Problem 54: Poker hands
In the card game poker, a hand consists of five cards and are ranked, from lowest to highest, in the following way:
- High Card: Highest value card.
- One Pair: Two cards of the same value.
- Two Pairs: Two different pairs.
- Three of a Kind: Three cards of the same value.
- Straight: All cards are consecutive values.
- Flush: All cards of the same suit.
- Full House: Three of a kind and a pair.
- Four of a Kind: Four cards of the same value.
- Straight Flush: All cards are consecutive values of same suit.
- Royal Flush: Ten, Jack, Queen, King, Ace, in same suit.
The cards are valued in the order:
2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, Jack, Queen, King, Ace.
If two players have the same ranked hands then the rank made up of the highest value wins; for example, a pair of eights beats a pair of fives (see example 1 below). But if two ranks tie, for example, both players have a pair of queens, then highest cards in each hand are compared (see example 4 below); if the highest cards tie then the next highest cards are compared, and so on.
Consider the following five hands dealt to two players:
| Hand | Player 1 | Player 2 | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5H 5C 6S 7S KD Pair of Fives | 2C 3S 8S 8D TD Pair of Eights | Player 2 |
| 2 | 5D 8C 9S JS AC Highest card Ace | 2C 5C 7D 8S QH Highest card Queen | Player 1 |
| 3 | 2D 9C AS AH AC Three Aces | 3D 6D 7D TD QD Flush with Diamonds | Player 2 |
| 4 | 4D 6S 9H QH QC Pair of Queens Highest card Nine | 3D 6D 7H QD QS Pair of Queens Highest card Seven | Player 1 |
| 5 | 2H 2D 4C 4D 4S Full House With Three Fours | 3C 3D 3S 9S 9D Full House with Three Threes | Player 1 |
The file, poker.txt, contains one-thousand random hands dealt to two players. Each line of the file contains ten cards (separated by a single space): the first five are Player 1’s cards and the last five are Player 2’s cards. You can assume that all hands are valid (no invalid characters or repeated cards), each player’s hand is in no specific order, and in each hand there is a clear winner.
How many hands does Player 1 win?
1. 扑克牌游戏的一些概念
让我们来弄清楚扑克牌的一些基本概念。
扑克牌有四种花色(Suit):草(梅)花C,红心H,黑桃S,方块D。

牌面大小有13个级别(Rank),从最大A到最小的 2依次为:
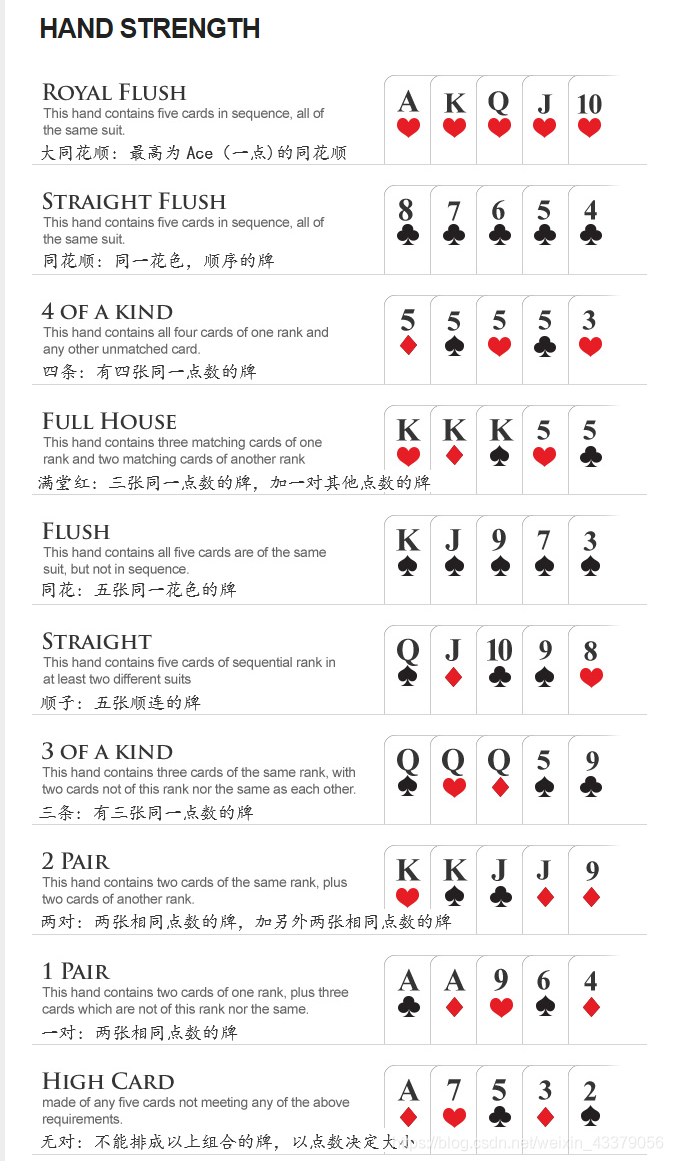
每一手牌的力量(Hand Strength)从大到小有10种优先级:
知道了Suit, Rank和 Hand Strength后,就很容易理解本题了。
2. 题目解析
扑克牌游戏中,一手牌包括5张牌,牌的大小顺序从低到高依次是2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, Jack, Queen, King, Ace,但Ace 也可以当作1,这是一个特例。我们可以定义每张牌的值从2到14。
每一手牌的力量从小到大依次是:无对(High Card),一对(One Pair) ,两对(Two Pairs),三条(Three of a Kind),顺子(Straight), 同花(Flush), 满堂红(Full House), 四条(Four of a Kind), 同花顺(Straight Flush), 大同花顺(Royal Flush)。我们可以定义优先级从1到10。
两个对手按照他们的手牌的力量(Hand Strength)比较他们的Rank,确定Player1 还是 Player 2谁获胜。
五个例子说明了两个人的手牌比较的过程和结果。
文件poker.txt有1000手牌,计算出第一个选手(人)的牌赢得多少手牌?
3. 解题思路
如果我们逐个判断每一手牌符合那个规则,那我们可能最多需要判断10次才能确认每一手牌的rank value, 因为我们需要从大到小逐次判断。如果这样做的话,很可能要写10个函数来判断Hand Strength每一种情况。
我们能不能找到一种通用的方法来量化每一手牌的力量呢?如果有的话,就很方便了,事实上,我们可以通过每一手牌的力量的顺序(score)和牌面的大小(card value) 两个维度来确认rank values,最后根据rank values 就可以判断两个人的手牌大小了。
例如:
C++ 代码(打开编译开关PE0050_DEBUG)后 打印输出的三个例子:
(“5D”, “8C”, “9S”, “JS”, “AC”) Rank: 1, (14, 11, 9, 8, 5)
(“2C”, “5C”, “7D”, “8S”, “QH”) Rank: 1, (12, 8, 7, 5, 2)
第一个例子,score 相同都是1, 符合High Card规则,然后,我们根据牌面大小列表 (14, 11, 9, 8, 5)和(12, 8, 7, 5, 2), 很容易知道 Player 2 获胜。Rank的值是类PlayerHandRank。
(“5H”, “5C”, “6S”, “7S”, “KD”) Rank: 2, (5, 13, 7, 6)
(“2C”, “3S”, “8S”, “8D”, “TD”) Rank: 2, (8, 10, 3, 2)
第二个例子,score 相同都是2, 符合One Pair规则,然后,我们根据牌面大小列表 (5, 13, 7, 6)和(8, 10, 3, 2), 知道一对8比一对5大,很容易知道 Player 2 获胜。
(“2D”, “9C”, “AS”, “AH”, “AC”) Rank: 4, (14, 9, 2)
(“3D”, “6D”, “7D”, “TD”, “QD”) Rank: 6, (12, 10, 7, 6, 3)
第三个例子,Player1 手牌的score 是4,Player2 手牌的score 是6, 符合Hand Strength 排序规则,然后很容易判断同花(Flush)大于三条(Three of a Kind),知道 Player 2 获胜。
Python 打印输出的两个例子:
[‘QS’, ‘QD’, ‘AC’, ‘AD’, ‘4C’] Rank: [2, (14, 12, 4)]
[‘6S’, ‘2D’, ‘AS’, ‘3H’, ‘KC’] Rank: [0, (14, 13, 6, 3, 2)]
第一个例子, Player 1获胜。Rank的值保存在一个tuple里。
[‘4C’, ‘7C’, ‘3C’, ‘TD’, ‘QS’] Rank: [0, (12, 10, 7, 4, 3)]
[‘9C’, ‘KC’, ‘AS’, ‘8D’, ‘AD’] Rank: [1, (14, 13, 9, 8)]
第二个例子, Player 2获胜。
4. C++程序设计
4.1 Class Diagram (类图)
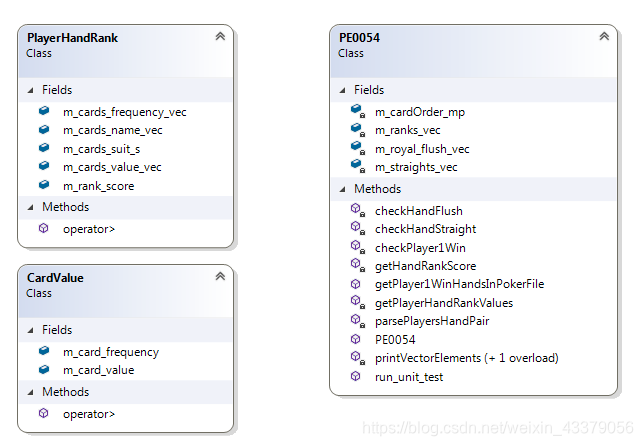
4.2 类 PlayerHandRank
我们把一手牌Hand的信息保存在类 PlayerHandRank里,在类里,我们定义了几个数据成员,还定义了操作符 operator > , 最后比较player1Rank和player2Rank,如果为true,那么Player1 win。
4.3 类 CardValue
我们很容易知道要把一手牌通过map来解析,就可以知道牌面大小和每张牌出现的次数,但map解析后的结果需要排序,排序的规则:牌出现的次数m_card_frequency 从大到小降序排列,牌面大小从高到低排序。这个排序通过定义operator > 来实现。
4.4 类 PE0054
我们定义了三个public的成员函数:
- 构造函数 PE0054()来初始化成员数据 m_cardOrder_mp和m_straights_vec。
- run_unit_test() 来运行单元测试用例。
- getPlayer1WinHandsInPokerFile()用来获得文件poker.txt里的所有1000手牌,得到player1获胜的数。
我们还定义了private的数据成员和方法:
- m_royal_flush_vec,初始化大同花顺的向量,用来判断大同花顺。
- m_cardOrder_mp,把牌面字符 ‘2’,‘3’, ‘4’, ‘5’, ‘6’, ‘7’, ‘8’, ‘9’, ‘T’, ‘J’, ‘Q’, ‘K’, ‘A’ 和2, 3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14关联起来,便于以后比较牌面大小。
- m_ranks_vec,定义了几种牌面出现的次数的模式,根据这种模式,getHandRankScore()根据索引值得到score。
- m_straights_vec,枚举所有可能的straight的模式,checkHandStraight()会用到。
- getPlayerHandRankValues(),计算每手牌的rank values,返回类型是类 PlayerHandRank。
- checkPlayer1Win(),根据player 1的hand rank和player 2的hand rank,如果结果是true, 判断player 1获胜。
- parsePlayersHandPair(),把每一组手牌拆解为player1的手牌(hand)和player2的手牌(hand)
- 内联函数 getHandRankScore(),初步计算一手牌的rank score。
- 内联函数 checkHandStraight(), 判断一手牌是否为顺子(straight)。
- 内联函数 checkHandFlush(),判断一手牌是否为同花(flush)。
- 内联函数 printVectorElements(), 打印向量成员,例如:(5,13,7,6)。
4.5 C++11特性
- 在类PE0054的定义中,我们初始化了成员变量,例如:m_royal_flush_vec , m_ranks_vec 和 m_straights_vec :
vector<int> m_royal_flush_vec = { 14, 13, 12, 11, 10 };
vector<vector<int>> m_ranks_vec = {{1, 1, 1, 1, 1}, {2, 1, 1, 1}, {2, 2, 1},
{3, 1, 1}, {}, {}, {3, 2}, {4, 1}};
vector<vector<int>> m_straights_vec = { {14, 5, 4, 3, 2} };
- 在函数getHandRankScore()和checkHandStraight()里,我们使用了for 和 auto的简化循环,例如:
for (auto v : m_straights_vec)
{
if (hand.m_cards_value_vec == v)
{
return true;
}
}
4.6 编译开关
- UNIT_TEST, 默认关闭。如果打开编译开关,main()将调用执行pe0054.run_unit_test(),一些单元测试的用例将执行,关掉编译开关,main()将调用执行函数pe0054.getPlayer1WinHandsInPokerFile(),从文件 poker.txt里读取数据,并返回结果。
- PE0054_DEBUG,默认关闭。如果打开编译开关,程序运行时的一些debug 信息被打印输出到屏幕,关掉编译开关,没有debug 信息被打印输出到屏幕。
5. Python程序设计
5.1 collections.Counter()
Counter(计数器)是对字典的补充,用于追踪值的出现次数。
Counter是一个继承了字典的类(Counter(dict)),注意其返回值是tuple.
5.2 zip(*)
zip() 函数用于将可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对应的元素打包成一个个元组,然后返回由这些元组组成的列表。如果各个迭代器的元素个数不一致,则返回列表长度与最短的对象相同,利用 * 号操作符,可以将元组解压为列表。
5.3 getPlayerHandRank()
这个函数用来获得每一手牌的rank values,结果保存在一个tuple里, 例如:[2, (14, 12, 4)]。
下面的代码是整个函数的核心代码,信息量很大:
score = [zip(*(sorted(((v, cards_value_dict[k]) \
for k,v in collections.Counter(x[0] for x in hand).items()),reverse=True)))]
可以毫不夸张地说,这道题的C++和Python代码都很经典,无论是解题思路还是代码本身都值得反复推敲,充分展现了程序设计之美。
C++ 11 代码
// PE0054.cpp has used C++ 11 features
// #include "pch.h" // this header file is required by MS Visual Studio 2017
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std;
//#define UNIT_TEST
//#define PE0054_DEBUG
// 1. High Card: Highest value card.
// 2. One Pair : Two cards of the same value.
// 3. Two Pairs : Two different pairs.
// 4. Three of a Kind : Three cards of the same value.
// 5. Straight : All cards are consecutive values.
// 6. Flush : All cards of the same suit.
// 7. Full House : Three of a kind and a pair.
// 8. Four of a Kind : Four cards of the same value.
// 9. Straight Flush : All cards are consecutive values of same suit.
// 10. Royal Flush : Ten, Jack, Queen, King, Ace, in same suit.
class PlayerHandRank
{
public:
int m_rank_score = 1; // 1..10
vector<int> m_cards_frequency_vec; // {1,1,1,1,1}, {2,1,1,1}, etc
vector<int> m_cards_value_vec; // {2, 3, ..., 14}
set<char> m_cards_suit_s; // {'S', 'H', 'C', 'D'}
vector<string> m_cards_name_vec; // {"QS", "QD", "AC", "AD", "4C"}
bool operator > (const PlayerHandRank& rank) const
{
if (m_rank_score == rank.m_rank_score)
{
return m_cards_value_vec > rank.m_cards_value_vec;
}
else
{
return m_rank_score > rank.m_rank_score;
}
}
};
class CardValue
{
public:
int m_card_value; // card value (m_cards_value_vec)
int m_card_frequency; // pair value (m_cards_frequency_vec)
bool operator > (const CardValue& cv) const
{
if (m_card_frequency == cv.m_card_frequency)
{
return m_card_value > cv.m_card_value;
}
else
{
return m_card_frequency > cv.m_card_frequency;
}
}
};
class PE0054
{
public:
PE0054();
void run_unit_test();
int getPlayer1WinHandsInPokerFile();
private:
vector<int> m_royal_flush_vec = { 14, 13, 12, 11, 10 };
//map<char, int> m_cardOrder_mp = { {'2',2},{'3', 3},{'4', 4},{'5', 5},{'6', 6},
//{'7',7}, {'8', 8},{'9', 9},{'T',10}, {'J', 11},{'Q', 12},{'K', 13},{'A', 14} };
map<char, int> m_cardOrder_mp;
vector<vector<int>> m_ranks_vec = {{1, 1, 1, 1, 1}, {2, 1, 1, 1}, {2, 2, 1},
{3, 1, 1}, {}, {}, {3, 2}, {4, 1}};
vector<vector<int>> m_straights_vec = { {14, 5, 4, 3, 2} };
PlayerHandRank getPlayerHandRankValues(vector<string>& handCards_vec);
bool checkPlayer1Win(PlayerHandRank& hand1, PlayerHandRank& hand2);
void parsePlayersHandPair (const string & hand_pair,
vector<string>& player1hand_cards,
vector<string>& player2hand_cards);
int getHandRankScore(PlayerHandRank &hand)
{
int score = 1;
for (auto v : m_ranks_vec)
{
if (hand.m_cards_frequency_vec == v)
{
break;
}
else
{
score++;
}
}
return score;
}
bool checkHandStraight(PlayerHandRank &hand)
{
for (auto v : m_straights_vec)
{
if (hand.m_cards_value_vec == v)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool checkHandFlush(PlayerHandRank &hand)
{
return (1 == hand.m_cards_suit_s.size());
}
void printVectorElements(vector<int> &vi)
{
int size = vi.size();
cout << "(";
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++)
{
cout << vi[i] << ", ";
}
cout << vi[size - 1] << ") ";
}
void printVectorElements(vector<string> &vs)
{
int size = vs.size();
cout << "(";
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++)
{
cout << "\"" << vs[i] << "\", ";
}
cout << "\"" << vs[size - 1] << "\") ";
}
};
PE0054::PE0054()
{
string cardsName = "23456789TJQKA";
for (int i = 2; i < 15; i++)
{
char c = cardsName[i - 2];
m_cardOrder_mp[c] = i;
}
vector<int> sv(5);
for (int i = m_cardOrder_mp['A']; i > m_cardOrder_mp['5']; i--)
{
// sv = {i, i-1, i-2, i-3, i-4}
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
sv[j] = i - j;
}
m_straights_vec.push_back(sv);
}
}
void PE0054::parsePlayersHandPair (const string & hand_pair,
vector<string>& player1_cards,
vector<string>& player2_cards)
{
string s(2, '0');
for (unsigned int k = 0, j = 0; k < hand_pair.size(); k++)
{
if (hand_pair[k] != ' ')
{
if (j < 5)
{
s[0] = hand_pair[k];
s[1] = hand_pair[k+1];
player1_cards[j] = s;
}
else
{
s[0] = hand_pair[k];
s[1] = hand_pair[k+1];
player2_cards[j-5] = s;
}
j++;
k++;
}
}
}
PlayerHandRank PE0054::getPlayerHandRankValues(vector<string>& handCards_vec)
{
PlayerHandRank PlayerHandRank;
map<char, int> cardsValue_mp;
char c;
PlayerHandRank.m_cards_name_vec = handCards_vec;
// "ASKD3DJD8H",
// cardsValue_mp = { {'A', 1}, {'K', 1}, {'3', 1}, {'J', 1}, {'8', 1} };
// PlayerHandRank.m_cards_suit_s = {'D', 'H', 'S'}
for (auto& v : handCards_vec)
{
c = v[0];
cardsValue_mp[c]++;
c = v[1];
PlayerHandRank.m_cards_suit_s.insert(c);
}
map<char, int>::iterator iter = cardsValue_mp.begin();
vector<CardValue> cv_vec;
CardValue cv;
while (iter != cardsValue_mp.end())
{
cv.m_card_value = m_cardOrder_mp[iter->first];
cv.m_card_frequency = iter->second;
cv_vec.push_back(cv);
iter++;
}
sort(cv_vec.begin(), cv_vec.end(), greater<CardValue>());
for (auto& x : cv_vec)
{
PlayerHandRank.m_cards_frequency_vec.push_back(x.m_card_frequency);
PlayerHandRank.m_cards_value_vec.push_back(x.m_card_value);
}
int score = getHandRankScore(PlayerHandRank);
if (true == checkHandStraight(PlayerHandRank))
{
score = 5; // straight
}
if (true == checkHandFlush(PlayerHandRank))
{
if (5 == score)
{
score = 9; // straight flush
}
else
{
score = 6; // flush
}
if (PlayerHandRank.m_cards_value_vec == m_royal_flush_vec)
{
score = 10; // Royal Flush
}
}
PlayerHandRank.m_rank_score = score;
return PlayerHandRank;
}
bool PE0054::checkPlayer1Win (PlayerHandRank& player1Rank,
PlayerHandRank& player2Rank)
{
#ifdef PE0054_DEBUG
printVectorElements(player1Rank.m_cards_name_vec);
cout << "Rank: " << player1Rank.m_rank_score << ", ";
printVectorElements(player1Rank.m_cards_value_vec);
cout << endl;
printVectorElements(player2Rank.m_cards_name_vec);
cout << "Rank: " << player2Rank.m_rank_score << ", ";
printVectorElements(player2Rank.m_cards_value_vec);
cout << endl;
#endif
return player1Rank > player2Rank;
}
void PE0054::run_unit_test()
{
struct _TestCase
{
string hand;
bool player1_win;
} TestCases [] = {
{"5H 5C 6S 7S KD 2C 3S 8S 8D TD", false},
{"5D 8C 9S JS AC 2C 5C 7D 8S QH", true},
{"2D 9C AS AH AC 3D 6D 7D TD QD", false},
{"4D 6S 9H QH QC 3D 6D 7H QD QS", true},
{"2H 2D 4C 4D 4S 3C 3D 3S 9S 9D", true},
{"6H 4H 5C 3H 2H 3S QH 5S 6S AS", true},
{"TS 8H 9S 6S 7S QH 3C AH 7H 8C", true},
{"6H 5D 7S 5H 9C 9H JH 8S TH 7H", false},
{"4C 4D 7H 7D QS 3C 3D AS 9S 9D", false},
{"4C 4D 7H 7D QS TD JD QD KD AD", false}
};
PlayerHandRank player1Rank, player2Rank;
vector<string> player1Cards(5), player2Cards(5);
int size = sizeof(TestCases) / sizeof(_TestCase);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
parsePlayersHandPair(TestCases[i].hand, player1Cards, player2Cards);
player1Rank = getPlayerHandRankValues(player1Cards);
player2Rank = getPlayerHandRankValues(player2Cards);
assert(TestCases[i].player1_win == \
checkPlayer1Win(player1Rank,player2Rank));
}
cout << size << " unit test cases are succesfully run." << endl;
}
int PE0054::getPlayer1WinHandsInPokerFile()
{
PlayerHandRank player1Rank, player2Rank;
vector<string> player1Cards(5), player2Cards(5);
char szBuf[32];
int player1_win_hands = 0;
ifstream in("p054_poker.txt");
if (!in) return 0;
while (in.getline(szBuf, 32))
{
parsePlayersHandPair (szBuf, player1Cards, player2Cards);
player1Rank = getPlayerHandRankValues(player1Cards);
player2Rank = getPlayerHandRankValues(player2Cards);
if (true == checkPlayer1Win(player1Rank, player2Rank))
{
#ifdef PE0054_DEBUG
cout << "Player 1 win"<<endl;
#endif
player1_win_hands++;
}
#ifdef PE0054_DEBUG
else
{
cout << "Player 2 win"<<endl;
}
#endif
}
in.close();
return player1_win_hands;
}
int main()
{
PE0054 pe0054;
#ifdef UNIT_TEST
pe0054.run_unit_test();
#else
int player1_win_hands = pe0054.getPlayer1WinHandsInPokerFile();
cout << "The file poker.txt contains 1000 random hands, and Player 1 wins ";
cout << player1_win_hands << " hands." << endl;
#endif
return 0;
}
Python 3.x 代码
import collections
def getHandRank(hand):
"""
High Card: (1,1,1,1,1) score value = 1
One Pair : (2,1,1,1) score value = 2
Two Pairs: (2,2,1) score value = 3
Three of a Kind: (3,1,1) score value = 4
Straight: () score value = 5
Flush: () score value = 6
Full House: (3,2) score value = 7
Four of a Kind: (4,1) score value = 8
Straight Flush: () score value = 9
Royal Flush: () score value = 10
"""
hand_strength_list = [(1,1,1,1,1),(2,1,1,1),(2,2,1),(3,1,1),(),(),(3,2),(4,1)]
cards_value_dict = {key:index for index,key in enumerate('23456789TJQKA', 2)}
straights_list = [(14, 5, 4, 3, 2)] # 'A' can also be used as 1
straights_list += [(v, v-1, v-2, v-3, v-4) for v in range(14, 5, -1)]
rank_score_tuple = [zip(*(sorted(((v, cards_value_dict[k]) \
for k,v in collections.Counter(x[0] for x in hand).items()),reverse=True)))]
rank_score_list = list(rank_score_tuple[0])
score_value = 1 + hand_strength_list.index(rank_score_list[0])
# check flush (6)
if len(set(card[1] for card in hand)) == 1: score_value = 6
# check straights (5) or straights flush (9)
if rank_score_list[1] in straights_list:
score_value = 9 if score_value == 6 else 5
# check royal flush (10)
if score_value == 9 and rank_score_list[1] == (14, 13, 12, 11, 10):
score_value = 10
# update rank_score_list[0] with score_value
rank_score_list[0] = score_value
#print(hand, 'Rank:', rank_score_list)
return rank_score_list
def main():
"""
['QS', 'QD', 'AC', 'AD', '4C'] Rank: [2, (14, 12, 4)]
['6S', '2D', 'AS', '3H', 'KC'] Rank: [0, (14, 13, 6, 3, 2)]
['4C', '7C', '3C', 'TD', 'QS'] Rank: [0, (12, 10, 7, 4, 3)]
['9C', 'KC', 'AS', '8D', 'AD'] Rank: [1, (14, 13, 9, 8)]
['AS', 'KD', '3D', 'JD', '8H'] Rank: [0, (14, 13, 11, 8, 3)]
['7C', '8C', '5C', 'QD', '6C'] Rank: [0, (12, 8, 7, 6, 5)]
"""
hands_pair = (line.split() for line in open('p054_poker.txt'))
print("The file poker.txt contains 1000 random hands, Player 1 wins ",end='')
print(sum(getHandRank(hand_pair[:5]) > getHandRank(hand_pair[5:]) \
for hand_pair in hands_pair))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Python 用类实现的代码 PokerGame.py
import collections
class PokerGame(object):
"""
Poker hands rank
"""
def __init__(self):
self.hand_strength_list = \
[(1,1,1,1,1),(2,1,1,1),(2,2,1),(3,1,1),(),(),(3,2),(4,1)]
self.cards_value_dict = \
{key: index for index, key in enumerate('23456789TJQKA', 2)}
self.straights_list = [(14, 5, 4, 3, 2)] # 'A' can also be used as 1
self.straights_list += \
[(v, v-1, v-2, v-3, v-4) for v in range(14, 5, -1)]
def getHandRank(self, hand):
"""
High Card: (1,1,1,1,1) score value = 1
One Pair : (2,1,1,1) score value = 2
Two Pairs: (2,2,1) score value = 3
Three of a Kind: (3,1,1) score value = 4
Straight: () score value = 5
Flush: () score value = 6
Full House: (3,2) score value = 7
Four of a Kind: (4,1) score value = 8
Straight Flush: () score value = 9
Royal Flush: () score value = 10
"""
rank_score_tuple = [zip(*(sorted(((v, self.cards_value_dict[k]) \
for k,v in collections.Counter(x[0] for x in hand).items()),reverse=True)))]
rank_score_list = list(rank_score_tuple[0])
score_value = 1 + self.hand_strength_list.index(rank_score_list[0])
# check flush (6)
if len(set(card[1] for card in hand)) == 1: score_value = 6
# check straights (5) or straights flush (9)
if rank_score_list[1] in self.straights_list:
score_value = 9 if score_value == 6 else 5
# check royal flush (10)
if score_value == 9 and rank_score_list[1] == (14, 13, 12, 11, 10):
score_value = 10
# update rank_score_list[0] with score_value
rank_score_list[0] = score_value
#print(hand, 'Rank:', rank_score_list)
return rank_score_list
def main():
"""
['QS', 'QD', 'AC', 'AD', '4C'] Rank: [2, (14, 12, 4)]
['6S', '2D', 'AS', '3H', 'KC'] Rank: [0, (14, 13, 6, 3, 2)]
['4C', '7C', '3C', 'TD', 'QS'] Rank: [0, (12, 10, 7, 4, 3)]
['9C', 'KC', 'AS', '8D', 'AD'] Rank: [1, (14, 13, 9, 8)]
['AS', 'KD', '3D', 'JD', '8H'] Rank: [0, (14, 13, 11, 8, 3)]
['7C', '8C', '5C', 'QD', '6C'] Rank: [0, (12, 8, 7, 6, 5)]
"""
pg = PokerGame()
hands_pair = (line.split() for line in open('p054_poker.txt'))
print("The file poker.txt contains 1000 random hands, Player 1 wins",end=' ')
print(sum(pg.getHandRank(hand_pair[:5]) > pg.getHandRank(hand_pair[5:]) \
for hand_pair in hands_pair))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()








 本文介绍了一种高效算法,用于判断扑克牌游戏中的手牌力量,通过量化手牌的组合,快速比较两位玩家的手牌大小,从而决定胜负。算法涵盖了从最高到最低级别的手牌类型,包括皇家同花顺、同花顺、四条、满堂红等,适用于多种扑克牌游戏场景。
本文介绍了一种高效算法,用于判断扑克牌游戏中的手牌力量,通过量化手牌的组合,快速比较两位玩家的手牌大小,从而决定胜负。算法涵盖了从最高到最低级别的手牌类型,包括皇家同花顺、同花顺、四条、满堂红等,适用于多种扑克牌游戏场景。
















 519
519

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








