用python构建一个简单的ANN(也称NN)网络
此代码实现了一个简单的神经网络训练过程
通过自定义的前向传播和反向传播过程,对输入数据进行训练。网络采用了两层全连接隐藏层,解构参考下图,每层都有可选择的激活函数(Sigmoid或ReLU)。
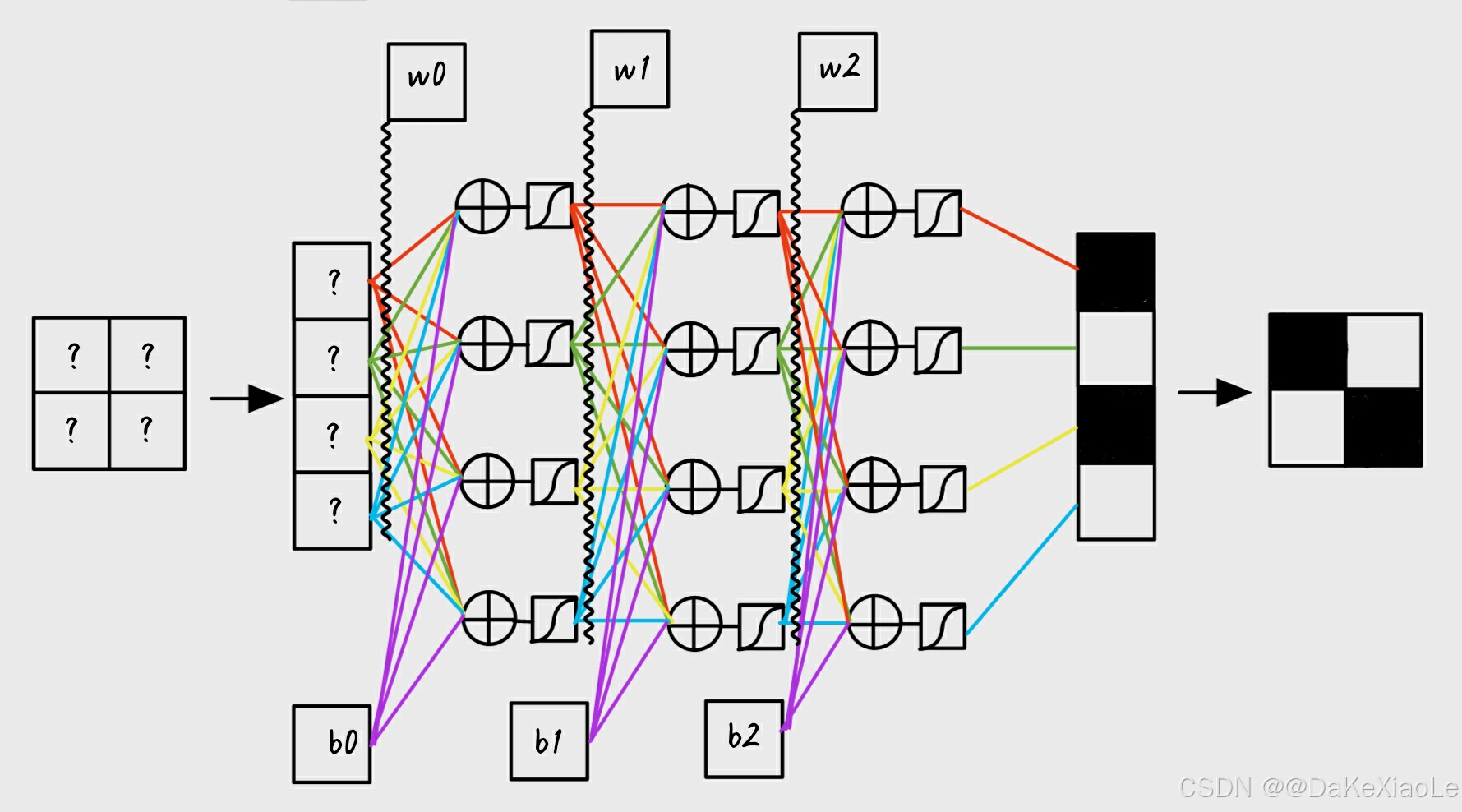
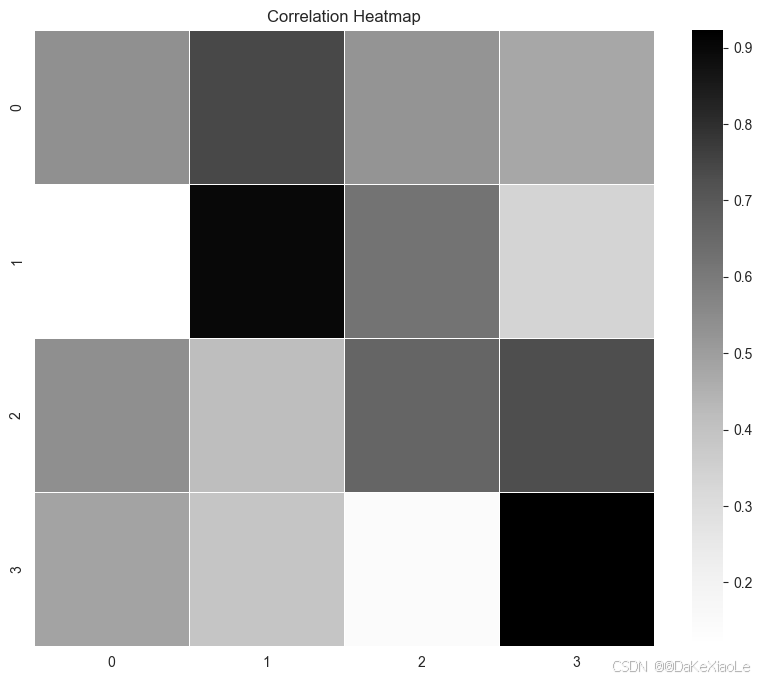
最终实现由随机产生的4x4的随机矩阵,
通过神经网络,生成我们初始规定的4x4图像数据,作为target图像。如下图

核心功能包括:
- 热力图可视化:通过 matplotlib 和 seaborn 绘制数据的热力图。
- 神经网络前向传播:计算网络每层的输出结果。
- 反向传播:计算各层的梯度,并根据损失函数更新权重和偏置。
- 损失计算:使用均方误差(MSE)作为损失函数,并在每次迭代后计算新的损失值。
- 可视化输出结果:使用 TensorBoard 保存并展示训练过程中的输出图像。
代码说明
相应库文件
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import numpy as np
import io # 用于在内存中保存图像
from PIL import Image # 用于打开并转换图像
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
定义目标target图像及网络参数
# 显示初始图像,生成一个简单的4x4图像数据作为target图像
img = np.array([[1, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 0]])
show_pic(img) # 可视化该图像
writer = SummaryWriter('logs') # TensorBoard日志记录器
# 定义每层神经元数量
num_hidden_layer0 = 16 # 第一隐藏层的神经元数量
num_hidden_layer1 = 16 # 第二隐藏层的神经元数量
# 定义学习率
learning_rate = 0.5
# 定义循环训练次数
times = 500
# 选择激活函数模式,可以选择 "ReLU" 或 "sigmoid"
active_mode = "sigmoid"

定义可视化以及激活、损失函数
# 可视化函数:用于显示数据的热力图
def show_pic(data):
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
sns.heatmap(
data,
cmap="Greys", # 颜色映射,使用灰度色
linewidths=0.5, # 单元格边框宽度
)
plt.title('Correlation Heatmap')
plt.show()
# 用于生成并保存图像到内存中的函数
def show(data):
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
sns.heatmap(
data,
cmap="Greys", # 颜色映射
linewidths=0.5, # 单元格边框宽度
)
plt.title('Correlation Heatmap')
# 将图片保存到内存中
buf = io.BytesIO()
plt.savefig(buf, format='png')
plt.close() # 关闭当前的plt窗口,防止内存泄露
buf.seek(0)
# 读取图片为PIL格式并转换为NumPy数组
img = Image.open(buf)
img = np.array(img) # 将图像转换为NumPy数组
return img
# 定义激活函数 Sigmoid
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x)) # Sigmoid激活函数
# 定义激活函数 ReLU
def ReLU(x):
return np.maximum(0, x) # ReLU激活函数
# 均方误差 (MSE) 损失函数
def mse_loss(predicted, target):
return np.mean((predicted - target) ** 2)
# MSE损失函数的导数,用于反向传播
def mse_loss_derivative(predicted, target):
return 2 * (predicted - target) / target.size
生成一个4x4的随机矩阵并初始化各层权重和偏置
# 输入数据 (生成一个4x4的随机矩阵并展示)。
# 用来生成由此图像变换到target图像的神经网络
input = np.random.rand(4, 4)
# 可视化该图像
show_pic(input)
# 将4x4矩阵展开为16x1列向量
input = input.reshape(-1, 1)
# 初始化第一层隐藏层的权重和偏置
weight0 = np.random.randn(num_hidden_layer0, input.shape[0]) # 16x16权重矩阵
bias0 = np.random.randn(num_hidden_layer0, 1) # 16x1偏置向量
# 初始化第二层隐藏层的权重和偏置
weight1 = np.random.randn(num_hidden_layer1, num_hidden_layer0) # 16x16权重矩阵
bias1 = np.random.randn(num_hidden_layer1, 1) # 16x1偏置向量
# 初始化输出层的权重和偏置
weight2 = np.random.randn(16, num_hidden_layer1) # 4x16权重矩阵
bias2 = np.random.randn(16, 1) # 4x1偏置向量
反向传递函数及注释说明
# 反向传播函数
def backpropagation(img, input, weight0, bias0, output0, weight1, bias1, output1, weight2, bias2, output, learning_rate, active_mode):
# ========================== 输出层梯度计算 ==========================
# MSE = [(y1 - R1)^2 + (y2 - R2)^2 +……(yn - Rn)^2 ]/n
# 我们的目标是最小化均方误差 (MSE),Ri为目标值(实际值),yi为模型预测值
# 所以首先对每个预测值 yi 计算均方误差 MSE 对 yi 的导数
# d_output_layer = 均方误差(MSE)对模型的预测输出 output 的导数
# MSE' ~~~mse_loss_derivative~~~> output
d_output_layer = mse_loss_derivative(output, img) # MSE的导数
# ========================== 激活函数的导数 ==========================
# 根据所使用的激活函数(ReLU 或 Sigmoid),计算损失MSE对激活函数输入x的导数
# 对于 ReLU:ReLU 的导数在输出 > 0 时为 1,输出 <= 0 时为 0
# 对于 Sigmoid:Sigmoid 的导数为 σ(x)(1 - σ(x)),其中 σ(x) 是 Sigmoid 函数的输出(output)
# MSE' ~~~mse_loss_derivative~~~> output ~~~ReLU'/Sigmoid'~~~> x
if active_mode == "ReLU":
d_output_layer *= (output > 0) # ReLU 的导数
else:
d_output_layer *= output * (1 - output) # Sigmoid 的导数
# ========================== 输出层权重和偏置的梯度更新 ==========================
# 通过链式法则,损失对输出层权重 weight2 和偏置 bias2 的导数可以用 d_output_layer 和上一层的输出计算得出
# 权重梯度:grad_weight2 = d_output_layer * output1.T
# 偏置梯度:grad_bias2 = d_output_layer 的累加和
# x = w1*out1 + w2*out2……wi*outi + b
# MSE' ~~~mse_loss_derivative~~~> output ~~~ReLU'/Sigmoid'~~~> x ~~~output1i~~~> wi
# MSE' ~~~mse_loss_derivative~~~> output ~~~ReLU'/Sigmoid'~~~> x ~~~1~~~> wi
# 其中d_hidden_layer 表示隐藏层2输人x对损失函数的梯度
grad_weight2 = np.dot(d_output_layer, output1.T) # 计算输出层权重的梯度
grad_bias2 = np.sum(d_output_layer, axis=1, keepdims=True) # 计算输出层偏置的梯度
# 使用梯度下降法更新输出层的权重和偏置
weight2 -= learning_rate * grad_weight2 # 更新输出层的权重
bias2 -= learning_rate * grad_bias2 # 更新输出层的偏置
# ========================== 隐藏层1的梯度更新 ==========================
# 通过反向传播计算隐藏层1的梯度
# d_hidden_layer1 表示隐藏层1输出(output1)对损失函数的梯度
# 损失函数对隐藏层1的输出导数是通过后续层传递过来的梯度计算得出:
# d_hidden_layer1 = 修改后的权重 * d_hidden_layer 表示隐藏层2输人x对损失函数的梯度
# 即 MSE' ~~~mse_loss_derivative~~~> output ~~~ReLU'/Sigmoid'~~~> x ~~~wi~~~> output1i
# 化简为 MSE' ~~~反向0层~~~> output1
d_hidden_layer1 = np.dot(weight2.T, d_output_layer)
# 根据激活函数选择(ReLU 或 Sigmoid)调整隐藏层1的导数
if active_mode == "ReLU":
d_hidden_layer1 *= (output1 > 0) # ReLU 的导数
else:
d_hidden_layer1 *= output1 * (1 - output1) # Sigmoid 的导数
# ========================== 隐藏层1的权重和偏置更新 ==========================
# MSE' ~~~反向0层~~~> output1 ~~~ReLU'/Sigmoid'~~~> x ~~~output1i~~~> wi
# MSE' ~~~反向0层~~~> output1 ~~~ReLU'/Sigmoid'~~~> x ~~~1~~~> wi
# 计算隐藏层1的权重和偏置的梯度,并使用梯度下降法进行更新
grad_weight1 = np.dot(d_hidden_layer1, output0.T) # 计算隐藏层1的权重梯度
grad_bias1 = np.sum(d_hidden_layer1, axis=1, keepdims=True) # 计算隐藏层1的偏置梯度
# 使用梯度下降法更新隐藏层1的权重和偏置
weight1 -= learning_rate * grad_weight1 # 更新隐藏层1的权重
bias1 -= learning_rate * grad_bias1 # 更新隐藏层1的偏置
# ========================== 隐藏层0的梯度更新 ==========================
# 通过反向传播计算隐藏层0的梯度
# d_hidden_layer0 表示隐藏层0输出(output0)对损失函数的梯度
d_hidden_layer0 = np.dot(weight1.T, d_hidden_layer1)
# 根据激活函数选择(ReLU 或 Sigmoid)调整隐藏层0的导数
if active_mode == "ReLU":
d_hidden_layer0 *= (output0 > 0) # ReLU 的导数
else:
d_hidden_layer0 *= output0 * (1 - output0) # Sigmoid 的导数
# ========================== 隐藏层0的权重和偏置更新 ==========================
# 计算隐藏层0的权重和偏置的梯度,并使用梯度下降法进行更新
grad_weight0 = np.dot(d_hidden_layer0, input.T) # 计算隐藏层0的权重梯度
grad_bias0 = np.sum(d_hidden_layer0, axis=1, keepdims=True) # 计算隐藏层0的偏置梯度
# 使用梯度下降法更新隐藏层0的权重和偏置
weight0 -= learning_rate * grad_weight0 # 更新隐藏层0的权重
bias0 -= learning_rate * grad_bias0 # 更新隐藏层0的偏置
# 返回更新后的权重和偏置
return weight0, bias0, weight1, bias1, weight2, bias2
前向传播函数及注释说明
# 前向传播函数
def forward(input, weight0, bias0, weight1, bias1, weight2, bias2, active_mode):
# 计算各层的输出
output0 = ReLU(np.dot(weight0, input) + bias0) if active_mode == "ReLU" else sigmoid(np.dot(weight0, input) + bias0)
output1 = ReLU(np.dot(weight1, output0) + bias1) if active_mode == "ReLU" else sigmoid(np.dot(weight1, output0) + bias1)
output = ReLU(np.dot(weight2, output1) + bias2) if active_mode == "ReLU" else sigmoid(np.dot(weight2, output1) + bias2)
return output0, output1, output
进入循环体
# 计算初始损失
img = img.reshape(-1, 1)
loss = mse_loss(input, img)
print("Initial loss:", loss)
# 训练过程
output0, output1, output = forward(input, weight0, bias0, weight1, bias1, weight2, bias2, active_mode)
for i in range(times +1):
# 反向传播
weight0, bias0, weight1, bias1, weight2, bias2 = backpropagation(img, input, weight0, bias0, output0, weight1, bias1, output1, weight2, bias2, output, learning_rate, active_mode)
# 前向传播
output0, output1, output = forward(input, weight0, bias0, weight1, bias1, weight2, bias2, active_mode)
# 添加图像到 TensorBoard 中 (注意要调整通道维度)
image_np = show(output.reshape(-1, 4))
writer.add_image('Heatmap', image_np.transpose(2, 0, 1), i) # 确保图像的通道为 (C, H, W)
# 计算并打印更新后的损失
new_loss = mse_loss(output, img)
print(f"Step {i}: Loss = {new_loss}")
# 关闭 TensorBoard 日志记录器
writer.close()
# 可视化该图像
show_pic(output.reshape(-1, 4))
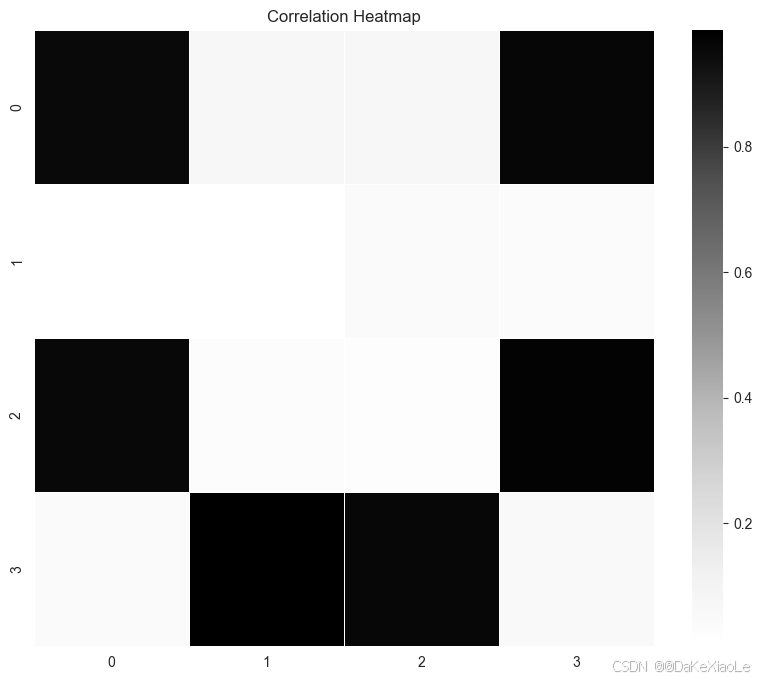

TensorBoard 保存并展示训练过程中的输出图像。
在新的locatio中输入,启动TensorBoard
tensorboard --logdir=logs
Serving TensorBoard on localhost; to expose to the network, use a proxy or pass --bind_all
TensorBoard 2.18.0 at http://localhost:6006/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
通过浏览器打开
结果参考绑定资源

























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








