题目来源:力扣
难度:简单
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5000]-5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:
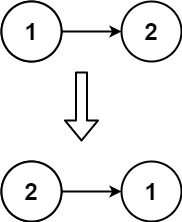
输入:head = [1,2] 输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]
1、双指针法
解题思路:
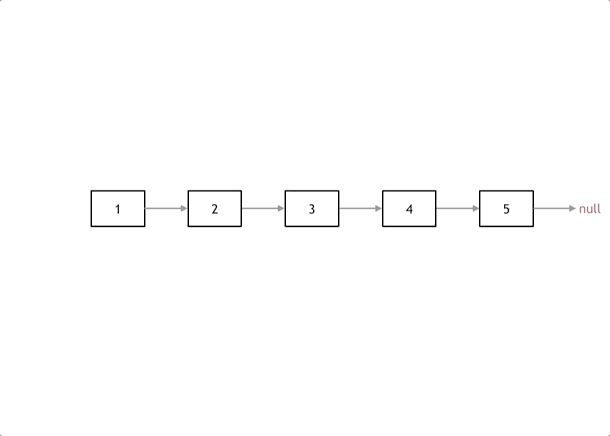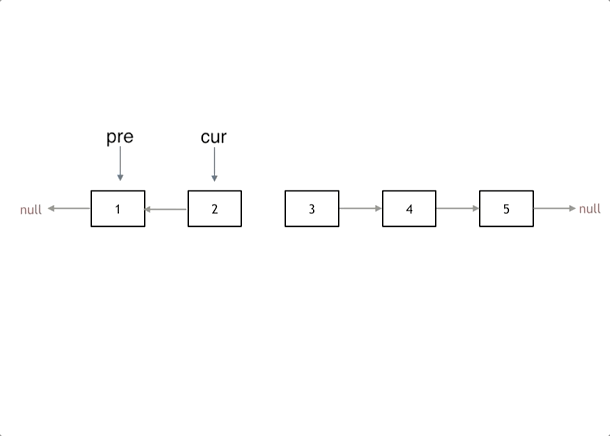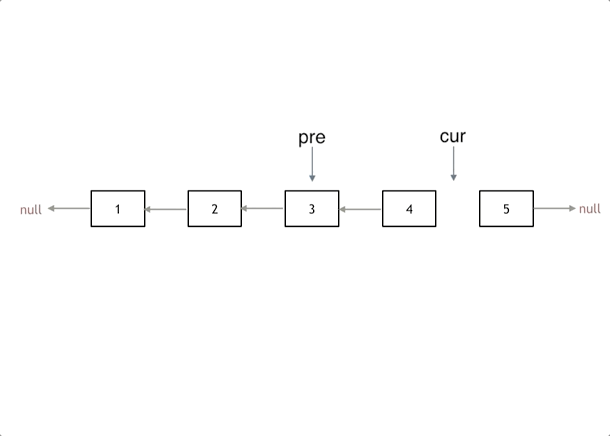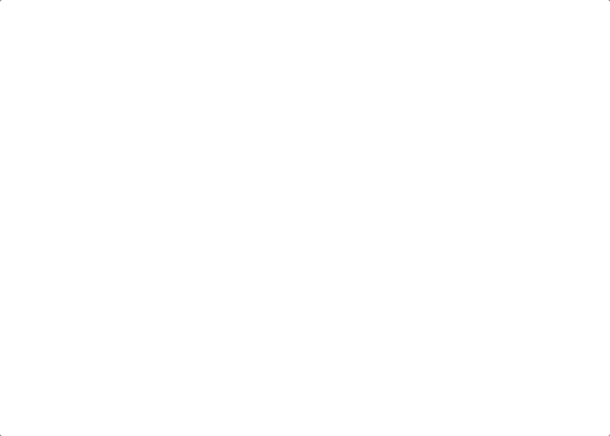
实现代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* pre = nullptr;//前一个节点
ListNode* cur = head;//当前节点
ListNode* h;//保存当前节点的下一个节点
while(cur){
h = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = h;
}
return pre;
}
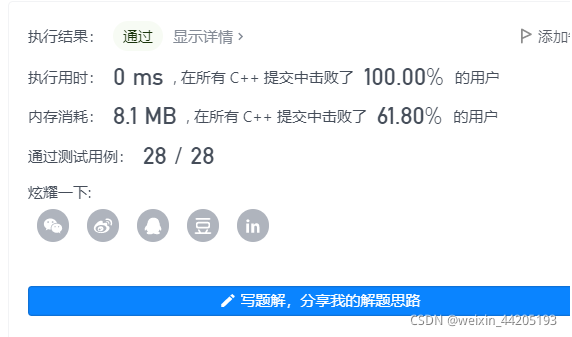
}; 
进阶:链表可以选用迭代或递归方式完成反转。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
2、递归
双指针法写出来之后,理解如下递归写法就不难了,代码逻辑都是一样的。
实现代码:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* pre,ListNode* cur){
if(cur == NULL) return pre;
ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
// 可以和双指针法的代码进行对比,如下递归的写法,其实就是做了这两步
// pre = cur;
// cur = temp;
return reverse(cur,temp);
}
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
// 和双指针法初始化是一样的逻辑
// ListNode* cur = head;
// ListNode* pre = NULL;
return reverse(NULL, head);
}
};






















 2190
2190

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










