目录
文本预处理、语言模型为大模型必学内容。RNN、GRU、LSTM、seq2seq了解即可。
1 文本预处理
1.1 库
import collections import re from d2l import torch as d2l
1.2 读取数据集
#@save d2l.DATA_HUB['time_machine'] = (d2l.DATA_URL + 'timemachine.txt', '090b5e7e70c295757f55df93cb0a180b9691891a') def read_time_machine(): #@save """将时间机器数据集加载到文本行的列表中""" with open(d2l.download('time_machine'), 'r') as f: lines = f.readlines() return [re.sub('[^A-Za-z]+', ' ', line).strip().lower() for line in lines] lines = read_time_machine() print(f'# 文本总行数: {len(lines)}') print(lines[0]) print(lines[10])
1.3 词元化
def tokenize(lines, token='word'): #@save """将文本行拆分为单词或字符词元""" if token == 'word': return [line.split() for line in lines] elif token == 'char': return [list(line) for line in lines] else: print('错误:未知词元类型:' + token) tokens = tokenize(lines) for i in range(11): print(tokens[i])
1.4 词表
class Vocab: #@save """文本词表""" def __init__(self, tokens=None, min_freq=0, reserved_tokens=None): if tokens is None: tokens = [] if reserved_tokens is None: reserved_tokens = [] # 按出现频率排序 counter = count_corpus(tokens) self._token_freqs = sorted(counter.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True) # 未知词元的索引为0 self.idx_to_token = ['<unk>'] + reserved_tokens self.token_to_idx = {token: idx for idx, token in enumerate(self.idx_to_token)} for token, freq in self._token_freqs: if freq < min_freq: break if token not in self.token_to_idx: self.idx_to_token.append(token) self.token_to_idx[token] = len(self.idx_to_token) - 1 def __len__(self): return len(self.idx_to_token) def __getitem__(self, tokens): if not isinstance(tokens, (list, tuple)): return self.token_to_idx.get(tokens, self.unk) return [self.__getitem__(token) for token in tokens] def to_tokens(self, indices): if not isinstance(indices, (list, tuple)): return self.idx_to_token[indices] return [self.idx_to_token[index] for index in indices] @property def unk(self): # 未知词元的索引为0 return 0 @property def token_freqs(self): return self._token_freqs def count_corpus(tokens): #@save """统计词元的频率""" # 这里的tokens是1D列表或2D列表 if len(tokens) == 0 or isinstance(tokens[0], list): # 将词元列表展平成一个列表 tokens = [token for line in tokens for token in line] return collections.Counter(tokens) vocab = Vocab(tokens) print(list(vocab.token_to_idx.items())[:10]) for i in [0, 10]: print('文本:', tokens[i]) print('索引:', vocab[tokens[i]])
2 语言模型
2.1 定义
建模:
假设序列长度为2,预测
,其中n是总次数、n(x)和
是单个单词和连续单词对的出现次数。序列长为3同理。
如果序列很长,文本量会出现数量不足的情况,很可能
,此时可以使用马尔科夫假设,即
一元语法:
二元语法:
2.2 代码
import random import torch from d2l import torch as d2l tokens = d2l.tokenize(d2l.read_time_machine()) # 因为每个文本行不一定是一个句子或一个段落,因此我们把所有文本行拼接到一起 corpus = [token for line in tokens for token in line] vocab = d2l.Vocab(corpus) vocab.token_freqs[:10] freqs = [freq for token, freq in vocab.token_freqs] d2l.plot(freqs, xlabel='token: x', ylabel='frequency: n(x)', xscale='log', yscale='log') bigram_tokens = [pair for pair in zip(corpus[:-1], corpus[1:])] bigram_vocab = d2l.Vocab(bigram_tokens) bigram_vocab.token_freqs[:10] trigram_tokens = [triple for triple in zip( corpus[:-2], corpus[1:-1], corpus[2:])] trigram_vocab = d2l.Vocab(trigram_tokens) trigram_vocab.token_freqs[:10] bigram_freqs = [freq for token, freq in bigram_vocab.token_freqs] trigram_freqs = [freq for token, freq in trigram_vocab.token_freqs] d2l.plot([freqs, bigram_freqs, trigram_freqs], xlabel='token: x', ylabel='frequency: n(x)', xscale='log', yscale='log', legend=['unigram', 'bigram', 'trigram'])
2.3 衡量语言模型好坏
平均交叉熵衡量语言模型好坏:
,p是语言模型预测概率,
是真实词。
历史原因,NLP使用困惑度(perplexity)exp(pai)来衡量,是平均每次可能选项,1表示完美、无穷大是最差情况。
2.4 梯度裁剪
迭代中计算这T个时间步上的梯度,在反向传播过程中产生长度为O(T)的矩阵乘法链,导致数值不稳定。
梯度裁剪可以有效预防梯度爆炸,如梯度长度超过
,那么拖影回长度
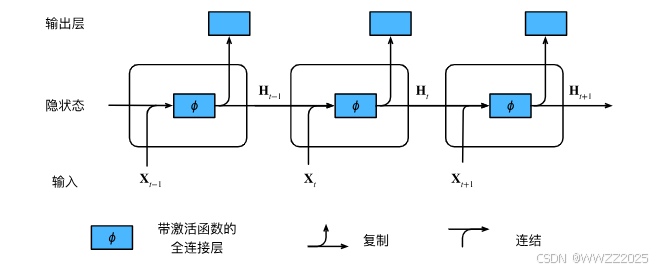
3 循环神经网络RNN
更新隐藏状态:
输出:
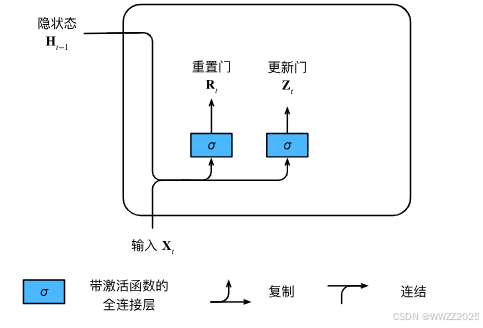
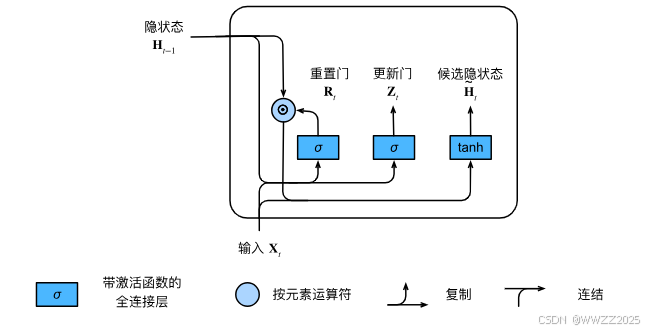
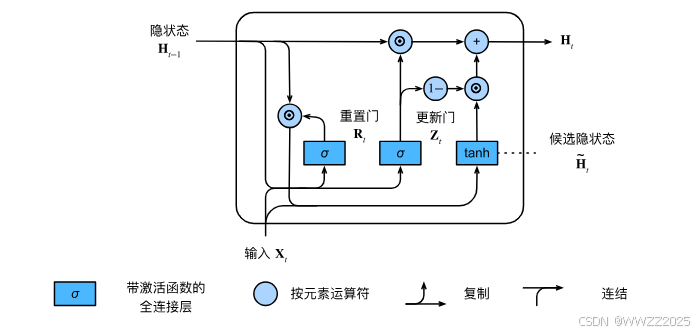
4 门控循环单元GRU
(1)重置门和隐藏门
(2)候选隐状态
(3)隐状态
5 长短期记忆网络LSTM
忘记门:将值朝0减少;
输入门:决定不是忽略掉输入数据;
输出门:决定是不是使用隐状态。
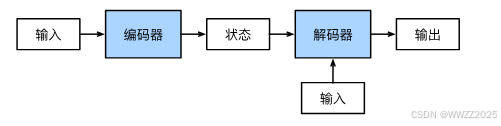
6 编码器-解码器架构
6.1 定义
编码器:它接受一个长度可变的序列作为输入, 并将其转换为具有固定形状的编码状态;
解码器:它将固定形状的编码状态映射到长度可变的序列。
6.2 代码
6.2.1 编码器
from torch import nn #@save class Encoder(nn.Module): """编码器-解码器架构的基本编码器接口""" def __init__(self, **kwargs): super(Encoder, self).__init__(**kwargs) def forward(self, X, *args): raise NotImplementedError
6.2.2 解码器
#@save class Decoder(nn.Module): """编码器-解码器架构的基本解码器接口""" def __init__(self, **kwargs): super(Decoder, self).__init__(**kwargs) def init_state(self, enc_outputs, *args): raise NotImplementedError def forward(self, X, state): raise NotImplementedError
6.2.3 合并
#@save class EncoderDecoder(nn.Module): """编码器-解码器架构的基类""" def __init__(self, encoder, decoder, **kwargs): super(EncoderDecoder, self).__init__(**kwargs) self.encoder = encoder self.decoder = decoder def forward(self, enc_X, dec_X, *args): enc_outputs = self.encoder(enc_X, *args) dec_state = self.decoder.init_state(enc_outputs, *args) return self.decoder(dec_X, dec_state)
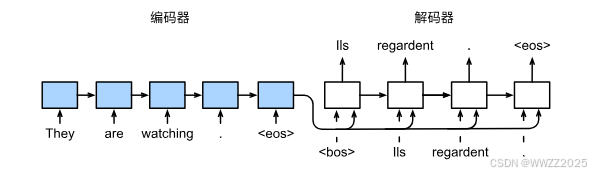
7 序列到序列学习seq2seq
指从一个句子生成另一个句子,编码器和解码器都是RNN,将编码器最后时间隐状态来初始解码器隐状态来完成信息传递,常用BLEU衡量生成序列好坏。应用:机器翻译。
BLEU:







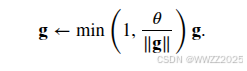
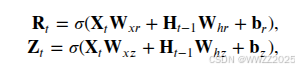

















 1643
1643

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








