使用SGLang部署的版本可查看另一篇文章:使用SGLang部署Qwen3 Reranker系列模型
实测使用VLLM部署的推理速度更快,QBS更高
VLLM安装
使用官方流程进行VLLM的安装(VLLM官方文档,Qwen官方VLLM安装文档)
conda create -n myenv python=3.10 -y
conda activate myenv
pip install vllm
VLLM部署Qwen3 Reranker系列(0.6B/4B/8B)模型
根据官方部署Reranker模型的教程,使用VLLM部署Qwen3 Reranker系列的模型时,会出现报错,显示不支持相应API(The model does not support Score API),先说结论,VLLM是可以部署Qwen3 Reranker系列的模型的,只是需要进行一定的转换。
首先, Qwen3-reranker 是 Qwen3ForCausalLM 架构的模型,也就是说,它本质是一个基于生成式的模型架构,VLLM官方显示是支持该形式的模型的。

然而,在实操过程中,会发现,当使用如下指令进行部署时
vllm serve {model_path}
会输出以下日志,在部署完成之后,VLLM会默认这个架构是一个生成式的模型,仅支持chat模板,也就是下图中的红色区域,白色区域的API是不可使用的。
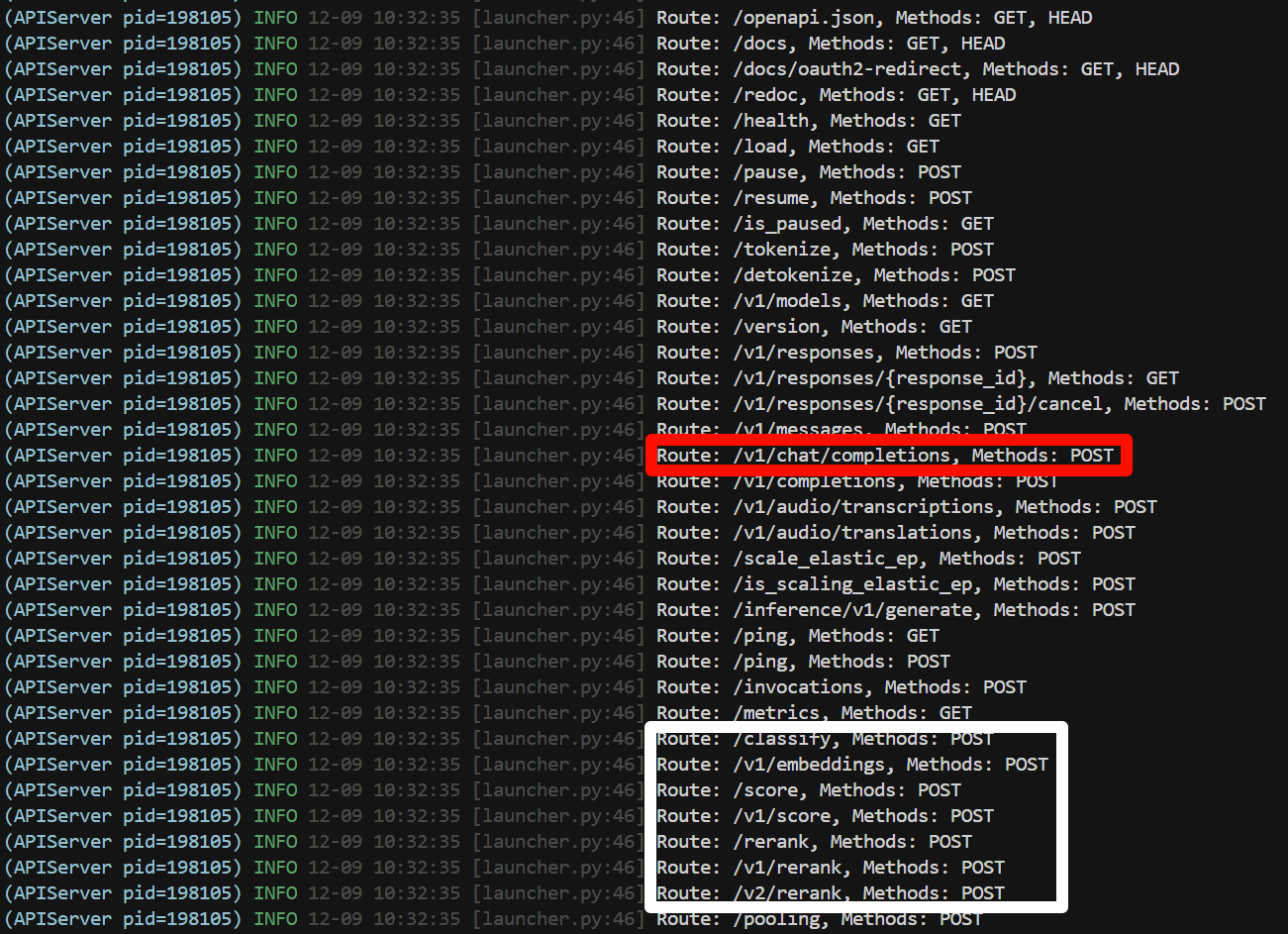
当按照官方教程构造client并进行白色区域的API使用时,会出现如下报错:
{'error': {'message': 'The model does not support Score API', 'type': 'BadRequestError', 'param': None, 'code': 400}}
这是因为,VLLM目前无法支持单个架构同时支持Embedding 和 Reranker,一个可行的方案就是,将 token_false_id = 2152 和 token_true_id = 9693 提取到一个二分类任务中,而不是当前的 151669 分类任务,最后使用vllm的 score API来进行推理的实现,也就是说,要将双向分类器变成单向分类器,将原始的 Qwen3ForCausalLM 架构转换为 Qwen3ForSequenceClassification 架构,可以使用如下代码。(代码来源)
import torch
from transformers import Qwen3ForCausalLM, Qwen3ForSequenceClassification, AutoTokenizer
def convert_model(model_path, save_path):
# --- Step 1: Load the Causal LM and extract lm_head weights ---
print(f"1. Loading Causal LM: {model_path}")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path)
causal_lm = Qwen3ForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_path)
# The lm_head is the final linear layer that maps hidden states to vocabulary logits
lm_head_weights = causal_lm.lm_head.weight
print(f" lm_head weight shape: {lm_head_weights.shape}") # (vocab_size, hidden_size)
# --- Step 2: Get the token IDs for "yes" and "no" ---
print("\n2. Finding token IDs for 'yes' and 'no'")
yes_token_id = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids("yes")
no_token_id = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids("no")
print(f" ID for 'yes': {yes_token_id}, ID for 'no': {no_token_id}")
# --- Step 3: Create the classifier vector ---
print("\n3. Creating the classifier vector from lm_head weights")
# Extract the specific rows (weight vectors) for our target tokens
yes_vector = lm_head_weights[yes_token_id]
no_vector = lm_head_weights[no_token_id]
# The new classifier is the difference between the 'yes' and 'no' vectors
classifier_vector = yes_vector - no_vector
print(f" Shape of the new classifier vector: {classifier_vector.shape}")
# --- Step 4: Load the model as a Sequence Classifier ---
print(f"\n4. Loading Sequence Classification model with num_labels=1")
# num_labels=1 is key for binary classification represented by a single logit
seq_cls_model = Qwen3ForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
model_path,
num_labels=1,
ignore_mismatched_sizes=True
)
# --- Step 5: Replace the classifier's weights ---
print("\n5. Replacing the randomly initialized classifier weights")
# The classification head in Qwen is named 'score'. It's a torch.nn.Linear layer.
# Its weight matrix has shape (num_labels, hidden_size), which is (1, hidden_size) here.
with torch.no_grad():
# We need to add a dimension to our vector to match the (1, hidden_size) shape
seq_cls_model.score.weight.copy_(classifier_vector.unsqueeze(0))
# It's good practice to zero out the bias for a clean transfer
if seq_cls_model.score.bias is not None:
seq_cls_model.score.bias.zero_()
print(" Classifier head replaced successfully.")
# --- Verification: Prove that the logic works ---
print("\n--- VERIFICATION ---")
text = "Is this a good example?"
inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt")
# A. Get logits from the original Causal LM
with torch.no_grad():
outputs_causal = causal_lm(**inputs)
last_token_logits = outputs_causal.logits[0, -1, :]
manual_logit_diff = last_token_logits[yes_token_id] - last_token_logits[no_token_id]
# Compute probs (yes/no) and extract 'yes' prob
concat_logits = torch.stack([last_token_logits[yes_token_id], last_token_logits[no_token_id]])
causal_prob = torch.softmax(concat_logits, dim=-1)[0]
# B. Get the single logit from our new Sequence Classification model
with torch.no_grad():
outputs_seq_cls = seq_cls_model(**inputs)
# Shape is (1, 1), squeeze to scalar
model_logit = outputs_seq_cls.logits.squeeze()
# Compute 'yes' prob
classification_prob = torch.sigmoid(model_logit)
print(f"Input text: '{text}'")
print(f"\nManual logit difference ('yes' - 'no'): {manual_logit_diff.item():.4f}")
print(f"Sequence Classification model output: {model_logit.item():.4f}")
print(f"Are they almost identical? {torch.allclose(manual_logit_diff, model_logit)}")
# Probs
print(f"\nCausal prob (2 classes): {causal_prob.item():.4f}")
print(f"Classification prob (1 class): {classification_prob.item():.4f}")
print(f"Are they almost identical? {torch.allclose(causal_prob, classification_prob)}")
seq_cls_model.save_pretrained(save_path)
tokenizer.save_pretrained(save_path)
print(f"Save model to: {save_path}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
model_path = "/home/Qwen/Qwen3-Reranker-0.6B"
save_path = "/home/Qwen/Qwen3-Reranker-0.6B-seqcls-converted"
convert_model(model_path, save_path)
以上代码,将model_path和save_path替换之后,就可直接使用,转换之后,结果是相同的,如下所示
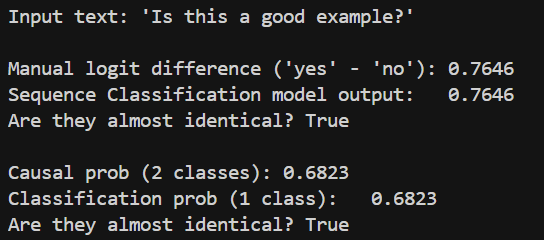
使用vllm进行部署:
vllm serve /home/Qwen/Qwen3-Reranker-0.6B-seqcls-converted \
--hf_overrides '{"architectures": ["Qwen3ForSequenceClassification"],"classifier_from_token": ["no", "yes"],"is_original_qwen3_reranker": true}' \
直接部署经常容易爆显存,建议加上
--gpu-memory-utilization 0.6参数
基于Qwen3官方文档,构造的client如下所示。
import requests
url = "http://127.0.0.1:8000/score"
MODEL_NAME = "Qwen3-Reranker-0.6B-seqcls-converted"
prefix = '<|im_start|>system\nJudge whether the Document meets the requirements based on the Query and the Instruct provided. Note that the answer can only be "yes" or "no".<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>user\n'
suffix = "<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\n<think>\n\n</think>\n\n"
query_template = "{prefix}<Instruct>: {instruction}\n<Query>: {query}\n"
document_template = "<Document>: {doc}{suffix}"
instruction = (
"Given a web search query, retrieve relevant passages that answer the query"
)
queries = [
"What is the capital of China?",
"Explain gravity",
]
documents = [
"I want yo eat an apple.",
"Gravity is a force that attracts two bodies towards each other. It gives weight to physical objects and is responsible for the movement of planets around the sun.",
]
queries = [
query_template.format(prefix=prefix, instruction=instruction, query=query)
for query in queries
]
documents = [
document_template.format(doc=doc, suffix=suffix) for doc in documents
]
response = requests.post(url,
json={
"text_1": queries,
"text_2": documents,
"truncate_prompt_tokens": -1,
}).json()
print(response)
最终输出如下所示,结果符合预期,转换后的模型效果与转换前是一致的。
{
'id': 'score-a918997f9ba1424f',
'object': 'list',
'created': 1765251739,
'model': '/home/Qwen/Qwen3-Reranker-0.6B-seqcls-converted',
'data': [{'index': 0, 'object': 'score', 'score': 0.0001038978953147307},
{'index': 1, 'object': 'score', 'score': 0.993419349193573}],
'usage': {'prompt_tokens': 188, 'total_tokens': 188, 'completion_tokens': 0, 'prompt_tokens_details': None}
}
参考解决方案
- vllm部署Qwen3-Reranker:https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm/pull/19260
- Qwen3-Reranker模型转换:https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen3-Reranker-0.6B/discussions/3
 VLLM部署Qwen3重排序模型
VLLM部署Qwen3重排序模型






















 7093
7093

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










