1、背景*
:定义了HTML和CSS的格式和样式规则,旨在改善协作编码,代码质量和规范基本结构。 它适用于使用HTML和CSS 的源代码文件,也包括GSS文件。 只要代码质量是可以被维护的,就能很好的被工具混淆、压缩和合并。
2、通用
2.1、通用样式规则
对嵌入的资源尽可能使用HTTPS协议,总是使用HTTPS协议引入图像和其他媒体资源,样式表,脚本等,除非相关文件确实不在HTTPS服务器上。(HTTPS即在HTTP下加入SSL加密层)SSL证书是一种数字证书,他使用协议在浏览器和 Web 服务器之间建立一条安全通道,从而实现:1、 数据信息在客户端和服务器之间的加密传输,保证双方传递信息的安全性,不可被第三方窃听; 2、 用户可以通过服务器证书验证他所访问的网站是否真实可靠。
2.2、通用格式规则
2.2.1、缩进规则:一次使用两个空格缩进,不要使用TAb缩进或者混用tab和空格缩进。
2.2.2、大小写:所有代码只使用小写:适用于标签名,(标签的)属性及属性值(text/CDATA例外), CSS选择器,(CSS的)属性与属性值(字符串除外)。
2.2.3、尾随空格:一行代码中,尾随空格是多余的有可能引起代码混乱,务必去掉尾随空格。
2.3、通用meta规则
2.3.1、编码:确保你的编码器使用UTF_8编码,且不含字节顺序标记(BOM)。在HTML模板和文件中指定编码 。 不需要指定样式表的编码,它默认为UTF-8。
2.3.2、注释:尽可能的去解释释你的代码,注明它包括什么,它的目的是什么,它能做什么, 为什么使用这个解决方 案,还是说只是因为偏爱如此呢?(但本规则可选,没必要每份代码都描述的很充分,它会增重HTML和CSS的代码。这取决于该项目的复杂程度。)
2.3.3、活动的条目:用TODO标记待办事项和真正活动的条目,不要用其他的,如@ 待办事项@;附加联系人(用户名或电子邮件列表),用括号括起来,例如 TODO(联系人) ;可在冒号之后附加活动条目说明等,例如 TODO: 活动条目说明。

3、HTML
**3.1、**HTML代码规则
3.1.1、文档类型:使用HTML5,HTML5是所有HTML文档的首选;推荐使用HTML(text/html)而非XHTML(application/XHTML+xml)原因一是浏览器基础支持缺失,二是优化空间相比,HTML空间更小。虽然HTML很好,但不用关闭单元素。比如,使用
, 而不是
。
3.1.2、HTML合法性:使用合法的HTML标签,使用工具如W3C HTML validator 验证(自己的HTML代码是否合法)。使用合法的HTML标签是可被衡量的规范,有助于编码者学习的技术要求和限制,并保证HTML的正确使用性。
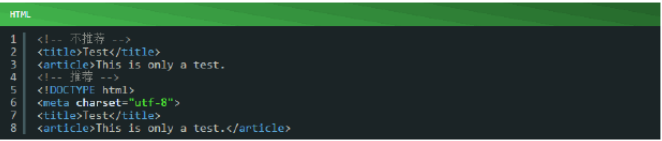
3.1.3、语义化:根据HTML各个元素的用途而去使用它们;使用元素 (有时候错称其为"标签") 要知道为什么去使用它们和是否正确。 例如,用heading元素构造标题, p 元素构造段落, a 元素构造锚点等;根据HTML各个元素的用途而去使用是很重要的,它涉及到文档的可访问性、重用和代码效率等问题。
3.1.4、多媒体后备方案:为多媒体提供备选内容;对于多媒体,如图像视频,和通过canvas读取的动画元素,确保提供备选方案;对于图像提供有意义的备选方案(alt)对于音频或视频使用有效的文案和副本来说明;提供原因:给盲人用户一些提示性文字,用alt告诉他这文案是关于什么,给没能理解视频和音频内容的用户一些提示。(图像的alt属性会产生冗余,如果使用图像只是为了不能立即使用css而装饰的就不需要用备选文案了,可使用alt=" ")
3.1.5、关注点分离:严格保持结构(标记),表现(样式),行为(脚本)分离,并让这三者之间的交互保持最低限度;确保文档和模板只包含HTML结构,把所有表现都放到样式表里,把所有的行为都放到脚本里。此外,尽量使脚本和样式表在文档模板中有最小接触面积,即减少外链;将表现和行为分开维护是很重要的,因为HTML文档结构和模板会比更新样式(css)和脚本(js)更花费时间。 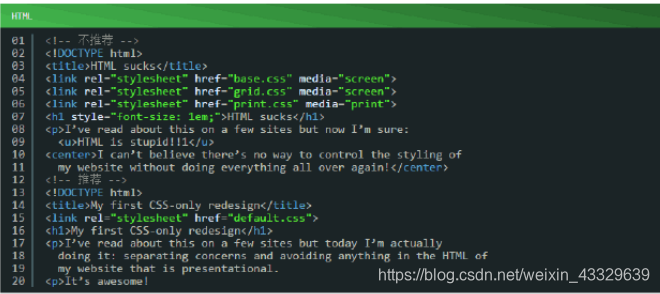
3.1.6、实体引用:不要用实体引用(HTML实体常用于生成那些键盘上没有的印刷字符,比如€、∞、≠、©等等;HTML实体以和号(&)开头,分号(;)结尾,两者之间表示实体的字符串(或数字))。
3.1.7、省略可选标签(可选择):哪些标签可省略参考 HTML5 specification(没必要省略所有可选标签)。
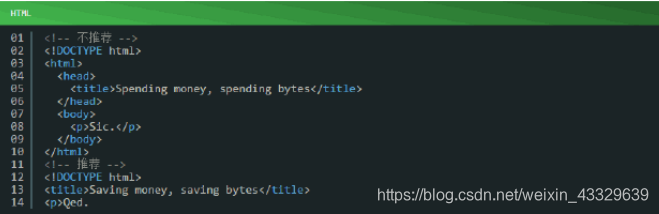
3.1.8、type属性:在样式表(css)和脚本(js)的标签中,不写type属性;HTML中默认type为type/css和type/JavaScript类型。
3.2、HTML代码格式规则
**3.2.1、**格式
每个块元素、列表元素或表格元素都独占一行,每个子元素都相对于父元素缩进。
独立元素的样式(as CSS allows elements to assume a different role per display property),将块元素列表元素或表格元素都放在新行。
另外,需要缩进块元素、列表元素或表格元素的子元素。
如果出现了列表项左右空文本节点问题,可以试试把所有的li元素放在同一行。
**3.2.2、**打破长行(可选)
虽然没有针对HTML的列限制建议,但如果想显著提高可读性,则可以考虑包装长行(即把一个很长的行写为两行);换行时每条延续线应至少比原始行缩进4个空格。
3.2.3、HTML引号
引用属性值时请使用双引号。在属性值周围使用double(“”)而不是单引号(’ ')。
Sign in
Sign in
4、CSS
4.1、CSS样式规则
4.1.1、css有效性
使用有效的css代码。除非是处理CSS校验器程序错误或者需要专有语法。
用类似 W3C CSS validator 这样的工具来进行有效性测试。
使用有效的CSS是重要的质量衡量标准,如果发现有的CSS代码没有任何效果的可以删除,确保CSS用法适当。
4.1.2、ID和class的命名
为Id和class取通用且有意义的名字。
应该从ID和class的名字上就能看出这元素是干嘛用的,而不是表象或模糊不清的命名。
应该优先考虑以这些元素具体目的来进行命名,这样他就最容易理解且最不容易改变。
通用名称可以加在兄弟元素都不特殊或没有个别意义的元素上,可以起名类似“helpers”这样的名字。
使用功能性或通用的名字会减少不必要的文档或模板修改。
/* Not recommended: meaningless不易理解,无意义 */
#yee-1901 {}
/* Not recommended: presentational 表达不具体*/
.button-green {}
.clear {}
/* Recommended: specific 明确详细*/
#gallery {}
#login {}
.video {}
/* Recommended: generic 通用(简短一点)/
.aux {}
.alt {}
4.1.3 ID and Class Name Style命名风格
Use ID and class names that are as short as possible but as long as necessary.非必要的情况下,ID和class的名称应该尽量简短。
Try to convey what an ID or class is about while being as brief as possible.简要传达ID或class是关于什么的。
Using ID and class names this way contributes to acceptable levels of understandability and code efficiency.使用ID和类名称可以提高可接受性可理解性和提高代码效率。
/ Not recommended /
#navigation {}不简短
.atr {}过于简短,不知道意思
/ Recommended /
#nav {}
.author {}
4.1.4 Type Selectors类型选择器
Avoid qualifying ID and class names with type selectors./避免使用类型选择器/
Unless necessary (for example with helper classes), do not use element names in conjunction with IDs or classes./非必要情况下(例如使用帮助程序类)不要使用元素标签名与ID和class进行组合/
Avoiding unnecessary ancestor selectors is useful for performance reasons./出于性能原因,避免使用不必要的父选择器很有用。/
/ Not recommended /
ul#example {}/使用了类型选择器/
div.error {}
/ Recommended /
#example {}
.error {}
4.1.5 Shorthand Properties属性缩写
Use shorthand properties where possible.写属性值的时候尽量使用缩写。
CSS offers a variety of shorthand properties (like font) that should be used whenever possible, even in cases where only one value is explicitly set.CSS很多属性都支持缩写,(如font)尽量使用缩写,甚至只设置一个值。
Using shorthand properties is useful for code efficiency and understandability.使用缩写可以提高代码的效率和方便理解。
/ Not recommended /
border-top-style: none;
font-family: palatino, georgia, serif;
font-size: 100%;
line-height: 1.6;
padding-bottom: 2em;
padding-left: 1em;
padding-right: 1em;
padding-top: 0;
/ Recommended */
border-top: 0;
font: 100%/1.6 palatino, georgia, serif;/缩写减少了代码浪费/
padding: 0 1em 2em; /padding:上 左 右 下/
4.1.6、 0 and Units
Omit unit specification after “0” values, unless required.省略0后面的单位。
Do not use units after 0 values unless they are required.非必要情况0后面不需要加单位的。
4.1.7、 Leading 0s零开头的小数
Omit leading “0”s in values省略0开头小数点前的0。.
Do not put 0s in front of values or lengths between -1 and 1.值或长度在-1与1之间的小数,小数前面的0可以忽略不写。
4.1.8、 Hexadecimal Notation十六进制
Use 3 character hexadecimal notation where possible.十六进制尽可能使用3个字符。
For color values that permit it, 3 character hexadecimal notation is shorter and more succinct.加颜色值时会用到它,使用3个字符的十六进制更短与简洁。
/* Not recommended /
color: #eebbcc;
/ Recommended */
color: #ebc;
4.1.9、 Prefixes前缀
Prefix selectors with an application-specific prefix (optional).选择器前加上特殊应用标识的前缀(可选)。
In large projects as well as for code that gets embedded in other projects or on external sites use prefixes (as namespaces) for ID and class names. Use short, unique identifiers followed by a dash.大型项目中最好在ID或class名字前加上这种标识型前缀(命名空间),使用短破折号链接。
Using namespaces helps preventing naming conflicts and can make maintenance easier, for example in search and replace operations.使用前缀可以防止命名冲突,方便维护,比如在搜索和替换操作上。
.adw-help {} /* AdWords /
#maia-note {} / Maia */
4.1.10、 ID and Class Name DelimitersID和class的命名定界符
Separate words in ID and class names by a hyphen.ID和class名字有多单词组合而成的用短破折号“-”分开。
Do not concatenate words and abbreviations in selectors by any characters (including none at all) other than hyphens, in order to improve understanding and scannability.别在选择器名字里用“-”以外的连接词(包括啥也没有),以增进对名字的理解和查找。
/* Not recommended: does not separate the words “demo” and “image” 没加“-”/
.demoimage {}
/ Not recommended: uses underscore instead of hyphen 用的下划线*/
.error_status {}
/* Recommended */
#video-id {}
.ads-sample {}
4.1.11、 Hacks
Avoid user agent detection as well as CSS “hacks”—try a different approach first.最好避免使用给死的CSS“hacks”——请尝试使用其他的解决办法。
It’s tempting to address styling differences over user agent detection or special CSS filters, workarounds, and hacks. Both approaches should be considered last resort in order to achieve and maintain an efficient and manageable code base. Put another way, giving detection and hacks a free pass will hurt projects in the long run as projects tend to take the way of least resistance. That is, allowing and making it easy to use detection and hacks means using detection and hacks more frequently—and more frequently is too frequently.虽然他很有诱惑力,可以当做用户代理检测或特殊的CSS过滤器,但它的行为太过频繁,会长期伤害项目的效率和代码管理,所以先找其他方法解决。
4.2 CSS Formatting Rules CSS代码格式规则
4.2.1 、 Declaration Order 声明顺序
Alphabetize declarations.依字母顺序进行声明
Put declarations in alphabetical order in order to achieve consistent code in a way that is easy to remember and maintain.都按字母顺序声明便于记忆和维护。
Ignore vendor-specific prefixes for sorting purposes. However, multiple vendor-specific prefixes for a certain CSS property should be kept sorted (e.g. -moz prefix comes before -webkit).忽略特定于供应商的前缀以进行排序。但是,应该对某个CSS属性的多个特定于供应商的前缀进行排序(例如-moz前缀在-webkit之前)。
background: fuchsia; border: 1px solid; -moz-border-radius: 4px; -webkit-border-radius: 4px; border-radius: 4px; color: black; text-align: center; text-indent: 2em;
4.2.2、 Block Content Indentation 代码块内容缩进
Indent all block content.缩进所有代码块({}之间)的内容。
Indent all block content, that is rules within rules as well as declarations, so to reflect hierarchy and improve understanding.缩进所有代码块内容,即规则和声明中的规则,以反映层次结构并提高理解。
@media screen, projection {
html {
background: #fff;
color: #444;
}
}
**4.2.3、** Declaration Stops 声明结束
Use a semicolon after every declaration.所有声明都要用“;”结尾
End every declaration with a semicolon for consistency and extensibility reasons.考虑到一致性和拓展性,请在每个声明尾部加上分号。
/* Not recommended /
.test {
display: block;
height: 100px
}
/ Recommended */
.test {
display: block;
height: 100px;
}
**4.2.4、** Property Name Stops 属性名结束
Use a space after a property name’s colon.在属性名冒号后加一个空格。
Always use a single space between property and value (but no space between property and colon) for consistency reasons.出于一致性的原因,在属性名和值之间加一个空字符(不是属性名和冒号之间)。
/* Not recommended /
h3 {
font-weight:bold;
}
/ Recommended */
h3 {
font-weight: bold;
}
**4.2.5、** Declaration Block Separation 声明块分离
Use a space between the last selector and the declaration block.在**最后一个选择器和声明块之间**使用**空格**。
Always use a single space between the last selector and the opening brace that begins the declaration block.始终在最后一个选择器和开始声明块的左大括号之间使用一个空格。
The opening brace should be on the same line as the last selector in a given rule.左大括号应该与给定规则中最后一个选择器位于同一行。(而不是像Java一样跳行)
/* Not recommended: missing space */
#video{
margin-top: 1em;
}
/* Not recommended: unnecessary line break /
#video
{
margin-top: 1em;
}
/ Recommended */
#video {
margin-top: 1em;
}
**4.2.6、** Selector and Declaration Separation 选择器和声明分离
Separate selectors and declarations by new lines.用新行分隔选择器和声明。
Always start a new line for each selector and declaration.始终为每个选择器和声明开始一个新行。
/* Not recommended /
a:focus, a:active {
position: relative; top: 1px;
}
/ Recommended */
h1,
h2,
h3 {
font-weight: normal;
line-height: 1.2;
}
4.2.7、 Rule Separation 规则分离
Separate rules by new lines.每个规则一个新行。
Always put a blank line (two line breaks) between rules.两规则之间隔行。
html {
background: #fff;
}
body {
margin: auto;
width: 50%;
**4.3 CSS Meta Rules CSS元数据规则**
**4.3.1、** Section Comments 注释部分
Group sections by a section comment (optional).按部分注释(可选)对部分进行分组。
If possible, group style sheet sections together by using comments. Separate sections with new lines.如果可能,请使用注释将样式表部分组合在一起。使用新行分隔部分。
/* Header */
#adw-header {}
/* Footer */
#adw-footer {}
/* Gallery */
.adw-gallery {}























 1104
1104

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








