剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
题目
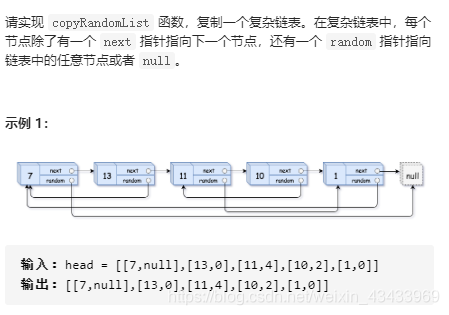
思路
使用hashmap存储新老节点,简单思路就是两次遍历进行对新复制的链表赋值,也可以使用图遍历(复杂度更低,可优化)
代码
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
HashMap<Node,Node> map=new HashMap<>();
Node cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
map.put(cur,new Node(cur.val));
cur=cur.next;
}
cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
// 通过map.get(cur.next)取出cur.next对应的value值即为新链表中的下一个节点值(保证是一个全新节点,否则只是对原有链表的浅复制,节点内存不变,无法通过)
map.get(cur).next=map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random=map.get(cur.random);
cur=cur.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
}
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, x: int, next: 'Node' = None, random: 'Node' = None):
self.val = int(x)
self.next = next
self.random = random
"""
class Solution:
def copyRandomList(self, head: 'Node') -> 'Node':
#注意此处新建hashmap时不是简单{},对内部进行初始化,否则会出现KeyError
map={None:None}
cur=head
while cur:
map[cur]=Node(cur.val)
cur=cur.next
cur=head
while cur:
map[cur].next=map[cur.next]
map[cur].random=map[cur.random]
cur=cur.next
return map[head]
剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
题目


思路

代码
class Solution {
Node head, pre;
public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) {
if(root==null) return null;
dfs(root);
pre.right = head;
head.left =pre;//进行头节点和尾节点的相互指向,这两句的顺序也是可以颠倒的
return head;
}
public void dfs(Node cur){
if(cur==null) return;
dfs(cur.left);
//pre用于记录双向链表中位于cur左侧的节点,即上一次迭代中的cur,当pre==null时,cur左侧没有节点,即此时cur为双向链表中的头节点
if(pre==null) head = cur;
//反之,pre!=null时,cur左侧存在节点pre,需要进行pre.right=cur的操作。
else pre.right = cur;
cur.left = pre;//pre是否为null对这句没有影响,且这句放在上面两句if else之前也是可以的。
pre = cur;//pre指向当前的cur
dfs(cur.right);//全部迭代完成后,pre指向双向链表中的尾节点
}
}
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
"""
class Solution:
def treeToDoublyList(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
def dfs(cur):
if not cur: return
dfs(cur.left) # 递归左子树
if self.pre: # 修改节点引用
self.pre.right, cur.left = cur, self.pre
else: # 记录头节点
self.head = cur
self.pre = cur # 保存 cur
dfs(cur.right) # 递归右子树
if not root: return
self.pre = None
dfs(root)
self.head.left, self.pre.right = self.pre, self.head
return self.head
剑指 Offer 39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
题目

思路

代码
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
// 方法一:摩尔投票法
// int votes=0;
// int x=nums[0];
// int len=nums.length;
// for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
// if(votes==0){
// x=nums[i];
// }
// if(nums[i]==x){
// votes++;
// }else{
// votes--;
// }
// }
// return x;
// 方法二:hashmap方法,遍历一遍计算最多的数值为哪个
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(!map.containsKey(nums[i])){
map.put(nums[i],1);
}else{
map.put(nums[i],map.get(nums[i])+1);
}
if(map.get(nums[i])>nums.length/2)
return nums[i];
}
return -1;
}
}
class Solution:
def majorityElement(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
# 方法一:摩尔投票
# votes,x=0,nums[0]
# for i in range(len(nums)):
# if votes==0:
# x=nums[i]
# if x==nums[i]:
# votes+=1
# else:
# votes-=1
# return x
# 方法二:hashmap,储存元素个数,超过列表长度的一般即为众数
map1={}
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] not in map1:
map1[nums[i]]=1
else:
map1[nums[i]]=map1[nums[i]]+1
if map1[nums[i]]>len(nums)/2 :
return nums[i]
return 0
























 172万+
172万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








