- 集合结构图
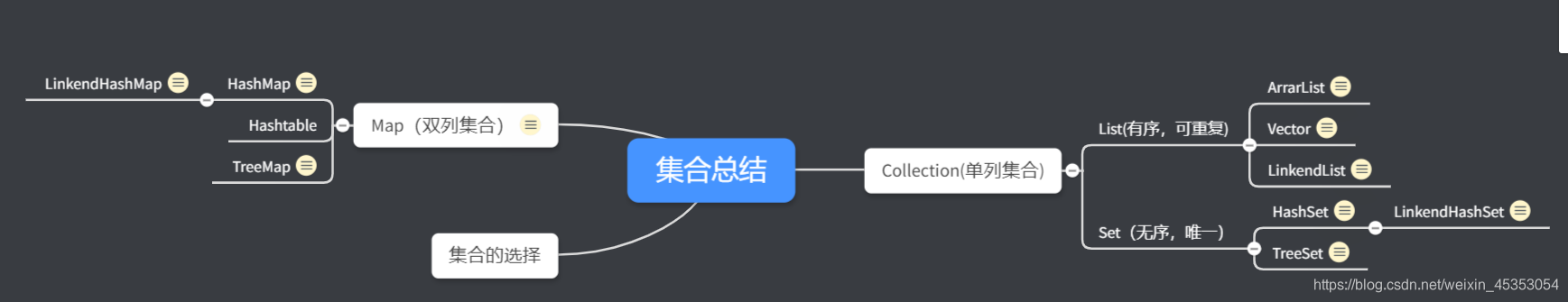
Collection
Collection的功能概述:
1 :添加功能
boolean add(object obj) :添加一个元素
boolean addAll (Collection c) : 添加一个集合的元素
2 :册除功能
void clear () :移除所有元素
boolean remove (object 0) :移除-一个元素
boolean removeAll (Collection c) :移除一个集合的元素
3 :判断功能
boolean contains (Object o) :判断集合中是否包含指定的元素
boolean containsAll (Collection c) :判断集合中是否包含指定的集合元素
boolean isEmpty() : 判断集合是否为空
4 :获取功能
Iterator iterator() (重点)
5 :长度功能
6 :交集功能
boolean retainAll (Collection c) :两个集合都有的元素
boolean addAll (Collection c) :添加一个集合的元素
boolean removeAll (Collection c) :移除一个集合的元素
boolean containsAll (Collection c) :判断集合中是否包含指定的集合元素
boolean retainAll (Collection c) :两个集合都有的元素
集合的遍历(迭代器)
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合
Collection c = new ArrayList();
// 添加元素
c.add("张无忌");
c.add("赵敏");
c.add("周芷若");
// 迭代器遍历
//通过集合对象获取迭代器对象
Iterator i = c.iterator();// 多态,实际返回是的子类对象
//通过迭代器对象的hasNext()方法判断有没有元素
while (i.hasNext()) {
//通过迭代器的方法next()获取元素
String s = (String) i.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
List
特点:有序可重复
遍历跟集合一样使用迭代器遍历
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合
List list = new ArrayList();
// 创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("张无忌", 23);
Student s2 = new Student("赵敏", 23);
Student s3 = new Student("周芷若", 23);
// 把学生添加到集合
list.add(s1);
list.add(s2);
list.add(s3);
// 遍历
Iterator i = list.iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
Student s = (Student) i.next();
System.out.println(s.getName() + "------" + s.getAge());
}
}
}
List集合的特有功能:
A:添加功能
void add(int, index, Object element) :在指定位置添加元素
B :获取功能
object get (int, index) :获取指定位置的元素
C :列表迭代器
ListIterator listIterator () : List集合特有的迭代器
D:册除功能
Object remove (int index) :根据索引册除元素,返回被删除的元素
E :修改功能
Object set (int index, Object element) :根据索引修改元素,返回被修饰的元素
List的子类特点
ArrayList :
底层数据结构是数组,查询快,增删慢。
线程不安全,效率高。
ArrayList储存自定义对象并排序:
public class CollectionsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合对象
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<Student>();
// 创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("林青霞", 27);
Student s2 = new Student("风清扬", 30);
Student s3 = new Student("刘晓曲", 28);
Student s4 = new Student("武鑫", 29);
Student s5 = new Student("林青霞", 27);
// 添加元素对象
list.add(s1);
list.add(s2);
list.add(s3);
list.add(s4);
list.add(s5);
// 排序
// 自然排序
// Collections.sort(list);
// 比较器排序
// 如果同时有自然排序和比较器排序,以比较器排序为主
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
int num = s2.getAge() - s1.getAge();
int num2 = num == 0 ? s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName())
: num;
return num2;
}
});
// 遍历集合
for (Student s : list) {
System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge());
}
}
}
Vector :
底层数据结构是数组,查询快,增删慢。
线程安全,效率低。
LinkedList :
底层数据结构是链表,查询慢,增删快。
线程不安全,效率高。
增强for遍历
格式:
for (元素数据类型变量:数组或者Collection集合) {
使用变量即可,该变量就是元素
}
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义数组
String[] s = { "张无忌", "风清扬", "令狐冲" };
// 遍历
for (String ss : s) {
System.out.println(ss);
}
}
}
aslist方法:把数组转成集合(集合的长度不能改变)
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] s = { "张无忌", "风清扬", "令狐冲" };
List<String> list = Arrays.asList(s);
System.out.println(list);
}
}
例:产生10个1到20的不重复随机数
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random r = new Random();
ArrayList<Integer> array = new ArrayList<>();
int count = 0;
while (count < 10) {
int n = r.nextInt(20) + 1;
if (!array.contains(n)) {
array.add(n);
count++;
}
}
for (Integer i : array) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
例2:
键盘录入多个数据,以0结束,要求在控制台输出这多个数据中的最大值
分析:
A:创建键盘录入数据对象
B:键盘录入多个数据,我们不知道多少个,所以用集合存储
C:以0结束,这个简单,只要键盘录入的数据是0,我就不继续录入数据了
D:把集合转成数组
E:对数组排序
F:获取该数组中的最大索引的值
public class ArrayListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建键盘录入数据对象
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 键盘录入多个数据,我们不知道多少个,所以用集合存储
ArrayList<Integer> array = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 以0结束,这个简单,只要键盘录入的数据是0,我就不继续录入数据了
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入数据:");
int number = sc.nextInt();
if (number != 0) {
array.add(number);
} else {
break;
}
}
// 把集合转成数组
// public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a)
Integer[] i = new Integer[array.size()];
// Integer[] ii = array.toArray(i);
array.toArray(i);
// System.out.println(i);
// System.out.println(ii);
// 对数组排序
// public static void sort(Object[] a)
Arrays.sort(i);
// 获取该数组中的最大索引的值
System.out.println("数组是:" + arrayToString(i) + "最大值是:"
+ i[i.length - 1]);
}
public static String arrayToString(Integer[] i) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("[");
for (int x = 0; x < i.length; x++) {
if (x == i.length - 1) {
sb.append(i[x]);
} else {
sb.append(i[x]).append(", ");
}
}
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
}
set
无序且唯一
HashSet:
底层数据结构是哈希表
哈希表依赖两个方法:hashCode ()和equals()
HashSet集合存储自定义对象并遍历。如果对象的成员变量值相同即为同一个对象
注意了:
你使用的是HashSet集合,这个集合的底层是哈希表结构。
而哈希表结构底层依赖:hashCode()和equals()方法。
如果你认为对象的成员变量值相同即为同一个对象的话,你就应该重写这两个方法。
如何重写呢?不同担心,自动生成即可。
public class DogDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合对象
HashSet<Dog> hs = new HashSet<Dog>();
// 创建狗对象
Dog d1 = new Dog("秦桧", 25, "红色", '男');
Dog d2 = new Dog("高俅", 22, "黑色", '女');
Dog d3 = new Dog("秦桧", 25, "红色", '男');
Dog d4 = new Dog("秦桧", 20, "红色", '女');
Dog d5 = new Dog("魏忠贤", 28, "白色", '男');
Dog d6 = new Dog("李莲英", 23, "黄色", '女');
Dog d7 = new Dog("李莲英", 23, "黄色", '女');
Dog d8 = new Dog("李莲英", 23, "黄色", '男');
// 添加元素
hs.add(d1);
hs.add(d2);
hs.add(d3);
hs.add(d4);
hs.add(d5);
hs.add(d6);
hs.add(d7);
hs.add(d8);
// 遍历
for (Dog d : hs) {
System.out.println(d.getName() + "---" + d.getAge() + "---"
+ d.getColor() + "---" + d.getSex());
}
}
}
public class Dog {
private String name;
private int age;
private String color;
private char sex;
public Dog() {
super();
}
public Dog(String name, int age, String color, char sex) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.color = color;
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public char getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(char sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + age;
result = prime * result + ((color == null) ? 0 : color.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
result = prime * result + sex;
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Dog other = (Dog) obj;
if (age != other.age)
return false;
if (color == null) {
if (other.color != null)
return false;
} else if (!color.equals(other.color))
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
if (sex != other.sex)
return false;
return true;
}
}
TreeSet
底层数据结构是红黑树。(是-一种自平衡的二叉树)
如何保证元素唯一性呢?
根据 比较的返回值是否是0来决定
如何保证元素的排序呢?
两种方式
自然排序(元素具备比较性):让元素所属的类实现Comparable接口
比较器排序(集合具备比较性):让集合接收一个Comparator 的实现类对象
自然排序:
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
//自然排序进行排序
TreeSet<Integer> t = new TreeSet<>();
// 添加元素
t.add(45);
t.add(23);
t.add(243);
t.add(76);
t.add(456);
t.add(34);
// 遍历
for (Integer i : t) {
System.out.print(i + " ");// 23 34 45 76 243 456
}
}
}
例:需求:请按照姓名的长度排序,如果名字相同,请按年龄排序
public class TreeSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合对象
TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>();
// 创建元素
Student s1 = new Student("linqingxia", 27);
Student s2 = new Student("zhangguorong", 29);
Student s3 = new Student("wanglihong", 23);
Student s4 = new Student("linqingxia", 27);
Student s5 = new Student("liushishi", 22);
Student s6 = new Student("wuqilong", 40);
Student s7 = new Student("fengqingy", 22);
Student s8 = new Student("linqingxia", 29);
// 添加元素
ts.add(s1);
ts.add(s2);
ts.add(s3);
ts.add(s4);
ts.add(s5);
ts.add(s6);
ts.add(s7);
ts.add(s8);
// 遍历
for (Student s : ts) {
System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge());
}
}
}
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student s) {
// 主要条件 姓名的长度
int num = this.name.length() - s.name.length();
// 姓名的长度相同,不代表姓名的内容相同
int num2 = num == 0 ? this.name.compareTo(s.name) : num;
// 姓名的长度和内容相同,不代表年龄相同,所以还得继续判断年龄
int num3 = num2 == 0 ? this.age - s.age : num2;
return num3;
}
}
例2
键盘录入5个学生信息(姓名,语文成绩,数学成绩,英语成绩),按照总分从高到低输出到控制台
分析:
A:定义学生类
B:创建一个TreeSet集合
C:总分从高到底如何实现呢?
D:键盘录入5个学生信息
E:遍历TreeSet集合
public class TreeSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个TreeSet集合
TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
// 总分从高到低
int num = s2.getSum() - s1.getSum();
// 总分相同的不一定语文相同
int num2 = num == 0 ? s1.getChinese() - s2.getChinese() : num;
// 总分相同的不一定数学相同
int num3 = num2 == 0 ? s1.getMath() - s2.getMath() : num2;
// 总分相同的不一定英语相同
int num4 = num3 == 0 ? s1.getEnglish() - s2.getEnglish() : num3;
// 姓名还不一定相同呢
int num5 = num4 == 0 ? s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName())
: num4;
return num5;
}
});
System.out.println("学生信息录入开始");
// 键盘录入5个学生信息
for (int x = 1; x <= 5; x++) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入第" + x + "个学生的姓名:");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入第" + x + "个学生的语文成绩:");
String chineseString = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入第" + x + "个学生的数学成绩:");
String mathString = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入第" + x + "个学生的英语成绩:");
String englishString = sc.nextLine();
// 把数据封装到学生对象中
Student s = new Student();
s.setName(name);
s.setChinese(Integer.parseInt(chineseString));
s.setMath(Integer.parseInt(mathString));
s.setEnglish(Integer.parseInt(englishString));
// 把学生对象添加到集合
ts.add(s);
}
System.out.println("学生信息录入完毕");
System.out.println("学习信息从高到低排序如下:");
System.out.println("姓名\t语文成绩\t数学成绩\t英语成绩");
// 遍历集合
for (Student s : ts) {
System.out.println(s.getName() + "\t" + s.getChinese() + "\t"
+ s.getMath() + "\t" + s.getEnglish());
}
}
}
public class Student {
// 姓名
private String name;
// 语文成绩
private int chinese;
// 数学成绩
private int math;
// 英语成绩
private int english;
public Student(String name, int chinese, int math, int english) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.chinese = chinese;
this.math = math;
this.english = english;
}
public Student() {
super();
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getChinese() {
return chinese;
}
public void setChinese(int chinese) {
this.chinese = chinese;
}
public int getMath() {
return math;
}
public void setMath(int math) {
this.math = math;
}
public int getEnglish() {
return english;
}
public void setEnglish(int english) {
this.english = english;
}
public int getSum() {
return this.chinese + this.math + this.english;
}
}
**
Map
**
Map集合的特点:
将键映射到值的对象。一个映射不能包含重复的键;每个键最多只能映射到-个值。
Map集合和Collect ion集合的区别?
Map集合存储元素是成对出现的,Map集合的键是唯一的,值是可重复的。
Collection集合存储元素是单独出现的,Collection的儿子Set是唯一的,List是可重复的。
注意:
A:Map集合的数据结构仅仅针对键有效,与值无关。
B:存储的是键值对形式的元素,键唯一值可重复。
Map集合的功能概述:
1 :添加功能
V put (K key,V value) :添加元素。
如果键是第一次存储,就直接存储元素,返回null
如果键不是第-次存在,就用值把以前的值替换掉,返回以前的值
2 :删除功能
void clear () :移除所有的键值对元素
V remove (object key) :根据键删除键值对元素,并把值返回
3 :判断功能
boolean containsKey (Object key) :判断集合是否包含指定的键
boolean containsValue (object value) : 判断集合是否包含指定的值
boolean isEmpty() : 判断集合是否为空
4 :获取功能
Set <Map. Entry<K,V>> entrySet () :
V get (Object key) :根据键获取值
Set keySet () :获取集合中所有键的集合
collection values () :获取集合中所有值的集合
5:长度功能
int size () :返回集合中的键值对的对数
遍历1:
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合
Map<String, String> m = new HashMap<String, String>();
// 创建元素添加到集合
m.put("张无忌", "赵敏");
m.put("杨过", "小龙女");
m.put("令狐冲", "任盈盈");
// 遍历
// 获取所有键
Set<String> set = m.keySet();
// 遍历键的集合,获得每一个键
for (String key : set) {
String string = m.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "----" + string);
}
}
}
遍历2:
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合
Map<String, String> m = new HashMap<String, String>();
// 创建元素添加到集合
m.put("张无忌", "赵敏");
m.put("杨过", "小龙女");
m.put("令狐冲", "任盈盈");
// 遍历
// 获取键值对对象
Set<Entry<String, String>> set = m.entrySet();
// 遍历键值对对象
for (Map.Entry<String, String> mm : set) {
String key = mm.getKey();
String value = mm.getValue();
System.out.println(mm.getKey() + "---" + mm.getValue());
}
}
}
HashMap:
底层数据结构是哈希表 线程不安全 效率高
哈希表依赖两个方法:hashCode ()和equals()
遍历:
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合
HashMap<Integer, String> m = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
// 创建元素添加到集合
m.put(23, "赵敏");
m.put(24, "小龙女");
m.put(35, "任盈盈");
// 遍历
Set<Integer> set = m.keySet();
for (Integer s : set) {
String string = m.get(s);
System.out.println(s + string);
}
}
}
值是对象的遍历:
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合
HashMap<String, Student> m = new HashMap<String, Student>();
Student s1 = new Student("张三丰", 108);
Student s2 = new Student("独孤求败", 56);
Student s3 = new Student("东方不败", 54);
m.put("1", s1);
m.put("2", s2);
m.put("3", s3);
Set<String> set = m.keySet();
for (String s : set) {
Student ss = m.get(s);
System.out.println(s + ":" + ss.getName() + ss.getAge());
}
}
}
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
键是对象的遍历:(注意要在Student里生成hashCode()和equals()方法)
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合
HashMap<Student, String> m = new HashMap<Student, String>();
Student s1 = new Student("张三丰", 108);
Student s2 = new Student("独孤求败", 56);
Student s3 = new Student("东方不败", 54);
m.put(s1,"1");
m.put(s2,"2");
m.put(s3,"3");
Set<Student> set = m.keySet();
for (Student s : set) {
String ss = m.get(s);
System.out.println(s.getName() + s.getAge()+":"+ss);
}
}
}
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + age;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Student other = (Student) obj;
if (age != other.age)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
}
LinkedHashMap:
是Map接口的哈希表和链接列表实现,具有可预知的迭代顺序。
由哈希表保证键的唯一性
由链表保证键盘的有序(存储和取出的顺序一致)
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合对象
LinkedHashMap<String, String> hm = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
// 创建并添加元素
hm.put("2345", "hello");
hm.put("1234", "world");
hm.put("3456", "java");
hm.put("1234", "javaee");
hm.put("3456", "android");
// 遍历
Set<String> set = hm.keySet();
for (String key : set) {
String value = hm.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "---" + value);
}
}
}
打印结果:
2345---hello
1234---javaee
3456---android
TreeMap:
是基于红黑树的Map接口的实现
遍历:(按年龄和名字)
public class TreeMapDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合对象
TreeMap<Student, String> tm = new TreeMap<Student, String>(
new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
// 主要条件
int num = s1.getAge() - s2.getAge();
// 次要条件
int num2 = num == 0 ? s1.getName().compareTo(
s2.getName()) : num;
return num2;
}
});
// 创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("潘安", 30);
Student s2 = new Student("柳下惠", 35);
Student s3 = new Student("唐伯虎", 33);
Student s4 = new Student("燕青", 32);
Student s5 = new Student("唐伯虎", 33);
// 存储元素
tm.put(s1, "宋朝");
tm.put(s2, "元朝");
tm.put(s3, "明朝");
tm.put(s4, "清朝");
tm.put(s5, "汉朝");
// 遍历
Set<Student> set = tm.keySet();
for (Student key : set) {
String value = tm.get(key);
System.out.println(key.getName() + "---" + key.getAge() + "---"
+ value);
}
}
}
打印结果:
潘安---30---宋朝
燕青---32---清朝
唐伯虎---33---汉朝
柳下惠---35---元朝
例子: 需求 :“aababcabcdabcde”,获取字符串中每一个字母出现的次数要求结果:a(5)b(4)c(3)d(2)e(1)
分析:
A:定义一个字符串(可以改进为键盘录入)
B:定义一个TreeMap集合
键:Character
值:Integer
C:把字符串转换为字符数组
D:遍历字符数组,得到每一个字符
E:拿刚才得到的字符作为键到集合中去找值,看返回值
是null:说明该键不存在,就把该字符作为键,1作为值存储
不是null:说明该键存在,就把值加1,然后重写存储该键和值
F:定义字符串缓冲区变量
G:遍历集合,得到键和值,进行按照要求拼接
H:把字符串缓冲区转换为字符串输出
public class TreeMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个字符串(可以改进为键盘录入)
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");
String line = sc.nextLine();
// 定义一个TreeMap集合
TreeMap<Character, Integer> tm = new TreeMap<Character, Integer>();
//把字符串转换为字符数组
char[] chs = line.toCharArray();
//遍历字符数组,得到每一个字符
for(char ch : chs){
//拿刚才得到的字符作为键到集合中去找值,看返回值
Integer i = tm.get(ch);
//是null:说明该键不存在,就把该字符作为键,1作为值存储
if(i == null){
tm.put(ch, 1);
}else {
//不是null:说明该键存在,就把值加1,然后重写存储该键和值
i++;
tm.put(ch,i);
}
}
//定义字符串缓冲区变量
StringBuilder sb= new StringBuilder();
//遍历集合,得到键和值,进行按照要求拼接
Set<Character> set = tm.keySet();
for(Character key : set){
Integer value = tm.get(key);
sb.append(key).append("(").append(value).append(")");
}
//把字符串缓冲区转换为字符串输出
String result = sb.toString();
System.out.println("result:"+result);
}
}
Collections:
是针对集合进行操作的工具类,都是静态方法。
面试题:
Collection和Collections的区别?
Collection:是单列集合的顶层接口,有子接口List和Set。
Collections:是针对集合操作的工具类,有对集合进行排序和二分查找的方法
要知道的方法
public static void sort(List list):排序 默认情况下是自然顺序。
public static int binarySearch(List<?> list,T key):二分查找
public static T max(Collection<?> coll):最大值
public static void reverse(List<?> list):反转
public static void shuffle(List<?> list):随机置换
public class CollectionsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合对象
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 添加元素
list.add(30);
list.add(20);
list.add(50);
list.add(10);
list.add(40);
System.out.println("list:" + list);
// public static <T> void sort(List<T> list):排序 默认情况下是自然顺序。
// Collections.sort(list);
// System.out.println("list:" + list);
// [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
// public static <T> int binarySearch(List<?> list,T key):二分查找
// System.out
// .println("binarySearch:" + Collections.binarySearch(list, 30));
// System.out.println("binarySearch:"
// + Collections.binarySearch(list, 300));
// public static <T> T max(Collection<?> coll):最大值
// System.out.println("max:"+Collections.max(list));
// public static void reverse(List<?> list):反转
// Collections.reverse(list);
// System.out.println("list:" + list);
//public static void shuffle(List<?> list):随机置换
Collections.shuffle(list);
System.out.println("list:" + list);
}
}





 本文深入讲解了Java集合框架中的各种集合类型,包括List、Set、Map等,详细介绍了它们的特性、功能及应用场景,特别强调了集合的遍历、排序和操作方法。
本文深入讲解了Java集合框架中的各种集合类型,包括List、Set、Map等,详细介绍了它们的特性、功能及应用场景,特别强调了集合的遍历、排序和操作方法。
















 1686
1686

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








