本节重点
在这个方法里会请求在1.1.2节里提到过的 CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 和 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor。
CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 会:
扫描方法上是否有@PostConstruct @PreDestroy注解
扫描方法和属性上是否有@Resource注解
注意,@Resource @PostConstruct @PreDestroy 是 JDK 的注解
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 会:
扫描方法和属性上是否有@Autowired @Value注解
注意,@Autowired @Value 是 Spring 的注解
扫描到了注解,就将注解和对应的属性或方法进行封装,最后都会放到 RootBeanDefinition 里的3个容器里。RootBeanDefinition 是对 BeanDefinition 的一个功能扩充。要记得 BeanDefinition 里可没有专门放这些数据的地方了。
这是 doCreateBean 的第二个很重要的方法。
回顾
第一个方法 createBeanInstance 通过构造函数创建了实例。
如果构造函数上有 @Autowired,对入参先进行实例化。
但如果类里还有其它属性上有 @Autowired,则还需要进行依赖注入。
跟源码
类 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
protected void applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(RootBeanDefinition mbd, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor bdp = (MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) bp;
bdp.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
}
}
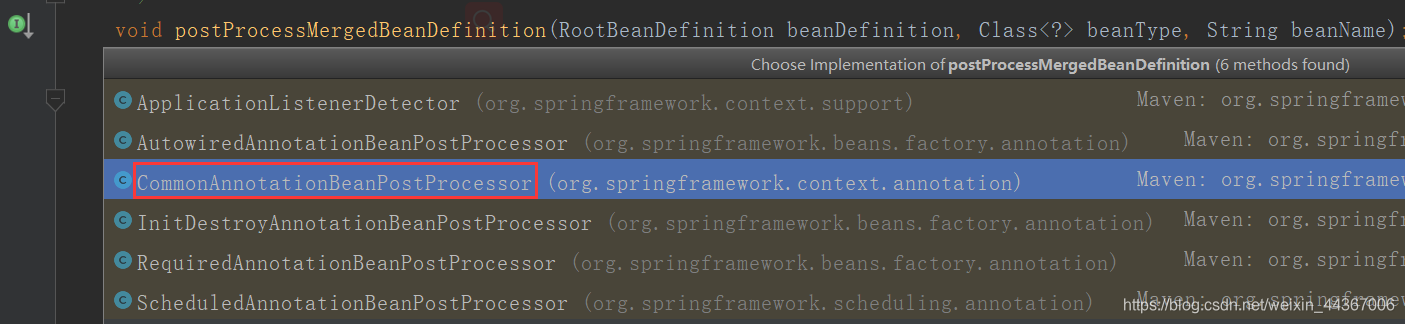
跟 postProcessMergedBeanDefinition:
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor
/*
* 1、扫描类里面的属性或者方法
* 2、判断属性或者方法上面是否有@PostConstruct @PreDestroy @Resource注解
* 3、如果有注解的属性或者方法,包装成一个类
* */
@Override
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
//扫描@PostConstruct @PreDestroy 1.4.2.2.1
//这里面也有一个checkConfigMembers,和下面的作用一样
super.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(beanDefinition, beanType, beanName);
//扫描@Resource,扫描属性和方法上面是否有@Resource注解,如果有则收集起来封装成对象 1.4.2.2.2
InjectionMetadata metadata = findResourceMetadata(beanName, beanType, null);
//包装到RootBeanDefinition里 1.4.2.2.3
metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
}
1.4.2.2.1 postProcessMergedBeanDefinition
类 InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
@Override
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
//对initMethods、destroyMethods、targetClass的封装
LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(beanType);
//把metadata里的元素放到externallyManagedInitMethods和externallyManagedDestroyMethods
//这两个容器在RootBeanDefinition里
//和1.4.2.2.3类似,那里有个externallyManagedConfigMembers,看那就够了
//那个容器也在RootBeanDefinition里
metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
}
跟 findLifecycleMetadata:
private LifecycleMetadata findLifecycleMetadata(Class<?> clazz) {
if (this.lifecycleMetadataCache == null) {
// Happens after deserialization, during destruction...
return buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz);
}
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
//值得学习的写法
LifecycleMetadata metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz);
if (metadata == null) {
synchronized (this.lifecycleMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz);
if (metadata == null) {
metadata = buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz);
this.lifecycleMetadataCache.put(clazz, metadata);
}
return metadata;
}
}
return metadata;
}
跟 buildLifecycleMetadata:
private LifecycleMetadata buildLifecycleMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
List<LifecycleElement> initMethods = new ArrayList<>();
List<LifecycleElement> destroyMethods = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<LifecycleElement> currInitMethods = new ArrayList<>();
final List<LifecycleElement> currDestroyMethods = new ArrayList<>();
//拿到所有的method,遍历每一个method,每一个method都执行下面的方法体
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
//initAnnotationType在CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的构造函数里赋值了,为PostConstruct.class
//如果有注解@PostConstruct
if (this.initAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.initAnnotationType)) {
LifecycleElement element = new LifecycleElement(method);
//收集到本类的容器
currInitMethods.add(element);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found init method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method);
}
}
//destroyAnnotationType在CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的构造函数里赋值了,为PreDestory.class
//如果有注解@PreDestory
if (this.destroyAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.destroyAnnotationType)) {
currDestroyMethods.add(new LifecycleElement(method));
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found destroy method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method);
}
}
});
//本类、所有父类有这2个注解的收集起来
initMethods.addAll(0, currInitMethods);
destroyMethods.addAll(currDestroyMethods);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
//循环,当父类不为空且不为Object
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return new LifecycleMetadata(clazz, initMethods, destroyMethods);
}
CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 的构造函数 1.1.2 节末尾有给出。
1.4.2.2.2 findResourceMetadata
private InjectionMetadata findResourceMetadata(String beanName, final Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
//主要看这个方法
metadata = buildResourceMetadata(clazz);
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}
跟 buildResourceMetadata:
private InjectionMetadata buildResourceMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();
//检查属性
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
if (webServiceRefClass != null && field.isAnnotationPresent(webServiceRefClass)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@WebServiceRef annotation is not supported on static fields");
}
currElements.add(new WebServiceRefElement(field, field, null));
}
else if (ejbRefClass != null && field.isAnnotationPresent(ejbRefClass)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@EJB annotation is not supported on static fields");
}
currElements.add(new EjbRefElement(field, field, null));
}
else if (field.isAnnotationPresent(Resource.class)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@Resource annotation is not supported on static fields");
}
if (!this.ignoredResourceTypes.contains(field.getType().getName())) {
currElements.add(new ResourceElement(field, field, null));
}
}
});
//检查方法
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
if (method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (webServiceRefClass != null && bridgedMethod.isAnnotationPresent(webServiceRefClass)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@WebServiceRef annotation is not supported on static methods");
}
if (method.getParameterCount() != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@WebServiceRef annotation requires a single-arg method: " + method);
}
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new WebServiceRefElement(method, bridgedMethod, pd));
}
else if (ejbRefClass != null && bridgedMethod.isAnnotationPresent(ejbRefClass)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@EJB annotation is not supported on static methods");
}
if (method.getParameterCount() != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@EJB annotation requires a single-arg method: " + method);
}
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new EjbRefElement(method, bridgedMethod, pd));
}
else if (bridgedMethod.isAnnotationPresent(Resource.class)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@Resource annotation is not supported on static methods");
}
Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (paramTypes.length != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@Resource annotation requires a single-arg method: " + method);
}
if (!this.ignoredResourceTypes.contains(paramTypes[0].getName())) {
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new ResourceElement(method, bridgedMethod, pd));
}
}
}
});
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return new InjectionMetadata(clazz, elements);
}
两段代码和 1.4.2.2.1 的两段代码类似,不赘述。
值得一提的是,无论是 field 还是 method 都封装到了 InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement 里。
跟 InjectedElement :
public abstract static class InjectedElement {
protected final Member member;
//是属性还是方法
protected final boolean isField;
@Nullable
protected final PropertyDescriptor pd;
@Nullable
protected volatile Boolean skip;
protected InjectedElement(Member member, @Nullable PropertyDescriptor pd) {
this.member = member;
this.isField = (member instanceof Field);
this.pd = pd;
}
public final Member getMember() {
return this.member;
}
protected final Class<?> getResourceType() {
if (this.isField) {
return ((Field) this.member).getType();
}
else if (this.pd != null) {
return this.pd.getPropertyType();
}
else {
return ((Method) this.member).getParameterTypes()[0];
}
}
跟 Member:
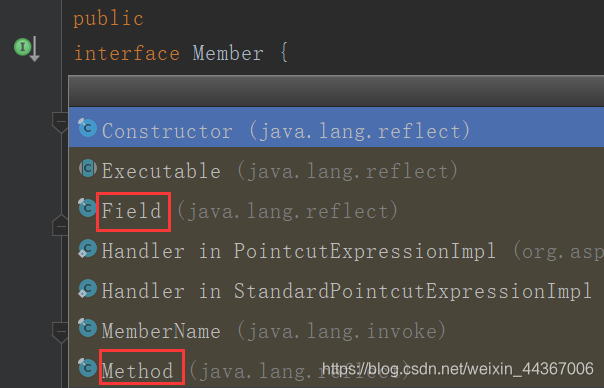
可以看出它既是 Field 的父类,也是 Method 的父类。现在算是搞明白 @Resource 既可以写在属性上也可以写在方法上的原因了吧。
1.4.2.2.3 checkConfigMembers
public void checkConfigMembers(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
Set<InjectedElement> checkedElements = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.injectedElements.size());
for (InjectedElement element : this.injectedElements) {
Member member = element.getMember();
if (!beanDefinition.isExternallyManagedConfigMember(member)) {
//注册到一个Set里
beanDefinition.registerExternallyManagedConfigMember(member);
checkedElements.add(element);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Registered injected element on class [" + this.targetClass.getName() + "]: " + element);
}
}
}
this.checkedElements = checkedElements;
}
跟 isExternallyManagedConfigMember 和 registerExternallyManagedConfigMember:
类 RootBeanDefinition
public void registerExternallyManagedConfigMember(Member configMember) {
synchronized (this.postProcessingLock) {
if (this.externallyManagedConfigMembers == null) {
this.externallyManagedConfigMembers = new HashSet<>(1);
}
this.externallyManagedConfigMembers.add(configMember);
}
}
public boolean isExternallyManagedConfigMember(Member configMember) {
synchronized (this.postProcessingLock) {
return (this.externallyManagedConfigMembers != null &&
this.externallyManagedConfigMembers.contains(configMember));
}
}
对于 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,处理逻辑和 CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 的 @Resource 一样都是创建一个 InjectionMetaData,不赘述。





 本文详细解析了Spring框架中Bean的后处理机制,包括CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor和AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的工作原理,以及它们如何处理@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy、@Resource和@Autowired注解。
本文详细解析了Spring框架中Bean的后处理机制,包括CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor和AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的工作原理,以及它们如何处理@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy、@Resource和@Autowired注解。
















 1323
1323

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








