Bean的装配方式
Bean的装配方式即Bean依赖注入的方式。Spring容器支持多种形式的Bean装配方式,如基于XML的装配、基于注解的装配(常用)和 自动装配。
基于XML的装配
依赖注入作用就是在使用Spring 框架创建对象时,动态地将其所依赖的对象注入Bean组件中。
主要有以下两种方式,在Spring实例化Bean的过程中,Spring首先会调用Bean的默认构造方法(无参)来实例化Bean对象,然后通过反射的方式调用setter方法来注入属性值。因此,在使用setter注入时,要求一个Bean必须满足以下两点:
- Bean类必须提供一个默认的无参构造方法。
- Bean类必须为需要注入的属性提供对应的setter方法
1、 setter注入(setter injection):IOC 容器通过setter赋值注入被依赖的实例。通过调用无参的构造器或者静态工厂方法实例化Bean,然后调用该Bean对象的setter方法实现setter方法的注入。
在配置文件里,需要使用元素的子元素来为属性注入值。
<bean id="bean的唯一标识" class="实现类" ...>
<property name="实体类的私有属性名">
....
</property>
</bean>
2、构造器注入(constructor injection):IOC容器通过构造方法注入被依赖的实例。基于构造方法的依赖注入通过调用带参数的构造方法来实现,每个参数代表着一个依赖。
在配置文件里,需要使用元素的子元素来定义构造方法的参数,可以使用value属性(或子元素)来设置该参数的值。
<bean id="bean的唯一标识" class="实现类" ...>
<constructor-arg value="值" type="实体类的私有属性类型" index="该属性在构造方法的下标索引" name="实体类的私有属性名"></constructor-arg>
....
<constructor-arg value="值" type="实体类的私有属性类型" index="该属性在构造方法的下标索引" name="实体类的私有属性名"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
如果 < constructor-arg >的顺序与构造方法参数的顺序不一致,则需要通过type或者index或name指定。
setter注入
使用setter注入需要:
- 提供默认无参构造 方法(下面AllCollection类中,由于没有重载构造方法,默认是由无参构造方法。)
- 为所有属性提供setter方法。
以集合类为例
AllCollection类
package club.johnny.polo;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
public class AllCollection {
private String [] arrayElement;
private Set<String> setElement;
private List<String> listElement;
private Map<String,String> mapElement;
private Properties propsElement ;
public Properties getPropsElement() {
return propsElement;
}
public void setPropsElement(Properties propsElement) {
this.propsElement = propsElement;
}
public void setListElement(List<String> listElement) {
this.listElement = listElement;
}
public String[] getArrayElement() {
return arrayElement;
}
public void setArrayElement(String[] arrayElement) {
this.arrayElement = arrayElement;
}
public Set<String> getSetElement() {
return setElement;
}
public void setSetElement(Set<String> setElement) {
this.setElement = setElement;
}
public List getListElement() {
return listElement;
}
public Map<String, String> getMapElement() {
return mapElement;
}
public void setMapElement(Map<String, String> mapElement) {
this.mapElement = mapElement;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String s="";
for(String as:arrayElement)
s+=as+" ";
return "list:" + listElement.toString()+"\nset:"+setElement.toString()+"\nmap:"+ mapElement.toString()+"\narray:"+s+"\npropsElement:"+propsElement.toString();
}
}
applicationContext.xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<bean id="collectionDemo" class="club.johnny.polo.AllCollection">
<property name="listElement">
<list>
<value>苹果</value>
<value>香蕉</value>
<value>水蜜桃</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="setElement">
<set>
<value>苹果2</value>
<value>香蕉2</value>
<value>水蜜桃2</value>
</set>
</property>
<property name="mapElement">
<map>
<entry>
<key><value>apple</value></key>
<value>苹果3</value>
</entry>
<entry>
<key><value>banana</value></key>
<value>香蕉3</value>
</entry>
<entry>
<key><value>peach</value></key>
<value>水蜜桃3</value>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="arrayElement">
<array>
<value>苹果4</value>
<value>香蕉4</value>
<value>水蜜桃4</value>
</array>
</property>
<property name="propsElement">
<props>
<prop key="apple5">苹果5</prop>
<prop key="banana5">香蕉5</prop>
<prop key="peach5">水蜜桃5</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>

property是bean元素的子元素,它用于调用Bean实例中的setListElement()方法完成属性的赋值,从而实现依赖注入。
< property > 标签的name属性表示Bean实例中的相应属性名,ref属性指定其属性值(对象类型的id)。
注意:
set、list、数组 各自都有自己的标签 ,但是也可以用< list> 代替以上三种。
构造器注入
Course类
package club.johnny.polo;
public class Course {
private String courseName;
private int courseHour ;
private Teacher teacher ;//授课老师 ,依赖于Teacher
public Course() {
}
public Course(Teacher teacher) {
this.teacher = teacher;
}
public Course(String courseName, int courseHour, Teacher teacher) {
this.courseName = courseName;
this.courseHour = courseHour;
this.teacher = teacher;
}
public String getCourseName() {
return courseName;
}
public void setCourseName(String courseName) {
this.courseName = courseName;
}
public int getCourseHour() {
return courseHour;
}
public void setCourseHour(int courseHour) {
this.courseHour = courseHour;
}
public Teacher getTeacher() {
return teacher;
}
public void setTeacher(Teacher teacher) {
this.teacher = teacher;
}
public void showInfo() {
System.out.println(this.courseName+","+this.courseHour+","+this.teacher.getName());
}
}
Teacher类
package club.johnny.polo;
public class Teacher {
private String name;
private int age ;
public Teacher() {
}
public Teacher(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Teacher(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/*
public Teacher(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
test测试类
package club.johnny.test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import club.johnny.polo.Course;
import club.johnny.polo.AllCollection;
public class Test {
public static void testConstructor() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Course course =(Course) context.getBean("courseDemo");
course.showInfo();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
testConstructor();
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 构造器 注入 -->
<bean id="myteacher" class="club.johnny.polo.Teacher">
<!-- 通过私有属性名指定 -->
<constructor-arg name="name" value="johnnylin"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="courseDemo" class="club.johnny.polo.Course">
<!-- 可以严格按照构造器的顺序也可以 -->
<constructor-arg index="0" value="java语言"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="15"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="teacher" ref="myteacher"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
自动装配
<bean id="course" class="org.johnny.entity.Course" autowire="byType" >
<property name="courseName" value="java"></property>
<property name="courseHour" value="200"></property>
</bean>
该Course类中有Teacher teacher 属性,并且 如果该ioc容器中恰好有一个 bean的id也是teacher,即 bean的id值=类的属性名。 则IOC 容器会自动装配。
几种特殊值的赋值
< property >的value属性 与 < property >的value标签区别:
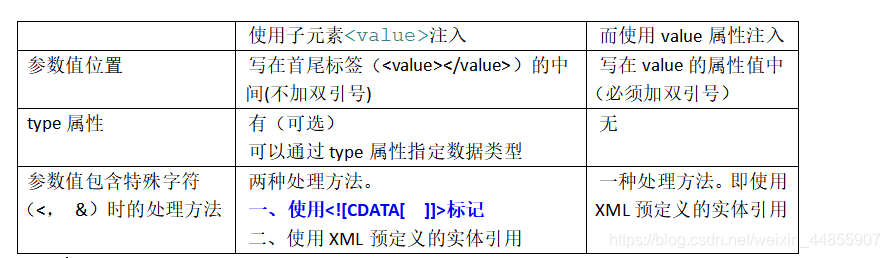
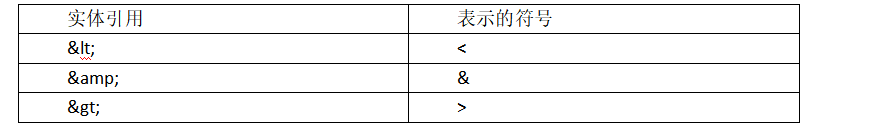
其中,XML预定义的实体引用如下表所示:
给对象类型赋值为null,注意没有子标签< value >
<property name="属性名">
<null/>
</property>
给属性赋值为 “”
<property name="类的私有属性名" value="">
</property>
或者
<property name="类的私有属性名" >
<value></value>
</property>
总结
无论以后我们需要什么对象,都可以直接去Spring IOC 容器中直接获取,而不需要自己操作。
分为两步:
-
先给SpringIOC容器存放对象并赋值 : 同 applicationContext.xml配置文件d额bean标签
-
拿对象
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“applicationContext.xml”);
context.getBean(“bean对象名字或id”);
而IOC容器赋值:如果是简单类型(8个基本+String),则使用
< property name="" value="8个基本数据类型"> < /property>
如果是对象类型,ref=“需要引用的id值”,因此实现了 对象与对象之间的依赖关系
<property name="" ref="需要引用的id值""> </property>
【注意】
在IOC 容器中定义bean的前提是,该bean的类必须提供了无参构造方法。





 本文介绍Spring框架中Bean的装配方式,包括基于XML的setter注入和构造器注入,以及自动装配等。并给出了具体的代码示例。
本文介绍Spring框架中Bean的装配方式,包括基于XML的setter注入和构造器注入,以及自动装配等。并给出了具体的代码示例。
















 1421
1421

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








