异常处理机制
- 抛出异常
- 捕获异常
异常处理五个关键字
try、catch、finally、throw、throws
捕获异常
格式:
try {
// 监控区,存放可能发生异常的代码
} catch (想要捕获的异常类型) {
// 发生异常后需要执行的处理代码} finally {
// 可选项
// 无论发不发生异常,都会执行的代码
}
使用例子:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
int b = 0;
// try 监控区
// catch(想要捕获的异常类型) 捕获异常
// finally 处理善后工作
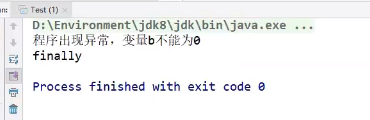
try {
System.out.println(a/b);
} catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("程序出现异常,变量b不能为0");
} finally {
System.out.println("finally");
}
// finally 可选项
// 例如 IO 的操作,需要关闭资源。
}
}
运行结果:
可以多个 catch
注意:捕获的顺序从小到大,即上面异常的类型不能大于下面的异常类型,否则会提示异常已经被覆盖。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
int b = 0;
try {
System.out.println(a/b);
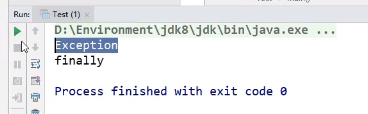
} catch(Error e) {
System.out.println("Error");
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("Exception");
} catch(Throwable e) {
System.out.println("Throwable");
} finally {
System.out.println("finally");
}
}
}
运行结果:
快速生成异常捕获代码
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
int b = 0;
// 选择下面这行可能会出现异常的代码
// Ctrl + Alt + T
// 然后选择 try/catch/finally
// System.out.println(a/b);
// 生成的代码如下:
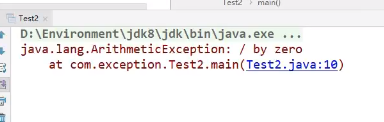
try {
System.out.println(a/b);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace(); // 打印错误的栈信息
} finally {}
}
}
运行结果:
抛出异常
throw 方法内抛出异常
格式:
throw new 异常类()
一般在方法中使用,如果这个方法处理不了这个异常,方法上抛出异常。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
int b = 0;
if (b==0) { // throw
throw new ArithmeticException(); // 主动抛出异常
}
System.out.println(a/b);
}
}
throws 方法上抛出异常
格式:
throws 异常类
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Test().test(1,0);
}
public void test(int a, int b) throws ArithmeticException {
if (b==0) { // throw
throw new ArithmeticException(); // 主动抛出异常
}
System.out.println(a/b);
}
}








 本文详细介绍了Java中的异常处理机制,包括try、catch、finally等关键字的使用方法,并提供了具体的代码示例来展示如何捕获和处理异常。
本文详细介绍了Java中的异常处理机制,包括try、catch、finally等关键字的使用方法,并提供了具体的代码示例来展示如何捕获和处理异常。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








