我们前边学到的数据流只能实现对基本数据类型和字符串类型的读写,并不能读取对象(字符串除外),如果要对某个对象进行读写操作,我们需要学习一对新的处理流:ObjectInputStream/ObjectOutputStream。
ObjectInputStream/ObjectOutputStream是以“对象”为数据源,但是必须将传输的对象进行序列化与反序列化操作。
【示例】
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Date;
public class TestObject {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//写出
ByteArrayOutputStream baos=new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(baos));
//操作数据类型+数据
oos.writeUTF("编码辛酸泪");
oos.writeInt(18);
oos.writeBoolean(false);
oos.writeChar('a');
//对象
oos.writeObject("谁解其中味");
oos.writeObject(new Date());
Employee emp=new Employee("马云",400);
oos.writeObject(emp);
oos.flush();
byte[] datas=baos.toByteArray();
System.out.println(datas.length);
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(datas));
//顺序与写出一致
String msg=ois.readUTF();
int age=ois.readInt();
boolean flah=ois.readBoolean();
char ch=ois.readChar();
System.out.println(flah);
Object str=ois.readObject();
Object date=ois.readObject();
Object employee=ois.readObject();
if(str instanceof String){
String strObj=(String) str;
System.out.println(strObj);
}
if(date instanceof Date){
Date dateObj=(Date) date;
System.out.println(dateObj);
}
if(employee instanceof Employee){
Employee empObj=(Employee) employee;
System.out.println(empObj.getName()+"-->"+empObj.getSalary());
}
}
}
class Employee implements Serializable{
private String name;
private int salary;
public Employee(){
}
public Employee(String name,int salary){
this.name=name;
this.salary=salary;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(int salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}
【运行结果】
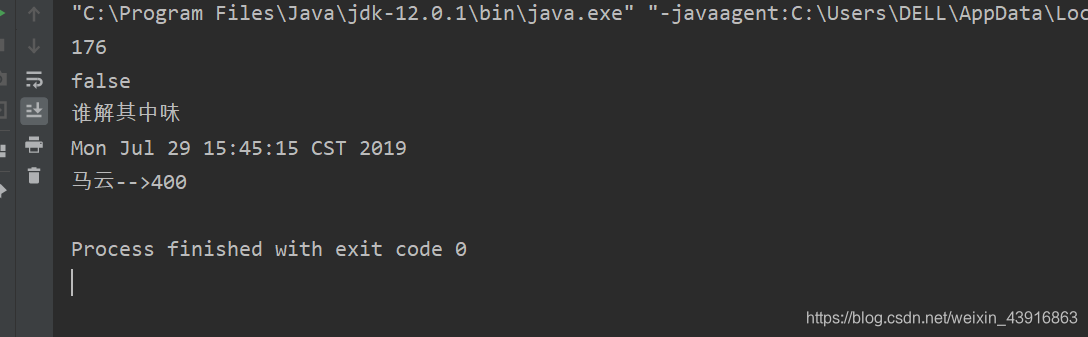
【示例】
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Date;
public class TestObject02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//写出
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("obj.ser")));
//操作数据类型+数据
oos.writeUTF("编码辛酸泪");
oos.writeInt(18);
oos.writeBoolean(false);
oos.writeChar('a');
//对象
oos.writeObject("谁解其中味");
oos.writeObject(new Date());
Employee emp=new Employee("马云",400);
oos.writeObject(emp);
oos.flush();
oos.close();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("obj.ser")));
//顺序与写出一致
String msg=ois.readUTF();
int age=ois.readInt();
boolean flah=ois.readBoolean();
char ch=ois.readChar();
System.out.println(flah);
Object str=ois.readObject();
Object date=ois.readObject();
Object employee=ois.readObject();
if(str instanceof String){
String strObj=(String) str;
System.out.println(strObj);
}
if(date instanceof Date){
Date dateObj=(Date) date;
System.out.println(dateObj);
}
if(employee instanceof Employee){
Employee empObj=(Employee) employee;
System.out.println(empObj.getName()+"-->"+empObj.getSalary());
}
ois.close();
}
}
【运行结果】
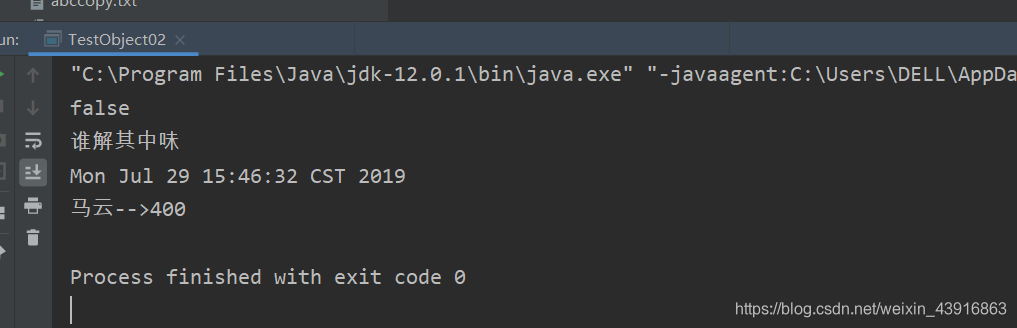
注意
1. 对象流不仅可以读写对象,还可以读写基本数据类型。
2. 使用对象流读写对象时,该对象必须序列化与反序列化。
3. 系统提供的类(如Date等)已经实现了序列化接口,自定义类必须手动实现序列化接口。





 本文详细介绍了如何使用Java的ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream进行对象的序列化与反序列化,包括基本数据类型和自定义对象的读写操作。通过两个示例,展示了如何将对象写入字节数组和文件,以及如何从字节数组和文件中读取对象。
本文详细介绍了如何使用Java的ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream进行对象的序列化与反序列化,包括基本数据类型和自定义对象的读写操作。通过两个示例,展示了如何将对象写入字节数组和文件,以及如何从字节数组和文件中读取对象。
















 1159
1159

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








