类String
所在的包:java.lang
public final class String extends Object implements Serializable, Comparable, CharSequence
String 类代表字符串。Java 程序中的所有字符串字面值(如 “abc”)都作为此类的实例实现。字符串是常量;它们的值在创建之后不能更改。字符串缓冲区支持可变的字符串。因为 String 对象是不可变的,所以可以共享
一、构造方法
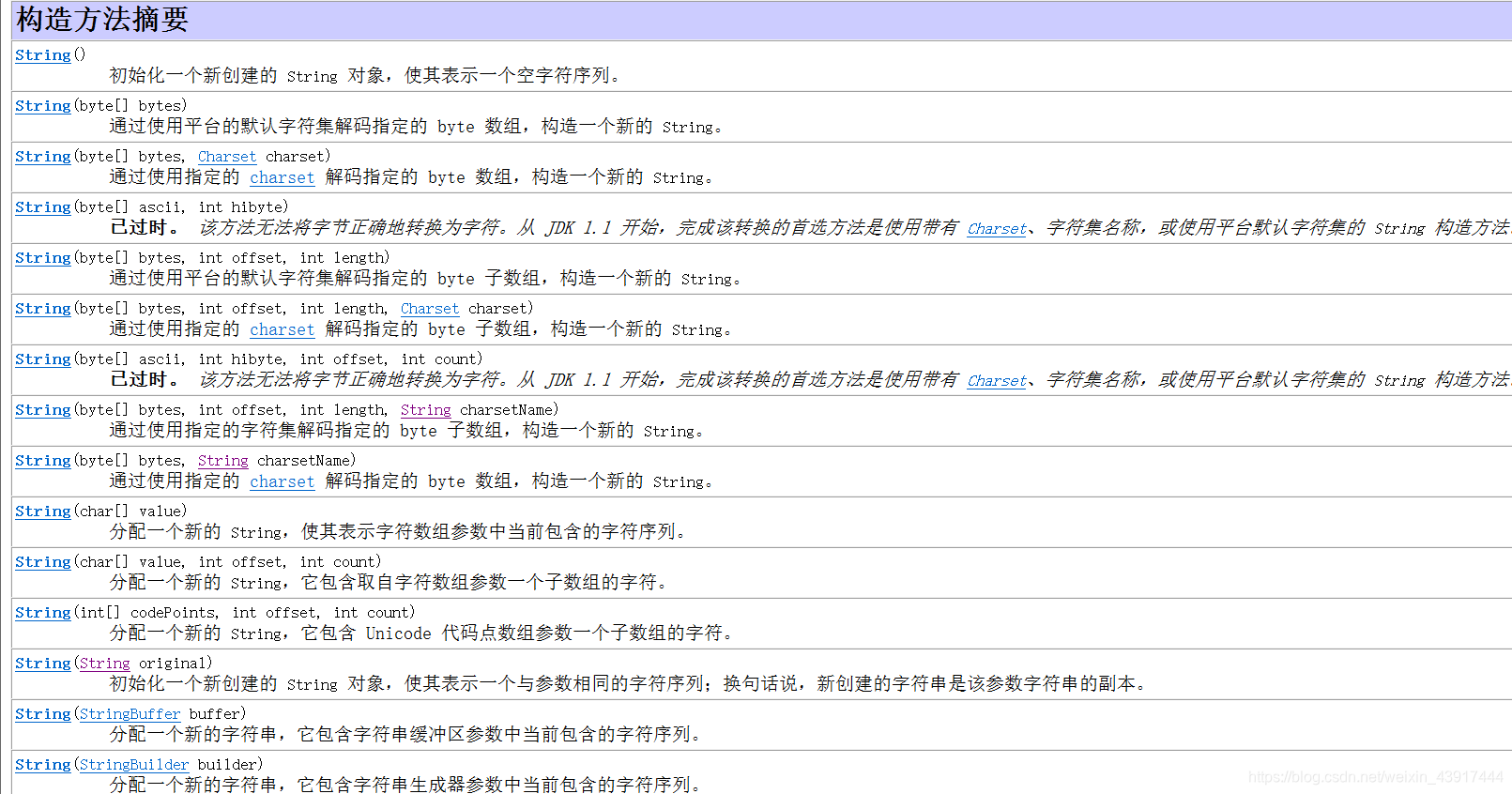
例子:
int [ ] arr ={97,98,99,100};
String s = new String(arr,0,3);//abc
//原因:由字符集解码所得
二、方法
1、比较
public boolean equals(Object an Object) // 区分大小写,返回值为正确或错误
将此字符串与指定的对象比较。当且仅当该参数不为 null,并且是与此对象表示相同字符序列的String 对象时,结果才为 true。
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String another String) // 不区分大小写
将此 String 与另一个 String比较,不考虑大小写。如果两个字符串的长度相同,并且其中的相应字符都相等(忽略大小写),则认为这两个字符串是相等的。
例子:
String s1="we are family";
String s2="we are family";
String s3="We Are Family";
System.out.println(s1==s2);//true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));//false 区分大小写
System.out.println("----------------------");
//boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str):比较字符串中的内容是否相同,忽略大小写
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2));
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s3));//忽略大小写
public int compareTo(String anotherString) //区分大小写,返回值为差值
按字典顺序比较两个字符串。
public int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) //不区分大小写
按字典顺序比较两个字符串,不考虑大小写。
String s1="abcde";
String s2="bcdef";
String s3="addef";
String s4="a";
String s5="ABCDE";
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2));//-1
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s3));//-2
//当两个字符串长度相等时,返回第一个不相同的字符差值
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s4));//4
//当两个字符串长度不等时,返回第一个字符串与第二个字符串的长度差值
//String compareToIgnoreCase():忽略大小写比较
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s5));//0
2、包含
public boolean contains(CharSequence s)
当且仅当此字符串包含指定的 char 值序列时,返回 true。
public boolean startsWith(String str)
判断是否以某个指定的字符串开头
public boolean endsWith(String str)
判断是否以某个指定的字符串结尾
例子:
String s1="我爱 babamama 哈哈";
String s2="babamama";
String s3="lala";
String s4="我爱";
String s5="哈哈";
System.out.println(s1.contains(s2));//true 包含
System.out.println(s1.contains(s3));//false 不包含
System.out.println("---------------------");
System.out.println(s1.startsWith(s4));//true
System.out.println(s1.startsWith(s5));//false
System.out.println(s1.endsWith(s4));//false
System.out.println(s1.endsWith(s5));//true
3、判断字符串是否为空
public boolean isEmpty()
当且仅当 length() 为0 时返回 true。
String s1="abc";
String s2="";
// String s3=null;
System.out.println(s1.isEmpty());//false
System.out.println(s2.isEmpty());//ftrue
// System.out.println(s3.isEmpty());//java.lang.NullPointerException空指针异常
/*
*""和null的区别
*""是字符串常量,同时也是一个String类的对象,既然是对象当然可以调用String类中的方法
*null是空常量,不可以调用任何方法,否则会出现空指针异常,null常量可以给任意的引用数据类型赋值
*/
4、通过索引找字符串&&通过字符串返回索引
public int length()
返回此字符串的长度。
例子:
int [ ] arr ={11,12,31,46,65};
int length1 = arr.length;//字符串中长度是字符串的属性
String str = "ankdfnvdn";
int length2 = str.length();//类中长度是方法
public char charAt(int index)
指定索引处的 char 值。
例子:
char c=s2.charAt(2);//我
System.out.println(c);
char c2=s2.charAt(5);
System.out.println(c2);//java.lang.StringIndexOutOfBoundsException,越界了
public int indexOf(int ch)
返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
public int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)
返回在此字符串中第一次出现指定字符处的索引,从指定的索引开始搜索。
public int indexOf(String str)
返回指定子字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
public int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex)
返回指定子字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引开始。
public int lastIndexOf(int ch)
返回指定字符在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引。
public int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)
返回指定字符在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引处开始进行反向搜索。
public int lastIndexOf(String str)
返回指定子字符串在此字符串中最右边出现处的索引。
public int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex)
返回指定子字符串在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引开始反向搜索。
例子:
String s1="abcdsf";
int a=s1.indexOf('d');
System.out.println(a);//3
int a1=s1.indexOf('z');
System.out.println(a1);//-1,如果不存在返回值就是-1
int b=s1.indexOf("cds");
System.out.println(b);//2,返回首元素的位置
int c=s1.indexOf("cs");
System.out.println(c);//-1,如果字符串并不相连返回值为-1
例子:
String s1="woaiwojia";
//int indexOf(int ch,int fromIndex):返回指定字符在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现的索引
int index1=s1.indexOf('a',3);
System.out.println(index1);//8
int index2=s1.indexOf('a',10);
System.out.println(index2);//-1,超过字符串长度的位置没有此字符,返回值为-1
//int indexOf(String str,int fromIndex):返回指定字符串在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引
int index3=s1.indexOf("aiw",1);
System.out.println(index3);//2
int index4=s1.indexOf("ao",1);
System.out.println(index4);//-1,没有此指定的字符串,返回值为-1
//int lastIndexOf()与上面的几种方法相同,就是从字符串最后开始找
5、截取字符串
public String substring(int beginIndex)//开始的位置到结束
返回一个新的字符串,它是此字符串的一个子字符串。
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) //开始的位置,末尾的位置,左闭右开
返回一个新字符串,它是此字符串的一个子字符串
例子:
String s1="anvnkvnsvvs";
//String substring(int start):从指定位置开始截取字符串,默认到末尾
String s2=s1.substring(2);
System.out.println(s2);//vnkvnsvvs
//String substring(int start,int end):从指定位置开始到指定位置结束截取字符串
String s3=s1.substring(2,5);
System.out.println(s3);//vnk,左闭右开
//经典面试题
s1.substring(2);
System.out.println(s1);//anvnkvnsvvs
//原因:substring方法返回值是一个字符串,但是没有定义新的变量去接受这个新的返回值,而且输出时是s1
6、获取字节数组
public byte[ ] getBytes()
使用平台的默认字符集将此 String 编码为 byte 序列,并将结果存储到一个新的 byte数组中。
public byte[ ] getBytes(Charset charset)
使用给定的 charset 将此 String编码到 byte 序列,并将结果存储到新的 byte 数组。
public byte[ ] getBytes(String charsetName)
使用指定的字符集将此 String 编码为 byte 序列,并将结果存储到一个新的 byte 数组中。
例子:
//byte[] getBytes():把字符串转换为字节数组
String s="abcdef";
byte [] arr1=s.getBytes();
for(int i=0;i<arr1.length;i++) {
System.out.print(arr1[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
String s1="你好啊,小朋友";
byte [] arr2=s1.getBytes();
for(int i=0;i<arr2.length;i++) {
System.out.print(arr2[i]+" ");
}
//都是负数,汉字是两个字节组成的,第一个字节必须是负数才是中文
//通过gbk码表将字符串转换成字节数组
6、将字符串转换成字符数组
public char[ ] toCharArray()
将此字符串转换为一个新的字符数组。
String s="heima";//自动装箱
char [] arr=s.toCharArray();
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
System.out.print (arr[i]+" ");
}
7、将任意形式的数据类型转换成String类型
public static String valueOf(boolean b)
返回 boolean 参数的字符串表示形式。
public static String valueOf(char c)
返回 char 参数的字符串表示形式。
public static String valueOf(char[] data)
返回 char 数组参数的字符串表示形式。
public static String valueOf(char[] data, int offset, int count)
返回 char数组参数的特定子数组的字符串表示形式。
public static String valueOf(double d)
返回 double 参数的字符串表示形式。
public static String valueOf(float f)
返回 float 参数的字符串表示形式。
public static String valueOf(int i)
返回 int 参数的字符串表示形式。
public static String valueOf(long l)
返回 long 参数的字符串表示形式。
public static String valueOf(Object obj)
返回 Object 参数的字符串表示形式。
例子:
char [] arr= {'a','b','c','d'};
String s=String.valueOf(arr);//string类中的方法
System.out.println(s);
String s1=new String(arr);//构造方法
System.out.println(s1);
String s2=String.valueOf(100);
System.out.println(s2);//100
System.out.println(s2+100);//100100是字符串,不是整数
Person p1=new Person("张三",23);
System.out.println(p1);//com.bean.Person@279f2327
String s3=String.valueOf(p1);//调用的是对象的toString方法
System.out.println(s3);//com.bean.Person@279f2327,原因是未在Person类中重写toString方法
8、将字符串全部转大写或小写
public String toUpperCase()
使用默认语言环境的规则将此 String 中的所有字符都转换为大写。
public String toUpperCase(Locale locale)
使用给定Locale 的规则将此 String 中的所有字符都转换为大写。
String s1="heiMA";
String s2="changxuYUAN";
String s3=s1.toLowerCase();//全部转小写
String s4=s2.toUpperCase();//全部转小写
System.out.println(s3);
System.out.println(s4);
String s5=s1.concat(s2);//连接字符串
System.out.println(s5);
System.out.println(s1+s2);//用+拼接字符串更加强大,可以用字符串与任意类型相加
9、连接字符串
public String concat(String str)
将指定字符串连接到此字符串的结尾。
注意:此方法只能连接两个字符串,作用并不强大,可以通过“+”来连接
例子在上面
10、替换元素&&消去空格
public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar)
返回一个新的字符串,它是通过用 newChar替换此字符串中出现的所有 oldChar 得到的。
public String replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement)
使用指定的字面值替换序列替换此字符串所有匹配字面值目标序列的子字符串。
public String trim()
返回字符串的副本,忽略前导空白和尾部空白。
例子:
//String replace(char old,char new)
String s1="abcdefg";
String s2=s1.replace('d', 'z');
System.out.println(s2);//abczefg
String s3=s1.replace('z', 'p');
System.out.println(s3);//abcdefg
//当需替换的字符在原字符串中不存在时,返回原字符串不改变
//String replace(String old,String new)
String s4=s1.replace("abc","aaa");
System.out.println(s4);//aaadefg
String s5=s1.replace("acd","aaa");
System.out.println(s5);//abcdefg
//当需要替换的字符串在原串中不完全正确存在时,返回原字符串不改变
//String trim():String的去除字符串两端的空格,可用于用户注册登录界面
String s=" hei hei ";
String s6=s.trim();
System.out.println(s6);//hei hei
三、例题
/**
*需求:模拟登陆,给三次机会,并提示还有几次
*用户名和密码都是admin
*分析:
*1、键盘录入登陆信息
*2、判断录入信息是否正确
*3、三次机会,循环产生
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
for(int i=2;i>=0;i--) {
System.out.println("请输入您的用户名:");
String usersname=sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入您的密码:");
String password=sc.nextLine();
//如果是字符串常量和字符串变量比较,通常是字符串常量调用方法,将变量当作参数传递,防止空指针异常,字符串变量可能会是null
if ("admin".equals(usersname) && "admin".equals(password)) {
System.out.println("用户"+usersname+"登陆成功");
break;//跳出循环
} else {
if (i==0) {
System.out.println("您今天的登录次数已用完");
} else {
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误"+"您还有"+i+"次机会");
}
}
}
//需求:遍历字符串
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s="abdvnskvndbs";
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++) {//通过for循环获取字符串中每个字符的索引
/*char ch=s.charAt(i);
System.out.println(ch);*/
System.out.println(s.charAt(i));//通过索引获取每一个字符
}
}
/*
*需求:统计一个字符串中大写字符、小写字符、数字字符 出现的次数,其他字符出现的次数
*ABCDEabcdef12345@#$%^@
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s="ABCDEabcdef12345@#$%^@";
int big=0;
int small=0;
int num=0;
int other=0;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++) {
//获取字符串中的单个字符,重点
char ch=s.charAt(i);
if(ch>='A'&&ch<='Z') {
big++;
} else if(ch>='a'&&ch<='z') {
small++;
} else if(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {
num++;
} else {
other++;
}
}
System.out.println(s+"中大写字符有"+big+"个");
System.out.println(s+"中小写字符有"+small+"个");
System.out.println(s+"中数字字符有"+num+"个");
System.out.println(s+"中其他字符有"+other+"个");
}
//需求:判断小串在大串中出现的次数
public static void main(String[] args) {
String max="woaiwojiawoaibabamama";
String min="wo";
int count=0;
int index=0;
while((index=max.indexOf(min))!=-1) {
//当索引值不为-1时,在max中可以找到min,则继续循环,并记录索引位置
count++;//计数器自增
max=max.substring(index+min.length());//将字符串进行改变,判断过的地方不再判断
}
System.out.println(count);
}
类StringBuffer
所在的包:java.lang
public final class StringBuffer extends Object implements Serializable, CharSequence
线程安全的可变字符序列。一个类似于 String的字符串缓冲区,但不能修改。虽然在任意时间点上它都包含某种特定的字符序列,但通过某些方法调用可以改变该序列的长度和内容。可将字符串缓冲区安全地用于多个线程。可以在必要时对这些方法进行同步,因此任意特定实例上的所有操作就好像是以串行顺序发生的,该顺序与所涉及的每个线程进行的方法调用顺序一致。
一、构造方法
public StringBuffer()
构造一个其中不带字符的字符串缓冲区,其初始容量为 16 个字符。
public StringBuffer(CharSequence seq)
public java.lang.StringBuilder(CharSequence seq) 构造一个字符串缓冲区,它包含与指定的 CharSequence 相同的字符。
public StringBuffer(int capacity)
构造一个不带字符,但具有指定初始容量的字符串缓冲区。
public StringBuffer(String str)
构造一个字符串缓冲区,并将其内容初始化为指定的字符串内容。
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();
System.out.println(sb.length());//0,容器中的字符个数,实际值
System.out.println(sb.capacity());//16,容器中初始字符个数,理论值
StringBuffer sb2=new StringBuffer(10);
System.out.println(sb2.length());//0,容器中的字符个数,实际值
System.out.println(sb2.capacity());//10,容器在初始化时规定的字符个数
StringBuffer sb3=new StringBuffer("vdvbkdv");
System.out.println(sb3.length());//7,容器中的字符个数,实际值
System.out.println(sb3.capacity());//23,容器初始化时的值+容器中扩展的字符串的值即字符串的length
二、方法
1、添加&&字符串形式表示
public StringBuffer append(boolean b)
将 boolean 参数的字符串表示形式追加到序列。
public StringBuffer append(char c)
将 char 参数的字符串表示形式追加到此序列。
public StringBuffer append(char[] str)
将 char 数组参数的字符串表示形式追加到此序列。
public StringBuffer append(char[] str, int offset, int len)
将 char数组参数的子数组的字符串表示形式追加到此序列。
public StringBuffer append(CharSequence s)
将指定的 CharSequence 追加到该序列。
public StringBuffer append(CharSequence s, int start, int end)
将指定 CharSequence的子序列追加到此序列。
public StringBuffer append(double d)
将 double 参数的字符串表示形式追加到此序列。
public StringBuffer append(float f)
将 float 参数的字符串表示形式追加到此序列。
public StringBuffer append(int i)
将 int 参数的字符串表示形式追加到此序列。
public StringBuffer append(long lng)
将 long 参数的字符串表示形式追加到此序列。
public StringBuffer append(Object obj)
追加 Object 参数的字符串表示形式。
public StringBuffer append(String str)
将指定的字符串追加到此字符序列。
public StringBuffer append(StringBuffer sb)
将指定的 StringBuffer 追加到此序列中。
public String toString()
返回此序列中数据的字符串表示形式。
例子:
//public StringBuffer append(String str);
//可以把任意类型数据添加到字符串缓冲区里面,并返回字符串缓冲区本身
//StringBuffer是字符串缓冲区,当new的时候是在堆内存创建了一个对象,底层是一个长度为16的字符数组,
//当调用添加方法是,不会再重新创建对象,在不断向原缓冲区添加字符
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();
System.out.println(sb.toString());//空
StringBuffer sb2=sb.append(true);
System.out.println(sb2.toString());//true
StringBuffer sb3=sb.append("heihei");
System.out.println(sb3.toString());//trueheihei
StringBuffer sb4=sb.append(100);
System.out.println(sb4.toString());//trueheihei100
//此时是一边在向缓冲区中添加东西,一边打印输出,输出结果是此时添加的结果
System.out.println(sb.toString());//trueheihei100
//StringBuffer重写了toString()方法,显示的是对象的属性值
System.out.println(sb2.toString());//trueheihei100
System.out.println(sb3.toString());//trueheihei100
System.out.println(sb4.toString());//trueheihei100
//说明四个引用指向同一个对象,此时缓冲区的内容完全相同,不在添加即不在改变
//理解:如同一杯鸡尾酒,你一边添加一边观察就会得到观察的东西,而你全部添加完在观察,不论是怎样观察都是一个结果
2、添加到指定位置
public StringBuffer insert(int offset, boolean b)
将 boolean参数的字符串表示形式插入此序列中。
public StringBuffer insert(int offset, char c)
将 char 参数的字符串表示形式插入此序列中。
public StringBuffer insert(int offset, char[] str)
将 char数组参数的字符串表示形式插入此序列中。
public StringBuffer insert(int index, char[] str, int offset, int len)
将数组参数 str的子数组的字符串表示形式插入此序列中。
public StringBuffer insert(int dstOffset, CharSequence s)
将指定 CharSequence 插入此序列中。
public StringBuffer insert(int dstOffset, CharSequence s, int start, int end)
将指定 CharSequence的子序列插入此序列中。
public StringBuffer insert(int offset, double d)
将 double 参数的字符串表示形式插入此序列中。
public StringBuffer insert(int offset, float f)
将 float 参数的字符串表示形式插入此序列中。
public StringBuffer insert(int offset, int i)
将 int 参数的字符串表示形式插入此序列中。
public StringBuffer insert(int offset, long l)
将 long 参数的字符串表示形式插入此序列中。
public StringBuffer insert(int offset, Object obj)
将Object 参数的字符串表示形式插入此字符序列中。
public StringBuffer insert(int offset, String str)
将字符串插入此字符序列中。
例子:
//public StringBuffer insert(int offset,String str):
//在指定位置把任意类型的数据插入到字符串缓冲区里面,并返回字符缓冲区本身
//StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();//java.lang.StringIndexOutOfBoundsException索引越界异常
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer("12345");
sb.insert(3,"heihei");
System.out.println(sb);//123heihei45
//在指定位置添加元素,如果没有指定位置的索引就会报索引越界异常
3、删除
public StringBuffer delete(int start, int end)
移除此序列的子字符串中的字符。
public StringBuffer deleteCharAt(int index)
移除此序列指定位置的 char。
例子:
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();
//sb.deleteCharAt(5);//java.lang.StringIndexOutOfBoundsException;
//当缓冲区中这个索引上没有元素的时候就会报缓冲区越界异常
sb.append("ABCDEFG");
//public StringBuffer deleteCharAt(int index):
//删除指定位置的字符,并返回本身
//sb.deleteCharAt(5);//ABCDEG
//System.out.println(sb);
//public StringBuffer delete(start, end):
//删除从指定位置开始到指定位置结束的内容,并返回本身
//sb.delete(1,3);
//System.out.println(sb);//ADEFG,左闭右开
sb.delete(0,sb.length());//清空缓冲区(常用)
System.out.println(sb);
//sb=new StringBuffer();
//System.out.println(sb);
//此方法也可以清空缓冲区,但是这种方法等于在堆内存中新开辟了一块存储区域
//将原来的存储区域当作了垃圾,这种方法不推荐,是对存储空间的浪费
4、逆置&&替换
public StringBuffer replace(int start, int end, String str)
使用给定String 中的字符替换此序列的子字符串中的字符。
public StringBuffer reverse()
将此字符序列用其反转形式取代。
例子:
//public StringBuffer replace(int start,int end,String str);
//StringBuffer的替换功能,从start到end用str替换
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer("heima");
sb.replace(0, 3, "bai");
System.out.println(sb);//baima
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer("heimabaimadoushihaoma");
StringBuffer sb1=new StringBuffer("我是个可爱的宝宝");
sb.reverse();
sb1.reverse();
System.out.println(sb);
System.out.println(sb1);
5、截取字符串
public String substring(int start)
返回一个新的 String,它包含此字符序列当前所包含的字符子序列。
public String substring(int start, int end)
返回一个新的 String,它包含此序列当前所包含的字符子序列。
例子:
//StringBuffer的截取功能
//注意返回值类型不再是StringBuffer本身
//public String substring(int start):
//从指定位置开始截取到末尾
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer("woshigekeaidebaobao");
String str=sb.substring(7);
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(sb);//截取的字符串是String类型的,并未改变StringBuffer
//public String substring(int start,int end):
//截取从指定位置开始到结束位置,包括开始位置,不包括结束位置,左闭右开
String str1=sb.substring(7,11);
System.out.println(str1);
6、String与StringBuffer的转换
1、String–>StringBuffer
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer("heiheideyanjing");
//通过构造方法将字符串转换为StringBuffer对象
System.out.println(sb);
StringBuffer sb1=new StringBuffer();
sb1.append("woshigekeaidebaobao");
//通过append方法将字符串转换成StringBuffer对象
System.out.println(sb1);
2、StringBuffer–>String
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer("heima");//创建StringBuffer对象
String str1=new String(sb);//通过构造方法
System.out.println(str1);
String str2=sb.toString();//通过toString方法
System.out.println(str2);
String str3=sb.substring(0,sb.length());//通过substring方法
System.out.println(str3);
三、例题
/*需求:把数组中的数据按照指定的格式拼接成一个字符串
*例如:
* int [] arr={1,2,3};
* out:
* "[1, 2, 3]"
*要StringBuffer的功能实现
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] arr= {1,2,3};
System.out.println(array2String(arr));
}
public static String array2String(int[] arr) {
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();
sb.append("[");
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
if(i==arr.length-1) {
sb.append(arr[i]).append("]");
} else {
sb.append(arr[i]).append(", ");
}
}
String str=sb.toString();
return str;
//return sb.toString();也可以
}
四、String,StringBuffer与StringBuilder的区别
String,StringBuffer与StringBuilder的区别
这是转载别人的,很全面,这里不再细说了,StringBuilder与StringBuffer的方法几乎是一样的,这里不再讲解




















 194
194

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








