公有继承基类和派生类之间构造和析构、赋值和拷贝构造函数的关系(下)
4、公有继承基类和派生类之间拷贝构造函数的关系
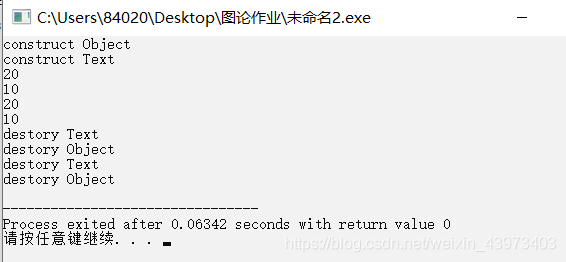
如果子类Text公有继承父类Object,在用已有的Text对象t1初始化Text对象t2时,如果没有写拷贝构造函数,系统的拷贝构造函数会把t1对象按位拷贝给t2对象,产生数据完全相同的t1和t2;
代码测试:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Object
{
private:
int val;
public:
Object(int a=0) :val(a)
{
cout<<"construct Object"<<endl;
}
~Object()
{
cout<<"destory Object"<<endl;
}
void showObject()
{
cout<<val<<endl;
}
} ;
class Text :public Object
{
private:
int num;
public:
Text(int b=0) :num(b),Object(b+10)
{
cout<<"construct Text"<<endl;
}
~Text()
{
cout<<"destory Text"<<endl;
}
void showText()
{
cout<<num<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Text t1(10);
Text t2(t1);
t1.showObject();
t1.showText();
t2.showObject();
t2.showText();
return 0;
}
如果父类写了拷贝构造函数,用t1初始化t2时,也能完成父类对象部分的拷贝
代码测试:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Object
{
private:
int val;
public:
Object(int a=0) :val(a)
{
cout<<"construct Object"<<endl;
}
~Object()
{
cout<<"destory Object"<<endl;
}
Object(const Object& obj):val(obj.val)
{
cout<<"copy construct Object"<<endl;
}
void showObject()
{
cout<<val<<endl;
}
} ;
class Text :public Object
{
private:
int num;
public:
Text(int b=0) :num(b),Object(b+10)
{
cout<<"construct Text"<<endl;
}
~Text()
{
cout<<"destory Text"<<endl;
}
void showText()
{
cout<<num<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Text t1(10);
Text t2(t1);
t1.showObject();
t1.showText();
t2.showObject();
t2.showText();
return 0;
}
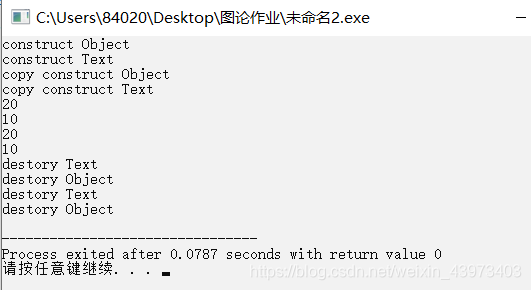
如果子类Text中写了拷贝构造函数,则需要在子类拷贝构造函数中调用父类的拷贝构造函数,这样才能完成t1对t2的初始化,如果子类拷贝构造函数中没有调用父类的拷贝构造函数,则t2的父类对象部分不会用t1的父类对象部分来初始化。
代码测试:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Object
{
private:
int val;
public:
Object(int a=0) :val(a)
{
cout<<"construct Object"<<endl;
}
~Object()
{
cout<<"destory Object"<<endl;
}
Object(const Object& obj):val(obj.val)
{
cout<<"copy construct Object"<<endl;
}
void showObject()
{
cout<<val<<endl;
}
} ;
class Text :public Object
{
private:
int num;
public:
Text(int b=0) :num(b),Object(b+10)
{
cout<<"construct Text"<<endl;
}
~Text()
{
cout<<"destory Text"<<endl;
}
Text(const Text& T) :num(T.num),Object(T)
{
cout<<"copy construct Text"<<endl;
}
void showText()
{
cout<<num<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Text t1(10);
Text t2(t1);
t1.showObject();
t1.showText();
t2.showObject();
t2.showText();
return 0;
}




 本文探讨了公有继承情况下基类与派生类之间的拷贝构造函数关系,包括系统默认拷贝构造函数的行为、父类拷贝构造函数的作用以及子类中显式定义拷贝构造函数的必要性。
本文探讨了公有继承情况下基类与派生类之间的拷贝构造函数关系,包括系统默认拷贝构造函数的行为、父类拷贝构造函数的作用以及子类中显式定义拷贝构造函数的必要性。

















 2099
2099

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










