PyTorch–用Variable实现线性回归
从中体会autograd的便捷之处
1.导入库
import torch as t
from torch.autograd import Variable as V
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from IPython import display
2.定义函数
#为了在不同的计算机运行一样,设置随机种子
t.manual_seed(1000)
def get_fake_data(batch_size=8):
x = t.rand(batch_size, 1) * 20
y = x * 2 + (1 + t.randn(batch_size, 1)) * 3
return x, y
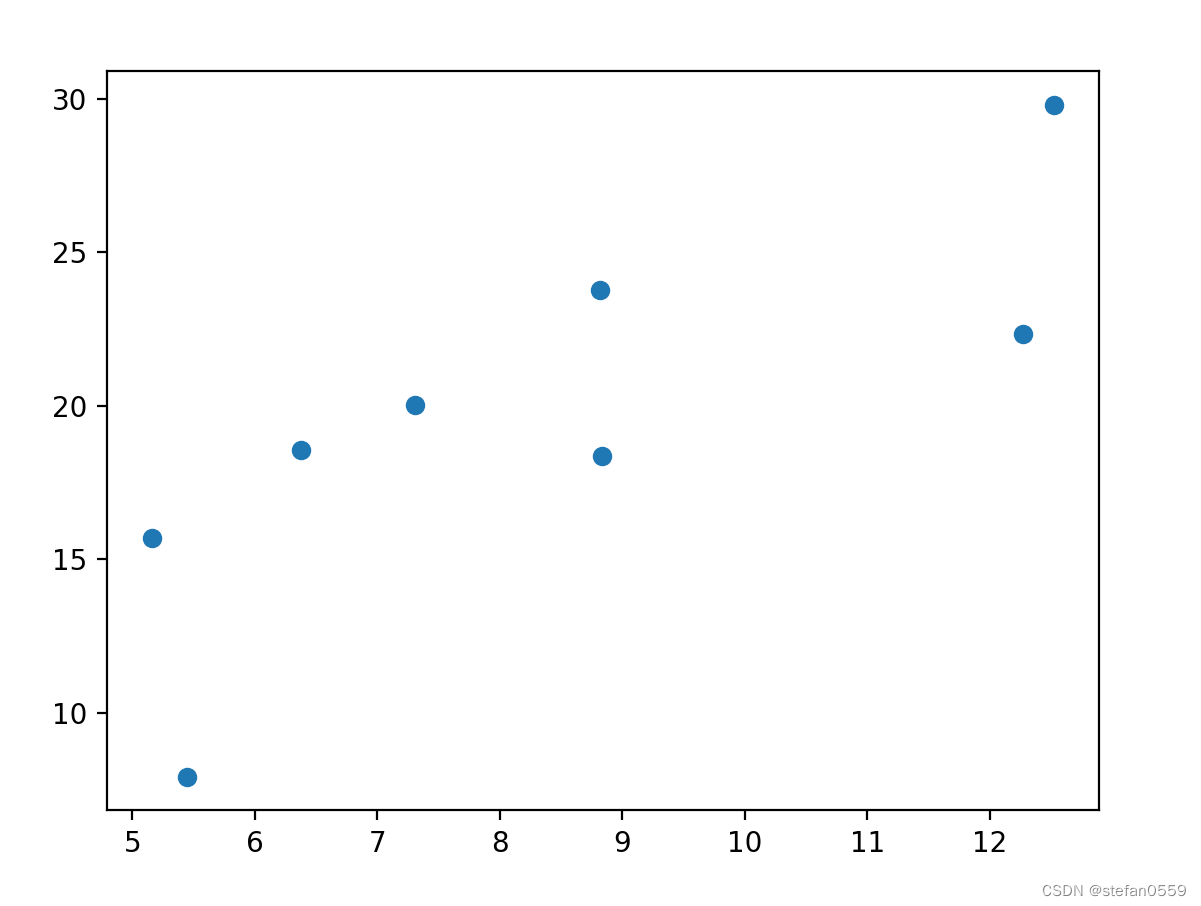
3.查看分布
x, y = get_fake_data()
plt.scatter(x.squeeze().numpy(), y.squeeze().numpy())
如下图
4.网络设计及画图
#随机初始化参数
w = V(t.rand(1, 1), requires_grad=True)
b = V(t.zeros(1, 1), requires_grad=True)
lr = 0.001
for i in range(8000):
x, y =get_fake_data()
x, y = V(x), V(y)
#forward
y_pred = x.mm(w) + b
loss = 0.5 * (y_pred - y) ** 2
loss = loss.sum()
#backward
loss.backward()
#更新参数
w.data.sub_(lr * w.grad.data)
b.data.sub_(lr * b.grad.data)
#梯度清零
w.grad.data.zero_()
b.grad.data.zero_()
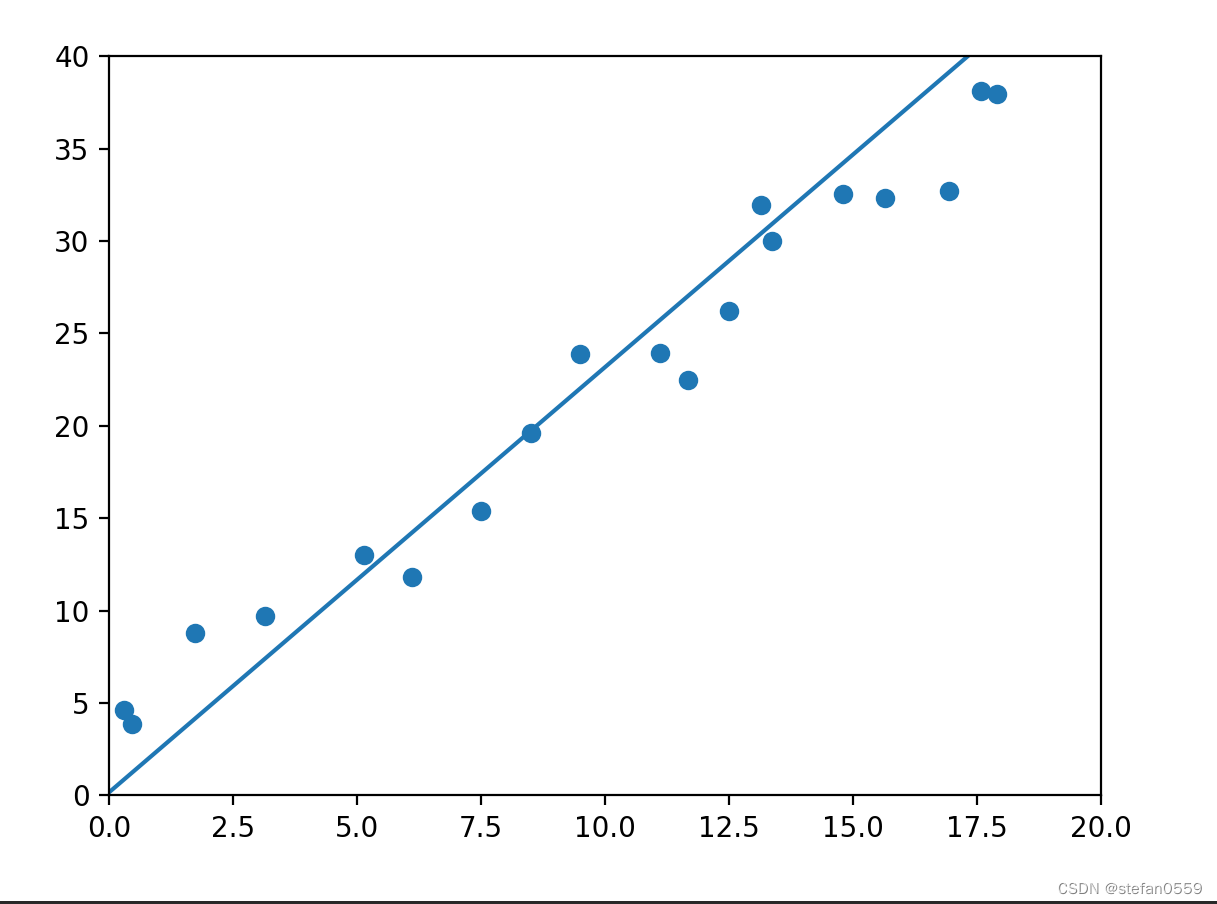
if i % 2000 == 0:
display.clear_output(wait=True)
x = t.arange(0, 20, dtype=t.float).view(-1, 1)
y = x.mm(w.data) + b.expand_as(x)
plt.plot(x.detach().numpy(), y.detach().numpy())#predicted
x2, y2 = get_fake_data(batch_size=20)
plt.scatter(x2.numpy(), y2.numpy())#true data
plt.xlim(0, 20)
plt.ylim(0, 40)
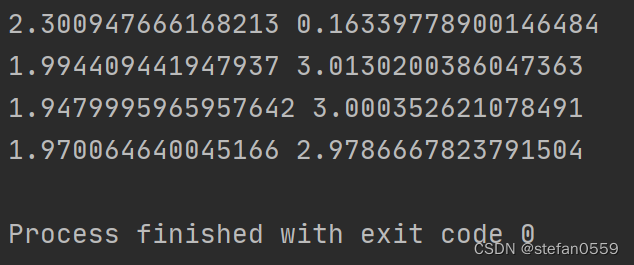
print(w.item(), b.item())
plt.show()
图如下
相关参数值





 本文通过使用PyTorch的autograd模块实现了一个简单的线性回归模型,并演示了如何通过迭代更新权重和偏差来最小化损失函数。通过可视化的手段展示了训练过程中的预测结果与真实数据之间的对比。
本文通过使用PyTorch的autograd模块实现了一个简单的线性回归模型,并演示了如何通过迭代更新权重和偏差来最小化损失函数。通过可视化的手段展示了训练过程中的预测结果与真实数据之间的对比。

















 461
461

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








