2.3.3. 杂波的时空相关性
2.3.3. Temporal and SpatialCorrelation of Clutter
杂波在时间上的去相关是由杂波内部运动引起的,例如树叶在风中或海面波浪中运动,以及杂波和目标的雷达目标几何结构的变化。
Clutter decorrelationin time is induced by internal motion for clutter, such as tree leaves movingin the wind or waves on the sea surface, and by changes in radar targetgeometry for both clutter and targets.
各方面的研究人员已经在实验上描述了由内部运动引起的杂波回波的去相关特性,或它们的等效功率谱。
Various investigatorshave experimentally characterized the decorrelation characteristics of clutterechoes due to internal motion, or equivalently, their power spectrum.
例如,建议用于估算带叶树木或雨水的RCS功率谱的模型使用了下面的三次谱表达式:
For example, onemodel suggested to estimate the power spectrum of the RCS of foliated trees orrain uses a cubic spectrum (Currie, 2010):

转折频率Fc是波长、风速(对于树林)或降雨率(对于雨水)的函数。
The corner frequencyFc is a function of the wavelength and either wind speed (for trees)or rain rate (for rain).
表2.7给出了一些测量样本值。
Some sample measuredvalues are given in Table 2.7.
Table 2.7. 雨和树杂波的三次方功率谱转折频率(Hz)Cubic PowerSpectrum Corner Frequencies (Hz) for Rain and Tree Clutter
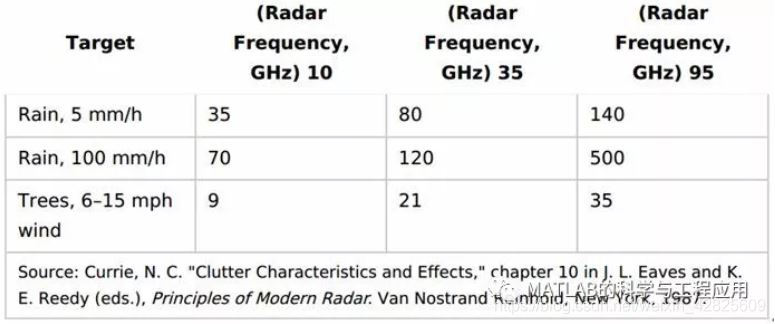
较高的转折频率(较宽的功率谱)意味着较短的去相关间隔(较窄的自相关函数)。
A higher cornerfrequency (wider power spectrum) implies a shorter decorrelation interval(narrower autocorrelation function).
较短的去相关时间使杂波信号更像白噪声,从而降低第5章中某些杂波抑制技术的有效性。
Shorter decorrelationtimes render the clutter signals more like white noise and degrade theeffectiveness of some of the clutter suppression techniques of Chap. 5.
注意,对于给定的天气条件,杂波在较高的雷达频率下会更快地去相关。(意味着高频段雷达的杂波白化比较严重!!!)
Notice that for agiven weather condition, the clutter decorrelates more rapidly at higher radarfrequencies.
图2.23绘制了风吹树木的杂波数据,这些数据也显示了杂波运动和雷达频率的增加使得去相关时间减少。
Figure 2.23 plotsadditional windblown tree clutter data that also show the decrease indecorrelation time for both increased clutter motion and increased radarfrequency.
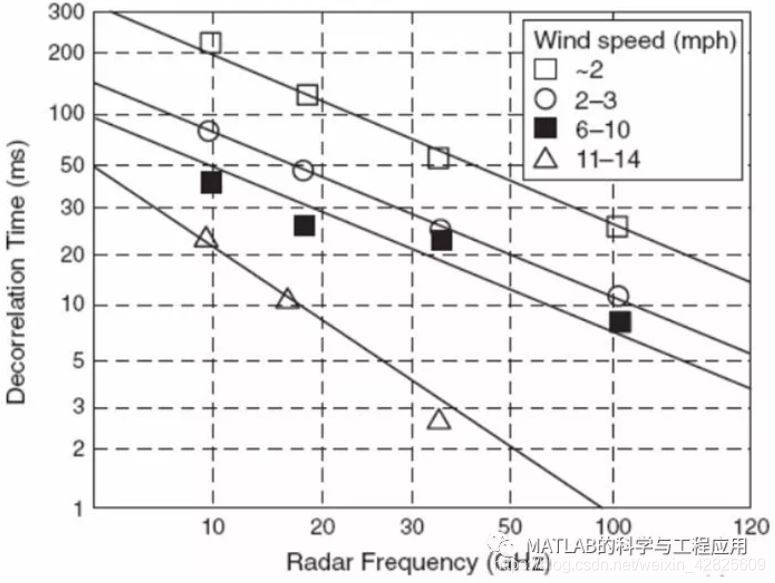
Figure 2.23. 风吹树木的杂波去相关时间与频率和风速的关系Decorrelation time of windblown tree clutter versus frequency andwind speed. [Data from Currie (2010)]
——本文译自Mark A. Richards所著的《Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing(Second edition)》
更多精彩文章请关注微信号:




 本文探讨了杂波在时间和空间上的相关性,解释了杂波内部运动如何导致杂波回波的去相关特性,包括树叶在风中或海面波浪的运动,以及雷达目标几何结构变化的影响。研究了不同条件下杂波的功率谱和去相关时间,指出在较高雷达频率下,杂波更快去相关,这将影响某些杂波抑制技术的效果。
本文探讨了杂波在时间和空间上的相关性,解释了杂波内部运动如何导致杂波回波的去相关特性,包括树叶在风中或海面波浪的运动,以及雷达目标几何结构变化的影响。研究了不同条件下杂波的功率谱和去相关时间,指出在较高雷达频率下,杂波更快去相关,这将影响某些杂波抑制技术的效果。
















 1395
1395

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








