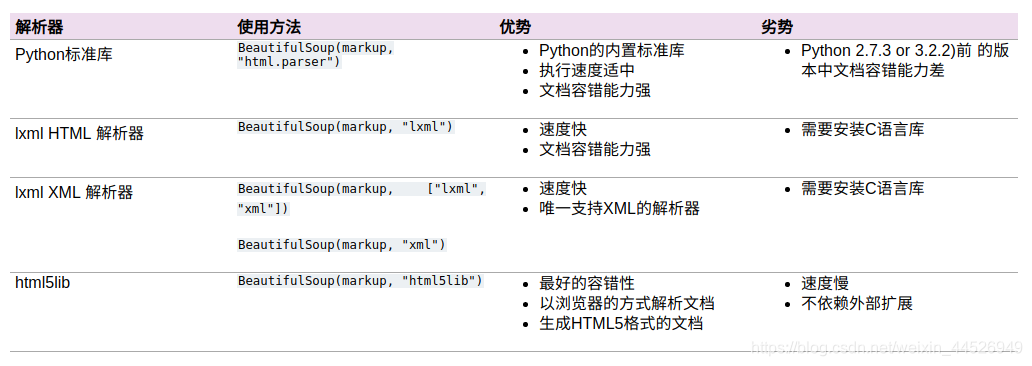
上一篇,学习了正则表达式(https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/weixin_44526949/article/details/86691142),关于正则表达式的特征构造是一个难点,要想能够灵活的驾驭这种方法,需要不断地练习和反复理解。本期将来学习BeautifulSoup模块的使用。BeautifulSoup是一个解析库,处理高效,支持多种解析器。利用它不用编写正则表达式即可方便地实现网页信息的提取。下面是BeautifulSoup的一些主要解析器:
下面以”爱丽丝梦游仙境“的文档来进行该模块的学习:
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,"lxml")
print(soup.prettify()) # 代码格式化,上面的html代码并不完整,对于双标签,并不全
# 而prettify()方法可以将其补全,并进行格式化输出
print(soup.title.string) # 选择title标签,并且打印出该标签中的内容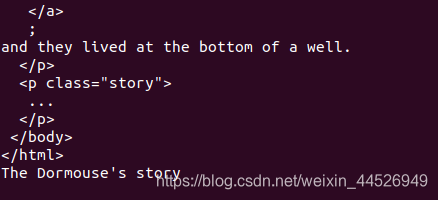
标签选择器
选择元素:
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml")
print(soup.title)
print(type(soup.title))
print(soup.head)
print(soup.p)
print(soup.title.name) # 打印标签的名称
# 获取属性
print(soup.p.attrs) # 默认第一个p标签
print(soup.p['class']) # 默认第一个p标签
# 获取内容
print(soup.p.string)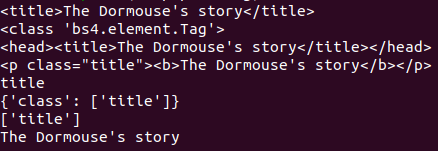
BeautifulSoup将HTML文档装换成一个树形结构,每一个节点都是python对象,所有的对象可以分成4类:Tag,NavigableString,BeautifulSoup,Comment。
Tag对象的基本用法
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml")
tag = soup.title
print(type(tag)) # 结果是一个<class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
# 一些Tag类的属性
print(tag.name) # title
tag = soup.p
print(tag['class']) # title
print(tag.attrs) #{'class':['title']}
tag的属性操作和方法和字典一样,可以当成字典来操作。
多值属性
关于多值属性,最典型的就是class属性:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
css_soup = BeautifulSoup('<p class="machine learning"></p>','lxml')
print(css_soup.p['class']) # ['machine','learning']
# 但是如果是xml格式,则会将class的值当成一个字符串
xml_soup = BeautifulSoup('<p class="machine learning"></p>','xml')
print(xml_soup.p['class']) # machine learning
其他的三个对象用的相对较少,其中NavigableString类来包装tag中的字符串,这种对象的字符串与python中的Unicode字符串相同,两者可以相互转换。而BeautifulSoup对象表示的是一个文档的全部内容,很多场合下,可以把它当做Tag对象。Comment对象,顾名思义,是用来处理网页中的注释内容的,它相当于一个特殊的NavigableString对象。关于更多的关于BeautifulSoup模块的用法,请参考官方文档(https://www.crummy.com/software/BeautifulSoup/bs4/doc/)。对于这些模块的使用,在学习时,可以大致了解下这些方法的作用,不需要刻意去记。在真正做网络爬虫的时候,按需来查即可,用的多了,自然就掌握了。





 本文介绍了BeautifulSoup模块的使用,展示了如何通过该模块高效地解析HTML文档,提取网页信息,避免了复杂的正则表达式编写。文章通过实例演示了标签选择器、属性获取及内容提取的方法。
本文介绍了BeautifulSoup模块的使用,展示了如何通过该模块高效地解析HTML文档,提取网页信息,避免了复杂的正则表达式编写。文章通过实例演示了标签选择器、属性获取及内容提取的方法。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










