总结自:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1jt411J7tC
19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
Given linked list: 1->2->3->4->5, and n = 2.
After removing the second node from the end, the linked list becomes 1->2->3->5.
Note:
Given n will always be valid.
Follow up:
Could you do this in one pass?
思路:
双指针,因为要删除倒数第n个节点,那么就要找到倒数第n+1个节点,所以其中一个指针先向右移动n个节点,这样当靠右的节点到达链表尾的时候,另一个指针即指向倒数第n+1个节点
要点:
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} // 用来初始化
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1); // auto会根据等号右边的值的类型对确定变量的类型
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1); // 跟上一条等价
因为可能删除的是头节点,因此我们创建一个虚拟的节点指向头节点,并且最终返回虚拟节点的下一个节点,这样当被删除的是头节点时也不需要特殊判断
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
auto first = dummy, second = dummy;
while(n--) first = first->next;
while(first->next)
{
first = first->next;
second = second->next;
}
second->next = second->next->next;
return dummy->next;
}
};
237. Delete Node in a Linked List
Write a function to delete a node (except the tail) in a singly linked list, given only access to that node.
Given linked list – head = [4,5,1,9], which looks like following:
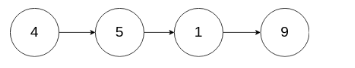
Example 1:
Input: head = [4,5,1,9], node = 5
Output: [4,1,9]
Explanation: You are given the second node with value 5, the linked list should become 4 -> 1 -> 9 after calling your function.
Example 2:
Input: head = [4,5,1,9], node = 1
Output: [4,5,9]
Explanation: You are given the third node with value 1, the linked list should become 4 -> 5 -> 9 after calling your function.
Note:
The linked list will have at least two elements.
All of the nodes’ values will be unique.
The given node will not be the tail and it will always be a valid node of the linked list.
Do not return anything from your function.
思路:一般要删除一个节点,我们要找到该节点的前一个节点,但这道题只给出要删除的节点,所以我们复制该节点的后一个节点的值,然后删除后一个节点,这样从整个链表上看就好像是删除了该节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void deleteNode(ListNode* node) {
node->val = node->next->val;
node->next = node->next->next;
// 上面两句可以简写为
// *(node) = *(node->next);
}
};
83. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
Given a sorted linked list, delete all duplicates such that each element appear only once.
Example 1:
Input: 1->1->2
Output: 1->2
Example 2:
Input: 1->1->2->3->3
Output: 1->2->3
思路:遍历一遍,如果该节点的值和下一个节点的值相同,就删去下一个节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
auto temp = head;
while(temp)
{
if(temp->next && temp->val == temp->next->val) // 注意判下个节点是否为空
temp-> next = temp->next->next;
else
// 只有当前后两个节点值都不同时才指向下一个节点
// 否则如果再下一个节点的值仍然跟前两个值相等,就会出错
temp = temp->next;
}
return head;
}
};
61. Rotate List
Given a linked list, rotate the list to the right by k places, where k is non-negative.
Example 1:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, k = 2
Output: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: 5->1->2->3->4->NULL
rotate 2 steps to the right: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
Example 2:
Input: 0->1->2->NULL, k = 4
Output: 2->0->1->NULL
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: 2->0->1->NULL
rotate 2 steps to the right: 1->2->0->NULL
rotate 3 steps to the right: 0->1->2->NULL
rotate 4 steps to the right: 2->0->1->NULL
思路:旋转k次,相当于以倒数第k个节点当头节点,链表尾指向原先的头节点,因此可以用19. Remove Nth Node From End of List的双指针方法定位两个目标节点,由于k可能很大,因此需要先取模
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {
if(!head) return NULL; // 判空
int n = 0;
for(auto p = head; p; p = p->next) n++;
k %= n;
auto left = head, right = head;
while(k--) right = right->next;
while(right->next)
{
left = left->next;
right = right->next;
}
right->next = head; // 链表末尾指向原先的头
head = left->next; // 新的头节点
left->next = NULL; // 新的链表尾
return head;
}
};
24. Swap Nodes in Pairs
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head.
You may not modify the values in the list’s nodes, only nodes itself may be changed.
Example:
Given 1->2->3->4, you should return the list as 2->1->4->3.
思路:头节点有变化,因此用一个虚拟节点指向头节点,用临时节点p遍历链表,用a和b分别表示p后面两个要交换的节点,交换结束后p指向a,继续交换后两个节点,如果长度为奇数,那最后一个节点不做改动
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
for(auto p = dummy; p->next && p->next->next;)
{
auto a = p->next, b = p->next->next;
p->next = b;
a->next = b->next;
b->next = a;
p = a;
}
return dummy->next; // 第一次循环时p和dummy指向同一个地址
// 因此p->next的改变相当于改变dummy->next
// 这跟int a = b,a改变后b不变不同
}
};
206. Reverse Linked List
Reverse a singly linked list.
Example:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
Output: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
Follow up:
A linked list can be reversed either iteratively or recursively. Could you implement both?
思路:类似于以c为媒介,交互a和b的值
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head) return NULL; // 判空
auto a = head, b = head->next;
head->next = NULL;
while(b) // b为空时,由于a在b的左侧,则此时a为头节点
{
auto c = b->next;
b->next = a;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return a;
}
};
92. Reverse Linked List II
Reverse a linked list from position m to n. Do it in one-pass.
Note: 1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ length of list.
Example:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4
Output: 1->4->3->2->5->NULL
思路:
由于头节点可能出现变化,使用一个虚拟节点
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL m = 2 n = 4
a b d c
a节点和c节点分别在要反转的链表两侧,我们先用206. Reverse Linked List的方法把d到d之间的链表反转,接着a节点的next指向d(1->4),b节点的next指向c(2->5)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) {
if(m == n) return head; // 特殊情况
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
auto a = dummy, d = dummy;
for(int i = 0; i < m - 1; i++) a = a->next;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) d = d->next;
auto b = a->next, c = d->next;
for(auto p = b, q = b->next; q != c;)
{
auto o = q->next;
q->next = p;
p = q;
q = o;
}
b->next = c;
a->next = d;
return dummy->next;
}
};
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
For example, the following two linked lists:
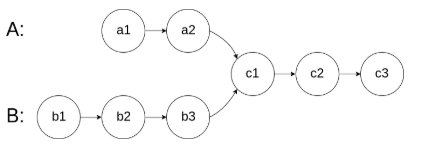
begin to intersect at node c1.
思路:设A的头节点到相交节点的长度为a(暂且假设相交),B的头节点到相交节点的长度为b,共同链表的长度为c
节点p从A头节点开始出发,走到链表尾之后转到B的头节点继续走,走到相交节点,则一共走了a+c+b个节点
节点q从B头节点开始出发,走到链表尾之后转到A的头节点继续走,走到相交节点,则一共走了a+b+c个节点
所以我们发现,只要p、q分别从两个链表头往下遍历,每次各自指向下一个节点,并在走到链表尾之后转向另一条链表继续遍历,如果两条链表有交点,则p、q必定在交点处相遇,即节点p == 节点q,为同一个节点,因为此时它们都走了a+b+c个节点,当然如果恰好a==b,则它们在第一次经过相交点时就会相遇
而如果两条链表没有交点,则在走完a+b个节点后,p和q分别为NULL,当然此时也满足p == q,但返回的结果时NULL
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
auto p = headA, q = headB;
while(p != q)
{
if(p) p = p->next;
else p = headB;
if(q) q = q->next;
else q = headA;
}
return p;
}
};
142. Linked List Cycle II
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer pos which represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to. If pos is -1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.
Note: Do not modify the linked list.
思路:快慢指针
假设有环,环的入口为b点,head(即a点)到b的距离为x
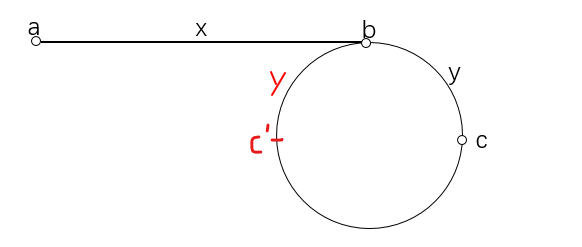
在head即a点设置快慢指针各一个,快指针一次移动两个节点,慢指针一次一个,我们假设慢指针移动到b时,快指针移动到c‘处(可能快指针已经绕环很多圈),设此时快指针到b的距离为y,然后继续移动,因为快指针的移动速度是慢指针移动速度的两倍,慢指针继续移动y个节点,快指针移动2y个节点,所以它们相遇的点c跟c’是对称的(都距离b点y个节点)
第一次相遇以后,将慢指针放回到head,即a点,然后两个指针都以每次一个节点的速度向前移动,它们再次相遇时的点就是环的入口
解释:因为慢指针第一次到达b点时,快指针已经移动了2x个节点,即快指针从b点开始移动x个节点以后会停留在c‘处,慢指针第二次到达b点时,由于快指针也是每次一个节点,因此也移动了x个节点,但此时的起点是c,由于c和c’是对称的,相当于我们把原先的起点b向前移动y个节点到c,那么原先的终点c’也随之向前移动y个节点,恰好是环的入口b
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
auto fast = head, slow = head;
while(fast) // 如果退出循环,说明有节点的next指向NULL,即没有环
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
if(fast) fast = fast->next;
else break;
if(fast == slow) // 第一次相遇以后
{
slow = head;
while(slow != fast)
{
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return fast;
}
}
return NULL;
}
};
148. Sort List
Sort a linked list in O(n log n) time using constant space complexity.
Example 1:
Input: 4->2->1->3
Output: 1->2->3->4
Example 2:
Input: -1->5->3->4->0
Output: -1->0->3->4->5
思路:
要求时间复杂度O(n log n),常数空间,如果使用快速排序等,递归时用到系统栈,则空间为O(log n)
使用归并排序的方法,不用递归,循环log n次,每次处理n个数据,所以为O(n log n)
比如第一次循环,两个数一组,按升序排号,第二次循环四个数一组,前两个数和后两个数都已经是升序,将它们归并以后,得到的四个数就是升序,再八个数一组……
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
int n = 0;
for(auto p = head; p; p = p->next) n++;
// 归并排序的思想
for(int i = 1; i < n; i *= 2) // 每次对2*i个数进行排序
{
auto cur = dummy;
for(int j = 0; j + i < n; j += i * 2)
{
auto left = cur->next, right = cur->next;
// left和right分别指向一组排好序的数字
for(int k = 0; k < i; k++) right = right->next;
int l = 0, r = 0;
// 进行归并
while(l < i && r < i && right)
if(left->val <= right->val)
{
cur->next = left;
cur = left;
left = left->next;
l++;
}
else
{
cur->next = right;
cur = right;
right = right->next;
r++;
}
// 结束后可能有一组数字还有剩余
while(l < i)
{
cur->next = left;
cur = left;
left = left->next;
l++;
}
// 有可能右边一组的长度不足
while(r < i && right)
{
cur->next = right;
cur = right;
right = right->next;
r++;
}
// 归并结束后,cur指向下一组要归并的数据的前一个节点
// 这样后一组2*i个数据排序时left和right都指向这2*i个节点的第一个节点
cur->next = right;
}
}
return dummy->next;
}
};







 本文深入解析链表算法,涵盖删除倒数第N个节点、删除链表节点、去除重复元素、链表旋转、节点配对交换、链表反转、链表区间反转、查找链表交点、检测链表环、链表排序等核心问题,提供详尽的思路与代码实现。
本文深入解析链表算法,涵盖删除倒数第N个节点、删除链表节点、去除重复元素、链表旋转、节点配对交换、链表反转、链表区间反转、查找链表交点、检测链表环、链表排序等核心问题,提供详尽的思路与代码实现。
















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








