高频题目100
1、LRU缓存机制(146、Medium)
1)题目要求
运用你所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制。它应该支持以下操作: 获取数据 get 和 写入数据 put 。
获取数据 get(key) - 如果关键字 (key) 存在于缓存中,则获取关键字的值(总是正数),否则返回 -1。
写入数据 put(key, value) - 如果关键字已经存在,则变更其数据值;如果关键字不存在,则插入该组「关键字/值」。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最久未使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。
进阶:
你是否可以在 O(1) 时间复杂度内完成这两种操作?
示例:
LRUCache cache = new LRUCache( 2 /* 缓存容量 */ );
cache.put(1, 1);
cache.put(2, 2);
cache.get(1); // 返回 1
cache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废
cache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
cache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废
cache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
cache.get(3); // 返回 3
cache.get(4); // 返回 4
2)我的解法
不会
3)其他解法
1、继承LinkedHashMap
源码分析点进链接看
class LRUCache extends LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer>{
private int capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
super(capacity, 0.75F, true);
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public int get(int key) {
return super.getOrDefault(key, -1);
}
// 这个可不写
public void put(int key, int value) {
super.put(key, value);
}
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> eldest) {
return size() > capacity;
}
}
作者:jeromememory
链接:link
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
2、HashMap+手写双向链表


public class LRUCache {
class DLinkedNode {
int key;
int value;
DLinkedNode prev;
DLinkedNode next;
public DLinkedNode() {}
public DLinkedNode(int _key, int _value) {key = _key; value = _value;}
}
private Map<Integer, DLinkedNode> cache = new HashMap<Integer, DLinkedNode>();
private int size;
private int capacity;
private DLinkedNode head, tail;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.size = 0;
this.capacity = capacity;
// 使用伪头部和伪尾部节点
head = new DLinkedNode();
tail = new DLinkedNode();
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
public int get(int key) {
DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) {
return -1;
}
// 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再移到头部
moveToHead(node);
return node.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) {
// 如果 key 不存在,创建一个新的节点
DLinkedNode newNode = new DLinkedNode(key, value);
// 添加进哈希表
cache.put(key, newNode);
// 添加至双向链表的头部
addToHead(newNode);
++size;
if (size > capacity) {
// 如果超出容量,删除双向链表的尾部节点
DLinkedNode tail = removeTail();
// 删除哈希表中对应的项
cache.remove(tail.key);
--size;
}
}
else {
// 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再修改 value,并移到头部
node.value = value;
moveToHead(node);
}
}
private void addToHead(DLinkedNode node) {
node.prev = head;
node.next = head.next;
head.next.prev = node;
head.next = node;
}
private void removeNode(DLinkedNode node) {
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
private void moveToHead(DLinkedNode node) {
removeNode(node);
addToHead(node);
}
private DLinkedNode removeTail() {
DLinkedNode res = tail.prev;
removeNode(res);
return res;
}
}
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:link
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
4)自己的优化代码
1、
class LRUCache extends LinkedHashMap<Integer,Integer>{
private int capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
super(capacity, 0.75F, true);//按照读取顺序,需要把第三个参数设为true
this.capacity=capacity;
}
public int get(int key) {
return super.getOrDefault(key,-1);
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
super.put(key,value);
}
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> eldest) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.size()>capacity;
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/
2、
class DbNode{
int key;
int val;
DbNode pre;
DbNode next;
DbNode(int key,int value){
this.key=key;
this.val=value;
}
}
class LRUCache{
Map<Integer,DbNode> map=new HashMap<>();
int capacity;
int cursize=0;
DbNode first,end;//加上假的头、尾指针,不然考虑各种情况太麻烦了
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity=capacity;
first=new DbNode(-1,-1);
end=new DbNode(-1,-1);
first.next=end;
end.pre=first;
}
public int get(int key) {
if(!map.containsKey(key))return -1;
DbNode cur=map.get(key);
delete(cur);
addToFirst(cur);
return first.next.val;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if(map.containsKey(key)){//如果已经有这个key了,除了更新值外,还要把它放到前面
map.get(key).val=value;
get(key);//相当于执行了一次get
return;
}
DbNode newNode=new DbNode(key,value);
addToFirst(newNode);
map.put(key,newNode);
cursize++;
if(cursize>capacity){//如果大于,删除链表结尾
int endkey=end.pre.key;
DbNode del=end.pre;
delete(del);
cursize--;
map.remove(endkey);
}
}
public void addToFirst(DbNode newNode){//插到前面
newNode.next=first.next;
newNode.pre=first;
first.next.pre=newNode;
first.next=newNode;
}
public void delete(DbNode del){//删除结点
del.next.pre=del.pre;
del.pre.next=del.next;
del=null;
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/
5)学到的东西
LRU
LinkedHashMap
双向链表:一定一定要有假的头尾指针,不然考虑的情况会过于麻烦
多刷几遍
2、接雨水(42、Hard)
1)题目要求
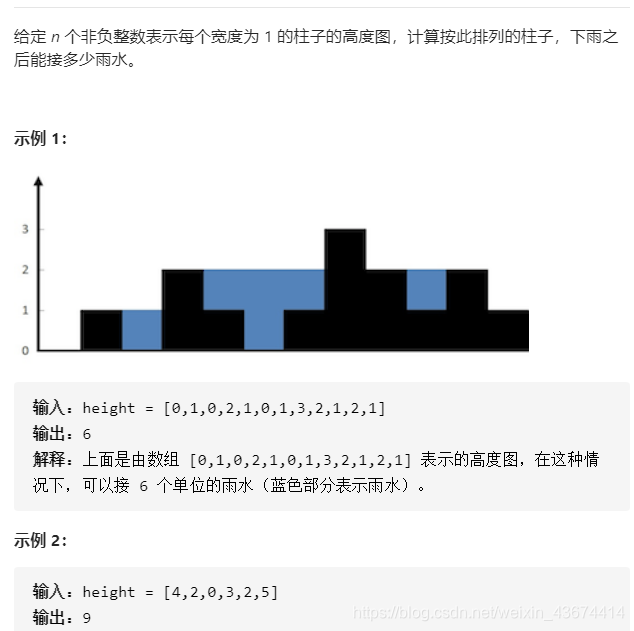
提示:
n == height.length
0 <= n <= 3 * 104
0 <= height[i] <= 105
2)我的解法
不会。。
3)其他解法

缓存两端最大值,从最大值较小的一边进行储水结算、移动,并更新最大值。
public int trap(int[] height) {
//长度为1或者2时,蓄水量一定为0
if(height.length<3) {
return 0;
}
//长度大于2的情况
int left = 0;//左指针
int right = height.length-1;//右指针
int leftmax = height[left];//左边最大值
int rightmax = height[right];//右边最大值
int res = 0;//记录蓄水量
while(left < right) {
if(leftmax < rightmax) {
//左侧最高值减去当前位置值就是该位置的蓄水量
res += leftmax - height[left++];
//更新左侧最大值
leftmax = Math.max(leftmax, height[left]);
}
else {
//右侧最高值减去当前位置值就是该位置的蓄水量
res += rightmax - height[right--];
//更新右侧最大值
rightmax = Math.max(rightmax, height[right]);
}
}
//注:某位置的蓄水量等于当前最高值减去该位置的值
return res;
}
作者:walkerwk
链接:link
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
4)自己的优化代码
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
if(height.length<=2)return 0;
int left=0;
int right=height.length-1;
int leftMax=height[left];
int rightMax=height[right];
int result=0;
while(left<right){
if(leftMax<rightMax){
result+=leftMax-height[left];
left++;
leftMax=Math.max(leftMax,height[left]);
}
else{
result+=rightMax-height[right];
right--;
rightMax=Math.max(rightMax,height[right]);
}
}
return result;
}
}
5)学到的东西
双指针
只要leftMax<rightMax,右边具体如何不影响左边,反之也一样
3、LFU 缓存(460、Hard)
1)题目要求
请你为 最不经常使用(LFU)缓存算法设计并实现数据结构。
实现 LFUCache 类:
LFUCache(int capacity) - 用数据结构的容量 capacity 初始化对象
int get(int key) - 如果键存在于缓存中,则获取键的值,否则返回 -1。
void put(int key, int value) - 如果键已存在,则变更其值;如果键不存在,请插入键值对。当缓存达到其容量时,则应该在插入新项之前,使最不经常使用的项无效。在此问题中,当存在平局(即两个或更多个键具有相同使用频率)时,应该去除 最久未使用 的键。
注意「项的使用次数」就是自插入该项以来对其调用 get 和 put 函数的次数之和。使用次数会在对应项被移除后置为 0 。
进阶:
你是否可以在 O(1) 时间复杂度内执行两项操作?
示例:
输入:
[“LFUCache”, “put”, “put”, “get”, “put”, “get”, “get”, “put”, “get”, “get”, “get”]
[[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [3], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
输出:
[null, null, null, 1, null, -1, 3, null, -1, 3, 4]
解释:
LFUCache lFUCache = new LFUCache(2);
lFUCache.put(1, 1);
lFUCache.put(2, 2);
lFUCache.get(1); // 返回 1
lFUCache.put(3, 3); // 去除键 2
lFUCache.get(2); // 返回 -1(未找到)
lFUCache.get(3); // 返回 3
lFUCache.put(4, 4); // 去除键 1
lFUCache.get(1); // 返回 -1(未找到)
lFUCache.get(3); // 返回 3
lFUCache.get(4); // 返回 4
提示:
0 <= capacity, key, value <= 104
最多调用 105 次 get 和 put 方法
2)我的解法
双HashMap+手写双向链表
class DbNode{
public int key;
public int val;
public int num=1;//次数
public DbNode pre;
public DbNode next;
public DbNode(int key,int val){
this.key=key;
this.val=val;
}
}
class LFUCache {
private int capacity;
private DbNode first;
private DbNode end;
private int size=0;
Map<Integer,DbNode> hash=new HashMap<>();//key即为key
Map<Integer,DbNode> hashOfNum=new HashMap<>();//key为使用频率,如果出现平局,其value是最新的DbNode
public LFUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity=capacity;
first=new DbNode(-1,-1);
end=new DbNode(-1,-1);
first.next=end;
end.pre=first;
}
public int get(int key) {
if(!hash.containsKey(key))return -1;
DbNode cur=hash.get(key);
if(cur==hashOfNum.get(cur.num)){//如果cur.num指针指向的就是cur,需改变该指针
if(cur.next.num==cur.num)hashOfNum.put(cur.num,cur.next);//如果它后面那个元素的num也是cur.num,则指向后面那个元素
else {//如果cur.num仅有一个元素,则删掉指针
hashOfNum.remove(cur.num);
if(!hashOfNum.containsKey(cur.num+1)){//如果不存在cur.num+1,则无需在链表中移动
hashOfNum.put(cur.num+1,cur);
cur.num++;
return cur.val;
}
}
}
remove(cur);
if(hashOfNum.containsKey(cur.num+1)){//如果存在指向cur.num+1的指针,则插在其指向元素的前面
add(cur,hashOfNum.get(cur.num+1));
}
else {
//如果不存在,则插到cur.num指向元素的前面
add(cur,hashOfNum.get(cur.num));
}
hashOfNum.put(cur.num+1,cur);
cur.num++;
return cur.val;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if(hash.containsKey(key)){//如果有
DbNode cur=hash.get(key);
cur.val=value;
get(key);//相当于get了一次
return;
}
size++;
if(size>capacity){//如果超过了capacity,则删去列表最后的元素
if(capacity==0)return;
if(end.pre==hashOfNum.get(end.pre.num)){//如果cur.num指针指向的就是cur,需改变该指针
hashOfNum.remove(end.pre.num);
}
hash.remove(end.pre.key);
remove(end.pre);
size--;
}
DbNode newNode=new DbNode(key,value);
hash.put(key,newNode);
if(hashOfNum.containsKey(1))add(newNode,hashOfNum.get(1));//如果存在使用一次的元素,插到其前面
else add(newNode,end);//否则插到最后
hashOfNum.put(1,newNode);//让使用一次的指针指向当前元素
}
public void add(DbNode newNode,DbNode next){//插在next的前面
DbNode pre=next.pre;
pre.next=newNode;
newNode.pre=pre;
newNode.next=next;
next.pre=newNode;
}
public void remove(DbNode del){
DbNode pre=del.pre;
DbNode next=del.next;
pre.next=next;
next.pre=pre;
}
}
/**
* Your LFUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LFUCache obj = new LFUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/
3)其他解法

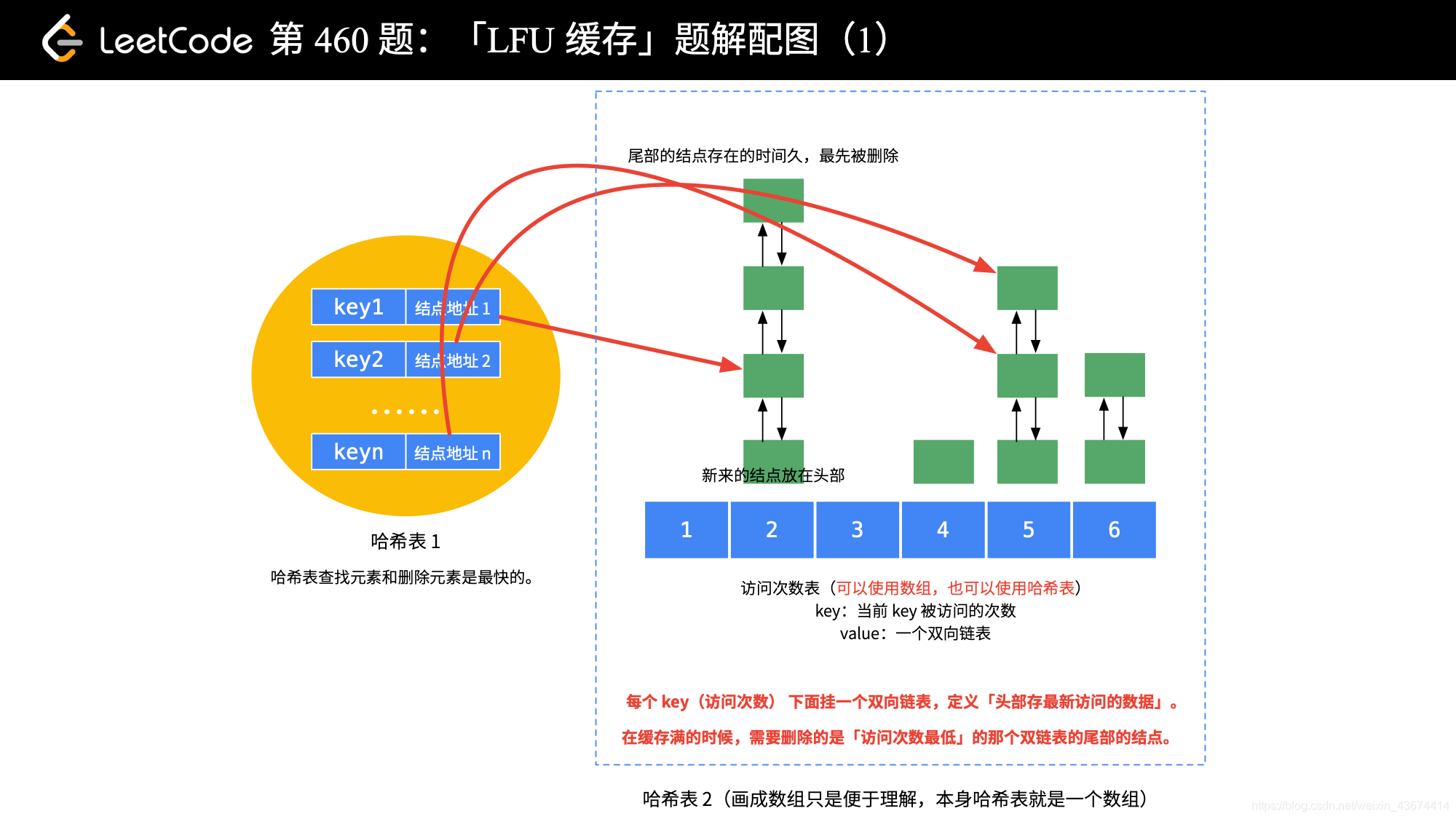

import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class LFUCache {
/**
* key 就是题目中的 key
* value 是结点类
*/
private Map<Integer, ListNode> map;
/**
* 访问次数哈希表,使用 ListNode[] 也可以,不过要占用很多空间
*/
private Map<Integer, DoubleLinkedList> frequentMap;
/**
* 外部传入的容量大小
*/
private Integer capacity;
/**
* 全局最高访问次数,删除最少使用访问次数的结点时会用到
*/
private Integer minFrequent = 1;
public LFUCache(int capacity) {
// 显式设置哈希表的长度 = capacity 和加载因子 = 1 是为了防止哈希表扩容带来的性能消耗
// 这一步操作在理论上的可行之处待讨论,实验下来效果是比较好的
map = new HashMap<>(capacity, 1);
frequentMap = new HashMap<>();
this.capacity = capacity;
}
/**
* get 一次操作,访问次数就增加 1;
* 从原来的链表调整到访问次数更高的链表的表头
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public int get(int key) {
// 测试测出来的,capacity 可能传 0
if (capacity == 0) {
return -1;
}
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
// 获得结点类
ListNode listNode = removeListNode(key);
// 挂接到新的访问次数的双向链表的头部
int frequent = listNode.frequent;
addListNode2Head(frequent, listNode);
return listNode.value;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
/**
* @param key
* @param value
*/
public void put(int key, int value) {
if (capacity == 0) {
return;
}
// 如果 key 存在,就更新访问次数 + 1,更新值
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
ListNode listNode = removeListNode(key);
// 更新 value
listNode.value = value;
int frequent = listNode.frequent;
addListNode2Head(frequent, listNode);
return;
}
// 如果 key 不存在
// 1、如果满了,先删除访问次数最小的的末尾结点,再删除 map 里对应的 key
if (map.size() == capacity) {
// 1、从双链表里删除结点
DoubleLinkedList doubleLinkedList = frequentMap.get(minFrequent);
ListNode removeNode = doubleLinkedList.removeTail();
// 2、删除 map 里对应的 key
map.remove(removeNode.key);
}
// 2、再创建新结点放在访问次数为 1 的双向链表的前面
ListNode newListNode = new ListNode(key, value);
addListNode2Head(1, newListNode);
map.put(key, newListNode);
// 【注意】因为这个结点是刚刚创建的,最少访问次数一定为 1
this.minFrequent = 1;
}
// 以下部分主要是结点类和双向链表的操作
/**
* 结点类,是双向链表的组成部分
*/
private class ListNode {
private int key;
private int value;
private int frequent = 1;
private ListNode pre;
private ListNode next;
public ListNode() {
}
public ListNode(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
/**
* 双向链表
*/
private class DoubleLinkedList {
/**
* 虚拟头结点,它无前驱结点
*/
private ListNode dummyHead;
/**
* 虚拟尾结点,它无后继结点
*/
private ListNode dummyTail;
/**
* 当前双向链表的有效结点数
*/
private int count;
public DoubleLinkedList() {
// 虚拟头尾结点赋值多少无所谓
this.dummyHead = new ListNode(-1, -1);
this.dummyTail = new ListNode(-2, -2);
dummyHead.next = dummyTail;
dummyTail.pre = dummyHead;
count = 0;
}
/**
* 把一个结点类添加到双向链表的开头(头部是最新使用数据)
*
* @param addNode
*/
public void addNode2Head(ListNode addNode) {
ListNode oldHead = dummyHead.next;
// 两侧结点指向它
dummyHead.next = addNode;
oldHead.pre = addNode;
// 它的前驱和后继指向两侧结点
addNode.pre = dummyHead;
addNode.next = oldHead;
count++;
}
/**
* 把双向链表的末尾结点删除(尾部是最旧的数据,在缓存满的时候淘汰)
*
* @return
*/
public ListNode removeTail() {
ListNode oldTail = dummyTail.pre;
ListNode newTail = oldTail.pre;
// 两侧结点建立连接
newTail.next = dummyTail;
dummyTail.pre = newTail;
// 它的两个属性切断连接
oldTail.pre = null;
oldTail.next = null;
// 重要:删除一个结点,当前双向链表的结点个数少 1
count--;
// 维护
return oldTail;
}
}
/**
* 将原来访问次数的结点,从双向链表里脱离出来
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
private ListNode removeListNode(int key) {
// 获得结点类
ListNode deleteNode = map.get(key);
ListNode preNode = deleteNode.pre;
ListNode nextNode = deleteNode.next;
// 两侧结点建立连接
preNode.next = nextNode;
nextNode.pre = preNode;
// 删除去原来两侧结点的连接
deleteNode.pre = null;
deleteNode.next = null;
// 维护双链表结点数
frequentMap.get(deleteNode.frequent).count--;
// 【注意】维护 minFrequent
// 如果当前结点正好在最小访问次数的链表上,并且移除以后结点数为 0,最小访问次数需要加 1
if (deleteNode.frequent == minFrequent && frequentMap.get(deleteNode.frequent).count == 0) {
// 这一步需要仔细想一下,经过测试是正确的
minFrequent++;
}
// 访问次数加 1
deleteNode.frequent++;
return deleteNode;
}
/**
* 把结点放在对应访问次数的双向链表的头部
*
* @param frequent
* @param addNode
*/
private void addListNode2Head(int frequent, ListNode addNode) {
DoubleLinkedList doubleLinkedList;
// 如果不存在,就初始化
if (frequentMap.containsKey(frequent)) {
doubleLinkedList = frequentMap.get(frequent);
} else {
doubleLinkedList = new DoubleLinkedList();
}
// 添加到 DoubleLinkedList 的表头
doubleLinkedList.addNode2Head(addNode);
frequentMap.put(frequent, doubleLinkedList);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LFUCache cache = new LFUCache(2);
cache.put(1, 1);
cache.put(2, 2);
System.out.println(cache.map.keySet());
int res1 = cache.get(1);
System.out.println(res1);
cache.put(3, 3);
System.out.println(cache.map.keySet());
int res2 = cache.get(2);
System.out.println(res2);
int res3 = cache.get(3);
System.out.println(res3);
cache.put(4, 4);
System.out.println(cache.map.keySet());
int res4 = cache.get(1);
System.out.println(res4);
int res5 = cache.get(3);
System.out.println(res5);
int res6 = cache.get(4);
System.out.println(res6);
}
}
作者:liweiwei1419
链接:link
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
4)自己的优化代码
class DbNode{
public int key;
public int val;
public int num=1;//次数
public DbNode pre;
public DbNode next;
public DbNode(int key,int val){
this.key=key;
this.val=val;
}
}
class LFUCache {
private int capacity;
private DbNode first;
private DbNode end;
private int size=0;
Map<Integer,DbNode> hash=new HashMap<>();//key即为key
Map<Integer,DbNode> hashOfNum=new HashMap<>();//key为使用频率,如果出现平局,其value是最新的DbNode
public LFUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity=capacity;
first=new DbNode(-1,-1);
end=new DbNode(-1,-1);
first.next=end;
end.pre=first;
}
public int get(int key) {
if(!hash.containsKey(key))return -1;
DbNode cur=hash.get(key);
if(cur==hashOfNum.get(cur.num)){//如果cur.num指针指向的就是cur,需改变该指针
if(cur.next.num==cur.num)hashOfNum.put(cur.num,cur.next);//如果它后面那个元素的num也是cur.num,则指向后面那个元素
else {//如果cur.num仅有一个元素,则删掉指针
hashOfNum.remove(cur.num);
if(!hashOfNum.containsKey(cur.num+1)){//如果不存在cur.num+1,则无需在链表中移动
hashOfNum.put(cur.num+1,cur);
cur.num++;
return cur.val;
}
}
}
remove(cur);
if(hashOfNum.containsKey(cur.num+1)){//如果存在指向cur.num+1的指针,则插在其指向元素的前面
add(cur,hashOfNum.get(cur.num+1));
}
else {
//如果不存在,则插到cur.num指向元素的前面
add(cur,hashOfNum.get(cur.num));
}
hashOfNum.put(cur.num+1,cur);
cur.num++;
return cur.val;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if(hash.containsKey(key)){//如果有
DbNode cur=hash.get(key);
cur.val=value;
get(key);//相当于get了一次
return;
}
size++;
if(size>capacity){//如果超过了capacity,则删去列表最后的元素
if(capacity==0)return;
if(end.pre==hashOfNum.get(end.pre.num)){//如果cur.num指针指向的就是cur,需删去该指针
hashOfNum.remove(end.pre.num);
}
hash.remove(end.pre.key);
remove(end.pre);
size--;
}
DbNode newNode=new DbNode(key,value);
hash.put(key,newNode);
if(hashOfNum.containsKey(1))add(newNode,hashOfNum.get(1));//如果存在使用一次的元素,插到其前面
else add(newNode,end);//否则插到最后
hashOfNum.put(1,newNode);//让使用一次的指针指向当前元素
}
public void add(DbNode newNode,DbNode next){//插在next的前面
DbNode pre=next.pre;
pre.next=newNode;
newNode.pre=pre;
newNode.next=next;
next.pre=newNode;
}
public void remove(DbNode del){
DbNode pre=del.pre;
DbNode next=del.next;
pre.next=next;
next.pre=pre;
}
}
5)学到的东西
双链表,
两个HashMap
HashMap里存一个链表
4、无重复字符的最长子串(3、Medium)
1)题目要求
给定一个字符串,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串 的长度。
示例 1:
输入: s = “abcabcbb”
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 “abc”,所以其长度为 3。
示例 2:
输入: s = “bbbbb”
输出: 1
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 “b”,所以其长度为 1。
示例 3:
输入: s = “pwwkew”
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 “wke”,所以其长度为 3。
请注意,你的答案必须是 子串 的长度,“pwke” 是一个子序列,不是子串。
示例 4:
输入: s = “”
输出: 0
提示:
0 <= s.length <= 5 * 104
s 由英文字母、数字、符号和空格组成
2)我的解法
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
char[] arr=s.toCharArray();
int start=0,end=0;
Map<Character,Integer> hash=new HashMap<>();
int max=0;
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(hash.containsKey(arr[i])&&hash.get(arr[i])>=start){
max=Math.max(max,end-start);
start=hash.get(arr[i])+1;
}
hash.put(arr[i],i);
end++;
}
return Math.max(max,end-start);
}
}
3)其他解法

class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
if (s.length()==0) return 0;
HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
int max = 0;
int left = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i ++){
if(map.containsKey(s.charAt(i))){
left = Math.max(left,map.get(s.charAt(i)) + 1);
}
map.put(s.charAt(i),i);
max = Math.max(max,i-left+1);
}
return max;
}
}
作者:powcai
链接:link
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
4)自己的优化代码
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
char[] arr=s.toCharArray();
int start=0,end=0;
Map<Character,Integer> hash=new HashMap<>();
int max=0;
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(hash.containsKey(arr[i])&&hash.get(arr[i])>=start){
max=Math.max(max,end-start);
start=hash.get(arr[i])+1;
}
hash.put(arr[i],i);
end++;
}
return Math.max(max,end-start);
}
}
5)学到的东西
滑动窗口
5、三数之和(15、Medium)
1)题目要求
给你一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?请你找出所有满足条件且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
示例:
给定数组 nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4],
满足要求的三元组集合为:
[
[-1, 0, 1],
[-1, -1, 2]
]
2)我的解法
只想到了暴力
3)其他解法

class Solution {
public static List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList();
int len = nums.length;
if(nums == null || len < 3) return ans;
Arrays.sort(nums); // 排序
for (int i = 0; i < len ; i++) {
if(nums[i] > 0) break; // 如果当前数字大于0,则三数之和一定大于0,所以结束循环
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) continue; // 去重
int L = i+1;
int R = len-1;
while(L < R){
int sum = nums[i] + nums[L] + nums[R];
if(sum == 0){
ans.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[L],nums[R]));
while (L<R && nums[L] == nums[L+1]) L++; // 去重
while (L<R && nums[R] == nums[R-1]) R--; // 去重
L++;
R--;
}
else if (sum < 0) L++;
else if (sum > 0) R--;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
作者:guanpengchn
链接: link
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
4)自己的优化代码
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> result=new ArrayList<>();
int left=0,right=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(i>0&&nums[i]==nums[i-1])continue;
left=i+1;right=nums.length-1;
while(left<right){
int sum=nums[i]+nums[left]+nums[right];
if(sum==0){
result.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[left],nums[right]));
while(left<nums.length-1&&nums[left]==nums[left+1])left++;
while(right>0&&nums[right]==nums[right-1])right--;
left++;right--;
}
else if(sum<0)left++;
else right--;
}
}
return result;
}
}
5)学到的东西
双指针、排序去重
6、两数相加(2、Medium)
1)题目要求
给出两个 非空 的链表用来表示两个非负的整数。其中,它们各自的位数是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且它们的每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
如果,我们将这两个数相加起来,则会返回一个新的链表来表示它们的和。
您可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
示例:
输入:(2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
输出:7 -> 0 -> 8
原因:342 + 465 = 807
2)我的解法
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
int jinwei=0;
ListNode head=l1;
ListNode pre=l1;
while(l1!=null&&l2!=null){
l1.val+=l2.val+jinwei;
if(l1.val>9){jinwei=1;l1.val-=10;}
else jinwei=0;
pre=l1;
l1=l1.next;
l2=l2.next;
}
if(l1==null&&l2!=null){
pre.next=l2;
l1=l2;
}
while(l1!=null){
l1.val+=jinwei;
if(l1.val>9){jinwei=1;l1.val-=10;}
else jinwei=0;
pre=l1;
l1=l1.next;
}
if(jinwei==1)pre.next=new ListNode(1);
return head;
}
}
3)其他解法
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode* head=new ListNode(-1);//存放结果的链表
ListNode* h=head;//移动指针
int sum=0;//每个位的加和结果
bool carry=false;//进位标志
while(l1!=NULL||l2!=NULL)
{
sum=0;
if(l1!=NULL)
{
sum+=l1->val;
l1=l1->next;
}
if(l2!=NULL)
{
sum+=l2->val;
l2=l2->next;
}
if(carry)
sum++;
h->next=new ListNode(sum%10);
h=h->next;
carry=sum>=10?true:false;
}
if(carry)
{
h->next=new ListNode(1);
}
return head->next;
}
};
作者:chenlele
链接:link
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
4)自己的优化代码
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
int jinwei=0;
ListNode head=l1;
ListNode pre=l1;
while(l1!=null&&l2!=null){
l1.val+=l2.val+jinwei;
if(l1.val>9){jinwei=1;l1.val-=10;}
else jinwei=0;
pre=l1;
l1=l1.next;
l2=l2.next;
}
if(l1==null&&l2!=null){
pre.next=l2;
l1=l2;
}
while(l1!=null){
l1.val+=jinwei;
if(l1.val>9){jinwei=1;l1.val-=10;}
else jinwei=0;
pre=l1;
l1=l1.next;
}
if(jinwei==1)pre.next=new ListNode(1);
return head;
}
}
5)学到的东西
链表
7、最长回文子串(5、Medium)
1)题目要求
给定一个字符串 s,找到 s 中最长的回文子串。你可以假设 s 的最大长度为 1000。
示例 1:
输入: “babad”
输出: “bab”
注意: “aba” 也是一个有效答案。
示例 2:
输入: “cbbd”
输出: “bb”
2)我的解法
1、超时
class Solution {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
int max=0;
if(s==null)return null;
String result=null;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
for(int j=i;j<s.length();j++){
if(IsPalindrome(s,i,j)&&j-i+1>max){
max=j-i+1;
result=s.substring(i,j+1);
}
}
}
return result;
}
boolean IsPalindrome(String s,int start,int end){
while(start<=end){
if(s.charAt(start)!=s.charAt(end))return false;
start++;end--;
}
return true;
}
}
3)其他解法

class Solution {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
int n = s.length();
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[n][n];
String ans = "";
for (int l = 0; l < n; ++l) {
for (int i = 0; i + l < n; ++i) {
int j = i + l;
if (l == 0) {
dp[i][j] = true;
} else if (l == 1) {
dp[i][j] = (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j));
} else {
dp[i][j] = (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j) && dp[i + 1][j - 1]);
}
if (dp[i][j] && l + 1 > ans.length()) {
ans = s.substring(i, i + l + 1);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}

class Solution {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() < 1) {
return "";
}
int start = 0, end = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
int len1 = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i);
int len2 = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i + 1);
int len = Math.max(len1, len2);
if (len > end - start) {
start = i - (len - 1) / 2;
end = i + len / 2;
}
}
return s.substring(start, end + 1);
}
public int expandAroundCenter(String s, int left, int right) {
while (left >= 0 && right < s.length() && s.charAt(left) == s.charAt(right)) {
--left;
++right;
}
return right - left - 1;
}
}

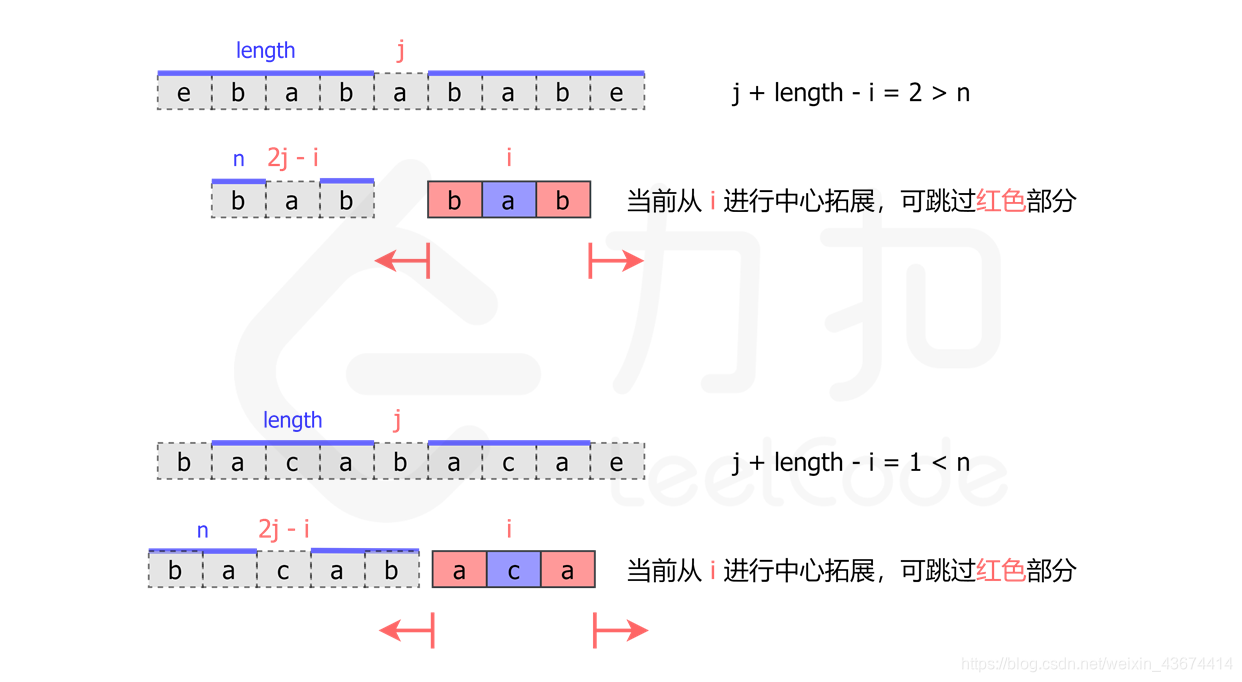

class Solution {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
int start = 0, end = -1;
StringBuffer t = new StringBuffer("#");
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {
t.append(s.charAt(i));
t.append('#');
}
t.append('#');
s = t.toString();
List<Integer> arm_len = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int right = -1, j = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {
int cur_arm_len;
if (right >= i) {
int i_sym = j * 2 - i;
int min_arm_len = Math.min(arm_len.get(i_sym), right - i);
cur_arm_len = expand(s, i - min_arm_len, i + min_arm_len);
} else {
cur_arm_len = expand(s, i, i);
}
arm_len.add(cur_arm_len);
if (i + cur_arm_len > right) {
j = i;
right = i + cur_arm_len;
}
if (cur_arm_len * 2 + 1 > end - start) {
start = i - cur_arm_len;
end = i + cur_arm_len;
}
}
StringBuffer ans = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = start; i <= end; ++i) {
if (s.charAt(i) != '#') {
ans.append(s.charAt(i));
}
}
return ans.toString();
}
public int expand(String s, int left, int right) {
while (left >= 0 && right < s.length() && s.charAt(left) == s.charAt(right)) {
--left;
++right;
}
return (right - left - 2) / 2;
}
}
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:link
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
4)自己的优化代码
1、动态规划
class Solution {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
if(s==null)return null;
String result="";
boolean[][] dp=new boolean[s.length()][s.length()];
for(int len=0;len<s.length();len++){
for(int i=0;i<s.length()-len;i++){
int j=i+len;
if(len==0)dp[i][j]=true;
else if(len==1)dp[i][j]=(s.charAt(i)==s.charAt(j));
else if(s.charAt(i)==s.charAt(j))dp[i][j]=dp[i+1][j-1];
if(dp[i][j]&&len+1>result.length())result=s.substring(i,j+1);
}
}
return result;
}
}
2、
class Solution {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
if(s==null)return null;
String result="";
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
int len1=MaxLen(s,i,i);
int len2=MaxLen(s,i,i+1);
int len=Math.max(len1,len2);
if(len>result.length())result=s.substring(i-(len-1)/2,i+len/2+1);
}
return result;
}
int MaxLen(String s,int i,int j){
int len=j-i-1;//如果j==i,初始为-1,否则初始为0
while(i>=0&&j<s.length()){
if(s.charAt(i)==s.charAt(j))len+=2;
else break;
i--;j++;
}
return len;
}
}
5)学到的东西
动态规划,用长度规划
从中间向两边扩散
8、 最长公共前缀(14、Easy)
1)题目要求
编写一个函数来查找字符串数组中的最长公共前缀。
如果不存在公共前缀,返回空字符串 “”。
示例 1:
输入: [“flower”,“flow”,“flight”]
输出: “fl”
示例 2:
输入: [“dog”,“racecar”,“car”]
输出: “”
解释: 输入不存在公共前缀。
说明:
所有输入只包含小写字母 a-z 。
2)我的解法
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
if(strs.length==0)return "";
for(int j=0;j<strs[0].length();j++){
for(int i=1;i<strs.length;i++){
if(j>=strs[i].length()||strs[i].charAt(j)!=strs[0].charAt(j)){
return sb.toString();
}
}
sb.append(strs[0].charAt(j));
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
3)其他解法

class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
if(strs.length == 0)
return "";
String ans = strs[0];
for(int i =1;i<strs.length;i++) {
int j=0;
for(;j<ans.length() && j < strs[i].length();j++) {
if(ans.charAt(j) != strs[i].charAt(j))
break;
}
ans = ans.substring(0, j);
if(ans.equals(""))
return ans;
}
return ans;
}
}
作者:guanpengchn
链接:link
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
4)自己的优化代码
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
if(strs.length==0)return "";
for(int j=0;j<strs[0].length();j++){
for(int i=1;i<strs.length;i++){
if(j>=strs[i].length()||strs[i].charAt(j)!=strs[0].charAt(j)){
return sb.toString();
}
}
sb.append(strs[0].charAt(j));
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
5)学到的东西
9、反转链表 II(92、Medium)
1)题目要求
反转从位置 m 到 n 的链表。请使用一趟扫描完成反转。
说明:
1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ 链表长度。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4
输出: 1->4->3->2->5->NULL
2)我的解法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
ListNode cur=head;
ListNode dummy=new ListNode(0);
dummy.next=head;
ListNode preM=dummy;
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){preM=cur;cur=cur.next;}
ListNode nodeM=cur;
ListNode pre=null;
for(int i=m;i<=n;i++){
ListNode Next=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=Next;
}
//cur为N后面那个,pre为N
preM.next=pre;
nodeM.next=cur;
return dummy.next;
}
}
3)其他解法
具体看链接
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
ListNode successor = null; // 后驱节点
// 反转以 head 为起点的 n 个节点,返回新的头结点
ListNode reverseN(ListNode head, int n) {
if (n == 1) {
// 记录第 n + 1 个节点
successor = head.next;
return head;
}
// 以 head.next 为起点,需要反转前 n - 1 个节点
ListNode last = reverseN(head.next, n - 1);
head.next.next = head;
// 让反转之后的 head 节点和后面的节点连起来
head.next = successor;
return last;
}
ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
// base case
if (m == 1) {
return reverseN(head, n);
}
// 前进到反转的起点触发 base case
head.next = reverseBetween(head.next, m - 1, n - 1);
return head;
}
}
作者:labuladong
链接:link
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
4)自己的优化代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
ListNode after=null;
ListNode reverse(ListNode head,int n){//从head,反转n个
if(n==1){
after=head.next;
return head;
}
ListNode last=reverse(head.next,n-1);
head.next.next=head;
head.next=after;
return last;
}
ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
if(m==1){
return reverse(head,n);
}
head.next=reverseBetween(head.next,m-1,n-1);
return head;
}
}
5)学到的东西
递归思想
多刷几遍
10、 K 个一组翻转链表(25、Hard)
1)题目要求
给你一个链表,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。
如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
示例:
给你这个链表:1->2->3->4->5
当 k = 2 时,应当返回: 2->1->4->3->5
当 k = 3 时,应当返回: 3->2->1->4->5
说明:
你的算法只能使用常数的额外空间。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
2)我的解法
1、递归
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
ListNode after=null;
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head,int n){
if(n==1){
after=head.next;
head.next=after;
return head;
}
ListNode last=reverse(head.next,n-1);
head.next.next=head;
head.next=after;
return last;
}
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode pre=head;
head=reverse(head,k);
ListNode cur=head;
ListNode temp=null;
while(true){
temp=after;
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++){//先判断after之后的是否大于K
if(temp==null)return head;//小于K直接返回
temp=temp.next;
}
cur=pre;//否则继续反转after之后的元素
pre=cur.next;
cur.next=reverse(cur.next,k);
}
}
}
2、迭代
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
ListNode after=null;
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head,int n){
ListNode pre=null;
ListNode cur=head;
while(n-->0){
ListNode Next=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=Next;
}
after=cur;
head.next=after;
return pre;
}
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode pre=head;
head=reverse(head,k);
ListNode cur=head;
ListNode temp=null;
while(true){
temp=after;
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++){//先判断after之后的是否大于K
if(temp==null)return head;//小于K直接返回
temp=temp.next;
}
cur=pre;//否则继续反转after之后的元素
pre=cur.next;
cur.next=reverse(cur.next,k);
}
}
}
3)其他解法
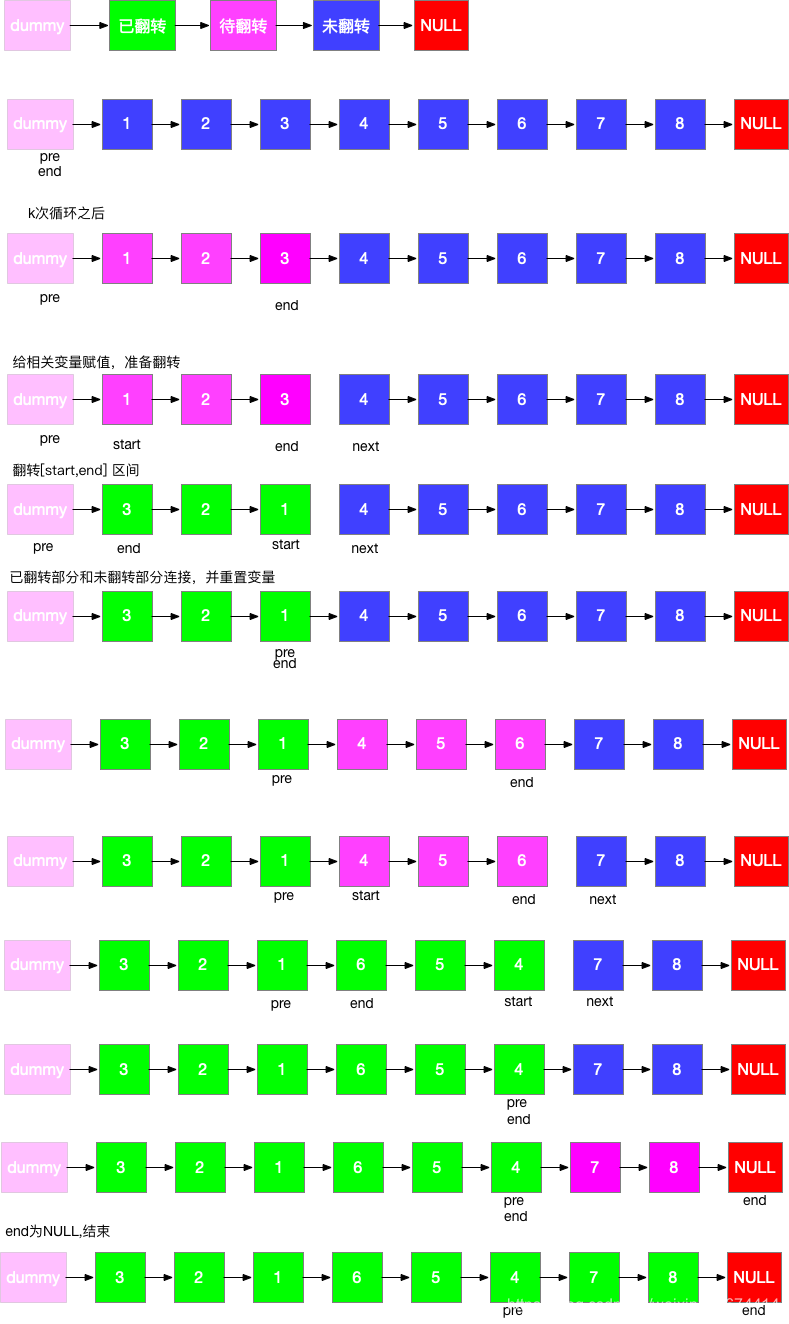


/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
//定义一个假的节点。
ListNode dummy=new ListNode(0);
//假节点的next指向head。
// dummy->1->2->3->4->5
dummy.next=head;
//初始化pre和end都指向dummy。pre指每次要翻转的链表的头结点的上一个节点。end指每次要翻转的链表的尾节点
ListNode pre=dummy;
ListNode end=dummy;
while(end.next!=null){
//循环k次,找到需要翻转的链表的结尾,这里每次循环要判断end是否等于空,因为如果为空,end.next会报空指针异常。
//dummy->1->2->3->4->5 若k为2,循环2次,end指向2
for(int i=0;i<k&&end != null;i++){
end=end.next;
}
//如果end==null,即需要翻转的链表的节点数小于k,不执行翻转。
if(end==null){
break;
}
//先记录下end.next,方便后面链接链表
ListNode next=end.next;
//然后断开链表
end.next=null;
//记录下要翻转链表的头节点
ListNode start=pre.next;
//翻转链表,pre.next指向翻转后的链表。1->2 变成2->1。 dummy->2->1
pre.next=reverse(start);
//翻转后头节点变到最后。通过.next把断开的链表重新链接。
start.next=next;
//将pre换成下次要翻转的链表的头结点的上一个节点。即start
pre=start;
//翻转结束,将end置为下次要翻转的链表的头结点的上一个节点。即start
end=start;
}
return dummy.next;
}
//链表翻转
// 例子: head: 1->2->3->4
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
//单链表为空或只有一个节点,直接返回原单链表
if (head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
//前一个节点指针
ListNode preNode = null;
//当前节点指针
ListNode curNode = head;
//下一个节点指针
ListNode nextNode = null;
while (curNode != null){
nextNode = curNode.next;//nextNode 指向下一个节点,保存当前节点后面的链表。
curNode.next=preNode;//将当前节点next域指向前一个节点 null<-1<-2<-3<-4
preNode = curNode;//preNode 指针向后移动。preNode指向当前节点。
curNode = nextNode;//curNode指针向后移动。下一个节点变成当前节点
}
return preNode;
}
}
作者:reals
链接:link
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
4)自己的优化代码
class Solution {
ListNode after=null;
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head,int n){
if(n==1){
after=head.next;
head.next=after;
return head;
}
ListNode last=reverse(head.next,n-1);
head.next.next=head;
head.next=after;
return last;
}
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode pre=head;
head=reverse(head,k);
ListNode cur=head;
ListNode temp=null;
while(true){
temp=after;
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++){//先判断after之后的是否大于K
if(temp==null)return head;//小于K直接返回
temp=temp.next;
}
cur=pre;//否则继续反转after之后的元素
pre=cur.next;
cur.next=reverse(cur.next,k);
}
}
}
5)学到的东西
链表一定要自己画图
递归





 本文精选了10道经典算法题目,包括LRU缓存机制、接雨水、LFU缓存等,提供了详细的解题思路、代码实现及优化方案。
本文精选了10道经典算法题目,包括LRU缓存机制、接雨水、LFU缓存等,提供了详细的解题思路、代码实现及优化方案。
















 927
927

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








