1、顺序
按顺序执行
a = 1
b = 2
c = 3
print(a == b)
print(a + b)
print(b * c)
DOS命令下运行D盘的‘文件ccc1.py

2、分支
2.1 条件分支 if 语句
语义:if 语句通常用来解决选择性问题,要么这样,要么那样
if 语句表达式:
# 第一种情况语句块
pass
elif 条件表达式:
#第二种情况语句块
pass
.......
else:
#其他情况语句块
pass
# if condition
condition = True
if condition:
print('do if')
语句块:缩进量一样的语句(像下面的4个print)
# if condition
condition = True
if condition:
print('do if')
print('do if')
print('do if')
print('do if')
# if condition
condition = True
a = 1
b = 2
if a == b:
print('do if')
else:
print('do else')
例如:模拟一个登陆用户名和密码
account = 'sniper'
password = '123456'
print('please input username:')
user_account = input()
print('input password:')
user_password = input()
if user_account == account and user_password == password:
print('success!')
else:
print('error!')
在上述基础上,想要知道是用户名错了还是密码错了
if user_account != account:
print('username error!')
elif user_password != password:
print('password error!')
else:
print('success!')
也可以,但是没有上面那种简洁
if user_account == account:
if user_password == password:
print('success!')
else:
print('password error!')
else:
print("username error!")
3、循环
3.1 while 循环
语义:满足一定的条件,那么循环将一直执行下去,直到
条件为假,循环停止
while 条件表达式:
#语句块
pass
else:
#语句块(循环正常结束时执行)
pass
进入无限循环(死循环),可用Ctrl+c 停止
condition = True
while condition:
print('hello python')
例如:
当x<=10时,执行下面两行循环体
x = 1
while x <= 10:
print(x)
x += 1

若调换下面两行代码顺序,则输出会不一样
(一个循环体中包含10,一个不包含10)
x = 1
while x <= 10:
x += 1
print(x)

循环是在条件不成立(即x等于11)的时候才结束的,执
行了else里面的打印
x = 1
while x <= 10:
print(x)
x += 1
else:
print('else:',x)

3.2 for 循环
语义:for循环的用处主要是遍历,遍历序列(列表、元
组、字符串)遍历字典的键等,除了遍历,for循环还能配
合range函数实现指定次数的循环
for 循环变量 in 序列:
# 语句块
pass
else:
# 语句块
pass
可用列表也可用元组
colors = ('red','green','blue','yellow','orange')
for color in colors:
print(color)

遍历多维(嵌套)列表
sequences = [['red','green','blue','yellow','orange'],[1,2,3]]
for x in sequences:
for y in x:
print(y)
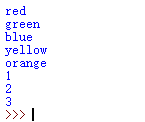
举例:
count = 0
colors = ('red','green','blue','yellow','orange')
for color in colors:
print(color)
count += 1
else:
print("else",count)

3.3 循环的2个强制结束
break :跳出,结束,当条件触发执行了break语句后,不管循环执行到第几次,列表有没有遍历完,都将结束。
continue:结束当前循环,它会处在循环体某个位置。循环还会继续,只是会跳出当前循环
break:直接结束循环,只打印yellow之前的
count = 0
colors = ('red','green','blue','yellow','orange')
for color in colors:
if color == 'yellow':
break
print(color)
count += 1

else是循环正常结束之后才会被执行,break强制退出会被认为是非正常结束,所以不会被执行。
count = 0
colors = ('red','green','blue','yellow','orange')
for color in colors:
if color == 'yellow':
break
print(color)
count += 1
else:
print("else",count)

continue:结束yellow循环,但还会执行下一个循环,打印出来只是没有yellow
count = 0
colors = ('red','green','blue','yellow','orange')
for color in colors:
if color == 'yellow':
continue
print(color)
count += 1

而continue会执行else并打印出来,所以continue只跳过了yellow那次的语句,其他语句会正常执行,continue也并不会被认为是强制结束循环,循环相当于正常循环
count = 0
colors = ('red','green','blue','yellow','orange')
for color in colors:
if color == 'yellow':
continue
print(color)
count += 1
else:
print("else",count)

while 和 for 最大的区别:能够确认次数用 for(例如遍历列表),不知道次数用 while(例如破解密码穷举法)
3.4 range函数
遍历 range()
开始是被包含在内的,结束时不包含在内的,后面是步长,正数代表从小到大,负数代表从大到小
range(1,10) 包含1 但不包含10
for i in range(1,10):
print(i)

从1到10,每次跳2个数
for i in range(1,10,2):
print(i)

包含9不包含1
for i in range(9,0,-1):
print(i)

例如:只想打印偶数
a = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
for x in a:
if x % 2 == 0:
continue
print(x,end=' |')

a = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
for index in range(0,10,2):
print(index)

造下标
a = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
for index in range(0,10,2):
print(a[index],end = ' |')

遍历切片
a = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
for x in a[::2]:
print(x,end=' |')






 本文详细介绍了Python编程中的流程控制,包括顺序执行、条件分支if语句、while和for循环的使用,以及如何通过break和continue控制循环流程。特别地,讨论了range函数在循环中的应用,帮助读者理解如何进行指定次数的循环和遍历操作。
本文详细介绍了Python编程中的流程控制,包括顺序执行、条件分支if语句、while和for循环的使用,以及如何通过break和continue控制循环流程。特别地,讨论了range函数在循环中的应用,帮助读者理解如何进行指定次数的循环和遍历操作。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








