CSS学习
语法:
语法: 选择器{
声明1;
声明2;
声明3;
声明4;
}
代码例子:
HTML:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!-- 规范<style 可以编写css代码,每一个声明,最好使用分号结尾>
语法: 选择器{
声明1;
声明2;
声明3;
声明4;
}
-->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="CSS/Style.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>我是标题</h1>
</body>
</html>
css:
h1{
color: aquamarine;
}
CSS的优势:
1、内容和表现分离
2、网页结构统一,可以实现复用
3、样式十分丰富
4、建议使用独立于HTML的CSS文件
5、利用SEO,容易被搜索引擎搜到
CSS的三种导入方式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!-- 内部样式-->
<style>
h1{
color: greenyellow;
}
</style>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css">
</head>
<body>
<!--
优先级:
行内样式>内部样式>外部样式
-->
<!--行内样式:在标签元素内,编写一个style属性,编写样式即可-->
<h1 style="color: red">我是标题</h1>
</body>
</html>
/*外部样式*/
h1{
color: yellow;
}
外部样式的两种写法:
- 链接式:html
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css">
- 导入式:CSS2.1特有的
<style>
/*导入式*/
@import url("css/style.css");
</style>
2、选择器
作用:选择页面上某一个或者某一个元素
2.1、基本选择器
1、标签选择器:选择一类标签 标签{}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
h1{
color: #31acaa;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>只因你太美</h1>
<h1>oh,baby</h1>
<p>xxx</p>
</body>
</html>
2、类选择器: 选择 所有class属性一样的的标签,跨标签, .类名{}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/*类选择器的格式 .class的名称{}
好处:可以多个标签归类,是同一个class,可以复用
*/
.kunkun {
color: #31acaa;
}
.zz{
color: greenyellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="kunkun">你好</h1>
<h1 class="zz">你们好</h1>
<h1 class="zz">我是你们的</h1>
<h1 class="kunkun">好盆友</h1>
</body>
</html>
3、id选择器:全局唯一 #id名{}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/*id选择器 :id必须全局唯一
#id名{}
不遵循就近原则 优先级是固定的
id选择器>class选择器>标签选择器
*/
.ss{
color: green;
}
#aa {
color: aqua;
}
#bb{
color: sienna;
}
h1{
color: blueviolet;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 id="aa">标签1</h1>
<h1 id="bb" >标签2</h1>
<h1 class="ss">标签3</h1>
<h1>标签4</h1>
<h1>标签5</h1>
<h1>标签6</h1>
<h1>标签7</h1>
</body>
</html>
优先级: id>class>标签
2.2、层次选择器
1、后代选择器:在某个元素的后面
/*后代选择器*/
body p{
/*body后面的p标签会被选择
*/
background-color: sienna;
}
2、子选择器 后面一代会被选择
/*子选择器*/
body>p{
/*body标签下面的这一层p标签被选择*/
background-color: blueviolet;
}
3、 相邻兄弟选择器 同辈
/*相邻兄弟选择器*/
.zhaozhao + p{
/*对下不对上,找到对应的class属性的下一个 p 标签*/
background-color: aquamarine;
}
4、通用选择器
/*通用选择器*/
.zhaozhao~{
/*找到对应class属性的下方的所有同级标签*/
background-color: green;
}
2.3、结构伪类选择器
/*选择ul的第一个子元素*/
ul li:first-child{
background-color: #31acaa;
}
/*选择ul的最后一个元素*/
ul li:last-child{
background-color: aquamarine;
}
/*选中p1*/
/*定位到父元素,选择当前的第一个元素,而且必须是当前元素才会生效*/
p:nth-child(1){
background-color: blueviolet;
}
p:nth-of-type(2){
/*定位到父元素 ,选择父元素下面子元素第二个类型为p的元素*/
background-color: chocolate;
}
2.4、属性选择器(常用)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.demo a {
float: left;
display: block;
height: 50px;
width: 50px;
border-radius: 15px;
background-color: #31acaa;
text-align: center;
color: gainsboro;
text-decoration: none;
margin-right: 10px;
font: bold 20px/50px Arial;
}
/*存在id的属性元素 a[]{}*/
a[id]{
background-color: sienna;
}
/*id等于last的元素*/
a[id=last]{
background-color: aqua;
}
/*class中有links属性的元素*/
a[class*="links"]{
background-color: blue;
}
/*href中以http开头的*/
a[href^=http]{
background-color: aqua;
}
/*href中以doc结尾的*/
a[href$=doc]{
background-color: chocolate;
}
</style>
</head>
<body class="demo">
<a href="http://www.baidu,com"class="links item first" id="first">1</a>
<a href="http://www.zz.com"class="links item ">2</a>
<a href="image/123.jpg"class="links item ">3</a>
<a href="image/ad.png"class="links item ">4</a>
<a href="image/cc.html"class="links item ">5</a>
<a href="abc"class="links item ">6</a>
<a href="/a/c"class="links item ">7</a>
<a href="abc.pdf"class="links item ">8</a>
<a href="sss.doc"class="links item ">9</a>
<a href="sasd.doc"class="links item last"id="last">10</a>
</body>
</html>

总结: *=含有元素
^=以…开头
$=以…结尾
3、美化网页元素
3.1、字体样式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
body{
font-family: 华文楷体;
color: #c4832d;
}
h1{
font-size: 50px;
}
.p1{
font-weight: bolder;
}
</style>
3.2、文本样式
- 颜色 color
- 文本对齐方式 text-align = center
- 首行缩进 text-indent :2em;
- 行高 line-height: 单行文字上下居中(与想要居中的对象行高设置相同就可以做到)
- 装饰(下划线) text-decoration : none(去掉超链接的下划线)
- 文本图片水平对齐:vertical-align:middle
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<style>
h1{
/*设置文本水平居中*/
text-align: center;
color: brown;
}
p{
/*设置文本首行缩进*/
text-indent: 2em;
color: sienna;
}
img,a{
/*设置图片与文字对齐*/
vertical-align: middle;
}
</style>

4、盒子模型
4.1边框
1、边框的粗细
2、边框的样式
3、边框的颜色
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/*去掉body默认的外边距*/
a,ul,li,p,body{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
/*border
粗细 样式 颜色
*/
#box{
width: 300px;
border: 1px solid red;
}
h2{
font-size: 16px;
background-color: chocolate;
line-height: 30px;
color: brown;
}
form{
background-color: chocolate;
}
div:nth-of-type(1) input{
border: 3px solid blanchedalmond;
}
div:nth-of-type(2) input{
border: 3px solid blanchedalmond;
}
div:nth-of-type(3) input{
border: 3px solid blanchedalmond;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<h2>会员登陆</h2>
<form action="#">
<div>
<span>用户名:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
<div>
<span>密码:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
<div>
<span>邮箱:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>

4.2、内外边距
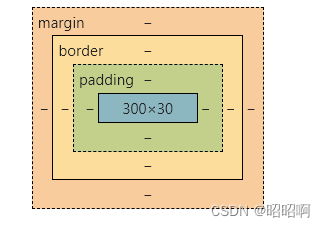
盒子大小的算法 :margin + border + padidng + 内容宽度
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/*去掉body默认的外边距*/
a,ul,li,p,body{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
/*border
粗细 样式 颜色
*/
#box{
width: 300px;
border: 1px solid red;
margin: 0 auto;
}
h2{
font-size: 16px;
background-color: chocolate;
line-height: 30px;
color: brown;
margin: 0;
}
form{
background-color: chocolate;
}
div:nth-of-type(1) input{
border: 3px solid blanchedalmond;
}
div:nth-of-type(2) input{
border: 3px solid blanchedalmond;
}
div:nth-of-type(3) input{
border: 3px solid blanchedalmond;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<h2>会员登陆</h2>
<form action="#">
<div>
<span>用户名:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
<div>
<span>密码:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
<div>
<span>邮箱:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
4.3、圆角边框
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/*圆角边框
如何变成圆形:将正方形的边长减半作为圆的半径
border-radius:四个参数 可以设置两个 对应左上、右下 右上、左上
四个参数是:
*/
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 3px solid red;
border-radius: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
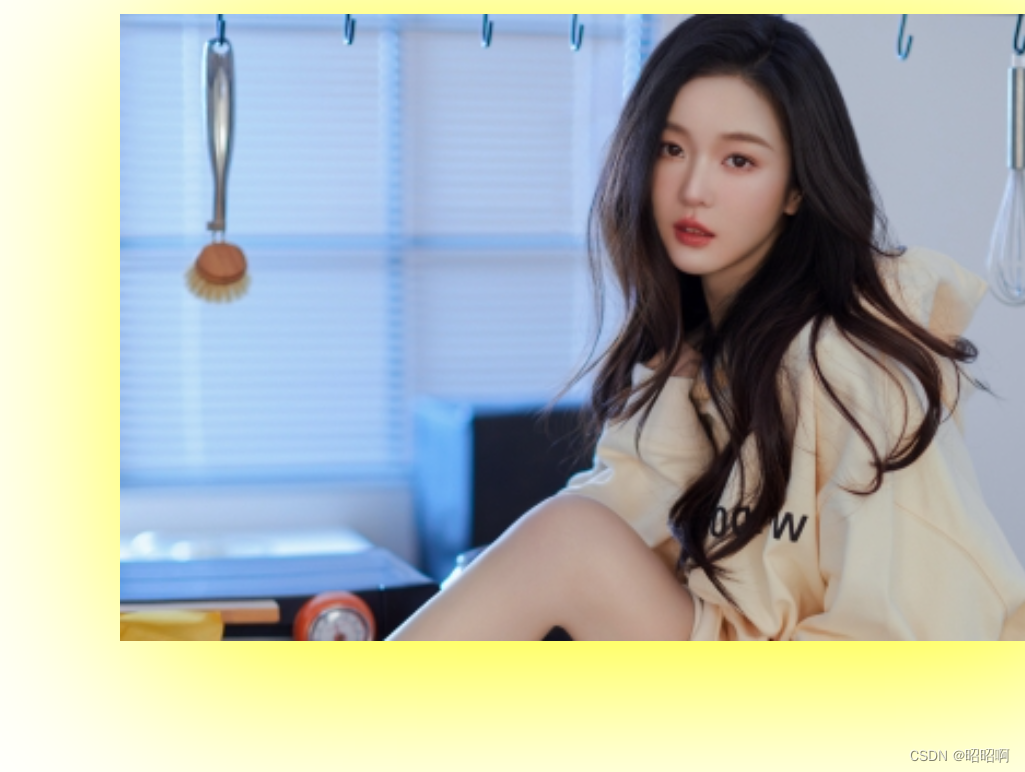
4.3、阴影
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
div{
width: 1000px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
img{
box-shadow: 10px 10px 100px yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div style="width: 500px;display: block;text-align: center">
<div>
<img src="image/a1.jpg" alt="">
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

5、浮动
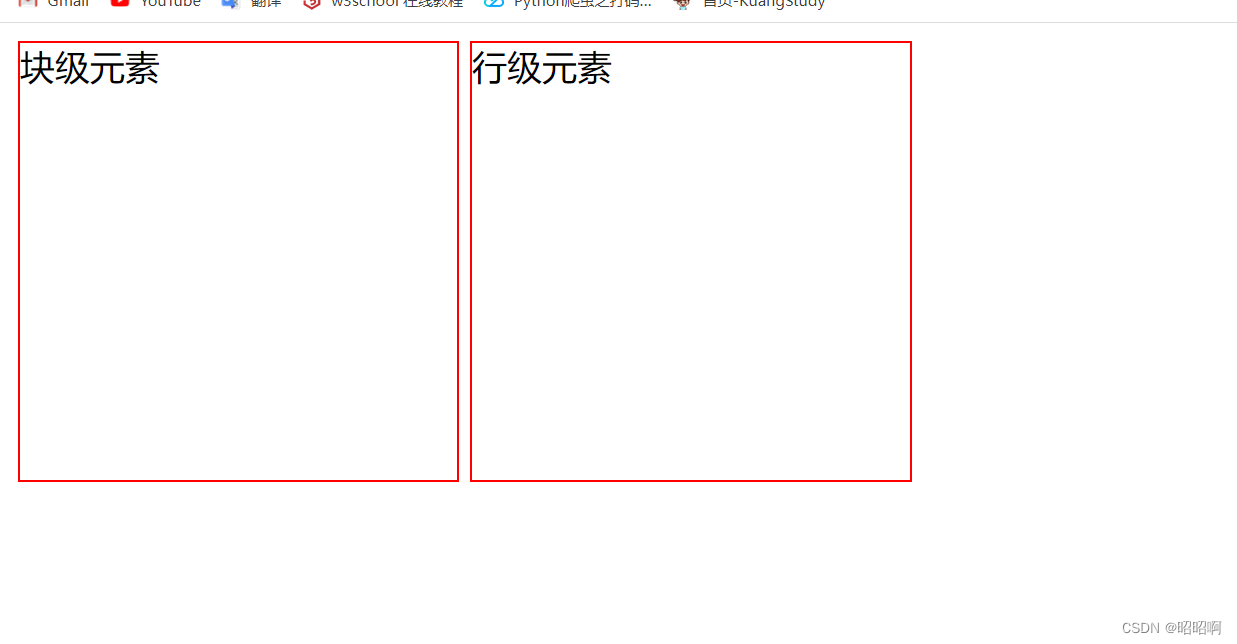
5.1、标准文档流
块级元素:独占一行
eg:h1~h6,p div 列表……
行级元素:不独占一行
eg:span a img strong……
块级元素可以包含行级元素,反之,则不可
5.2、dispaly
block 块元素
inline 行内元素
inline-block 是块级元素,但是可以内联,在一行展示
none
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
div{
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
display: inline-block;
border: 1px solid red;
}
span{
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
border: 1px solid red;
display: inline-block;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>块级元素
</div>
<span>行级元素</span>
</body>
</html>
5.3、float
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<div class="zz1">
<img src="images/a.jpg" alt="">
</div>
<div class="zz2">
<img src="images/b.jpg" alt="">
</div>
<div class="zz3">
<img src="images/c.jpg" alt="">
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
.zz1{
float: left;
}
#box{
border: 1px solid red;
width: 800px;
height: 300px;
}
.zz2{
float: left;
}
.zz3{
float: left;
}

5.4、父级元素边框塌陷问题
1、clear
/*clear
right:清除右侧浮动
left:清除左侧浮动
both:清除两侧浮动
*/
解决方法:
1、增大父级元素的大小
#box{
border: 1px solid red;
width: 1000px;
height: 300px;
}
2、设置一个空的div,将空的div清除浮动,将内外边距设为0,也可以达到效果
<div class="clear1"></div>
.clear1{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
clear: both;
}

3、overflow
在父级元素增加一个 overflow:hidden;
#box{
border: 1px solid red;
overflow: hidden;
}
4、在父类添加一个伪类 :after
#box:after{
content: '';
display: block;
clear: both;
}
原理就是跟方法二一样,只是避免了在html中添加空的div
小结:
- 浮动元素后面加一个空的div 简单,但是代码中避免空div
- 设置父元素的高度,简单,但有限制
- overflow 简单,但是会有下拉框,在有些场景并不合适(不美观)
- 父类后加伪类:after 写法稍微复杂,但是没什么副作用,推荐使用
5.5、对比
- dispaly
不能控制左右,但没有边框塌陷问题
- float
可控制左右,但是会造成父级边框塌陷问题 需要清除浮动
6、定位
6.1、相对定位
相对定位:position:relation;
相对于原来的位置,来进行指定偏移
top: -20px;
left: 10px;
bottom: 20px;
right: 30px;
练习:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
#father{
border: 1px red solid;
width: 700px;
height: 700px;
padding: 100px;
}
.a {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid black;
border-radius: 16px;
}
a {
margin: 0 auto;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
line-height: 200px;
text-align: center;
color: white;
text-decoration: none;
display: block;
}
a:hover{
background-color: #c4832d;
}
#a1{
background-color: aqua;
position: relative;
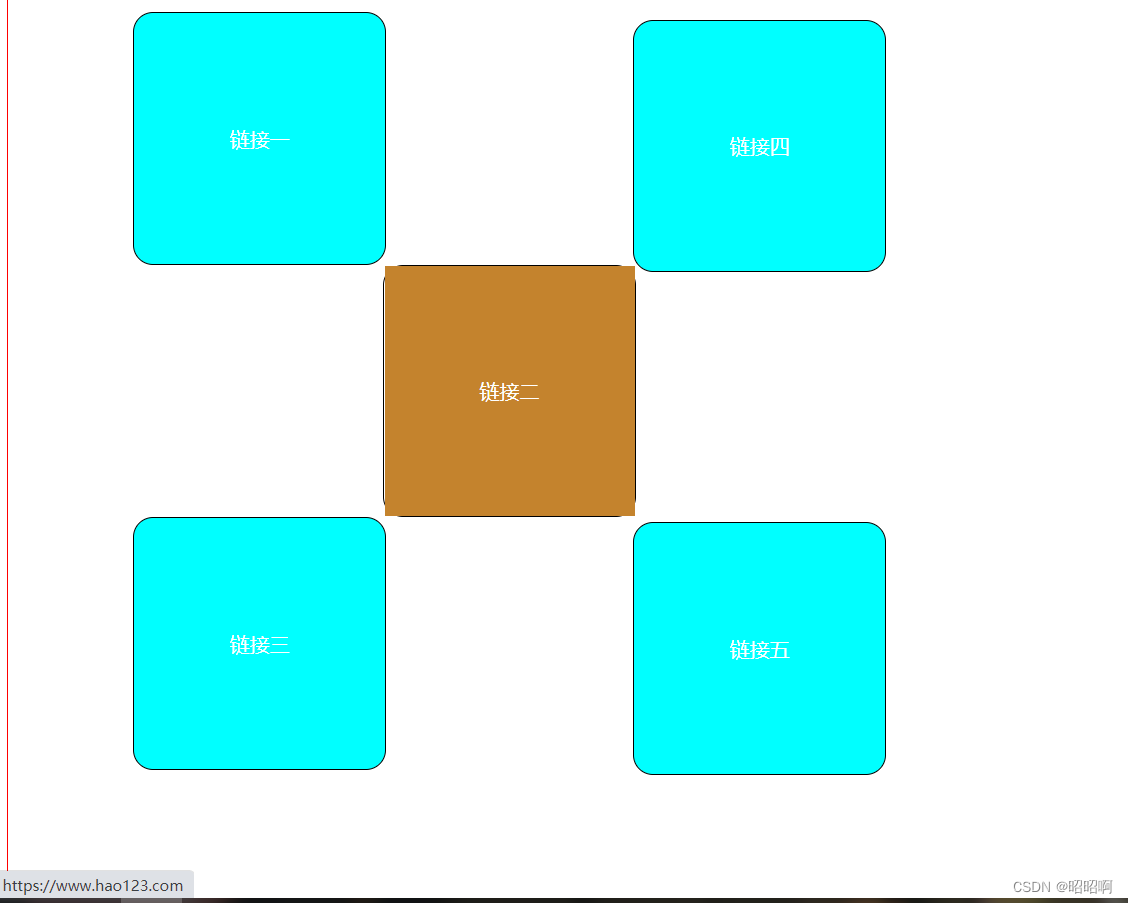
6.2、绝对定位
定位:基于xxx定位,上下左右
1、没有父级元素的前提下,相当于浏览器定位
2、假设父级元素存在定位,我们通常会以父级单位为参照进行偏移
3、在父级元素内移动,不能超过
相对于父级或者浏览器的位置,进行指定的偏移,绝对定位的话,不在标准文档流中,原来的位置不会被保留
6.3、固定定位
postion :fixed
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
body{
height: 1000px;
}
div:nth-of-type(1){
/*绝对定位 相当于浏览器
*/
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #c4832d;
position: absolute;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
}
div:nth-of-type(2){
/*固定定位: fixed
*/
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: chartreuse;
position: fixed;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
</div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
6.4、z-index
mg-r11kGfGU-1666578637659)]
6.2、绝对定位
定位:基于xxx定位,上下左右
1、没有父级元素的前提下,相当于浏览器定位
2、假设父级元素存在定位,我们通常会以父级单位为参照进行偏移
3、在父级元素内移动,不能超过
相对于父级或者浏览器的位置,进行指定的偏移,绝对定位的话,不在标准文档流中,原来的位置不会被保留
6.3、固定定位
postion :fixed
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
body{
height: 1000px;
}
div:nth-of-type(1){
/*绝对定位 相当于浏览器
*/
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #c4832d;
position: absolute;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
}
div:nth-of-type(2){
/*固定定位: fixed
*/
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: chartreuse;
position: fixed;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
</div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>




















 2018
2018

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








