- 题目描述
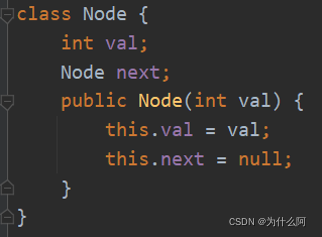
请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
普通单链表:
复杂链表:
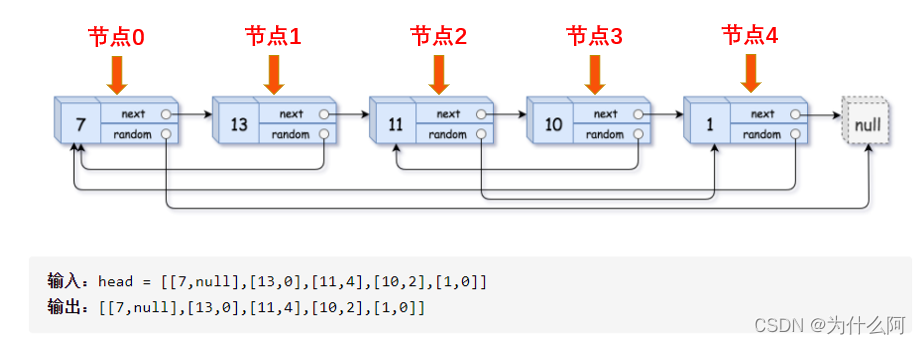
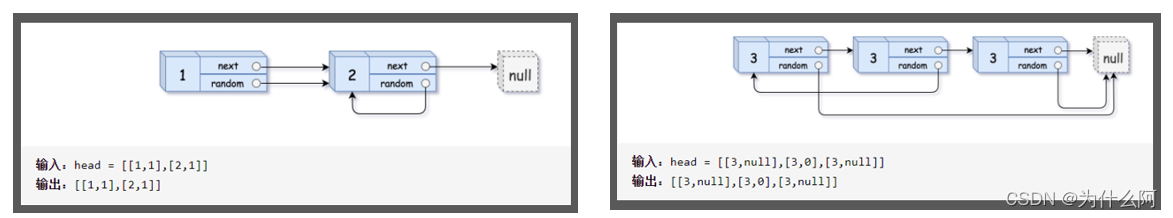

- 解题方法
① 组装
② 哈希表
③ 拼接拆分
① 解法一:组装
- 判断head是否为null,是则直接返回。
- 将链表结点按顺序存入list_1。
- 找出每个节点的random指向的位置,存入list_2。
- 把list_1和list_2进行组装返回。
完整代码
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head){
if(head == null){
return null;
}
//把结点按照顺序存入list_1
Node tmp = head;//保护head
List<Node> list_1 = new ArrayList<>();
while(tmp != null){
list_1.add(new Node(tmp.val));
tmp = tmp.next;
}
//找出每个结点的random指向位置存入list_2
List<Integer> list_2 = new ArrayList<>();
Node tmp2 = head;
int count = 0;
while (tmp2 != null){
tmp = head;
count = 0;
if(tmp2.random == null){
list_2.add(-1);
}
else{
while(tmp !=null){
if(tmp2.random==tmp){
break;
}
count++;
tmp = tmp.next;
}
list_2.add(count);
}
tmp2 = tmp2.next;
}
//两个list组装
tmp = list_1.get(0);
if(list_2.get(0) != -1){
tmp.random = list_1.get(list_2.get(0));
}
Node result = tmp;
for(int i=1;i<list_1.size();i++){
tmp.next = list_1.get(i);
if(list_2.get(i) != -1){
tmp.next.random = list_1.get(list_2.get(i));
}
tmp = tmp.next;
}
return result;
}
}
运行结果


② 解法二:哈希表
- 创建HashMap集合。
- 顺序遍历,存储原结点和新结点(先存储结点值val) 。
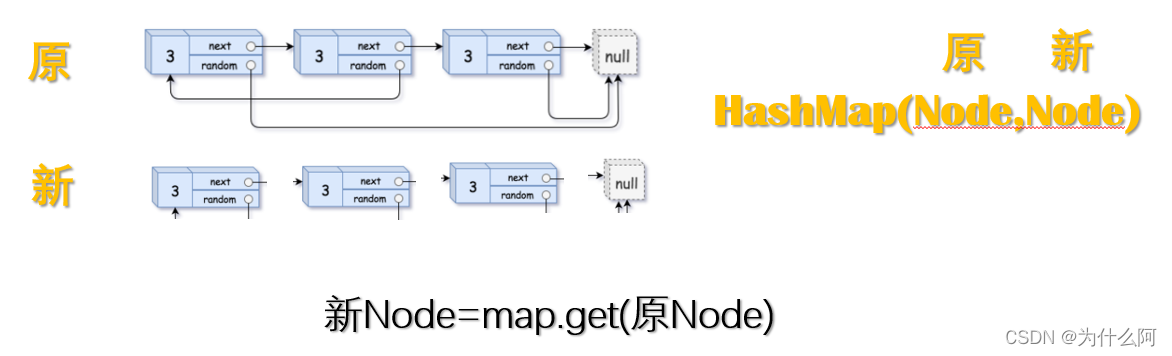
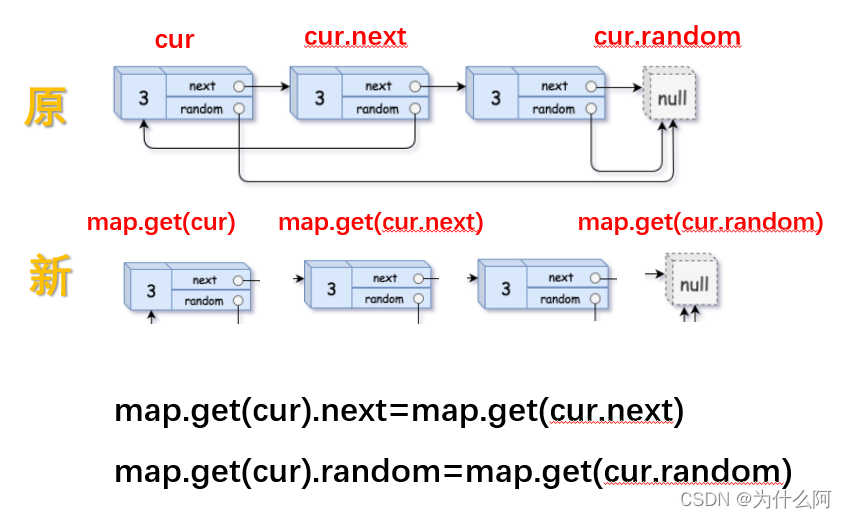
- 复制结点 next指向和 random指向。
完整代码
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution { //HashMap实现
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
HashMap<Node,Node> map = new HashMap<>(); //创建HashMap集合
Node cur=head;
//复制结点值
while(cur!=null){
//存储put:<key,value1>
map.put(cur,new Node(cur.val)); //顺序遍历,存储老结点和新结点(先存储新创建的结点值)
cur=cur.next;
}
//复制结点指向
cur = head;
while(cur!=null){
//得到get:<key>.value2,3
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next); //新结点next指向同旧结点的next指向
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random); //新结点random指向同旧结点的random指向
cur = cur.next;
}
//返回复制的链表
return map.get(head);
}
}
运行结果

③ 解法三:拼接拆分
- 遍历链表,在各原节点后边复制一个新的节点形成新的链表。
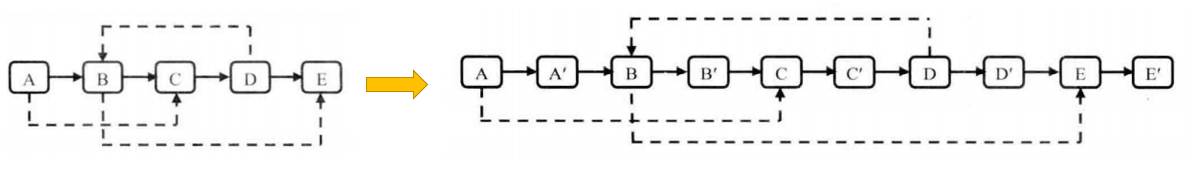
- 遍历链表,将原节点的random域复制给新节点。
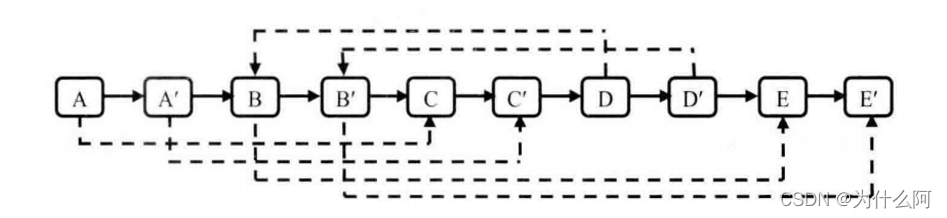
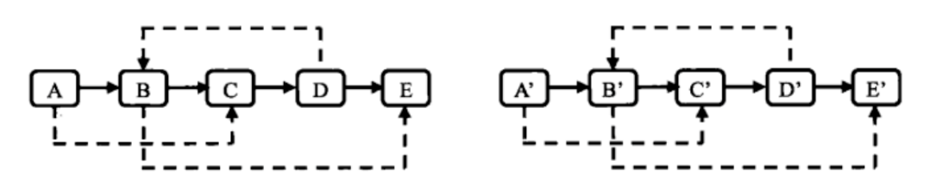
- 将新链表拆分为旧链表和新的克隆链表。
完整代码
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null)
return head;
// Step1: 并排复制原链表的所有结点,直接放在原相同节点后面
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
Node clone = new Node(cur.val);
clone.next = cur.next;
cur.next = clone;
cur = clone.next;
}
// Step2: 建立 random 链接,与原链表结点的 random 链接一一对应
cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
Node cloneRandom = cur.next;
if (cur.random != null)
cloneRandom.random = cur.random.next;
cur = cloneRandom.next;
}
// Step3: 复制成功,将新复制的链表从原链表中剥拆分出来
cur = head;
Node cloneNewHead = head.next;
while (cur.next != null) {
Node nextNode = cur.next;
cur.next = nextNode.next;
cur = nextNode;
}
return cloneNewHead;
}
}
运行结果







 本文介绍了三种方法来复制一个复杂链表,其中每个节点包含next和random指针。解法一通过组装新链表和random指针实现,解法二利用哈希表存储节点及其对应的复制节点,解法三则是通过拼接新节点到原链表再拆分。每种方法都给出了详细的代码实现和运行结果。
本文介绍了三种方法来复制一个复杂链表,其中每个节点包含next和random指针。解法一通过组装新链表和random指针实现,解法二利用哈希表存储节点及其对应的复制节点,解法三则是通过拼接新节点到原链表再拆分。每种方法都给出了详细的代码实现和运行结果。
















 2027
2027

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








