Shell 是一个用 C 语言编写的程序,它是用户使用 Linux 的桥梁。Shell 既是一种命令语言,又是一种程序设计语言。
Shell 是指一种应用程序,这个应用程序提供了一个界面,用户通过这个界面访问操作系统内核的服务。
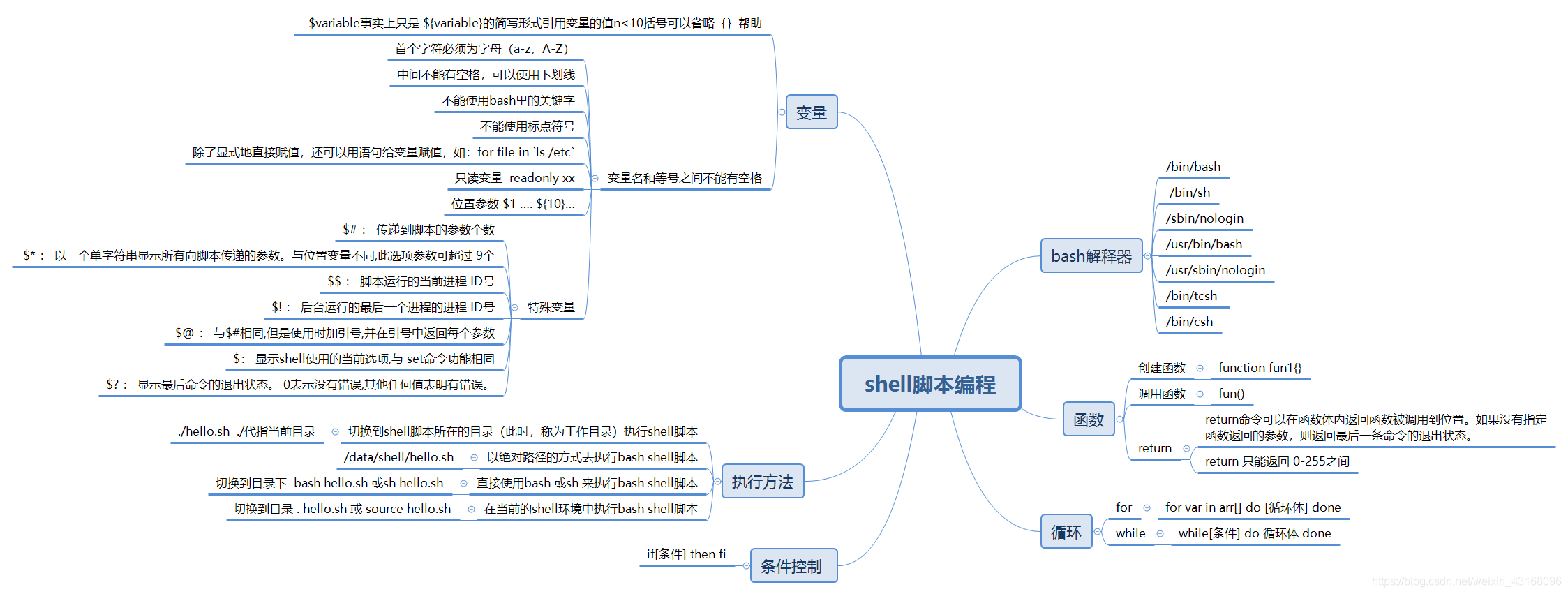
Shell 脚本(shell script),是一种为 shell 编写的脚本程序。
业界所说的 shell 通常都是指 shell 脚本,但shell 和 shell script 是两个不同的概念,本文出现的 “shell编程” 都是指 shell 脚本编程,不是指开发 shell 自身。
与所有的编程语言一致先编写第一个shell脚本
用vi/vim编辑器编写脚本如下
#!/bin/bash #指定bash解释器
echo “hello word” #主体部分,也是输出语句
保存.sh格式
执行脚本输出
hello word
前面提到shell不仅是编程语言,还是一种命令语言,它可以直接在脚本里执行命令。
#!/bin/bash
echo “hello word”
echo “the time is :” $(date)
执行脚本
[root@localhost ~]# sh 1
hello word
the time is : Wed Nov 14 06:57:42 EST 2018
当然除了系统内置的一些参数命令外,shell也可以自己定义
#!/bin/bash
echo “hello word”
date=$(date)
echo "the time is : $date "
执行脚本
[root@localhost ~]# sh 1
hello word
the time is : Wed Nov 14 06:57:42 EST 2018
同样也可以进行运算 bc支持浮点、scale浮点精确度
#!/bin/bash
var1=10
var2=20.23
result1=$(echo "scale=2; $var1 + var2"∣bc)result2=var2" | bc)
result2=var2"∣bc)result2=(echo "scale=2; $var1 - var2"∣bc)result3=var2" | bc)
result3=var2"∣bc)result3=(echo "scale=2; $var1 * var2"∣bc)result4=var2" | bc)
result4=var2"∣bc)result4=(echo “scale=2; $var1 / $var2” | bc)
echo The result is $result1
echo The result is $result2
echo The result is $result3
echo The result is $result4
执行脚本
[root@localhost ~]# sh 1
The result is 30.23
The result is -10.23
The result is 202.30
The result is .49
shell判断语句,if[条件] then fi 或者 if[条件] then else fi
#!/bin/bash
value1=10
value2=11
if [ $value1 -gt 5 ]
then
echo “The value $value1 is greater than 5”
fi
if [ $value1 -eq $value2 ]
then
echo “The values are equal”
else
echo “The values are different”
fi
循环for (()) do done
#!/bin/bash
for ((i=1;i<=9;i++))
do
for ((j=1;j<i;j++))
do
echo -e “i∗i*i∗j=[[[i*$j]\t\c”
done
echo
done
输出
[root@localhost ~]# sh 1
21=2
31=3 32=6
41=4 42=8 43=12
51=5 52=10 53=15 54=20
61=6 62=12 63=18 64=24 65=30
71=7 72=14 73=21 74=28 75=35 76=42
81=8 82=16 83=24 84=32 85=40 86=48 87=56
91=9 92=18 93=27 94=36 95=45 96=54 97=63 98=72
break、continue
#!/bin/bash
for var1 in 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
do
if [ $var1 -eq 5 ]
then
break
fi
echo “Iteration number: $var1”
done
echo “The for loop is completed”
执行结果:
[root@localhost ~]# sh 1
Iteration number: 1
Iteration number: 2
Iteration number: 3
Iteration number: 4
The for loop is completed
#!/bin/bash
for var1 in 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
do
if [ $var1 -eq 5 ]
then
continue
fi
echo “Iteration number: $var1”
done
echo “The for loop is completed”
执行结果
[root@localhost ~]# sh 1
Iteration number: 1
Iteration number: 2
Iteration number: 3
Iteration number: 4
Iteration number: 6
Iteration number: 7
Iteration number: 8
Iteration number: 9
Iteration number: 10
The for loop is completed
读参#shell会将一些位置参数的 特殊变量输入到命令行中的所有参数 #位置参数的标准表示,$0是程序名,$1是第一个参数,$2是第二个参数,依次类推,直到$9
#!/bin/bash
factorial=1
for (( number = 1; number <= 1;number++))dofactorial=1 ; number++ ))
do
factorial=1;number++))dofactorial=[ $factorial * $number ]
done
echo The factorial of $1 is $factorial
执行结果:[root@localhost ~]# sh 1 3
The factorial of 3 is 6
#!/bin/bash
total=$[ $1 * $2 ]
echo The first parameter is $1.
echo The second parameter is $2.
echo The total value is $total.
执行结果
[root@localhost ~]# sh 1 3 4
The first parameter is 3.
The second parameter is 4.
The total value is 12.
#bash shell为此提供了read命令 #read命令从标准输入(键盘)或另一个文件描述符中接受输入。在收到输入后,read命令会将数据放进一个变量
#!/bin/bash
echo -n "Enter your name: " #-n不会在字符串末尾换行
read name
echo "Hello $name, welcome to my program. "
执行结果:
[root@localhost ~]# sh 1
Enter your name: linux
Hello linux, welcome to my program.
函数function:
#!/bin/bash
function fun
{
echo “this is function”
}
fun
执行结果:this is function




 本文介绍Shell作为Linux用户操作系统的桥梁,不仅是一种命令语言,也是一种程序设计语言。文章详细讲解了Shell脚本的基础,包括如何编写和执行第一个脚本,以及如何在脚本中执行命令、进行运算、使用判断和循环语句等。
本文介绍Shell作为Linux用户操作系统的桥梁,不仅是一种命令语言,也是一种程序设计语言。文章详细讲解了Shell脚本的基础,包括如何编写和执行第一个脚本,以及如何在脚本中执行命令、进行运算、使用判断和循环语句等。
















 3万+
3万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








