28.布尔表达式练习
前言
在编程中,布尔逻辑可以说是无处不在的,它们是计算机的基础部分。
一、Atom文本编辑器
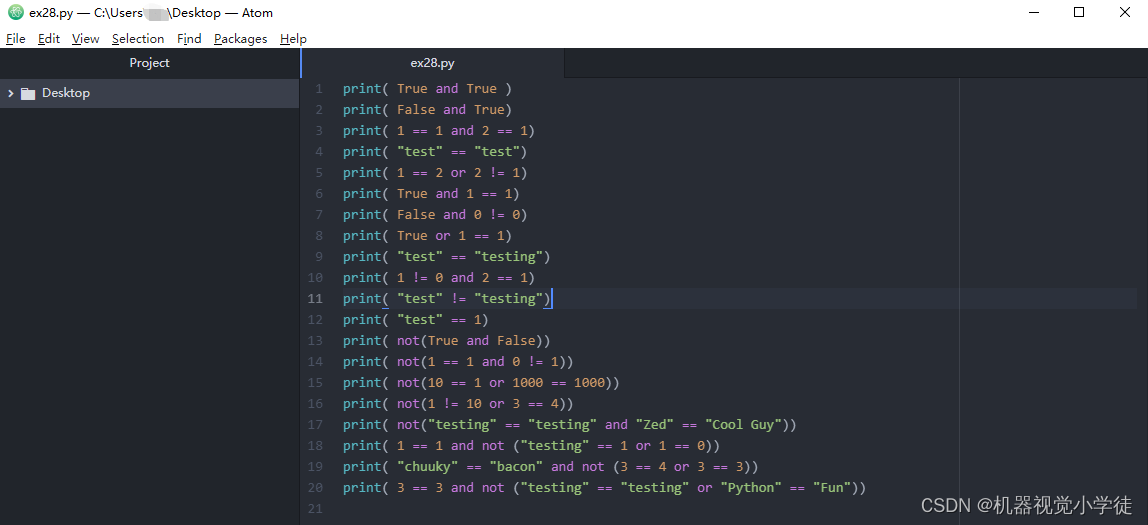
print( True and True )
print( False and True)
print( 1 == 1 and 2 == 1)
print( "test" == "test")
print( 1 == 2 or 2 != 1)
print( True and 1 == 1)
print( False and 0 != 0)
print( True or 1 == 1)
print( "test" == "testing")
print( 1 != 0 and 2 == 1)
print( "test" != "testing")
print( "test" == 1)
print( not(True and False))
print( not(1 == 1 and 0 != 1))
print( not(10 == 1 or 1000 == 1000))
print( not(1 != 10 or 3 == 4))
print( not("testing" == "testing" and "Zed" == "Cool Guy"))
print( 1 == 1 and not ("testing" == 1 or 1 == 0))
print( "chuuky" == "bacon" and not (3 == 4 or 3 == 3))
print( 3 == 3 and not ("testing" == "testing" or "Python" == "Fun"))
二、运行Python程序
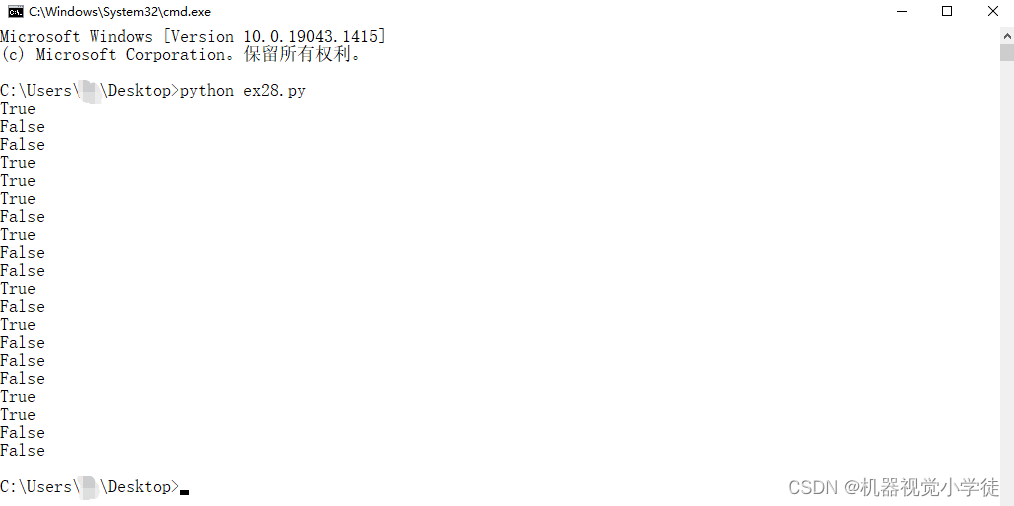
在Window上键入Python就可以看到结果。
python ex28.py
三、逻辑表达式简单流程
1、流程
所有的布尔逻辑表达方式都可以用下面的简单流程得到结果:
(1) 找到相等判断的部分(==或!=),将其改写为其最终值(True或False)
(2) 找到括号中的and/or,计算出它们的值
(3) 找到每一个not,解出它们的值
(4) 找到剩下的and/or,解出它们的值
(5) 都做完后,剩下的结果应该就是True或者False了
2、示例
3 != 4 and not ("testing" != "test" or "Python" == "Python")
(1) 解出每一个相等判断:
3 != 4 为True,True and not (“testing” != “test” or “Python” == “Python”)
“testing” != “test” 为True,True and not (True or “Python” == “Python”)
“Python” == “Python” 为True, True and not (True or True)
(2) 找到括号中的and/or:
True and not (True)
(3) 找到每一个not,并将其取反:
True and False
(4) 找到剩下的and/or,解出它们的值:
True and False为 False
3、注意事项
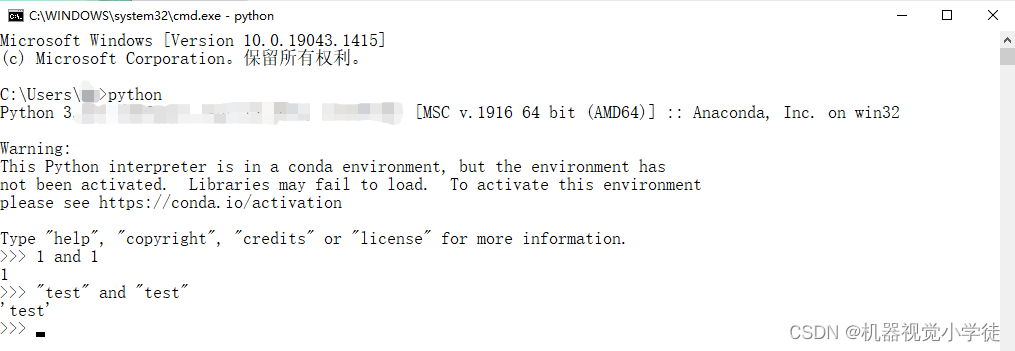
(1) 1 and 1 返回 1,“test” and “test” 返回“test” ,在Python语言中,和很多编程语言类似,都是给布尔表达式返回两个被操作对象的一个,而非True或者False。
(2) Python中的 != 是主流用法, <> 将逐渐被废弃。
(3) 短路逻辑:任何以False开头的and语句都会直接被处理成False,不会继续检查后面的语句。任何包含True的or语句,只要处理到True,就不会继续向下推算,而是直接返回True了。
总结
以上内容介绍了Python的布尔表达式,有关Python、数据科学、人工智能等文章后续会不定期发布,请大家多多关注,一键三连哟(●’◡’●)。





 本文详细解析了Python中的布尔表达式及其运算规则,包括逻辑运算符and、or、not的使用方法,以及如何通过简单的流程步骤来理解复杂的布尔逻辑表达式。
本文详细解析了Python中的布尔表达式及其运算规则,包括逻辑运算符and、or、not的使用方法,以及如何通过简单的流程步骤来理解复杂的布尔逻辑表达式。

















 727
727

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










