写在前面的话:本人是19届毕业生,专业为机械设计制造及其自动化,在大四实习的时候,选择了一家公司去实习,该公司为一个java培训结构。作为一个半路出家的和尚,在找工作上遇到很多坎坷,迄今为止,我已面试5家公司,每家公司都需要笔试,很显然,我的所有找工作经历都是死在了笔试上。今天,是我面试的最后一家公司,从公司走出来,突然觉得离开了爸妈,离开了学校,我什么都不是。但是,值得庆幸的是,这五家公司的面试终于打醒了我,让我知道自己到底输在哪里。(本博客会持续更新,直到找到工作为止!!!!)
1.面试心得
每家公司都有自己的业务,所使用的语言,开发流程,开发环境,开发手段都不一样。所以,对面试者的要求也不一样。
我去的这几家公司,大致要求为:给三个文件中的代码写注释(使用eclipse);做一套java基础试题,根据自己所学的语言,能做多少做多少,里面涉及到基本概念,编程题等;第三家公司是做一套排序题,里面有集合,日期等;第四家公司有点扯,给我甩了一套英语试题(看来该公司对英语要求高);第五家就是今天的面试公司,做一套笔试题,里面涉及到SQL语句的编写,集合的排序,二进制字符串的加法,TCP如何判断对方已经断开连接以及最后一题多线程编程需要注意什么。
静下心来好好复习了差不多一个星期,把基础知识捡回来很多,这个星期继续投递简历,总算是功夫不负有心人,陆陆续续也有公司给我面试邀请,可把我高兴坏了,今天是面试第三天,面试了一家公司,问的问题还是比较基础,但是呢,有些知识点还是没有回答得很好,现在来做个总结。
2.笔试题
排序题:
1.冒泡排序:(思路:小的数往上冒,大的数往下沉)
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] arr = {1,9,7,5,8,3};
BubbleSort(arr);
public static void BubbleSort(int[] arr){
int temp;//过度变量
for(int i = 0;i<arr.length-1;i++){
for(int j = arr.length-1;j<i;j--){
if(arr[j] < arr[j-1]){
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j-1];
arr[j-1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}
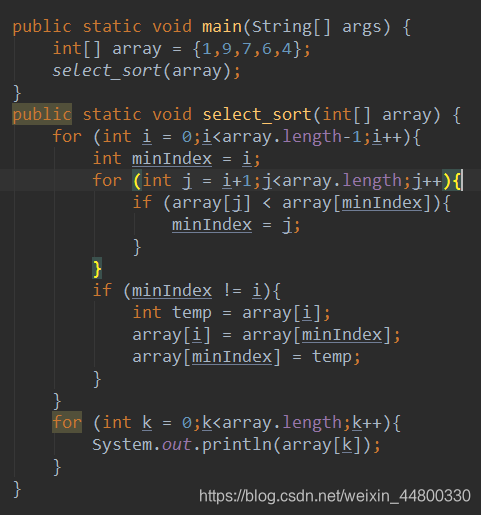
2.选择排序
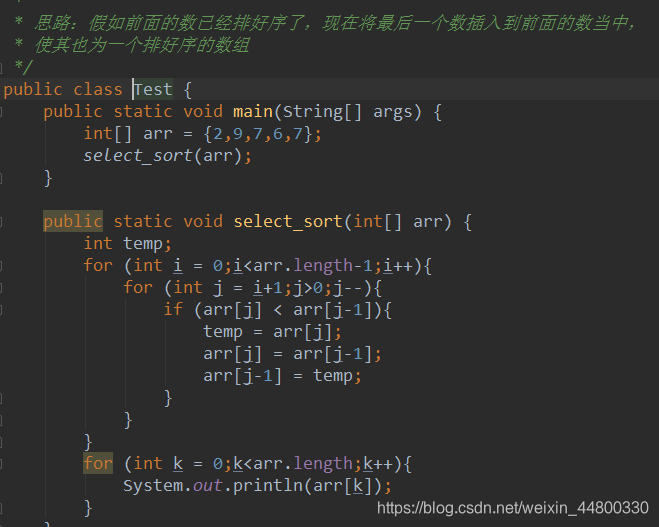
3.插入排序
4.java实现二进制加法
例如:"11" + "1" = "100";
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "11";
String b = "1";
function(a,b);
}
public static void function(String a,String b){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
int sum = 0;
int pre = 0;
while (a.length() != b.length()){
if (a.length() > b.length()){
b = "0" + b;
}else {
a = "0" + a;
}
}
for (int i = a.length()-1; i >=0; i++) {
x = a.charAt(i) - '0';
y = b.charAt(i) - '0';
sum = x+y+pre;
if (sum >= 2){
pre = 1;
sb.append(sum - 2);
}else {
pre = 0;
sb.append(sum);
}
}
if (pre == 1){
sb.append("1");
}
String result = sb.reverse().toString();
System.out.println(result);
}
}
5.利用二分法寻找有序数组中指定数字出现的次数
思路:首先利用二分法寻找到元素的位置,如果没有找到就返回0,如果找到了,就记录当前位置,然后向两边判断
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,2,2,2,3,4};
int key = 9;
int count = function(arr,key);
if (count == 0){
System.out.println("该元素不存在!!!");
}else {
System.out.println(key+"出现了"+count+"次");
}
}
public static int function(int[] arr,int key){
int min = 0;
int max = arr.length - 1;
int mid = 0;
int temp = 0;
int count = 0;
while (min <= max){
mid = (min + max )/2;
if (arr[mid] > key){
max = mid-1;
}else if (arr[mid] < key){
min = mid +1;
}else {
temp = mid;
count++;
while (arr[++mid] == key)
count++;
while (arr[--temp] == key)
count++;
return count;
}
}
return 0;
}
}
6.判断一个字符串是否是回文(对称)字符串 例如"ABCCBA"
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "ABCgA";
boolean b = isHaHa(str);
System.out.println(b);
}
public static boolean isHuiWen(String str){
if (str == null){
// return false;
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(str);
sb.reverse();
return sb.toString().equals(str);
}
public static boolean isHaHa(String str){
if (str == null){
return false;
}
int length = str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < length / 2; i++) {
if (str.charAt(i) != str.charAt(length-i-1)){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
7.多线程服务器
思路:首先需要创建服务器套接字对象ServerSocket对象,指明自己的端口号,然后服务器必须知道是哪个客户端与自己连接,然后就通过获取到的客户端套接字对象来获取几个流对象,然后进行数据的封装以及回响给客户端一个消息
现在以将一张图片发送到服务器,然后服务器将图片存储到磁盘中,最后响应一条消息给客户端为例做代码书写。
run方法:
public class Server implements Runnable{
private Socket client;
public Server(Socket client){
this.client = client;
}
public void run(){
try {
InputStream in = client.getInputStream();
File file = new File("E:\\upload");
if (!file.exists()){
file.mkdirs();
}
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file+"\\12.jpg");
int len = 0;
byte[] data = new byte[1024];
while ((len = in.read(data)) != -1){
fos.write(data,0,len);
}
OutputStream out = client.getOutputStream();
out.write("收到".getBytes());
fos.close();
}catch (Exception e){
}
测试服务器:
public class TestServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8002);
while (true){
Socket client = server.accept();
new Thread(new Server(client)).start();
}
}
}
8.关于递归的知识
我在做权限项目中的模块编写的时候,写权限树的时候,用到了递归的技术。
现在对递归技术做一个总结:





















 1095
1095

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








