在使用ffmpeg进行开发的时候,AVFormatContext是一个非常重要的数据结构,它是ffmpeg解封装(解复用,demux,如flv,mp4,rmvb,avi)的核心。
本文以demux一个mp4文件为例,揭开ffmpeg解复用的工程实现的神秘面纱,整个解复用流程比较复杂,涉及的数据结构比较多,看完本文需要足够的耐心,可以收藏本文,分步阅读,整个解复用流程将会变得"心中有谱"。通常解复用一个视频文件,主要有3大步:open、read、parse。
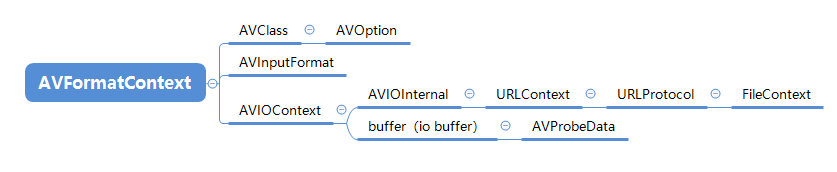
核心结构体关系
首先,梳理一下几个主要结构体之间关系,解复用是以AVFormatContext为中心,然后涉及AVOption、AVClass、AVIOContext、URLContext、URLProtocol、AVProbeData、AVInputFormat
流程梳理
以avformat_open_input()为起点,逐层梳理。avformat_open_input内部的调用关系如下图:
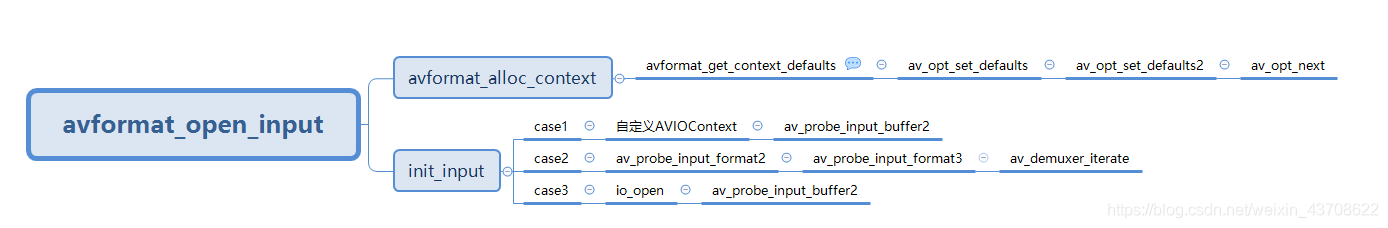
后面的行文内容,将遵循上图骨架,依次展开。
avformat_alloc_context
avformat_alloc_context()从命名上就可以猜测出其用途,分配avformat context,另外还有一些初始化的工作。
AVFormatContext *avformat_alloc_context(void)
{
AVFormatContext *ic;
ic = av_malloc(sizeof(AVFormatContext)); // 分配AVFormatContext
if (!ic) return ic;
avformat_get_context_defaults(ic); // 相当于AVFormatContext的初始化,稍后会展开讲解该函数
// 分配AVFormatInternal,该成员仅AVFormatContext内部使用
ic->internal = av_mallocz(sizeof(*ic->internal));
if (!ic->internal) {
avformat_free_context(ic);
return NULL;
}
ic->internal->offset = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;
ic->internal->raw_packet_buffer_remaining_size = RAW_PACKET_BUFFER_SIZE;
ic->internal->shortest_end = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;
return ic;
}
avformat_get_context_defaults
static void avformat_get_context_defaults(AVFormatContext *s)
{
memset(s, 0, sizeof(AVFormatContext));
// 指定 av_format_context_class,它是一个AVCLASS静态变量
s->av_class = &av_format_context_class;
s->io_open = io_open_default;
s->io_close = io_close_default;
av_opt_set_defaults(s);
}
av_format_context_class是一个AVClass静态变量,它的主要作用是支持avformat context可配置,具体原理可参考ffmpeg-AVOption详解,此处不再赘述。
io_open_default()和io_close_default()也是比较重要的两个函数,在后面讲解init_input()时再展开。
av_opt_set_defaults
void av_opt_set_defaults(void *s)
{
av_opt_set_defaults2(s, 0, 0);
}
void av_opt_set_defaults2(void *s, int mask, int flags)
{
const AVOption *opt = NULL;
while ((opt = av_opt_next(s, opt))) {
void *dst = ((uint8_t*)s) + opt->offset;
if ((opt->flags & mask) != flags)
continue;
if (opt->flags & AV_OPT_FLAG_READONLY)
continue;
switch (opt->type) {
case AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST:
/* Nothing to be done here */
break;
case AV_OPT_TYPE_BOOL:
case AV_OPT_TYPE_FLAGS:
case AV_OPT_TYPE_INT:
case AV_OPT_TYPE_INT64:
case AV_OPT_TYPE_UINT64:
case AV_OPT_TYPE_DURATION:
case AV_OPT_TYPE_CHANNEL_LAYOUT:
case AV_OPT_TYPE_PIXEL_FMT:
case AV_OPT_TYPE_SAMPLE_FMT:
write_number(s, opt, dst, 1, 1, opt->default_val.i64);
break;
case AV_OPT_TYPE_DOUBLE:
case AV_OPT_TYPE_FLOAT: {
double val;
val = opt->default_val.dbl;
write_number(s, opt, dst, val, 1, 1);
}
break;
case AV_OPT_TYPE_RATIONAL: {
AVRational val;
val = av_d2q(opt->default_val.dbl, INT_MAX);
write_number(s, opt, dst, 1, val.den, val.num);
}
break;
case AV_OPT_TYPE_COLOR:
set_string_color(s, opt, opt->default_val.str, dst);
break;
case AV_OPT_TYPE_STRING:
set_string(s, opt, opt->default_val.str, dst);
break;
case AV_OPT_TYPE_IMAGE_SIZE:
set_string_image_size(s, opt, opt->default_val.str, dst);
break;
case AV_OPT_TYPE_VIDEO_RATE:
set_string_video_rate(s, opt, opt->default_val.str, dst);
break;
case AV_OPT_TYPE_BINARY:
set_string_binary(s, opt, opt->default_val.str, dst);
break;
case AV_OPT_TYPE_DICT:
/* Cannot set defaults for these types */
break;
default:
av_log(s, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "AVOption type %d of option %s not implemented yet\n",
opt->type, opt->name);
}
}
}
av_opt_set_defaults(s)的作用是对AVFormatContext的可配置成员初始化。 av_opt_set_defaults2()函数的核心在第9行,通过av_opt_next遍历avformat_options,对变量s(即AVFormatContext)的可配置成员进行初始化。
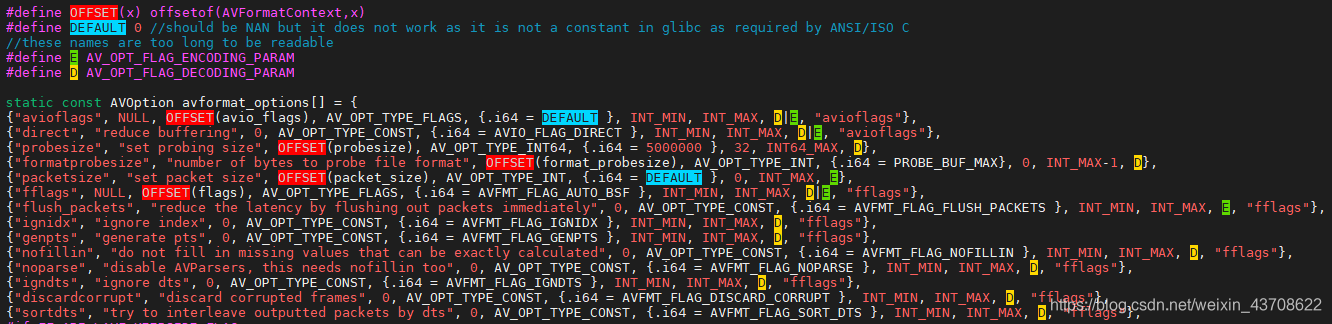
av_opt_next
const AVOption *av_opt_next(const void *obj, const AVOption *last)
{
const AVClass *class;
if (!obj)
return NULL;
class = *(const AVClass**)obj;
if (!last && class && class->option && class->option[0].name)
return class->option;
if (last && last[1].name)
return ++last;
return NULL;
}
第6行用了一个小技巧,由于AVFormatContext结构体的第一个成员是const AVClass *av_class; 将AVFormatContext指针强转为AVClass指针,这样,便可访问到option成员,也就是avformat_options数组,即可访问其中的每一个配置选项。如暂不能理解,可参考ffmpeg-AVOption详解一文。
好,小结一下,avformat_alloc_context()函数主要干了哪些事儿:分配AVFormatContext、设置av_class(关联AVOptions)、设置io_open、设置io_close、avformat_options初始化AVFormatContext。
init_input
从init_input函数的定义上来看,是打开输入视频文件以及探测视频文件的容器格式,具体怎么实现的呢?keep moving…
/* Open input file and probe the format if necessary. */
static int init_input(AVFormatContext *s, const char *filename,
AVDictionary **options)
{
int ret;
AVProbeData pd = { filename, NULL, 0 };
int score = AVPROBE_SCORE_RETRY;
if (s->pb) { // 当s->pb由用户分配时执行,即AVIOContext
s->flags |= AVFMT_FLAG_CUSTOM_IO;
if (!s->iformat)
return av_probe_input_buffer2(s->pb, &s->iformat, filename,
s, 0, s->format_probesize);
else if (s->iformat->flags & AVFMT_NOFILE)
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING, "Custom AVIOContext makes no sense and "
"will be ignored with AVFMT_NOFILE format.\n");
return 0;
}
if ((s->iformat && s->iformat->flags & AVFMT_NOFILE) ||
(!s->iformat && (s->iformat = av_probe_input_format2(&pd, 0, &score))))
return score;
if ((ret = s->io_open(s, &s->pb, filename, AVIO_FLAG_READ | s->avio_flags, options)) < 0)
return ret;
if (s->iformat)
return 0;
return av_probe_input_buffer2(s->pb, &s->iformat, filename,
s, 0, s->format_probesize);
}
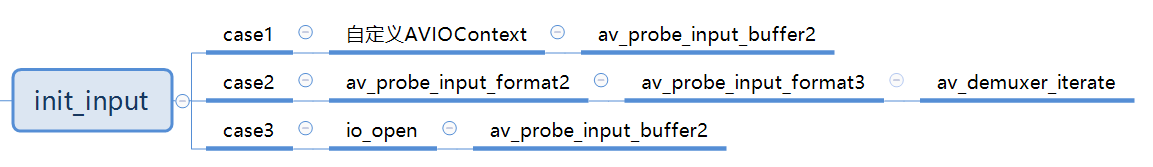
case1 对应 第9~18行;case 2 对应 第20~22行;case3 对应 第24~29行;本文示例中,走的流程是case3。
s->io_open是由avformat_get_context_defaults函数设置,即为io_open_default。
io_open_default
static int io_open_default(AVFormatContext *s, AVIOContext **pb,
const char *url, int flags, AVDictionary **options)
{
int loglevel;
if (!strcmp(url, s->url) ||
s->iformat && !strcmp(s->iformat->name, "image2") ||
s->oformat && !strcmp(s->oformat->name, "image2")
) {
loglevel = AV_LOG_DEBUG;
} else
loglevel = AV_LOG_INFO;
av_log(s, loglevel, "Opening \'%s\' for %s\n", url, flags & AVIO_FLAG_WRITE ? "writing" : "reading");
#if FF_API_OLD_OPEN_CALLBACKS
FF_DISABLE_DEPRECATION_WARNINGS
if (s->open_cb)
return s->open_cb(s, pb, url, flags, &s->interrupt_callback, options);
FF_ENABLE_DEPRECATION_WARNINGS
#endif
return ffio_open_whitelist(pb, url, flags, &s->interrupt_callback, options, s->protocol_whitelist, s->protocol_blacklist);
}
ffio_open_whitelist
ffio_open_whitelist调用了两个主要函数ffurl_open_whitelist和ffio_fdopen,接下来逐步分解。
int ffio_open_whitelist(AVIOContext **s, const char *filename, int flags,
const AVIOInterruptCB *int_cb, AVDictionary **options,
const char *whitelist, const char *blacklist
)
{
URLContext *h;
int err;
err = ffurl_open_whitelist(&h, filename, flags, int_cb, options, whitelist, blacklist, NULL);
if (err < 0)
return err;
err = ffio_fdopen(s, h);
if (err < 0) {
ffurl_close(h);
return err;
}
return 0;
}
ffurl_open_whitelist
ffmpeg对输入的视频形式做了高度封装,通过URLContext和URLProtocol两个结构体来实现,以支持各种输入协议。可参考ffmpeg-URLContext和URLProtocol详解一文。
int ffurl_open_whitelist(URLContext **puc, const char *filename, int flags,
const AVIOInterruptCB *int_cb, AVDictionary **options,
const char *whitelist, const char* blacklist,
URLContext *parent)
{
AVDictionary *tmp_opts = NULL;
AVDictionaryEntry *e;
// 分配URLContext
int ret = ffurl_alloc(puc, filename, flags, int_cb);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
if (parent)
av_opt_copy(*puc, parent);
if (options &&
(ret = av_opt_set_dict(*puc, options)) < 0)
goto fail;
if (options && (*puc)->prot->priv_data_class &&
(ret = av_opt_set_dict((*puc)->priv_data, options)) < 0)
goto fail;
if (!options)
options = &tmp_opts;
av_assert0(!whitelist ||
!(e=av_dict_get(*options, "protocol_whitelist", NULL, 0)) ||
!strcmp(whitelist, e->value));
av_assert0(!blacklist ||
!(e=av_dict_get(*options, "protocol_blacklist", NULL, 0)) ||
!strcmp(blacklist, e->value));
if ((ret = av_dict_set(options, "protocol_whitelist", whitelist, 0)) < 0)
goto fail;
if ((ret = av_dict_set(options, "protocol_blacklist", blacklist, 0)) < 0)
goto fail;
if ((ret = av_opt_set_dict(*puc, options)) < 0)
goto fail;
// 打开视频文件
ret = ffurl_connect(*puc, options);
if (!ret)
return 0;
fail:
ffurl_close(*puc);
*puc = NULL;
return ret;
}
ffurl_alloc
ffurl_alloc函数 根据filename找到匹配的URLProtocol并分配URLContext。ffurl_alloc的详细解释可参考ffmpeg-URLContext和URLProtocol详解一文。
ffurl_connect
ffurl_connect函数最终调用uc->prot->url_open或uc->prot->url_open2,以ff_file_protocol为例,就是调用file_open(),打开filename文件。
int ffurl_connect(URLContext *uc, AVDictionary **options)
{
int err;
AVDictionary *tmp_opts = NULL;
AVDictionaryEntry *e;
if (!options)
options = &tmp_opts;
// Check that URLContext was initialized correctly and lists are matching if set
av_assert0(!(e=av_dict_get(*options, "protocol_whitelist", NULL, 0)) ||
(uc->protocol_whitelist && !strcmp(uc->protocol_whitelist, e->value)));
av_assert0(!(e=av_dict_get(*options, "protocol_blacklist", NULL, 0)) ||
(uc->protocol_blacklist && !strcmp(uc->protocol_blacklist, e->value)));
if (uc->protocol_whitelist && av_match_list(uc->prot->name, uc->protocol_whitelist, ',') <= 0) {
av_log(uc, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Protocol '%s' not on whitelist '%s'!\n", uc->prot->name, uc->protocol_whitelist);
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
if (uc->protocol_blacklist && av_match_list(uc->prot->name, uc->protocol_blacklist, ',') > 0) {
av_log(uc, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Protocol '%s' on blacklist '%s'!\n", uc->prot->name, uc->protocol_blacklist);
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
if (!uc->protocol_whitelist && uc->prot->default_whitelist) {
av_log(uc, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "Setting default whitelist '%s'\n", uc->prot->default_whitelist);
uc->protocol_whitelist = av_strdup(uc->prot->default_whitelist);
if (!uc->protocol_whitelist) {
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
}
} else if (!uc->protocol_whitelist)
av_log(uc, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "No default whitelist set\n"); // This should be an error once all declare a default whitelist
if ((err = av_dict_set(options, "protocol_whitelist", uc->protocol_whitelist, 0)) < 0)
return err;
if ((err = av_dict_set(options, "protocol_blacklist", uc->protocol_blacklist, 0)) < 0)
return err;
// 打开文件
err =
uc->prot->url_open2 ? uc->prot->url_open2(uc,
uc->filename,
uc->flags,
options) :
uc->prot->url_open(uc, uc->filename, uc->flags);
av_dict_set(options, "protocol_whitelist", NULL, 0);
av_dict_set(options, "protocol_blacklist", NULL, 0);
if (err)
return err;
uc->is_connected = 1; // 标记为connected
/* We must be careful here as ffurl_seek() could be slow,
* for example for http */
if ((uc->flags & AVIO_FLAG_WRITE) || !strcmp(uc->prot->name, "file"))
if (!uc->is_streamed && ffurl_seek(uc, 0, SEEK_SET) < 0)
uc->is_streamed = 1;
return 0;
}
分析到这里,文章开头提到的三大步:open、read、parse中的open的流程已经明朗!!!
小结一下,通过filename(url)自动匹配正确URLProtocol,分配URLContext,"绑定"相应的protocol context(如,FileContext),关联相应的open、read等直接操作视频文件(流)的接口。
搞定了open,接下来分析read。
ffio_fdopen
int ffio_fdopen(AVIOContext **s, URLContext *h)
{
AVIOInternal *internal = NULL;
uint8_t *buffer = NULL;
int buffer_size, max_packet_size;
max_packet_size = h->max_packet_size;
if (max_packet_size) {
buffer_size = max_packet_size; /* no need to bufferize more than one packet */
} else {
buffer_size = IO_BUFFER_SIZE;
}
// 重要:分配AVIOContext的io buffer,用于预取视频数据的缓存, io buffer大小为32k
// 即AVIOContext->buffer
buffer = av_malloc(buffer_size);
if (!buffer)
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
// AVIOInternal指针, 指向URLContext
internal = av_mallocz(sizeof(*internal));
if (!internal)
goto fail;
// 保存URLContext地址
internal->h = h;
// 分配AVIOContext, 设置read_packet、write_packet、seek函数, 对应为io_read_packet、io_write_packet、io_seek;将URLContext通过internal传递给AVIOContext->opaque成员
*s = avio_alloc_context(buffer, buffer_size, h->flags & AVIO_FLAG_WRITE,
internal, io_read_packet, io_write_packet, io_seek);
if (!*s)
goto fail;
(*s)->protocol_whitelist = av_strdup(h->protocol_whitelist);
if (!(*s)->protocol_whitelist && h->protocol_whitelist) {
avio_closep(s);
goto fail;
}
(*s)->protocol_blacklist = av_strdup(h->protocol_blacklist);
if (!(*s)->protocol_blacklist && h->protocol_blacklist) {
avio_closep(s);
goto fail;
}
(*s)->direct = h->flags & AVIO_FLAG_DIRECT;
(*s)->seekable = h->is_streamed ? 0 : AVIO_SEEKABLE_NORMAL;
(*s)->max_packet_size = max_packet_size;
(*s)->min_packet_size = h->min_packet_size;
if(h->prot) {
(*s)->read_pause = io_read_pause;
(*s)->read_seek = io_read_seek;
if (h->prot->url_read_seek)
(*s)->seekable |= AVIO_SEEKABLE_TIME;
}
(*s)->short_seek_get = io_short_seek;
(*s)->av_class = &ff_avio_class;
return 0;
fail:
av_freep(&internal);
av_freep(&buffer);
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
}
avio_alloc_context
AVIOContext *avio_alloc_context(
unsigned char *buffer,
int buffer_size,
int write_flag,
void *opaque,
int (*read_packet)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size),
int (*write_packet)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size),
int64_t (*seek)(void *opaque, int64_t offset, int whence))
{
// 分配AVIOContext
AVIOContext *s = av_malloc(sizeof(AVIOContext));
if (!s)
return NULL;
// 初始化AVIOContext
ffio_init_context(s, buffer, buffer_size, write_flag, opaque,
read_packet, write_packet, seek);
return s;
}
ffio_init_context
ffio_init_context初始化AVIOContext中的成员。需要重点关注的成员有两个:buffer和opaque。
将ffio_fdopen中第15行malloc的buffer保存在s->buffer中。
int ffio_init_context(AVIOContext *s,
unsigned char *buffer,
int buffer_size,
int write_flag,
void *opaque,
int (*read_packet)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size),
int (*write_packet)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size),
int64_t (*seek)(void *opaque, int64_t offset, int whence))
{
memset(s, 0, sizeof(AVIOContext));
s->buffer = buffer;
s->orig_buffer_size =
s->buffer_size = buffer_size;
s->buf_ptr = buffer;
s->buf_ptr_max = buffer;
s->opaque = opaque;
s->direct = 0;
url_resetbuf(s, write_flag ? AVIO_FLAG_WRITE : AVIO_FLAG_READ);
s->write_packet = write_packet;
s->read_packet = read_packet;
s->seek = seek;
s->pos = 0;
s->eof_reached = 0;
s->error = 0;
s->seekable = seek ? AVIO_SEEKABLE_NORMAL : 0;
s->min_packet_size = 0;
s->max_packet_size = 0;
s->update_checksum = NULL;
s->short_seek_threshold = SHORT_SEEK_THRESHOLD;
if (!read_packet && !write_flag) {
s->pos = buffer_size;
s->buf_end = s->buffer + buffer_size;
}
s->read_pause = NULL;
s->read_seek = NULL;
s->write_data_type = NULL;
s->ignore_boundary_point = 0;
s->current_type = AVIO_DATA_MARKER_UNKNOWN;
s->last_time = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;
s->short_seek_get = NULL;
s->written = 0;
return 0;
}
分析到这里,io_open_default()分析完了,可以得到一个初步结论,AVFormatContext,AVIOContext,URLContext,ULRProtocol,以及protocol context都已经关联起来。
av_probe_input_buffer2
从函数名做个猜测:probe input buffer,即探测 输入buffer,输入buffer是什么?也就是AVIOContext的io buffer(AVFormatContext->pb、AVIOContext->buffer)。
av_probe_input_buffer2(s->pb, &s->iformat, filename,s, 0, s->format_probesize);
int av_probe_input_buffer2(AVIOContext *pb, AVInputFormat **fmt,
const char *filename, void *logctx,
unsigned int offset, unsigned int max_probe_size)
{
// 这里引入了AVProbeData,这也是一个非常关键的数据结构,在探测过程中有用。
AVProbeData pd = { filename ? filename : "" };
uint8_t *buf = NULL;
int ret = 0, probe_size, buf_offset = 0;
int score = 0;
int ret2;
if (!max_probe_size)
max_probe_size = PROBE_BUF_MAX;
else if (max_probe_size < PROBE_BUF_MIN) {
av_log(logctx, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"Specified probe size value %u cannot be < %u\n", max_probe_size, PROBE_BUF_MIN);
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
if (offset >= max_probe_size)
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
if (pb->av_class) {
uint8_t *mime_type_opt = NULL;
char *semi;
av_opt_get(pb, "mime_type", AV_OPT_SEARCH_CHILDREN, &mime_type_opt);
pd.mime_type = (const char *)mime_type_opt;
semi = pd.mime_type ? strchr(pd.mime_type, ';') : NULL;
if (semi) {
*semi = '\0';
}
}
#if 0
if (!*fmt && pb->av_class && av_opt_get(pb, "mime_type", AV_OPT_SEARCH_CHILDREN, &mime_type) >= 0 && mime_type) {
if (!av_strcasecmp(mime_type, "audio/aacp")) {
*fmt = av_find_input_format("aac");
}
av_freep(&mime_type);
}
#endif
// PROBE_BUF_MIN = 2048;
// max_probe_size = PROBE_BUF_MAX = 32768;
for (probe_size = PROBE_BUF_MIN; probe_size <= max_probe_size && !*fmt;
probe_size = FFMIN(probe_size << 1,
FFMAX(max_probe_size, probe_size + 1))) {
score = probe_size < max_probe_size ? AVPROBE_SCORE_RETRY : 0;
/* Read probe data. */
// buf缓存默认大小为2k+32
if ((ret = av_reallocp(&buf, probe_size + AVPROBE_PADDING_SIZE)) < 0)
goto fail;
// 读取视频数据,例如,file_read();后面再展开将avio_read,此处理解即可
if ((ret = avio_read(pb, buf + buf_offset,
probe_size - buf_offset)) < 0) {
/* Fail if error was not end of file, otherwise, lower score. */
if (ret != AVERROR_EOF)
goto fail;
score = 0;
ret = 0; /* error was end of file, nothing read */
}
buf_offset += ret;
if (buf_offset < offset)
continue;
pd.buf_size = buf_offset - offset;
// 将buf缓存保存到AVProbeData中
pd.buf = &buf[offset];
memset(pd.buf + pd.buf_size, 0, AVPROBE_PADDING_SIZE);
/* Guess file format. */
// 根据AVPorbeData中的视频数据,探测出输入视频的容器格式,即 AVInputFormat,ffmpeg支持的AVInputFormat定义在demuxer_list.c中
*fmt = av_probe_input_format2(&pd, 1, &score);
if (*fmt) {
/* This can only be true in the last iteration. */
if (score <= AVPROBE_SCORE_RETRY) {
av_log(logctx, AV_LOG_WARNING,
"Format %s detected only with low score of %d, "
"misdetection possible!\n", (*fmt)->name, score);
} else
av_log(logctx, AV_LOG_DEBUG,
"Format %s probed with size=%d and score=%d\n",
(*fmt)->name, probe_size, score);
#if 0
FILE *f = fopen("probestat.tmp", "ab");
fprintf(f, "probe_size:%d format:%s score:%d filename:%s\n", probe_size, (*fmt)->name, score, filename);
fclose(f);
#endif
}
}
if (!*fmt)
ret = AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;
fail:
/* Rewind. Reuse probe buffer to avoid seeking. */
// 这个函数的作用非常有意思,后文单独一小节讲解
ret2 = ffio_rewind_with_probe_data(pb, &buf, buf_offset);
if (ret >= 0)
ret = ret2;
av_freep(&pd.mime_type);
return ret < 0 ? ret : score;
}
avio_read
// avio_read的buf参数是指AVProbeData中的buffer
int avio_read(AVIOContext *s, unsigned char *buf, int size)
{
int len, size1;
size1 = size;
while (size > 0) {
// 首次读文件时,s->buf_end和s->buf_ptr都指向io buffer首地址, len=0
// 获取待探测数据长度
len = FFMIN(s->buf_end - s->buf_ptr, size);
if (len == 0 || s->write_flag) {
if((s->direct || size > s->buffer_size) && !s->update_checksum) {
// bypass the buffer and read data directly into buf
len = read_packet_wrapper(s, buf, size);
if (len == AVERROR_EOF) {
/* do not modify buffer if EOF reached so that a seek back can
be done without rereading data */
s->eof_reached = 1;
break;
} else if (len < 0) {
s->eof_reached = 1;
s->error= len;
break;
} else {
s->pos += len;
s->bytes_read += len;
size -= len;
buf += len;
// reset the buffer
s->buf_ptr = s->buffer;
s->buf_end = s->buffer/* + len*/;
}
} else {
// 第一次调用avio_read(),会执行fill_buffer,从文件中读取32k的数据填充到io buffer中
fill_buffer(s);
len = s->buf_end - s->buf_ptr;
if (len == 0)
break;
}
} else {
// 从AVIOContext的io buffer拷贝len大小的数据到AVProbeData的buffer中,一般len=2k
memcpy(buf, s->buf_ptr, len);
buf += len;
s->buf_ptr += len;
size -= len;
}
}
if (size1 == size) {
if (s->error) return s->error;
if (avio_feof(s)) return AVERROR_EOF;
}
return size1 - size;
}
fill_buffer
static void fill_buffer(AVIOContext *s)
{
int max_buffer_size = s->max_packet_size ?
s->max_packet_size : IO_BUFFER_SIZE;
uint8_t *dst = s->buf_end - s->buffer + max_buffer_size < s->buffer_size ?
s->buf_end : s->buffer;
int len = s->buffer_size - (dst - s->buffer);
/* can't fill the buffer without read_packet, just set EOF if appropriate */
if (!s->read_packet && s->buf_ptr >= s->buf_end)
s->eof_reached = 1;
/* no need to do anything if EOF already reached */
if (s->eof_reached)
return;
if (s->update_checksum && dst == s->buffer) {
if (s->buf_end > s->checksum_ptr)
s->checksum = s->update_checksum(s->checksum, s->checksum_ptr,
s->buf_end - s->checksum_ptr);
s->checksum_ptr = s->buffer;
}
/* make buffer smaller in case it ended up large after probing */
if (s->read_packet && s->orig_buffer_size && s->buffer_size > s->orig_buffer_size) {
if (dst == s->buffer && s->buf_ptr != dst) {
int ret = ffio_set_buf_size(s, s->orig_buffer_size);
if (ret < 0)
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING, "Failed to decrease buffer size\n");
s->checksum_ptr = dst = s->buffer;
}
av_assert0(len >= s->orig_buffer_size);
len = s->orig_buffer_size;
}
// 从文件中读取32k的数据填充到io buffer中
len = read_packet_wrapper(s, dst, len);
if (len == AVERROR_EOF) {
/* do not modify buffer if EOF reached so that a seek back can
be done without rereading data */
s->eof_reached = 1;
} else if (len < 0) {
s->eof_reached = 1;
s->error= len;
} else {
s->pos += len;
s->buf_ptr = dst;
s->buf_end = dst + len;
s->bytes_read += len;
}
}
read_packet_wrapper
s->read_packet和s->opaque都是在ffio_fdopen中指定,分别为io_read_packet和URLContext。
static int read_packet_wrapper(AVIOContext *s, uint8_t *buf, int size)
{
int ret;
if (!s->read_packet)
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
ret = s->read_packet(s->opaque, buf, size);
#if FF_API_OLD_AVIO_EOF_0
if (!ret && !s->max_packet_size) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_WARNING, "Invalid return value 0 for stream protocol\n");
ret = AVERROR_EOF;
}
#else
av_assert2(ret || s->max_packet_size);
#endif
return ret;
}
io_read_packet
static int io_read_packet(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size)
{
AVIOInternal *internal = opaque;
return ffurl_read(internal->h, buf, buf_size);
}
int ffurl_read(URLContext *h, unsigned char *buf, int size)
{
if (!(h->flags & AVIO_FLAG_READ))
return AVERROR(EIO);
return retry_transfer_wrapper(h, buf, size, 1, h->prot->url_read);
}
// ffurl_read将h->prot->url_read赋给transfer_func,以FileContext为例,h->prot->url_read即为file_read()
static inline int retry_transfer_wrapper(URLContext *h, uint8_t *buf,
int size, int size_min,
int (*transfer_func)(URLContext *h,
uint8_t *buf,
int size))
{
int ret, len;
int fast_retries = 5;
int64_t wait_since = 0;
len = 0;
while (len < size_min) {
if (ff_check_interrupt(&h->interrupt_callback))
return AVERROR_EXIT;
ret = transfer_func(h, buf + len, size - len);
if (ret == AVERROR(EINTR))
continue;
if (h->flags & AVIO_FLAG_NONBLOCK)
return ret;
if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN)) {
ret = 0;
if (fast_retries) {
fast_retries--;
} else {
if (h->rw_timeout) {
if (!wait_since)
wait_since = av_gettime_relative();
else if (av_gettime_relative() > wait_since + h->rw_timeout)
return AVERROR(EIO);
}
av_usleep(1000);
}
} else if (ret == AVERROR_EOF)
return (len > 0) ? len : AVERROR_EOF;
else if (ret < 0)
return ret;
if (ret) {
fast_retries = FFMAX(fast_retries, 2);
wait_since = 0;
}
len += ret;
}
return len;
}
分析到这里,我们知道fill_buffer函数从视频文件中读取了32k的数据到AVIOContext的io buffer中。然后,avio_read函数的第41~44行,从AVIOContext的io buffer拷贝len大小的数据到AVProbeData的buffer中,一般len=2k。至此,完成了文章开头提到的三大步:open、read、parse中的read的流程。
接着,调用av_probe_input_format2()
av_probe_input_format2
AVInputFormat *av_probe_input_format2(AVProbeData *pd, int is_opened, int *score_max)
{
int score_ret;
AVInputFormat *fmt = av_probe_input_format3(pd, is_opened, &score_ret);
if (score_ret > *score_max) {
*score_max = score_ret;
return fmt;
} else
return NULL;
}
av_probe_input_format3
根据AVPorbeData中的视频数据,探测出输入视频的容器格式,获取AVInputFormat。
av_probe_input_format3()函数的作用是基于某种"匹配方法",探测(找出)输入视频的容器格式。"匹配方法"有3种:
- demuxer的read_probe()函数;(主要的匹配方法,最常用,不同的demuxer的read_probe实现不同)
- 基于文件后缀名;
- 基于mime_type;
AVInputFormat *av_probe_input_format3(AVProbeData *pd, int is_opened,
int *score_ret)
{
AVProbeData lpd = *pd;
const AVInputFormat *fmt1 = NULL;
AVInputFormat *fmt = NULL;
int score, score_max = 0;
void *i = 0;
const static uint8_t zerobuffer[AVPROBE_PADDING_SIZE];
enum nodat {
NO_ID3,
ID3_ALMOST_GREATER_PROBE,
ID3_GREATER_PROBE,
ID3_GREATER_MAX_PROBE,
} nodat = NO_ID3;
if (!lpd.buf)
lpd.buf = (unsigned char *) zerobuffer;
if (lpd.buf_size > 10 && ff_id3v2_match(lpd.buf, ID3v2_DEFAULT_MAGIC)) {
int id3len = ff_id3v2_tag_len(lpd.buf);
if (lpd.buf_size > id3len + 16) {
if (lpd.buf_size < 2LL*id3len + 16)
nodat = ID3_ALMOST_GREATER_PROBE;
lpd.buf += id3len;
lpd.buf_size -= id3len;
} else if (id3len >= PROBE_BUF_MAX) {
nodat = ID3_GREATER_MAX_PROBE;
} else
nodat = ID3_GREATER_PROBE;
}
// 遍历解复用器列表
while ((fmt1 = av_demuxer_iterate(&i))) {
if (!is_opened == !(fmt1->flags & AVFMT_NOFILE) && strcmp(fmt1->name, "image2"))
continue;
score = 0;
if (fmt1->read_probe) {
// 调用解复用器的read_probe,通过解析视频数据内容,获取视频的得分值
score = fmt1->read_probe(&lpd);
if (score)
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_TRACE, "Probing %s score:%d size:%d\n", fmt1->name, score, lpd.buf_size);
if (fmt1->extensions && av_match_ext(lpd.filename, fmt1->extensions)) {
switch (nodat) {
case NO_ID3:
score = FFMAX(score, 1);
break;
case ID3_GREATER_PROBE:
case ID3_ALMOST_GREATER_PROBE:
score = FFMAX(score, AVPROBE_SCORE_EXTENSION / 2 - 1);
break;
case ID3_GREATER_MAX_PROBE:
score = FFMAX(score, AVPROBE_SCORE_EXTENSION);
break;
}
}
} else if (fmt1->extensions) {
if (av_match_ext(lpd.filename, fmt1->extensions))
score = AVPROBE_SCORE_EXTENSION;
}
if (av_match_name(lpd.mime_type, fmt1->mime_type)) {
if (AVPROBE_SCORE_MIME > score) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "Probing %s score:%d increased to %d due to MIME type\n", fmt1->name, score, AVPROBE_SCORE_MIME);
score = AVPROBE_SCORE_MIME;
}
}
if (score > score_max) {
score_max = score;
fmt = (AVInputFormat*)fmt1;
} else if (score == score_max)
fmt = NULL;
}
if (nodat == ID3_GREATER_PROBE)
score_max = FFMIN(AVPROBE_SCORE_EXTENSION / 2 - 1, score_max);
*score_ret = score_max;
return fmt;
}
av_demuxer_iterate
const AVInputFormat *av_demuxer_iterate(void **opaque)
{
static const uintptr_t size = sizeof(demuxer_list)/sizeof(demuxer_list[0]) - 1;
uintptr_t i = (uintptr_t)*opaque;
const AVInputFormat *f = NULL;
if (i < size) {
f = demuxer_list[i];
} else if (outdev_list) {
f = indev_list[i - size];
}
if (f)
*opaque = (void*)(i + 1);
return f;
}
demuxer_list是定义在demuxer_list.c中的不同容器格式的解复用器列表,当前ffmpeg版本(4.0.2)有285个demuxer。每个demuxer由AVInputFormat结构体表示。av_demuxer_iterate()函数的作用就是遍历解复用器列表。
static const AVInputFormat * const demuxer_list[] = {
&ff_aa_demuxer,
&ff_aac_demuxer,
&ff_ac3_demuxer,
&ff_acm_demuxer,
&ff_act_demuxer,
...
&ff_mov_demuxer,
...
}
以ff_mov_demuxer为例,
AVInputFormat ff_mov_demuxer = {
.name = "mov,mp4,m4a,3gp,3g2,mj2",
.long_name = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL("QuickTime / MOV"),
.priv_class = &mov_class,
.priv_data_size = sizeof(MOVContext),
.extensions = "mov,mp4,m4a,3gp,3g2,mj2",
.read_probe = mov_probe,
.read_header = mov_read_header,
.read_packet = mov_read_packet,
.read_close = mov_read_close,
.read_seek = mov_read_seek,
.flags = AVFMT_NO_BYTE_SEEK,
};
mov_probe
mov_probe对AVProveData->buf中的视频数据进行解析,最终返回一个score值。
static int mov_probe(AVProbeData *p)
{
int64_t offset;
uint32_t tag;
int score = 0;
int moov_offset = -1;
/* check file header */
offset = 0;
for (;;) {
/* ignore invalid offset */
if ((offset + 8) > (unsigned int)p->buf_size)
break;
tag = AV_RL32(p->buf + offset + 4);
switch(tag) {
/* check for obvious tags */
case MKTAG('m','o','o','v'):
moov_offset = offset + 4;
case MKTAG('m','d','a','t'):
case MKTAG('p','n','o','t'): /* detect movs with preview pics like ew.mov and april.mov */
case MKTAG('u','d','t','a'): /* Packet Video PVAuthor adds this and a lot of more junk */
case MKTAG('f','t','y','p'):
if (AV_RB32(p->buf+offset) < 8 &&
(AV_RB32(p->buf+offset) != 1 ||
offset + 12 > (unsigned int)p->buf_size ||
AV_RB64(p->buf+offset + 8) == 0)) {
score = FFMAX(score, AVPROBE_SCORE_EXTENSION);
} else if (tag == MKTAG('f','t','y','p') &&
( AV_RL32(p->buf + offset + 8) == MKTAG('j','p','2',' ')
|| AV_RL32(p->buf + offset + 8) == MKTAG('j','p','x',' ')
)) {
score = FFMAX(score, 5);
} else {
score = AVPROBE_SCORE_MAX;
}
offset = FFMAX(4, AV_RB32(p->buf+offset)) + offset;
break;
/* those are more common words, so rate then a bit less */
case MKTAG('e','d','i','w'): /* xdcam files have reverted first tags */
case MKTAG('w','i','d','e'):
case MKTAG('f','r','e','e'):
case MKTAG('j','u','n','k'):
case MKTAG('p','i','c','t'):
score = FFMAX(score, AVPROBE_SCORE_MAX - 5);
offset = FFMAX(4, AV_RB32(p->buf+offset)) + offset;
break;
case MKTAG(0x82,0x82,0x7f,0x7d):
case MKTAG('s','k','i','p'):
case MKTAG('u','u','i','d'):
case MKTAG('p','r','f','l'):
/* if we only find those cause probedata is too small at least rate them */
score = FFMAX(score, AVPROBE_SCORE_EXTENSION);
offset = FFMAX(4, AV_RB32(p->buf+offset)) + offset;
break;
default:
offset = FFMAX(4, AV_RB32(p->buf+offset)) + offset;
}
}
if(score > AVPROBE_SCORE_MAX - 50 && moov_offset != -1) {
/* moov atom in the header - we should make sure that this is not a
* MOV-packed MPEG-PS */
offset = moov_offset;
while(offset < (p->buf_size - 16)){ /* Sufficient space */
/* We found an actual hdlr atom */
if(AV_RL32(p->buf + offset ) == MKTAG('h','d','l','r') &&
AV_RL32(p->buf + offset + 8) == MKTAG('m','h','l','r') &&
AV_RL32(p->buf + offset + 12) == MKTAG('M','P','E','G')){
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_WARNING, "Found media data tag MPEG indicating this is a MOV-packed MPEG-PS.\n");
/* We found a media handler reference atom describing an
* MPEG-PS-in-MOV, return a
* low score to force expanding the probe window until
* mpegps_probe finds what it needs */
return 5;
}else
/* Keep looking */
offset+=2;
}
}
return score;
}
对MP4文件的解析不是本文的范畴,故不再展开。可参考mp4-文件格式浅析。
至此,完成了文章开头提到的三大步:open、read、parse中的parse的流程。
最后,再解读一下我们前面提到的一个非常有意思的函数ffio_rewind_with_probe_data。
ffio_rewind_with_probe_data
int ffio_rewind_with_probe_data(AVIOContext *s, unsigned char **bufp, int buf_size)
{
int64_t buffer_start;
int buffer_size;
int overlap, new_size, alloc_size;
uint8_t *buf = *bufp;
// buf_size = 2048
// *bufp 为AVProbeData中的buf
if (s->write_flag) {
av_freep(bufp);
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
// buffer_size = 32768,即32K;AVIOContext的io buffer的大小
buffer_size = s->buf_end - s->buffer;
/* the buffers must touch or overlap */
// s->pos = 32768
// buffer_start = 0
if ((buffer_start = s->pos - buffer_size) > buf_size) {
av_freep(bufp);
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
// overlap = 2048-0
overlap = buf_size - buffer_start;
// new_size = 2048+32768-2048=32768
new_size = buf_size + buffer_size - overlap;
// s->buffer_size = 32768
// alloc_size = 32768
alloc_size = FFMAX(s->buffer_size, new_size);
if (alloc_size > buf_size) // 32768 > 2048
// 扩容buf, 将AVProbeData中buf内存扩大到alloc_size
if (!(buf = (*bufp) = av_realloc_f(buf, 1, alloc_size)))
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
if (new_size > buf_size) { // 32768 > 2048
// 将s->buffer(即AVIOContext的io buffer)中未消费的数据拷贝到buf+buf_size
memcpy(buf + buf_size, s->buffer + overlap, buffer_size - overlap);
buf_size = new_size; // 更新AVProbeData的buf的size
}
av_free(s->buffer);// 释放掉ffio_fdopen中申请的io buffer
s->buf_ptr = s->buffer = buf; // s—>buffer(即AVIOContext的io buffer)指向AVProbeData的buf
s->buffer_size = alloc_size; // 更新s->buffer_size
s->pos = buf_size; // 更新s->pos,该成员记录着seek文件的position
s->buf_end = s->buf_ptr + buf_size; // 更新s->buffer的末尾边界
s->eof_reached = 0;
return 0;
}
代码看到这里,不禁想问,为什么要ffio_rewind_with_probe_data函数,它的作用是什么?从函数的命名上看,表达的意思就是:将IOContext的io buffer 倒回到AVProbeData的buffer。倒回的具体实现核心点就是上面代码的第36行、第41行。我认为,将ffio_rewind_with_probe_data命名改为ffio_update_with_probe_data似乎更容易"见名知意",将AVIOContext->buffer更新为AVProbeData->buf。AVProbeData->buf初始分配是在av_probe_input_buffer2函数中调用av_reallocp()分配,avio_read()从AVIOContext->buffer中拷贝len(如,2k)大小的数据到AVProbeData->buf中,然后执行av_probe_input_format2()探测视频的AVInputFormat(也就是视频的封装格式,如,MP4等),av_probe_input_format2的输入为AVProbeData;由于在探测视频的AVInputFormat的过程中,AVProbeData->buf中的数据已经处理过了一遍,因此,这部分数据在后面的流程中就没有必要再重复处理,那么,将AVProbeData->buf的内存的大小扩容到和AVIOContext->buffer的内存的大小相同,并将AVIOContext->buffer内存中的未处理数据拷贝到AVProbeData->buf的相应位置,最后AVIOContext->buffer和AVProbeData->buf都指向相同的内存地址。
总结
本文通过以一个mp4文件为filename,对avformat_open_input函数的深入分析,掌握了ffmpeg解复用的实现方法,3大步:open、read、parse。以AVFormatContext为中心,通过对filename或url的判断,匹配对应的URLProtocol,找到具体的protocol context以及分配URLContext,open 视频,关联read函数;然后通过AVIOContext 缓存一部分视频数据,再利用AVProbeData中的缓存去探测视频的封装格式,最终获取相应的AVInputFormat。以上便是对avformat_open_input的整体性概括。








 本文深入分析了ffmpeg在解封装mp4文件时的流程,从avformat_open_input开始,详细讲解了如何打开输入文件、探测文件格式、分配和初始化AVFormatContext、AVIOContext及URLContext,以及如何读取和解析数据。重点介绍了avformat_alloc_context、avformat_get_context_defaults、av_opt_set_defaults、io_open_default、ffio_open_whitelist、ffurl_alloc、avio_alloc_context等关键函数的作用。最后,探讨了ffio_rewind_with_probe_data函数,它是如何将AVIOContext的iobuffer更新为AVProbeData的buf的。
本文深入分析了ffmpeg在解封装mp4文件时的流程,从avformat_open_input开始,详细讲解了如何打开输入文件、探测文件格式、分配和初始化AVFormatContext、AVIOContext及URLContext,以及如何读取和解析数据。重点介绍了avformat_alloc_context、avformat_get_context_defaults、av_opt_set_defaults、io_open_default、ffio_open_whitelist、ffurl_alloc、avio_alloc_context等关键函数的作用。最后,探讨了ffio_rewind_with_probe_data函数,它是如何将AVIOContext的iobuffer更新为AVProbeData的buf的。

















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










