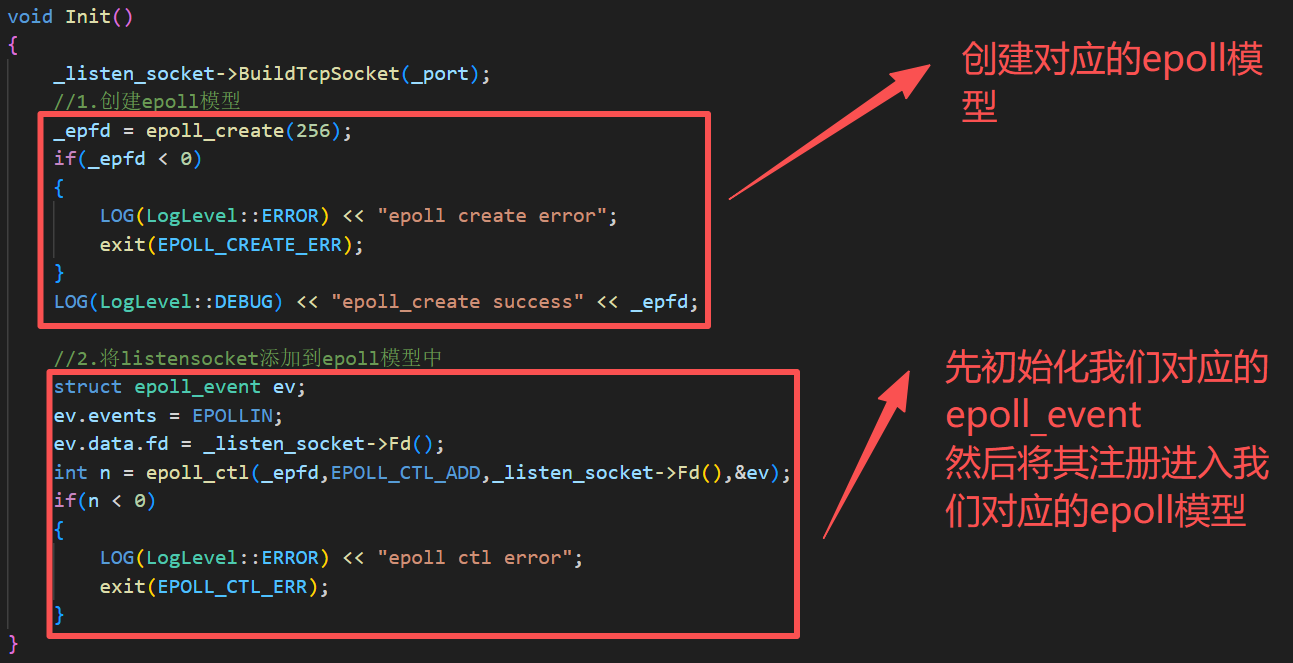
void Init()
{
_listen_socket->BuildTcpSocket(_port);
//1.创建epoll模型
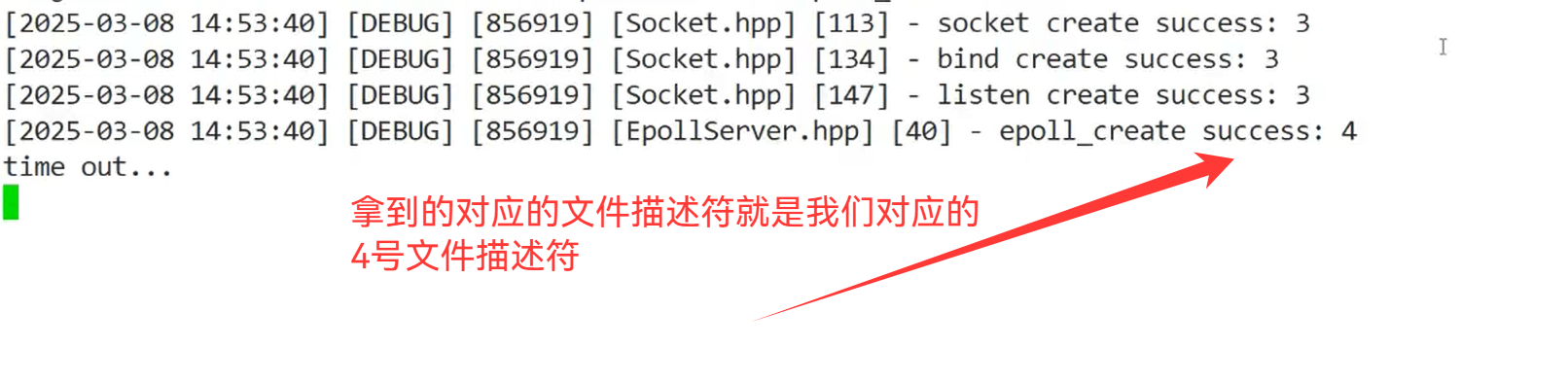
_epfd = epoll_create(256);
if(_epfd < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::ERROR) << "epoll create error";
exit(EPOLL_CREATE_ERR);
}
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "epoll_create success" << _epfd;
//2.将listensocket添加到epoll模型中
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
ev.data.fd = _listen_socket->Fd();
int n = epoll_ctl(_epfd,EPOLL_CTL_ADD,_listen_socket->Fd(),&ev);
if(n < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::ERROR) << "epoll ctl error";
exit(EPOLL_CTL_ERR);
}
}
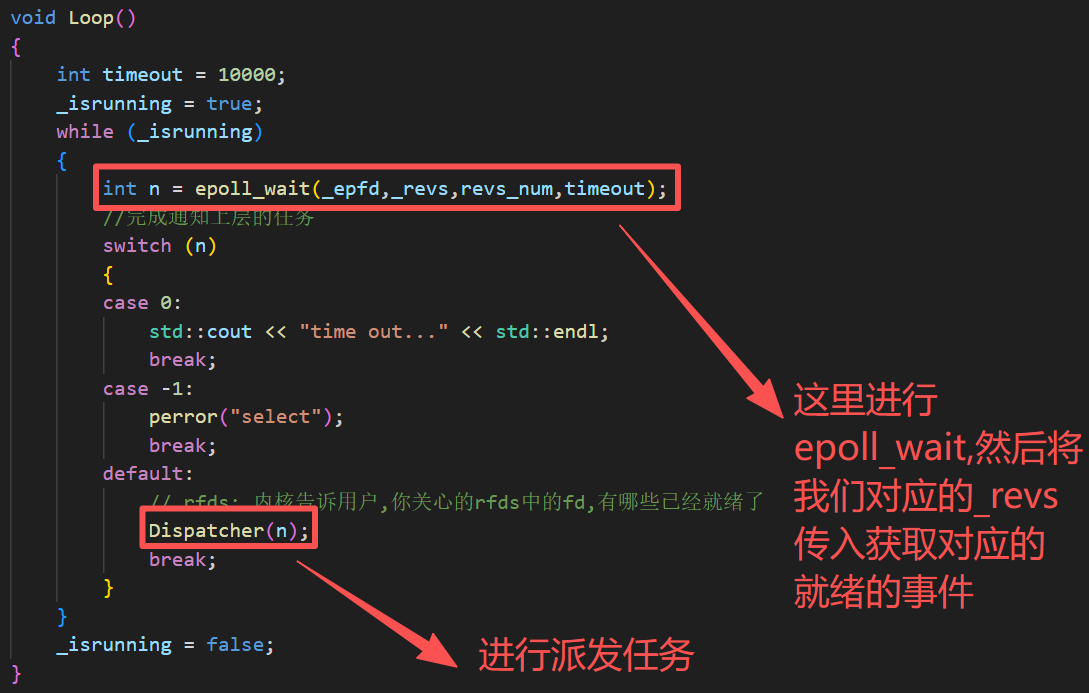
void Loop()
{
int timeout = 10000;
_isrunning = true;
while (_isrunning)
{
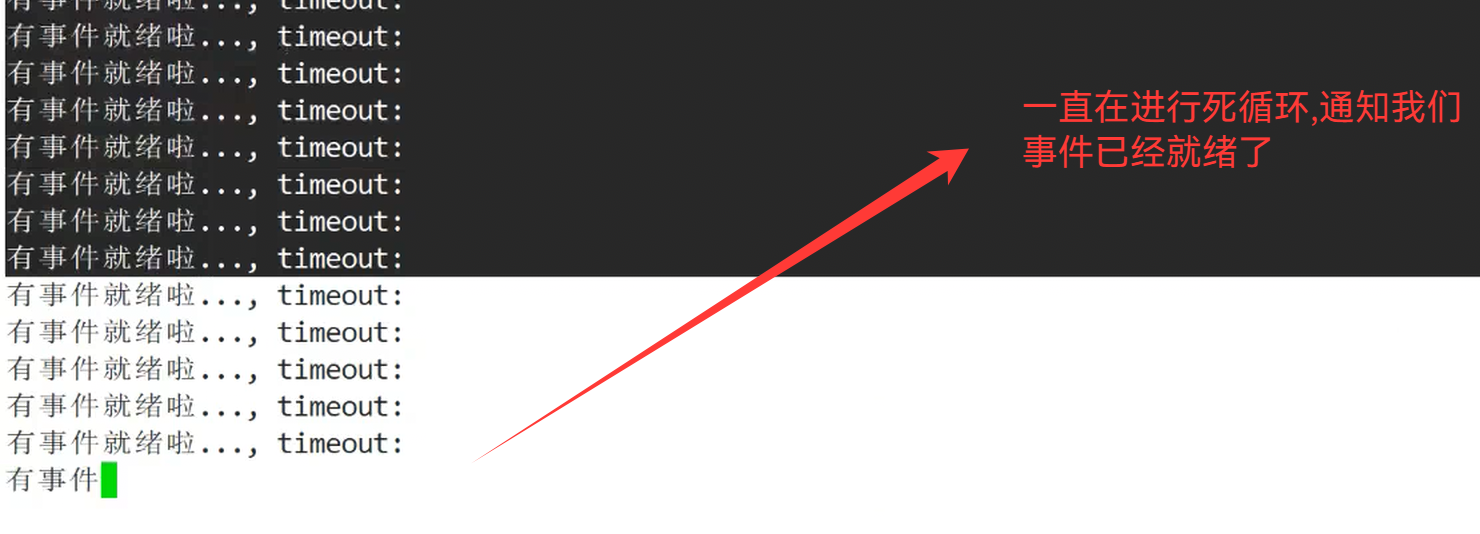
int n = epoll_wait(_epfd,_revs,revs_num,timeout);
//完成通知上层的任务
switch (n)
{
case 0:
std::cout << "time out..." << std::endl;
break;
case -1:
perror("select");
break;
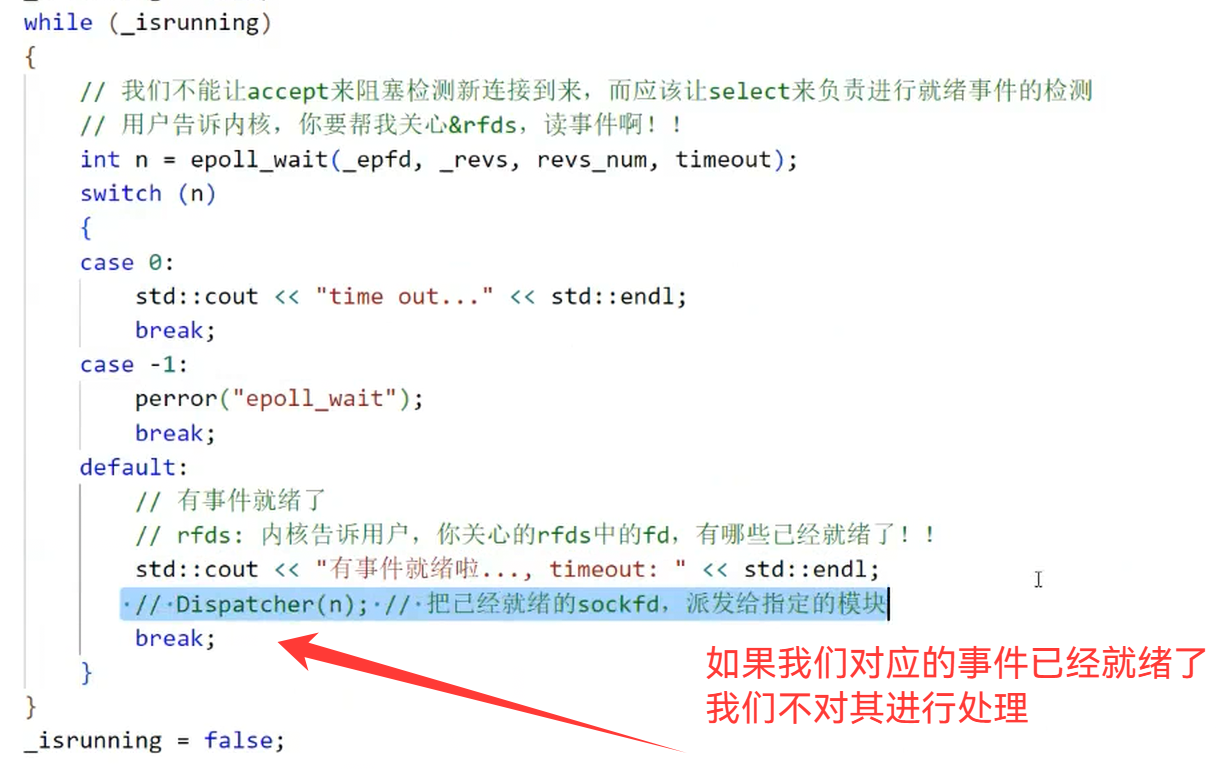
default:
// rfds: 内核告诉用户,你关心的rfds中的fd,有哪些已经就绪了
Dispatcher(n);
break;
}
}
_isrunning = false;
}
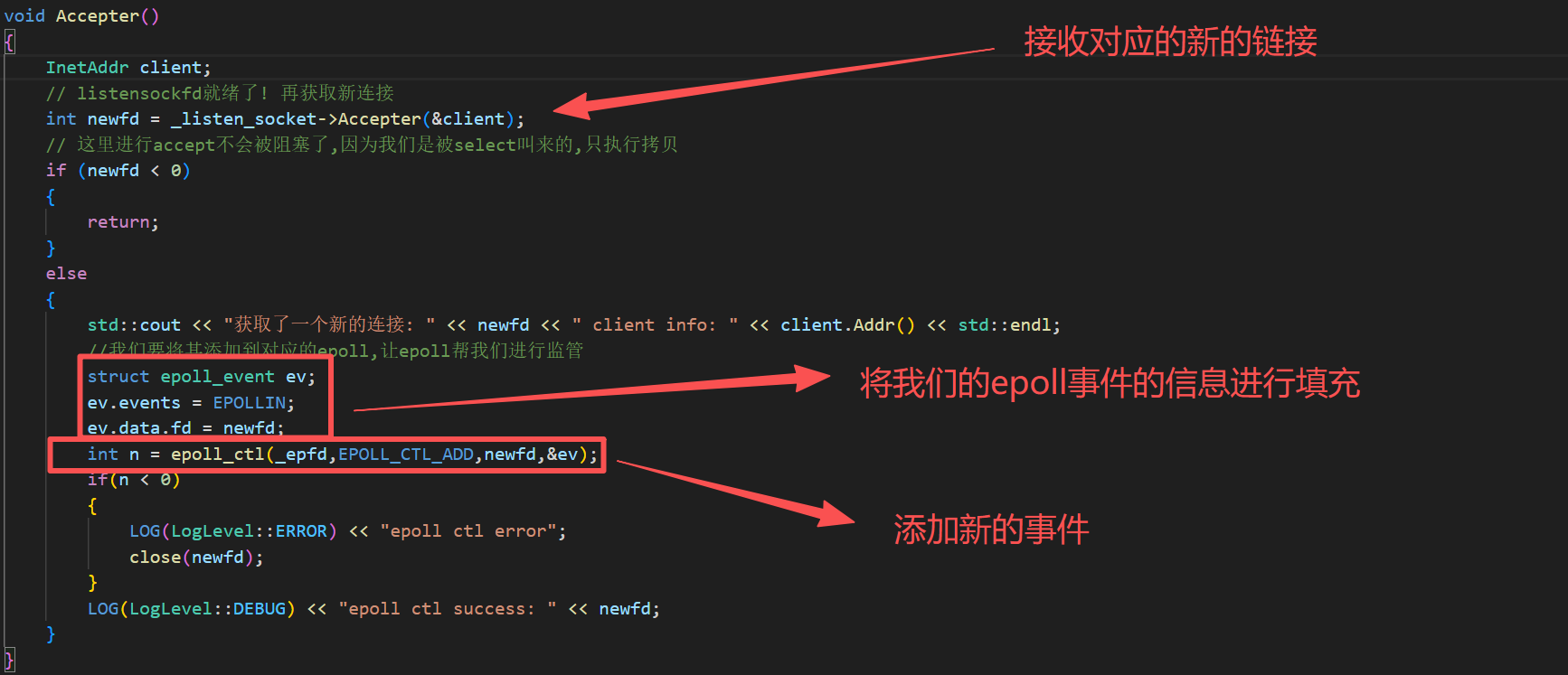
void Accepter()
{
InetAddr client;
// listensockfd就绪了! 再获取新连接
int newfd = _listen_socket->Accepter(&client);
// 这里进行accept不会被阻塞了,因为我们是被select叫来的,只执行拷贝
if (newfd < 0)
{
return;
}
else
{
std::cout << "获取了一个新的连接: " << newfd << " client info: " << client.Addr() << std::endl;
//我们要将其添加到对应的epoll,让epoll帮我们进行监管
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
ev.data.fd = newfd;
int n = epoll_ctl(_epfd,EPOLL_CTL_ADD,newfd,&ev);
if(n < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::ERROR) << "epoll ctl error";
close(newfd);
}
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "epoll ctl success: " << newfd;
}
}
void Recver(int fd)
{
char buffer[1024];
ssize_t n = recv(fd,buffer,sizeof(buffer)-1,0);
if(n > 0)
{
buffer[n] = 0;
std::cout << "client# " <<buffer << std::endl;
std::string message = "echo# ";
message += buffer;
send(fd,message.c_str(),message.size(),0);
}
else if(n == 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "客户端退出, sockfd: " << fd;
//把对应的文件描述符从epoll中进行移除
//在移除的时候,我们应该将其先进行移除,再关闭
int m = epoll_ctl(_epfd,EPOLL_CTL_DEL,fd,nullptr);
if(m < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::ERROR) << "epoll ctl error";
return;
}
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "epoll ctl success: " << fd;
close(fd);
}
else
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "客户端读取出错, sockfd: " << fd;
//把对应的文件描述符从epoll中进行移除
int m = epoll_ctl(_epfd,EPOLL_CTL_DEL,fd,nullptr);
if(m < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::ERROR) << "epoll ctl error";
return;
}
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "epoll ctl success: " << fd;
close(fd);
}
}
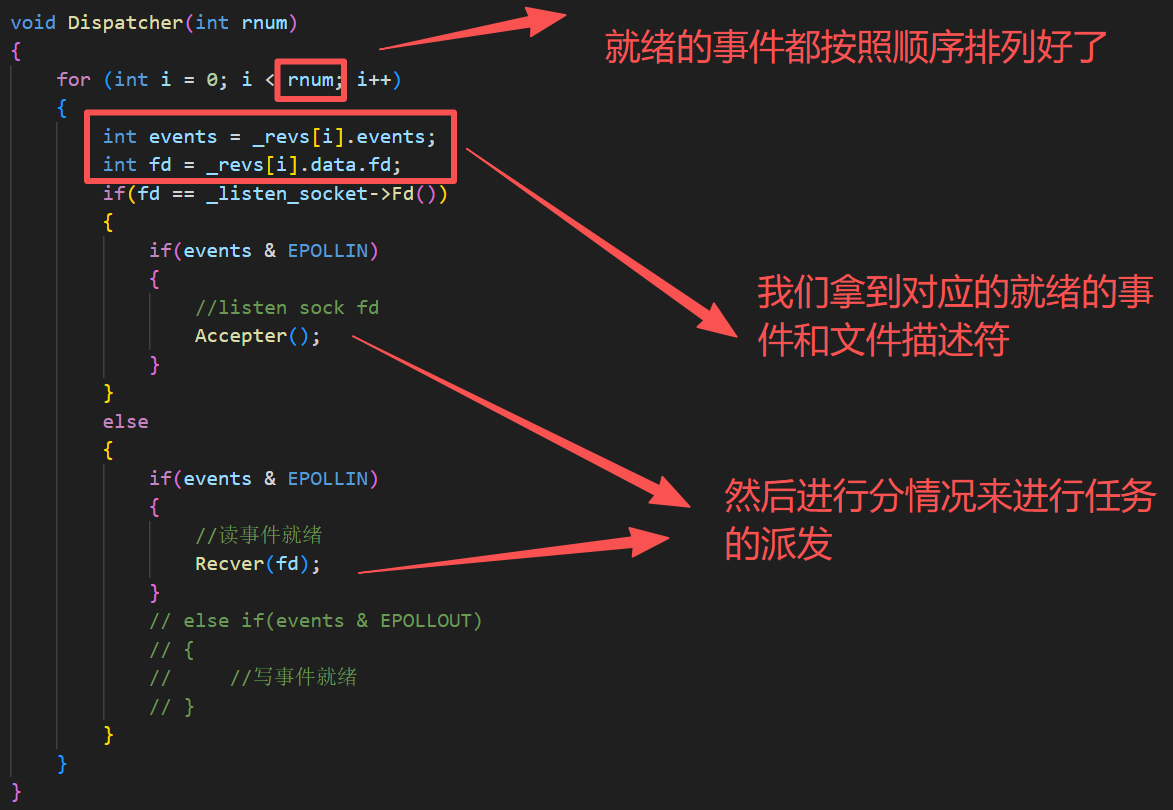
void Dispatcher(int rnum)
{
for (int i = 0; i < rnum; i++)
{
int events = _revs[i].events;
int fd = _revs[i].data.fd;
if(fd == _listen_socket->Fd())
{
if(events & EPOLLIN)
{
//listen sock fd
Accepter();
}
}
else
{
if(events & EPOLLIN)
{
//读事件就绪
Recver(fd);
}
// else if(events & EPOLLOUT)
// {
// //写事件就绪
// }
}
}
}
~EpollServer()
{
_listen_socket->Close();
if(_epfd >= 0)
{
close(_epfd);
}
}
private:
uint16_t _port;
std::unique_ptr<Socket> _listen_socket;
bool _isrunning;
int _epfd;
struct epoll_event _revs[revs_num];
};



五.epoll的工作模式: ET && LT

1.什么是ET,LT?
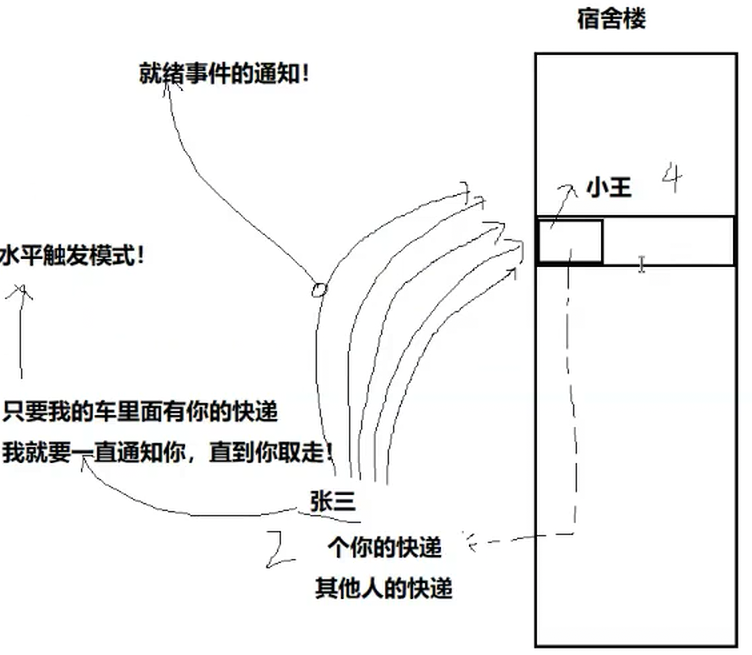
(LT模式)水平触发模式: 只要底层有数据,就一直告知上层,条件是就绪的
(ET模式)边缘触发模式: 当收到新的数据是就会通知对方一次!(从无到有,从有到多,变化(增多)的时候,才进行通知对方)
所谓的张三就是我们对应的 (epoll && LT),快递就是我们对应的数据,小车就是我们的输入缓冲区
打电话就是我们的通知机制

![]()

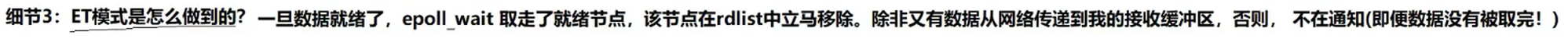

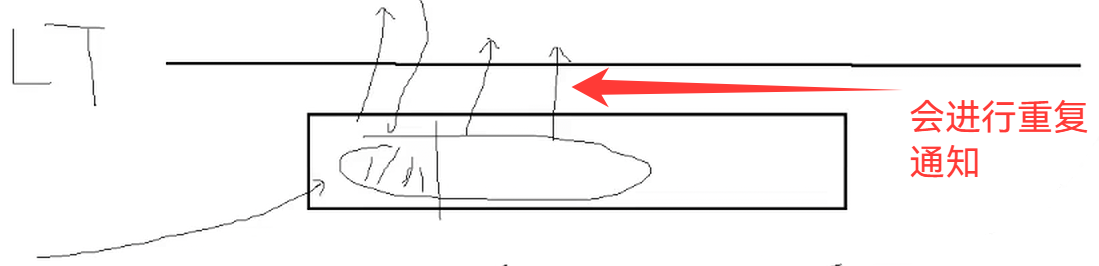
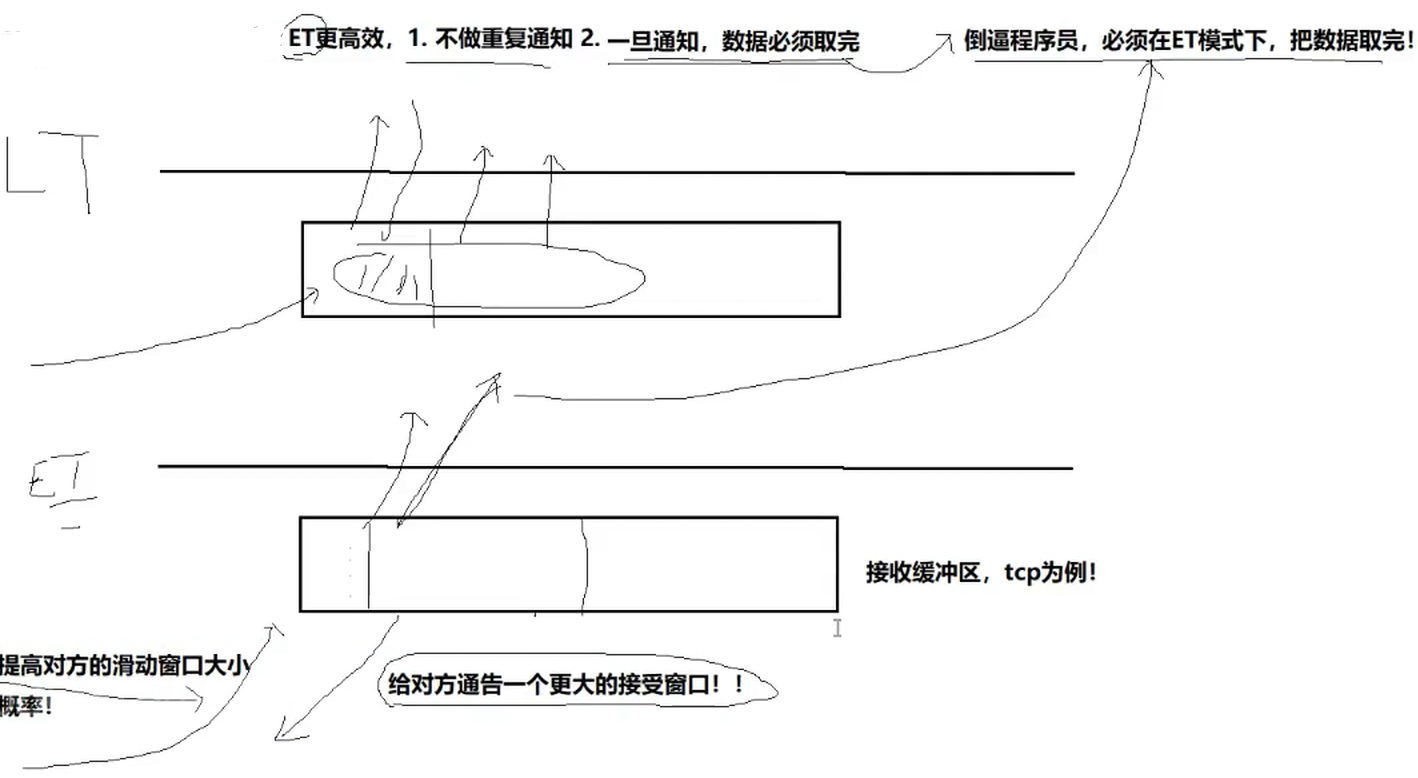
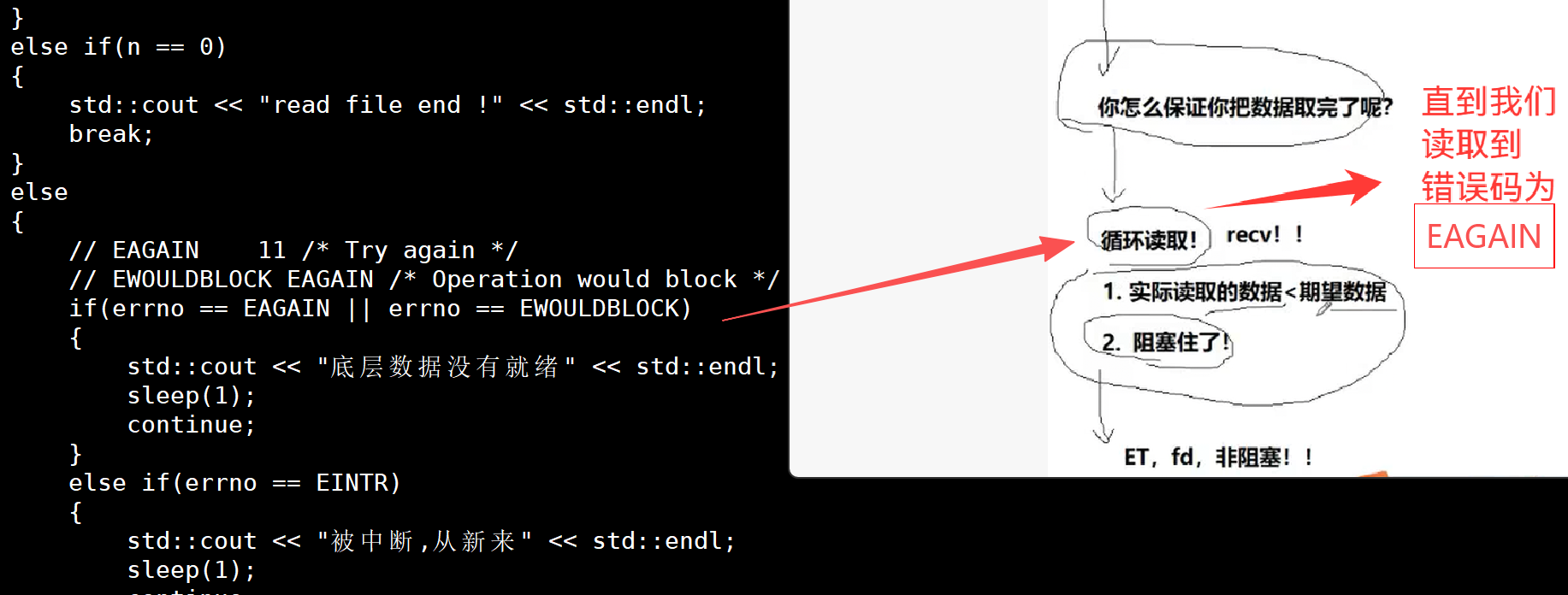
所以ET单位时间内,IO吞吐量更多

但是ET这样做是有代价的!!!
![]()
![]()

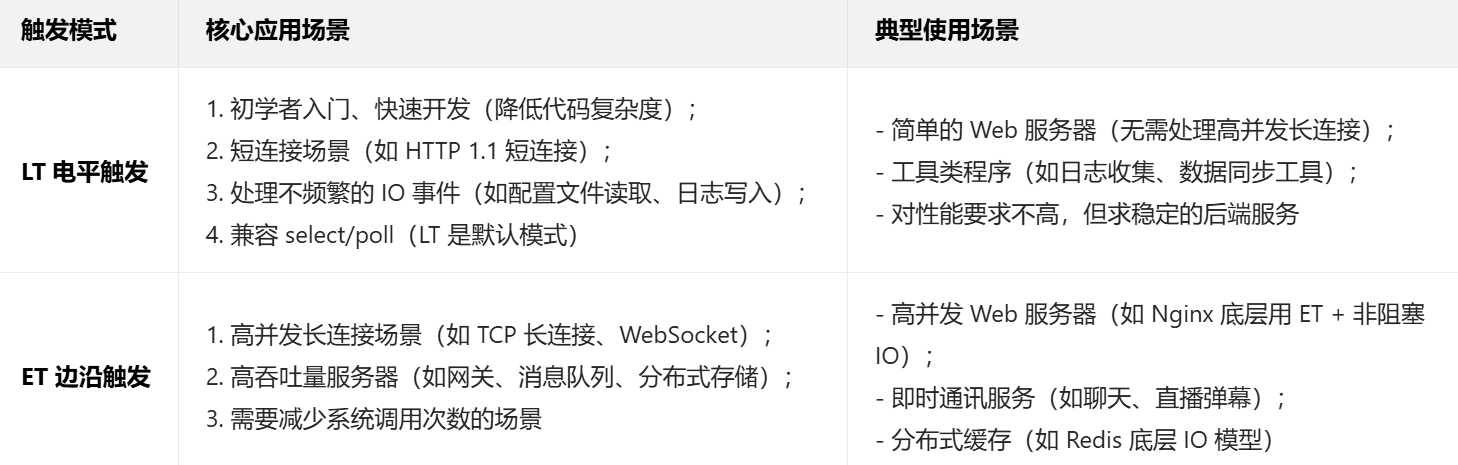
2.为啥要有LT,ET?
![]()
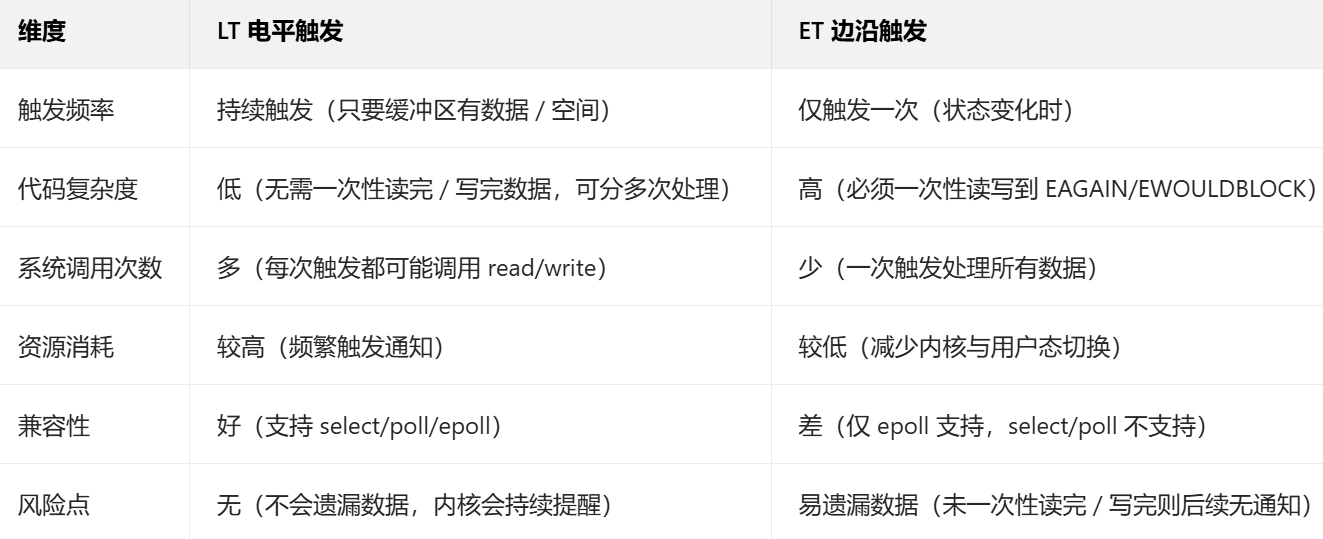
3.各自的特点是什么?我应该用哪一个?
根据我们的场景进行使用即可





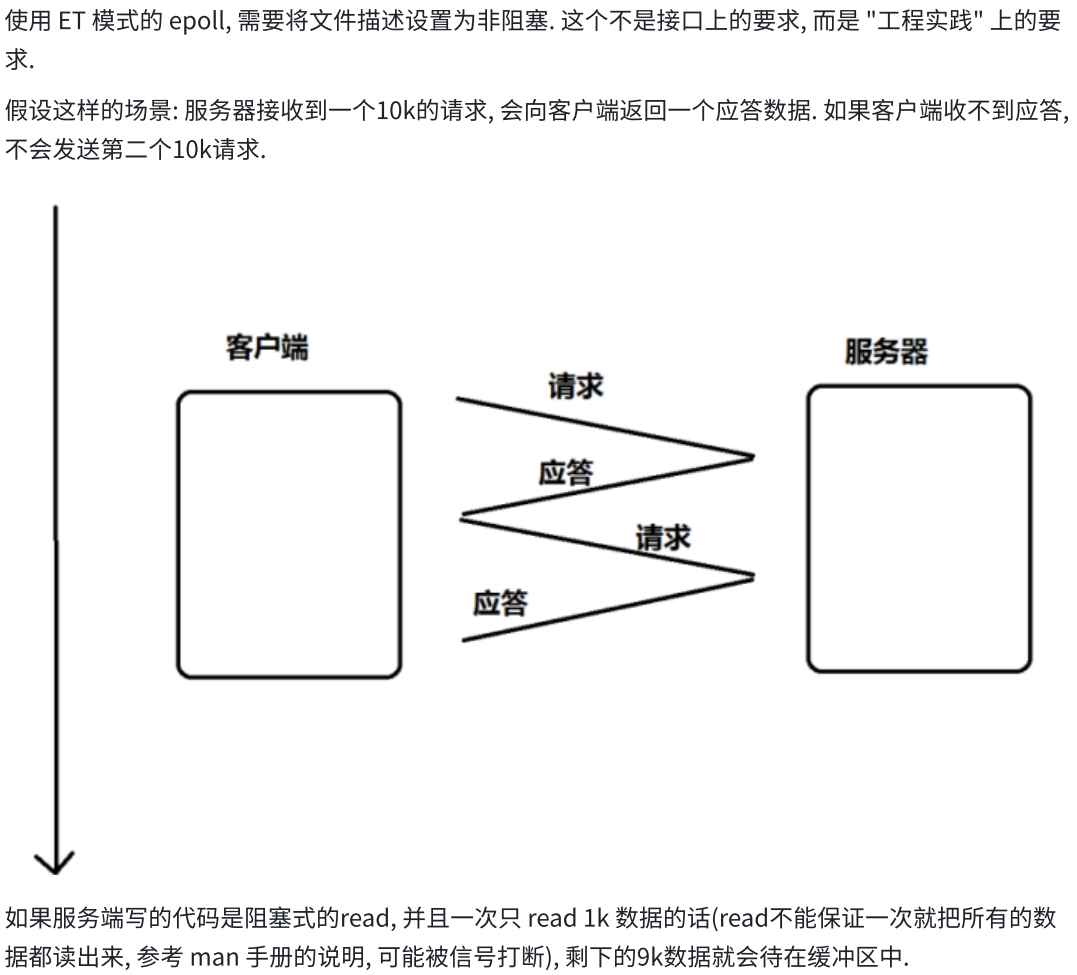
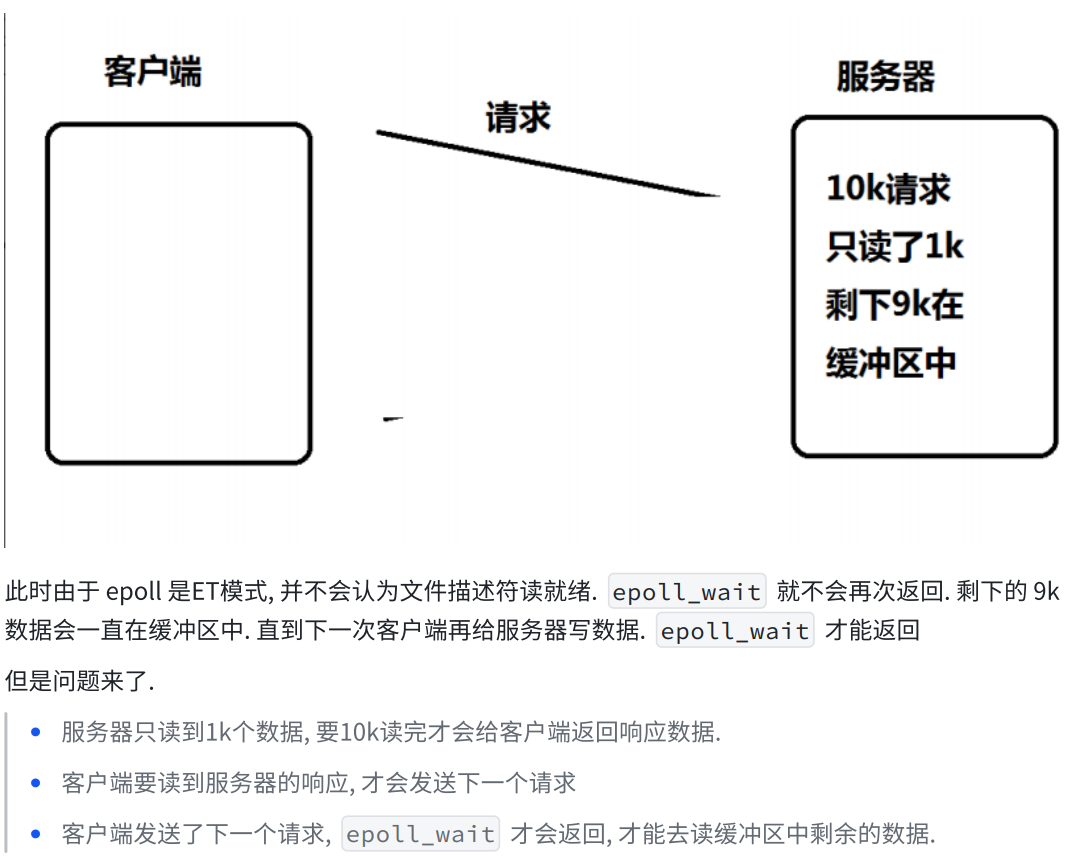
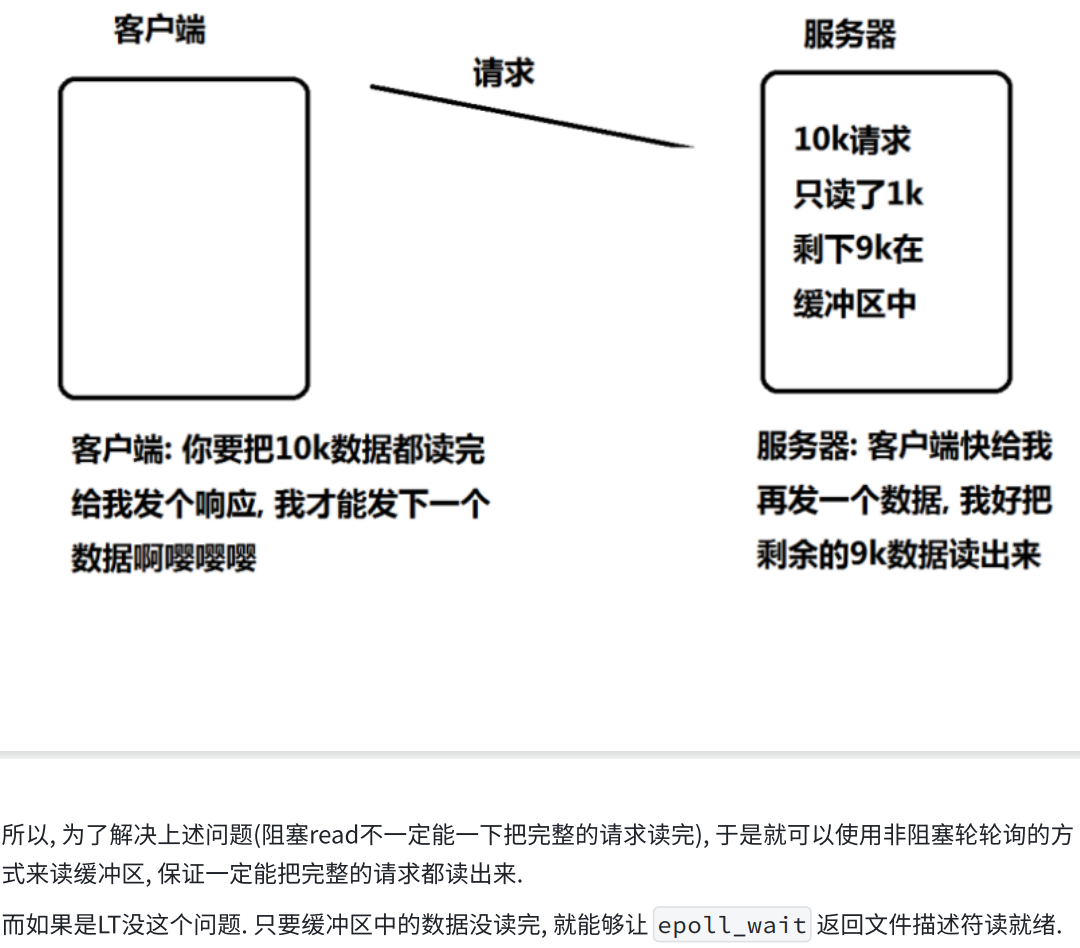

六.epoll代码的设计
1.软件分层的设计

我们对应的EpollServer向上看到的都是我们对应的Connection
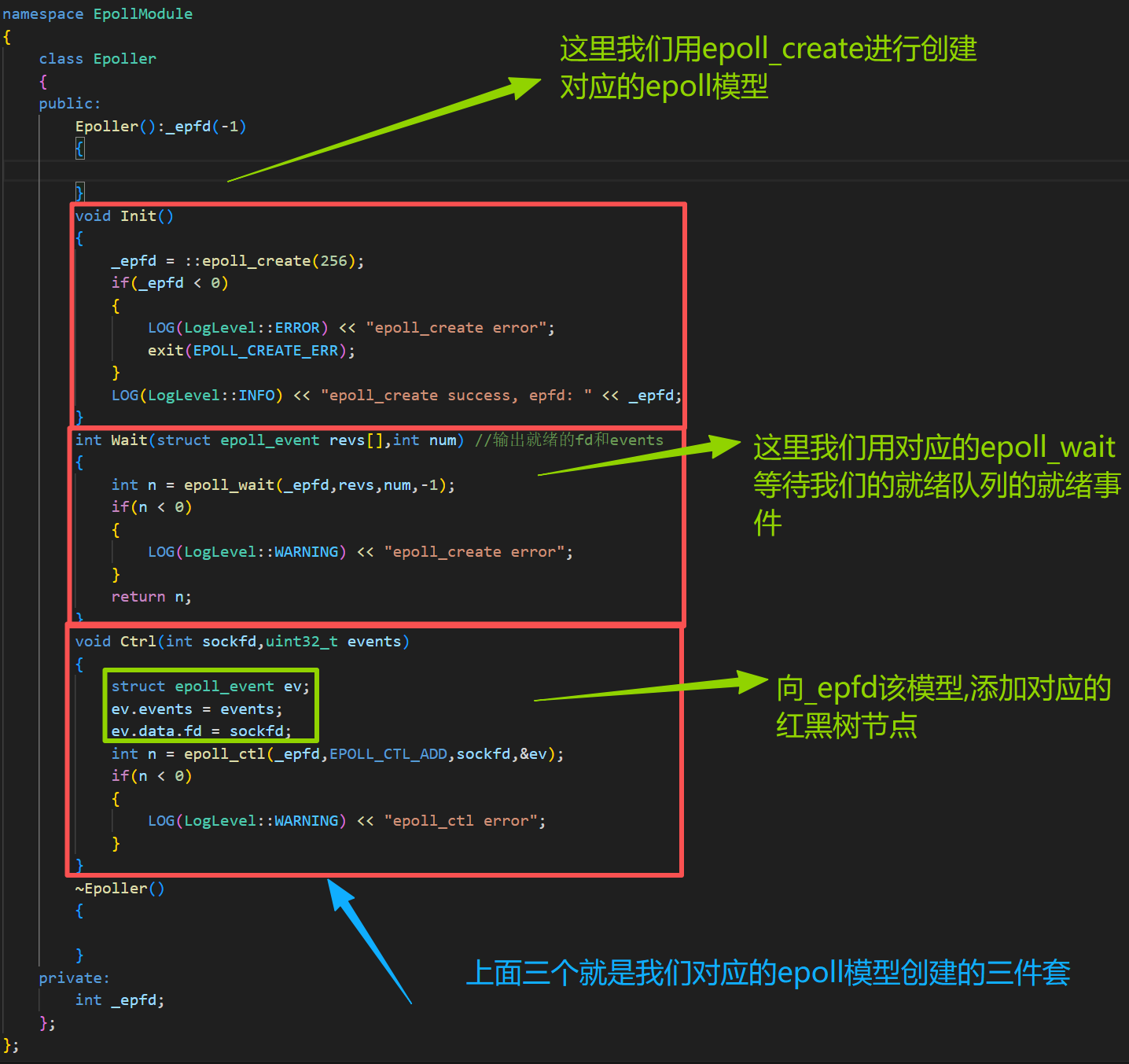
2.epoller模型封装(最基本的检测模型(底层))
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include "Log.hpp"
#include "Common.hpp"
using namespace LogModule;
namespace EpollModule
{
class Epoller
{
public:
Epoller():_epfd(-1)
{
}
void Init()
{
_epfd = ::epoll_create(256);
if(_epfd < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::ERROR) << "epoll_create error";
exit(EPOLL_CREATE_ERR);
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "epoll_create success, epfd: " << _epfd;
}
int Wait(struct epoll_event revs[],int num) //输出就绪的fd和events
{
int n = epoll_wait(_epfd,revs,num,-1);
if(n < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::WARNING) << "epoll_create error";
}
return n;
}
void Ctrl(int sockfd,uint32_t events)
{
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events = events;
ev.data.fd = sockfd;
int n = epoll_ctl(_epfd,EPOLL_CTL_ADD,sockfd,&ev);
if(n < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::WARNING) << "epoll_ctl error";
}
}
~Epoller()
{
}
private:
int _epfd;
};
};
3.EpollServer.hpp的设计
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <unordered_map>
#include "Epoller.hpp"
#include "Connection.hpp"
using namespace EpollModule;
using connection_t = std::shared_ptr<Connection>;
class EpollServer
{
const static int event_num = 64;
public:
EpollServer():_isrunning(false),_epoller(std::make_unique<Epoller>())
{
_epoller->Init();
}
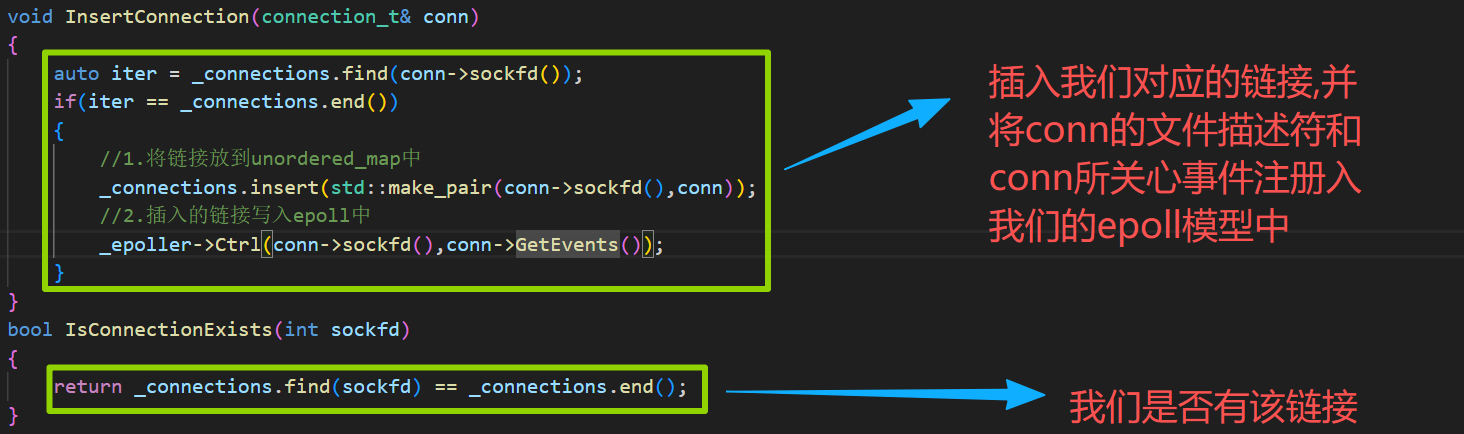
void InsertConnection(connection_t& conn)
{
auto iter = _connections.find(conn->sockfd());
if(iter == _connections.end())
{
//1.将链接放到unordered_map中
_connections.insert(std::make_pair(conn->sockfd(),conn));
//2.插入的链接写入epoll中
_epoller->Ctrl(conn->sockfd(),conn->GetEvents());
}
}
bool IsConnectionExists(int sockfd)
{
return _connections.find(sockfd) == _connections.end();
}
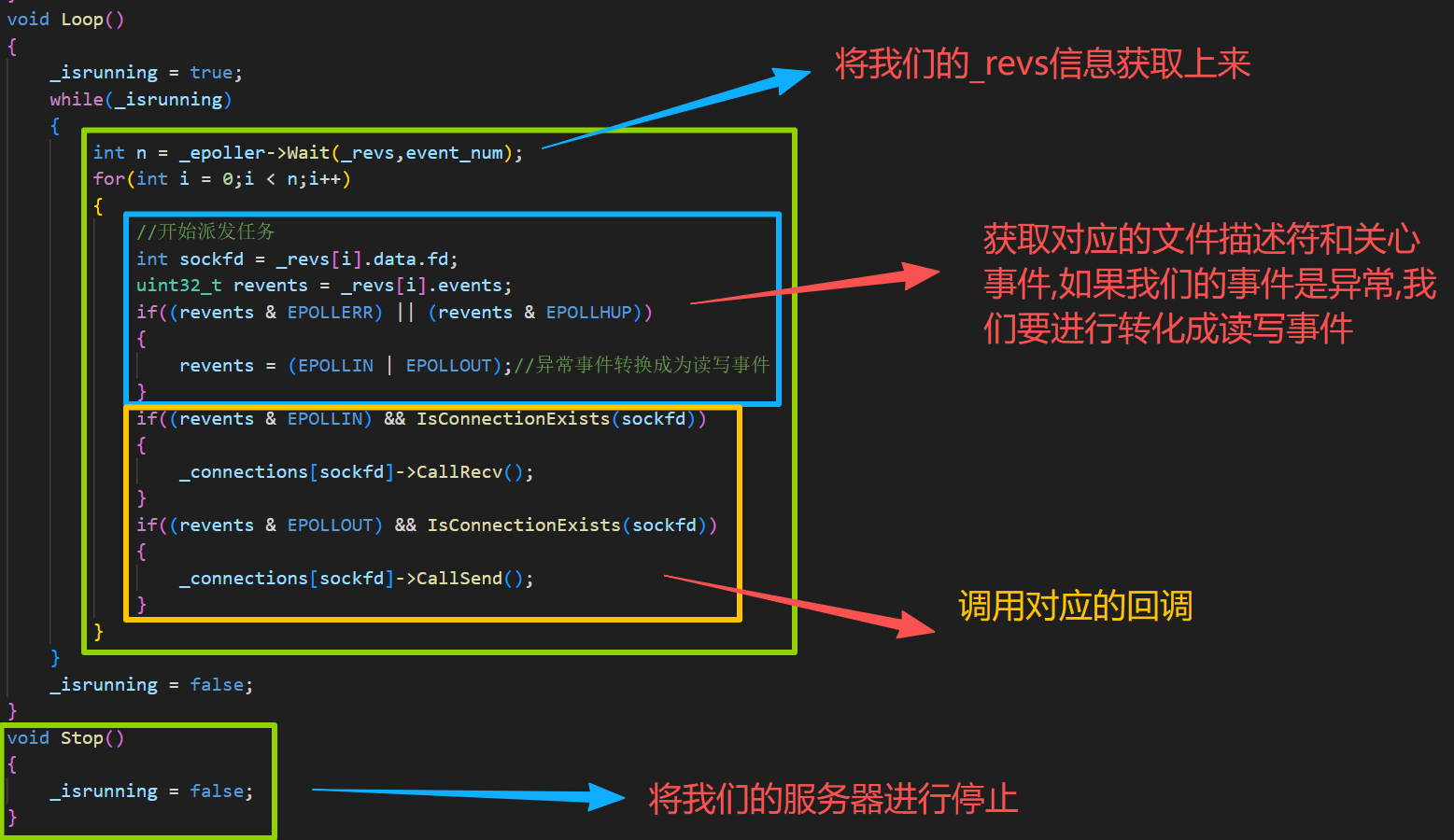
void Loop()
{
_isrunning = true;
while(_isrunning)
{
int n = _epoller->Wait(_revs,event_num);
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
//开始派发任务
int sockfd = _revs[i].data.fd;
uint32_t revents = _revs[i].events;
if((revents & EPOLLERR) || (revents & EPOLLHUP))
{
revents = (EPOLLIN | EPOLLOUT);//异常事件转换成为读写事件
}
if((revents & EPOLLIN) && IsConnectionExists(sockfd))
{
_connections[sockfd]->CallRecv();
}
if((revents & EPOLLOUT) && IsConnectionExists(sockfd))
{
_connections[sockfd]->CallSend();
}
}
}
_isrunning = false;
}
void Stop()
{
_isrunning = false;
}
~EpollServer()
{
}
private:
std::unique_ptr<Epoller> _epoller;
std::unordered_map<int,connection_t> _connections; //服务器内部所有的链接
bool _isrunning;
struct epoll_event _revs[event_num];
};


4.Connection.hpp的设计
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <functional>
#include "InetAddr.hpp"
// #include "EpollServer.hpp"
class EpollServer;
using func_t = std::function<void()>;
// 普通 fd, Listensockfd
//让我们对fd的处理方式采用同一种方式
//描述一个链接
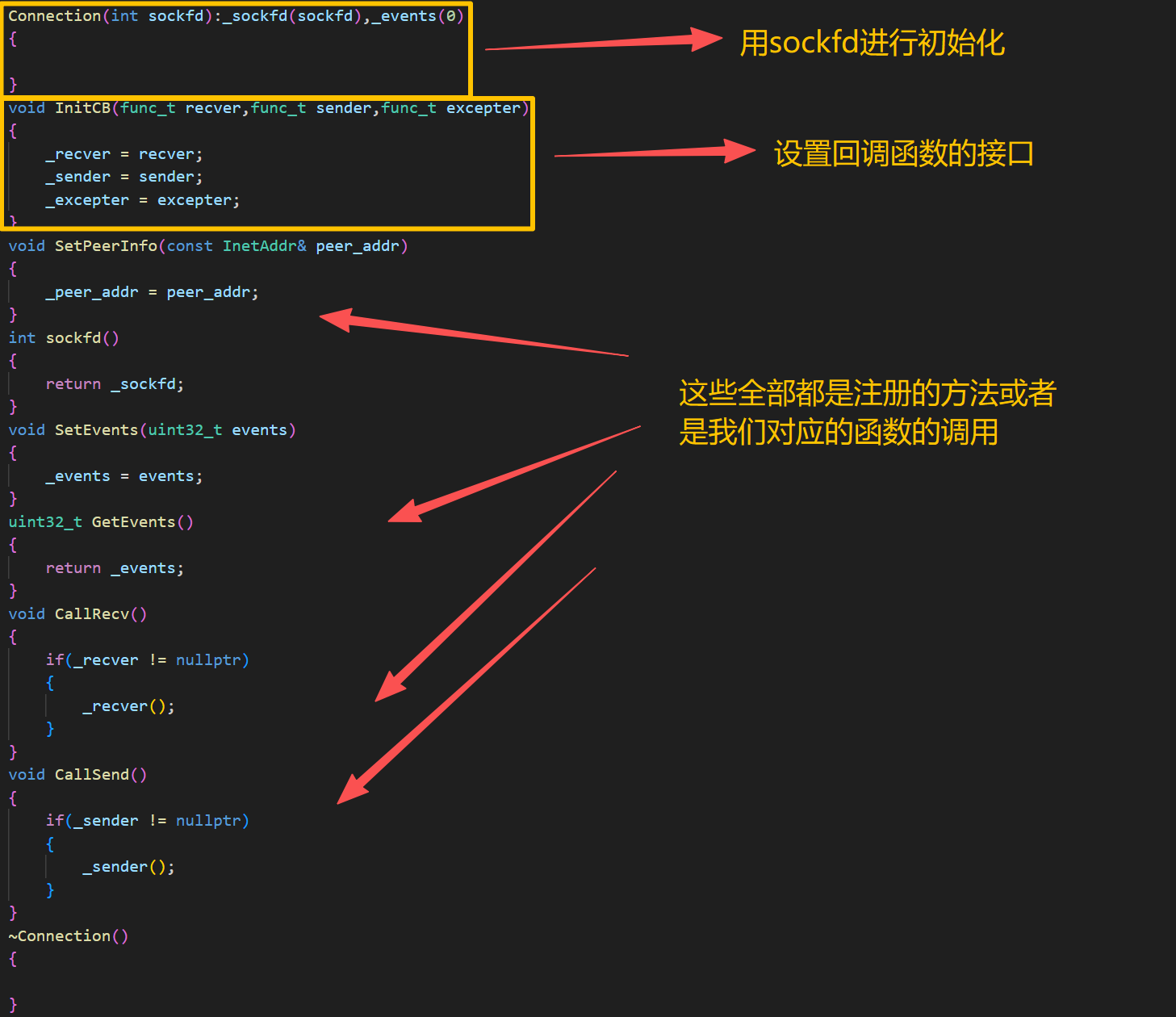
class Connection
{
public:
Connection(int sockfd):_sockfd(sockfd),_events(0)
{
}
void InitCB(func_t recver,func_t sender,func_t excepter)
{
_recver = recver;
_sender = sender;
_excepter = excepter;
}
void SetPeerInfo(const InetAddr& peer_addr)
{
_peer_addr = peer_addr;
}
int sockfd()
{
return _sockfd;
}
void SetEvents(uint32_t events)
{
_events = events;
}
uint32_t GetEvents()
{
return _events;
}
void CallRecv()
{
if(_recver != nullptr)
{
_recver();
}
}
void CallSend()
{
if(_sender != nullptr)
{
_sender();
}
}
~Connection()
{
}
private:
int _sockfd;
std::string _inbuffer;
std::string _outbuffer;
InetAddr _peer_addr; //对应的客户端
//回调方法
func_t _recver;
func_t _sender;
func_t _excepter;
//添加一个指针
EpollServer* _owner;
//关心的事件
uint32_t _events;
};

5.Listener.hpp的设计
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include "Socket.hpp"
#include "Log.hpp"
using namespace SocketModule;
using namespace LogModule;
//专门负责获取链接的模块
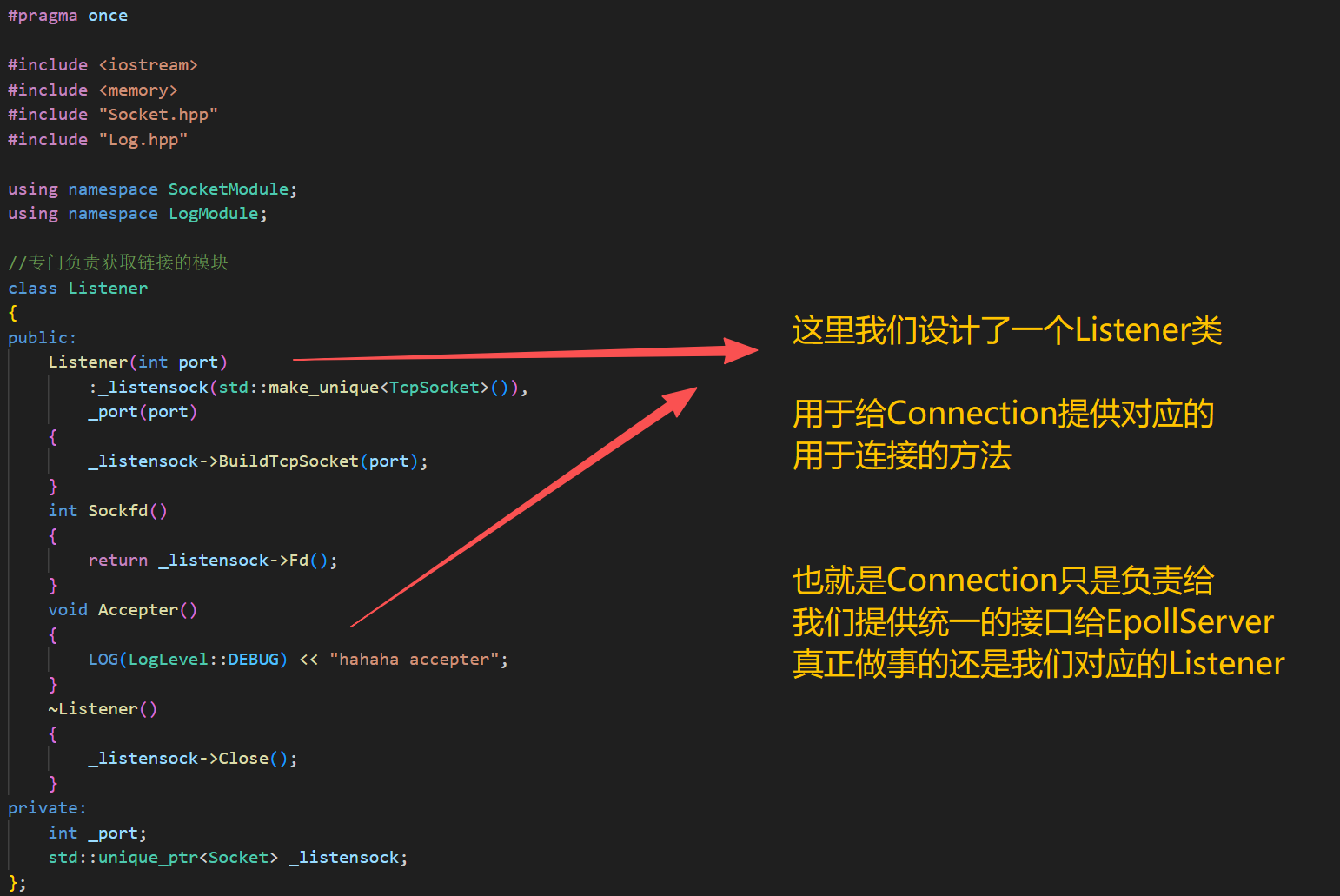
class Listener
{
public:
Listener(int port)
:_listensock(std::make_unique<TcpSocket>()),
_port(port)
{
_listensock->BuildTcpSocket(port);
}
int Sockfd()
{
return _listensock->Fd();
}
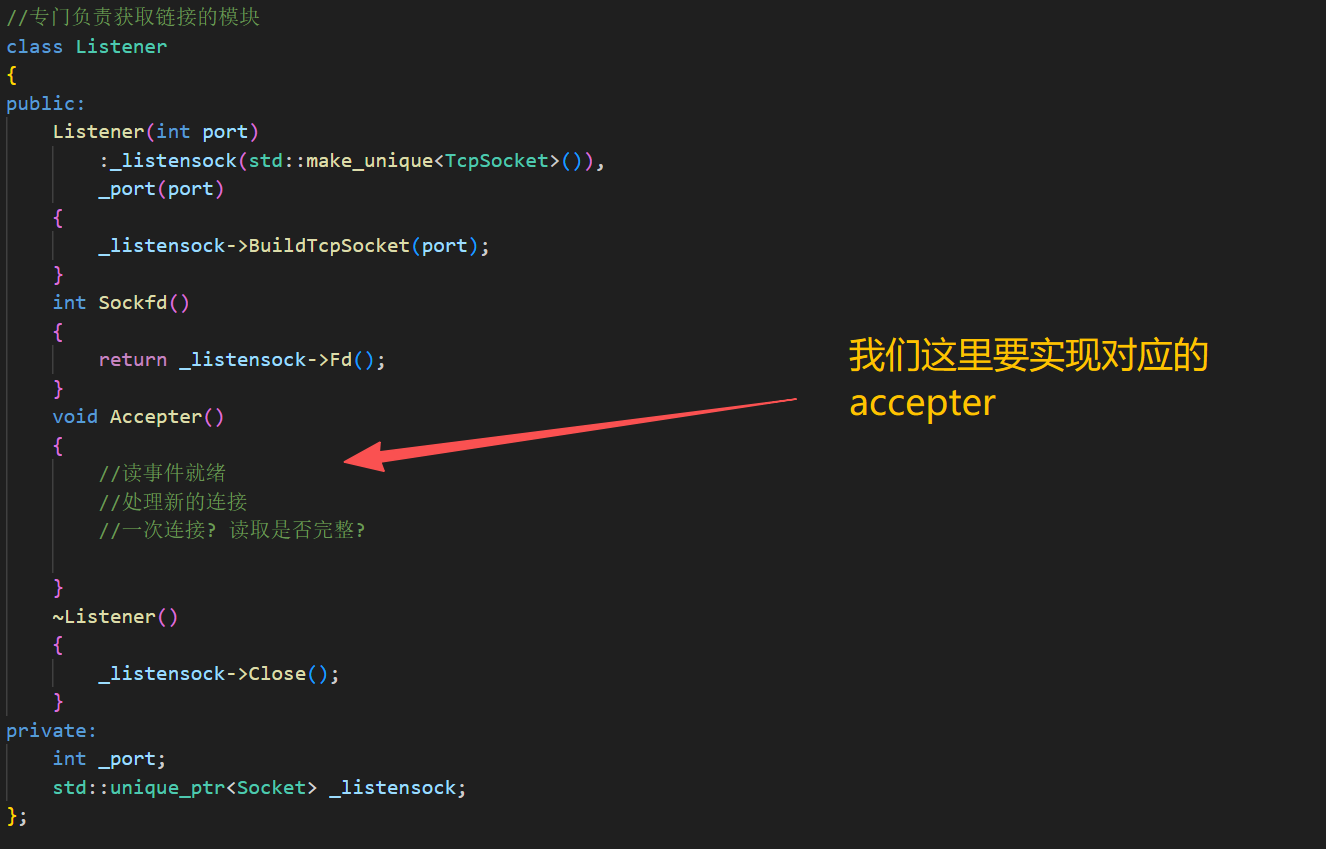
void Accepter()
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "hahaha accepter";
}
~Listener()
{
_listensock->Close();
}
private:
int _port;
std::unique_ptr<Socket> _listensock;
};
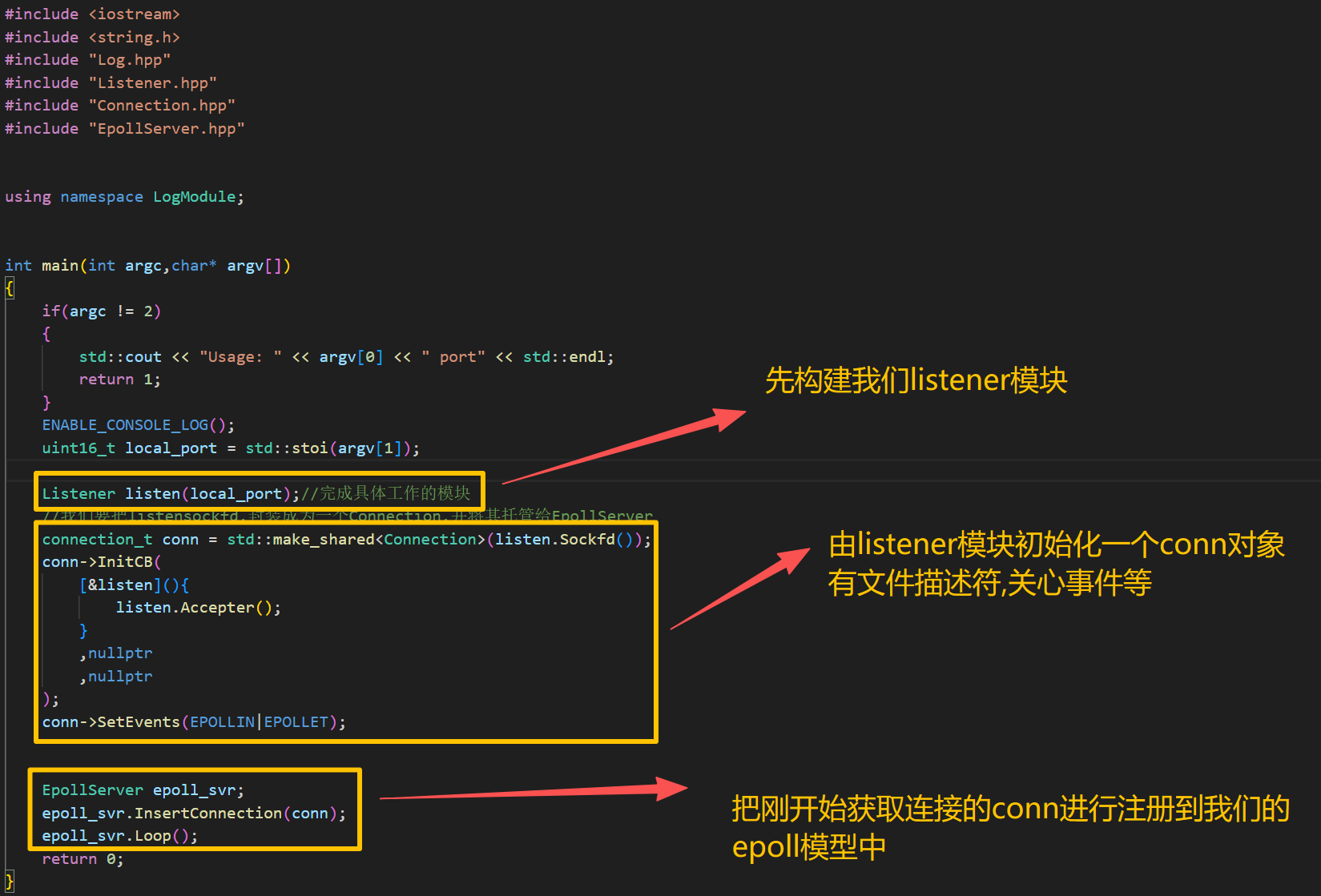
6.Main.cpp设计
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include "Log.hpp"
#include "Listener.hpp"
#include "Connection.hpp"
#include "EpollServer.hpp"
using namespace LogModule;
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
if(argc != 2)
{
std::cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " port" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
ENABLE_CONSOLE_LOG();
uint16_t local_port = std::stoi(argv[1]);
Listener listen(local_port);//完成具体工作的模块
//我们要把listensockfd,封装成为一个Connection,并将其托管给EpollServer
connection_t conn = std::make_shared<Connection>(listen.Sockfd());
conn->InitCB(
[&listen](){
listen.Accepter();
}
,nullptr
,nullptr
);
conn->SetEvents(EPOLLIN|EPOLLET);
EpollServer epoll_svr;
epoll_svr.InsertConnection(conn);
epoll_svr.Loop();
return 0;
}

7.代码修改
class Connection
{
public:
Connection(int sockfd):_sockfd(sockfd),_events(0)
{
}
void InitCB(func_t recver,func_t sender,func_t excepter)
{
_recver = recver;
_sender = sender;
_excepter = excepter;
}
void SetPeerInfo(const InetAddr& peer_addr)
{
_peer_addr = peer_addr;
}
int sockfd()
{
return _sockfd;
}
void SetEvents(uint32_t events)
{
_events = events;
}
uint32_t GetEvents()
{
return _events;
}
void CallRecv()
{
if(_recver != nullptr)
{
_recver();
}
}
void CallSend()
{
if(_sender != nullptr)
{
_sender();
}
}
~Connection()
{
}
private:
int _sockfd;
std::string _inbuffer;
std::string _outbuffer;
InetAddr _peer_addr; //对应的客户端
//回调方法
func_t _recver;
func_t _sender;
func_t _excepter;
//添加一个指针
EpollServer* _owner;
//关心的事件
uint32_t _events;
};
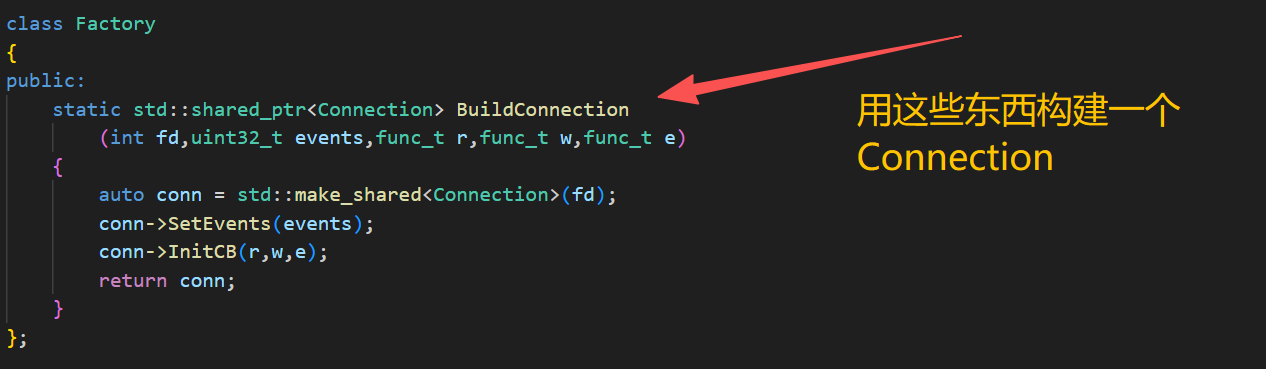
class Factory
{
public:
static std::shared_ptr<Connection> BuildConnection
(int fd,uint32_t events,func_t r,func_t w,func_t e)
{
auto conn = std::make_shared<Connection>(fd);
conn->SetEvents(events);
conn->InitCB(r,w,e);
return conn;
}
};
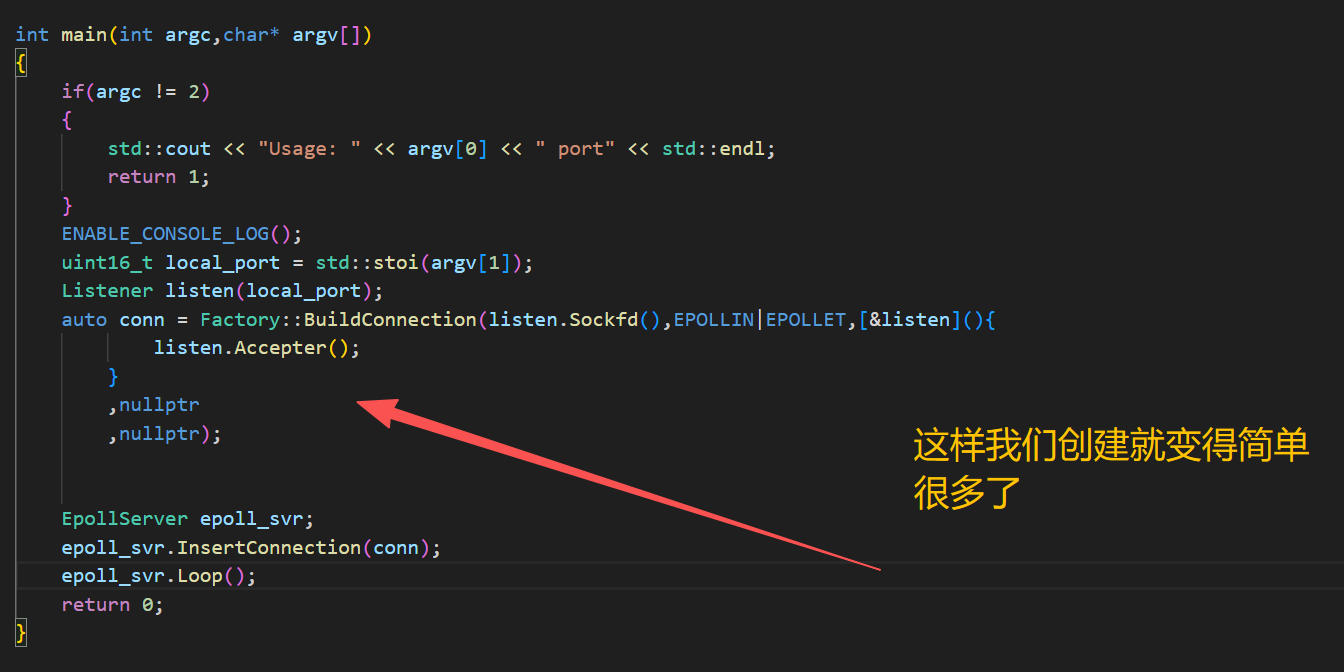
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include "Log.hpp"
#include "Listener.hpp"
#include "Connection.hpp"
#include "EpollServer.hpp"
using namespace LogModule;
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
if(argc != 2)
{
std::cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " port" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
ENABLE_CONSOLE_LOG();
uint16_t local_port = std::stoi(argv[1]);
Listener listen(local_port);
auto conn = Factory::BuildConnection(listen.Sockfd(),EPOLLIN|EPOLLET,[&listen](){
listen.Accepter();
}
,nullptr
,nullptr);
EpollServer epoll_svr;
epoll_svr.InsertConnection(conn);
epoll_svr.Loop();
return 0;
}
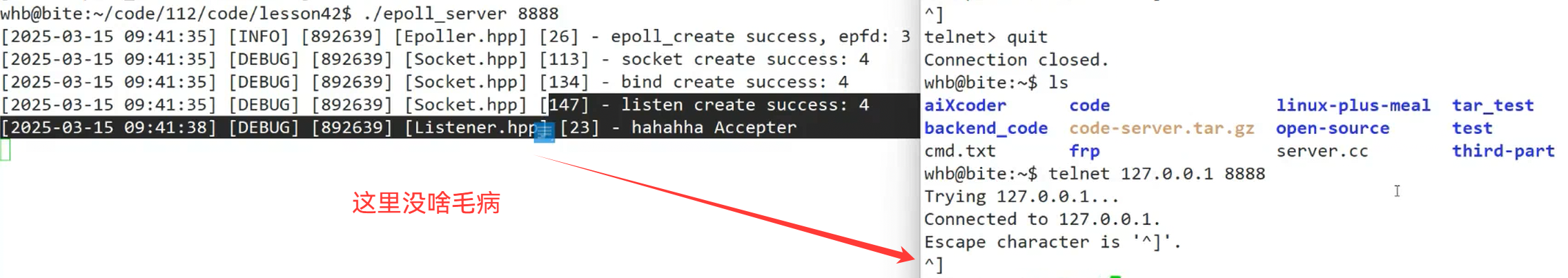
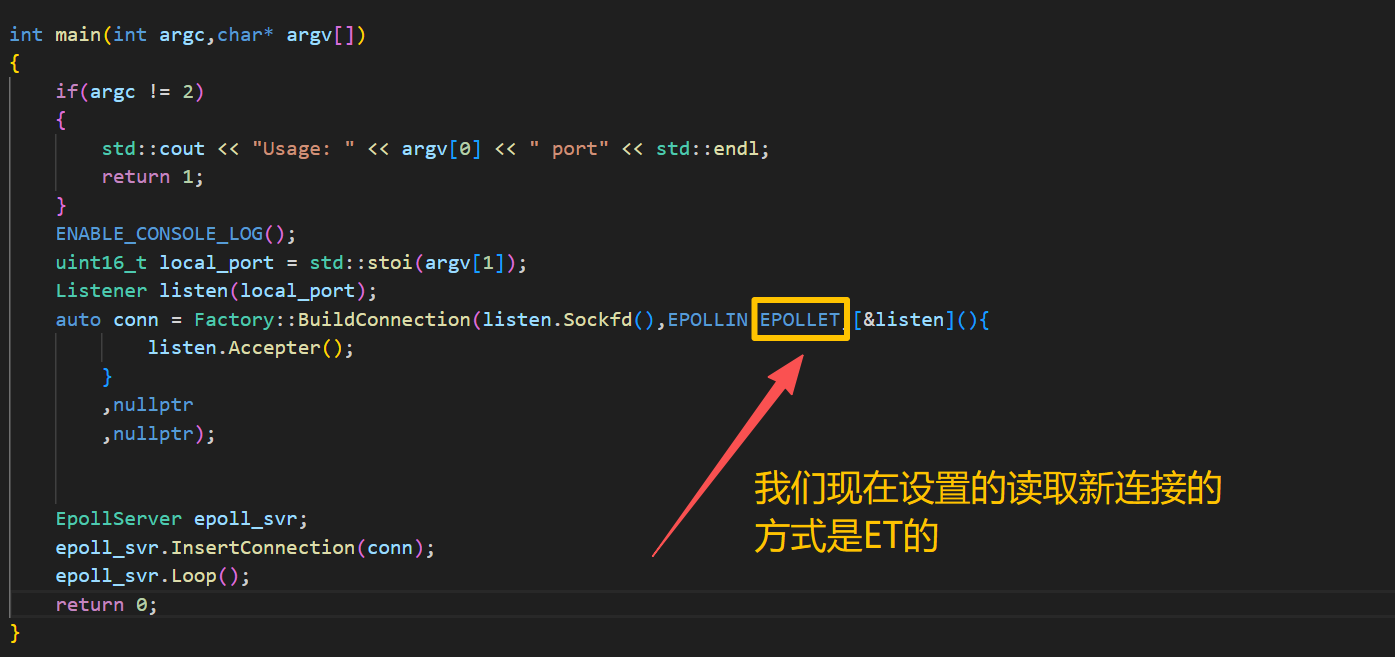
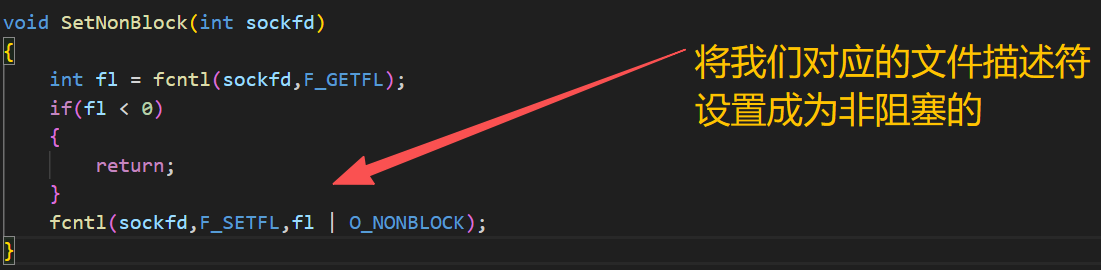
void SetNonBlock(int sockfd)
{
int fl = fcntl(sockfd,F_GETFL);
if(fl < 0)
{
return;
}
fcntl(sockfd,F_SETFL,fl | O_NONBLOCK);
}
未完待续....





















 956
956

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








