positon的四个常用基本属性详解:
1、relative:相对定位。相对于其当前所在位置进行定位,比如“left:20”会向元素的leift位置添加20像素。
2、absolute:绝对定位。生成绝对定位的元素,相对于static定位以外的第一个父元素进行定位。元素的位置可以通过left、right、top、bottom来定义。
3、static:静态定位。默认值,没有定位,元素出现在正常流中(忽略top、bottom、left、right或z-index的声明)。
4、fixed:生成固定定位的元素,相对于浏览器窗口进行定位,位置不会随网页进行改变。元素的位置通过left、top、right、bottom属性进行定位。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<style>
.one{
background-color: red;
border: 1px solid gray;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
float: left;
position:relative;
margin: 150px 150px;
}
.one_11{
background-color: blue;
border: 1px solid gray;
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
/*float: left;*/
left: 70px;
top: 70px;
position: absolute;
}
.one_12{
background-color: gold;
border: 1px solid gray;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
/*float: left;*/
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
position: absolute;
}
.one_13{
background-color: orange;
border: 1px solid gray;
width: 80px;
height: 80px;
/*float: left;*/
top: 80px;
position: absolute;
}
.one_14{
background-color: purple;
border: 1px solid gray;
width: 80px;
height: 80px;
/*float: left;*/
position: absolute;
}
.one1{
background-color: green;
border: 1px solid gray;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
/*float: left;*/
position: absolute;
}
.one2{
background-color: pink;
border: 1px solid gray;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
/*float: left;*/
position: fixed;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
}
</style>
<body>
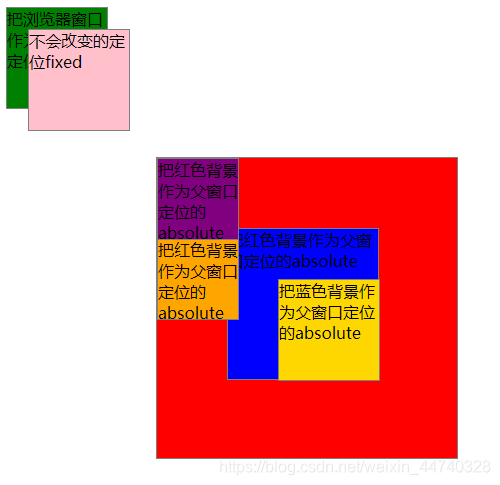
<div class="one">
<div class="one_11">把红色背景作为父窗口定位的absolute
<div class="one_12">把蓝色背景作为父窗口定位的absolute
</div>
</div>
<div class="one_13">把红色背景作为父窗口定位的absolute
</div>
<div class="one_14">把红色背景作为父窗口定位的absolute
</div>
</div>
<div class="one1">把浏览器窗口作为父窗口的定位absolute</div>
<div class="one2">不会改变的定位fixed</div>
</body>
</html>
运行结果:




 本文深入解析了CSS中的四种基本定位方式:relative、absolute、static和fixed的特性与使用场景。通过实例代码展示了每种定位方式如何影响元素的位置,并解释了它们之间的区别。
本文深入解析了CSS中的四种基本定位方式:relative、absolute、static和fixed的特性与使用场景。通过实例代码展示了每种定位方式如何影响元素的位置,并解释了它们之间的区别。
















 1486
1486

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








