内核模块
makefile
ARCH=x86
CROSS_CMPILE=
KVERSION = $(shell uname -r)
KERNEL_DIR = /lib/modules/$(KVERSION)/build
.PHONY:all clean
all:
make -C $(KERNEL_DIR) M=$(shell pwd) modules
clean:
make -C $(KERNEL_DIR) M=$(shell pwd) modules clean
rm -rf modules.order
obj-m += kernel_io.o
kernel_io.c
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
static int major = 0;
static char sdata[64] = {0};
static int sdatalen = 0;
static struct class* class_for_hello;
// 与struct file_operations 中的read格式匹配
static ssize_t hello_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
copy_to_user(buf, sdata, sdatalen);
return sdatalen;
}
// 与struct file_operations 中的write格式匹配
static ssize_t hello_write (struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
sdatalen=size;
copy_from_user(sdata, buf, sdatalen);
return sdatalen;
}
// 文件操作描述体
static struct file_operations hello_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = hello_read,
.write = hello_write,
};
int __init hello_init(void) {
printk("hello drv init\n");
major = register_chrdev(0, "hello_drv", &hello_fops);
class_for_hello = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "helloclass");
/* create /dev/hellodev */
device_create(class_for_hello, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "hellodev");
return 0;
}
void __exit hello_exit(void) {
printk("hello drv exit\n");
device_destroy(class_for_hello, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(class_for_hello);
unregister_chrdev(major, "hello_drv");
}
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
用户app
user_io.c
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int fd;
char buf[1024];
int len;
int ret;
/* 1. 判断参数 */
if (argc < 2) {
printf("Usage: %s -w <string>\n", argv[0]);
printf(" %s -r\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 2. 打开文件 */
fd = open("/dev/hellodev", O_RDWR);
if (fd == -1) {
printf("can not open file /dev/hellodev\n");
return -1;
}
printf("open file /dev/hellodev ok\n");
/* 3. 写文件或读文件 */
if ((0 == strcmp(argv[1], "-w")) && (argc == 3)) {
len = strlen(argv[2]) + 1;
len = len < 1024 ? len : 1024;
ret = write(fd, argv[2], len);
printf("write driver: %d\n", ret);
}
else {
len = read(fd, buf, 1024);
printf("read driver: %d\n", len);
buf[1023] = '\0';
printf("APP read : %s\n", buf);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
效果
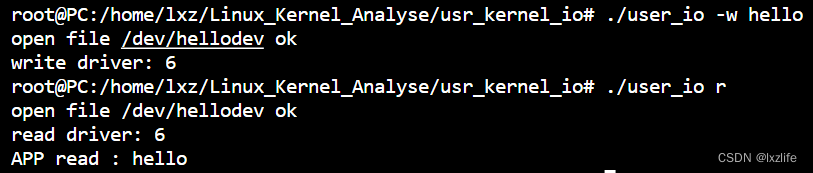
 Linux内核模块:设备驱动与用户空间交互示例
Linux内核模块:设备驱动与用户空间交互示例





 该文章展示了一个简单的Linux内核模块,创建了一个设备驱动,该驱动注册了一个字符设备并实现了读写操作。用户空间应用通过打开/dev/hellodev文件进行通信,实现数据的读写。内核模块通过`module_init`和`module_exit`宏注册初始化和退出函数,而用户应用程序则通过标准I/O函数与驱动交互。
该文章展示了一个简单的Linux内核模块,创建了一个设备驱动,该驱动注册了一个字符设备并实现了读写操作。用户空间应用通过打开/dev/hellodev文件进行通信,实现数据的读写。内核模块通过`module_init`和`module_exit`宏注册初始化和退出函数,而用户应用程序则通过标准I/O函数与驱动交互。
















 7385
7385

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








