1.构造器实例化Bean1
2.静态工厂·方式的实例·化·Bean2
3.实例工厂·方式实例化Bean3
4.作用域的种类·singleton和prototype
分别定义类Bean1,Bean2,Bean3 和singleton、prototype
.静态工厂·方式的实例·化·Bean2
package com.itcast.bean.constructor;
public class Bean2Factory {
public static Bean2 getBean() {
return new Bean2();
}
}
实例工厂·方式实例化Bean3
package com.itcast.bean.constructor;
public class Bean3Factory {
public Bean3 getBean3() {
Bean3 bean3=new Bean3();
return bean3;
}
}
package com.itcast.bean.constructor;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class BeanTest {
@Test
public void beantest() {
// 1.初始化spring容器,加载配置文件
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"applicationContext.xml");
Bean1 bean1 = (Bean1) ac.getBean("bean1");
System.out.println("bean1="+bean1);
//验证
Bean2 bean2 = (Bean2) ac.getBean("bean2");
System.out.println("bean2="+bean2);
Bean3 bean3 = (Bean3) ac.getBean("bean3");
System.out.println("bean3="+bean3);
Singleton singleton1=(Singleton) ac.getBean("singleton");
Singleton singleton2=(Singleton) ac.getBean("singleton");
System.out.println("-------------------------------");
System.out.println("singleton1="+singleton1);
System.out.println("singleton2="+singleton2);
System.out.println("-------------------------------");
Prototype prototype1=(Prototype) ac.getBean("prototype");
Prototype prototype2=(Prototype) ac.getBean("prototype");
System.out.println("prototype1="+prototype1);
System.out.println("prototype2="+prototype2);
}
}

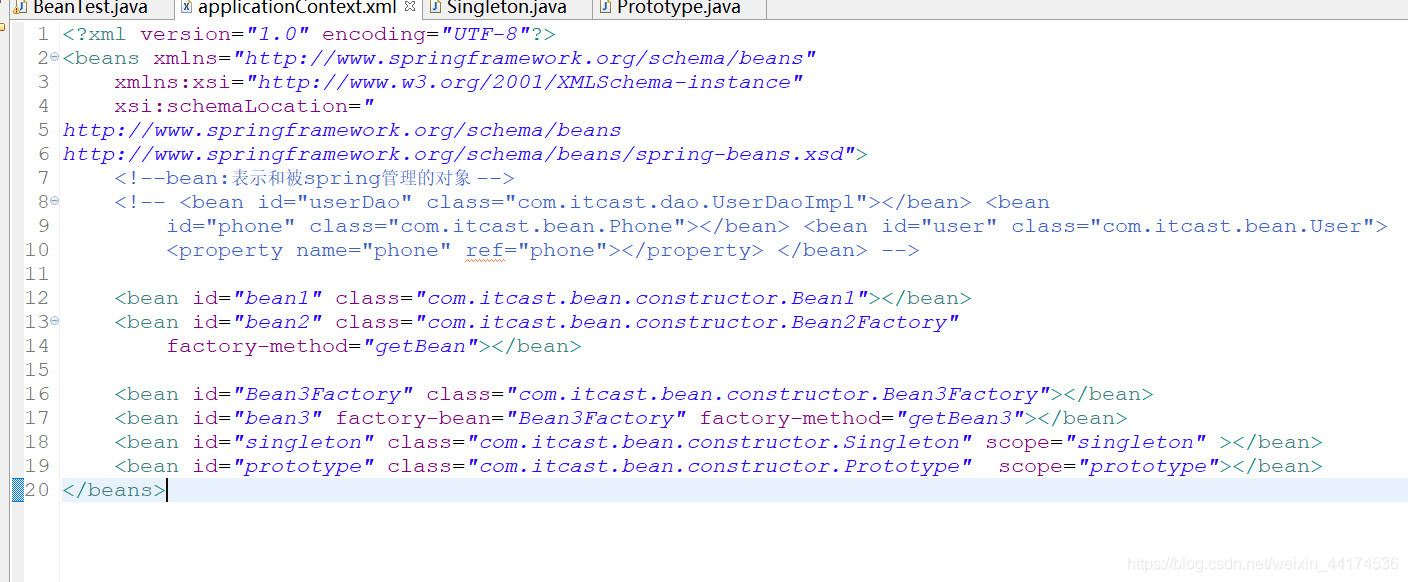
<bean id="bean1" class="com.itcast.bean.constructor.Bean1"></bean>
<bean id="bean2" class="com.itcast.bean.constructor.Bean2Factory"
factory-method="getBean"></bean>
<bean id="Bean3Factory" class="com.itcast.bean.constructor.Bean3Factory"></bean>
<bean id="bean3" factory-bean="Bean3Factory" factory-method="getBean3"></bean>
<bean id="singleton" class="com.itcast.bean.constructor.Singleton" scope="singleton" ></bean>
<bean id="prototype" class="com.itcast.bean.constructor.Prototype" scope="prototype"></bean>
1)id: Bean 的唯一标识名。它必须是合法的 XML ID,在整个 XML 文档中唯一。
(2)name: 用来为 id 创建一个或多个别名。它可以是任意的字母符合。多个别名之间用逗号或空格分开。
(3)class: 用来定义类的全限定名(包名+类名)。只有子类 Bean 不用定义该属性。
(4)parent: 子类 Bean 定义它所引用它的父类 Bean。这时前面的 class 属性失效。子类 Bean 会继承父类 Bean 的所有属性,子类 Bean 也可以覆盖父类 Bean 的属性。注意:子类 Bean 和父类 Bean 是同一个 Java 类。
(5)abstract(默认为”false”):用来定义 Bean 是否为抽象 Bean。它表示这个 Bean 将不会被实例化,一般用于父类 Bean,因为父类 Bean 主要是供子类 Bean 继承使用。
(6)singleton(默认为“true”):定义 Bean 是否是 Singleton(单例)。如果设为“true”,则在 BeanFactory 作用范围内,只维护此 Bean 的一个实例。如果设为“flase”,Bean将是 Prototype(原型)状态,BeanFactory 将为每次 Bean 请求创建一个新的 Bean 实例。





 本文详细介绍了Spring框架中Bean的四种实例化方式:构造器、静态工厂、实例工厂及默认实例化,并探讨了singleton和prototype两种作用域的区别。通过代码示例,展示了如何在XML配置文件中定义这些Bean及其作用域。
本文详细介绍了Spring框架中Bean的四种实例化方式:构造器、静态工厂、实例工厂及默认实例化,并探讨了singleton和prototype两种作用域的区别。通过代码示例,展示了如何在XML配置文件中定义这些Bean及其作用域。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








