“负责”的进程等待
什么是进程等待?
进程等待就是父进程等待子进程结束并退出,然后回收子进程。
为什么要进行进程等待?
- 如果子进程退出,父进程不对子进程做出处理的话,就会造成僵尸进程,那么这个时候只要父进程不退出,那么子进程一直占用资源,就会造成内存泄漏。并且僵尸进程不可以被信号终止掉。这个问题是非常严重的。
- 子进程退出保持僵尸进程状态是为了返回信息让父进程回收,所以进程等待也可以回收子进程的退出信息,说白了就是父进程派给子进程的干的事情,干完了结果是什么,这就是为什么要回收子进程的原因之一。
- 父进程通过进程等待的方式,回收子进程资源,获取子进程信息。
进程等待的方法:
-
pid_t wait(int *status),包含在头文件#include <sys/wait.h>里面-
wait(int *status)这个调用是阻塞式等待,就是说如果父进程走到这里,如果有子进程,则必须等到子进程退出才会结束,并且返回子进程的pid。如果没有子进程,就会返回-1。来看个例子:#include <iostream> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <unistd.h> int main(void) { std::cout << "Process Wait Test" << std::endl; pid_t ret = fork(); if (ret == 0)//child { std::cout << "I am child, And my id is : " << getpid() << std::endl; sleep(1); exit(1); } pid_t ret1 = wait(NULL); std::cout << "I am parent, And my id is : " << getpid() << std::endl; std::cout << "Waited for " << ret1 << " process." << std::endl; ret1 = wait(NULL); std::cout << "Waited for " << ret1 << " process." << std::endl; return 0; }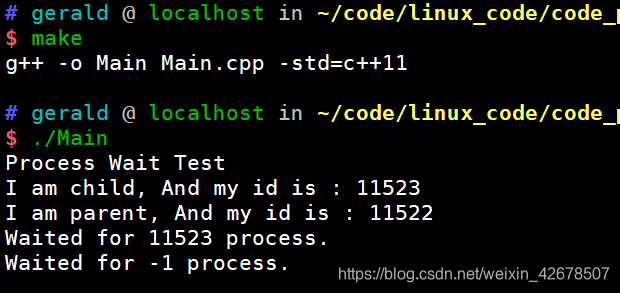
可以看出,父进程从
wait(NULL)处开始等待,等子进程结束在继续执行。然后若没有子进程则返回-1。 -
wait(NULL)是等待任意一个进程。 -
wait(NULL)的调用次数必须和子进程一致,不然会造成僵尸进程。#include <iostream> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <unistd.h> int main(void) { std::cout << "Process Wait Test" << std::endl; pid_t ret = fork(); if (ret == 0)//child { std::cout << "I am child, And my id is : " << getpid() << std::endl; sleep(1); exit(1); } pid_t ret1 = fork(); if (ret1 == 0)//child { std::cout << "I am child, And my id is : " << getpid() << std::endl; sleep(1); exit(1); } pid_t ret2 = wait(NULL); std::cout << "I am parent, And my id is : " << getpid() << std::endl; std::cout << "Waited for " << ret2 << " process." << std::endl; while(1) { } return 0; }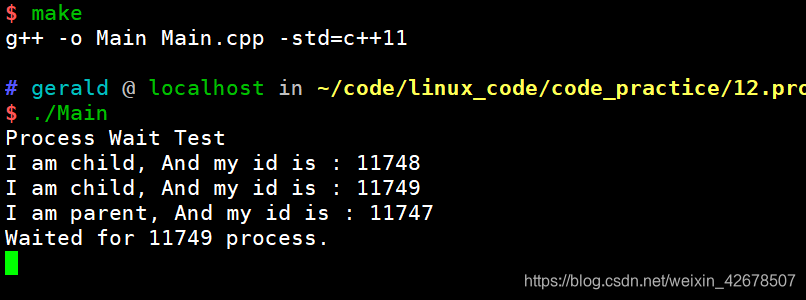
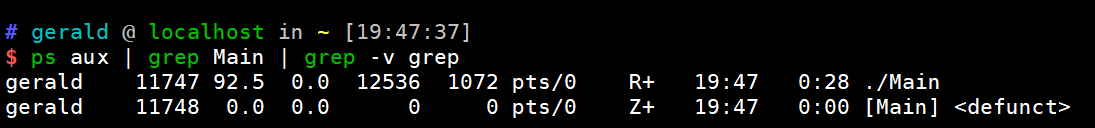
若父进程只调用一次
wait(NULL),则有一个进程不会被回收。 -
wait(int *status)的参数表示退出码+是否正常退出。如果不关心退出码或是否正常退出,就跟我上面一样,填NULL。下面再讲。
-
-
pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *status, int option)这个调用除了上面的功能外还加了一些功能。-
返回值:
- 若正常调用正常,返回子进程的
pid。 - 若没有等到子进程(下面搭配选项说),返回0。
- 若调用出错(就是没有子进程),返回-1。
- 若正常调用正常,返回子进程的
-
参数:
pid:pid= -1 跟wait(NULL)一样,等待任意一个进程。pid= 某个子进程的pid,表示等待指定子进程。
status:- WIFEXITED(status): 若为正常终止子进程返回的状态,则为真。(查看进程是否是正常退出)
- WEXITSTATUS(status): 若WIFEXITED非零,提取子进程退出码。(查看进程的退出码)
option:- WNOHANG:若
pid指定的子进程没有结束,则waitpid()函数返回0,不予以等待。若正常结束,则返回该子进程的ID。这个是非阻塞等待。所以这个选项经常搭配循环使用,称为轮询。 - 0: 阻塞等待。
- WNOHANG:若
#include <iostream> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <unistd.h> int main(void) { std::cout << "Process Wait Test" << std::endl; pid_t ret = fork(); if (ret == 0)//child { std::cout << "I am child, And my id is : " << getpid() << std::endl; sleep(1); exit(1); } pid_t ret1 = fork(); if (ret1 == 0)//child { std::cout << "I am child, And my id is : " << getpid() << std::endl; sleep(1); exit(1); } pid_t ret2; while (1) { ret2 = waitpid(ret, NULL, WNOHANG); if (ret2 != 0) break; } std::cout << "I am parent, And my id is : " << getpid() << std::endl; std::cout << "Waited for " << ret2 << " process." << std::endl; pid_t ret3; while (1) { ret3 = waitpid(ret1, NULL, WNOHANG); if (ret3 != 0) break; } std::cout << "I am parent, And my id is : " << getpid() << std::endl; std::cout << "Waited for " << ret3 << " process." << std::endl; return 0; }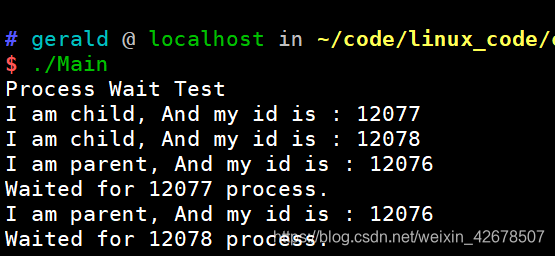
-
-
获取子进程status
-
这是一个整型变量,但是系统只用它的低16位,也就是说,
status这个整数只有低两个字节有用。 -
次八位是退出码,第七位是终止信号,第八位是表示是否吐核(core dump)。
-
我们来画个图理解一下:
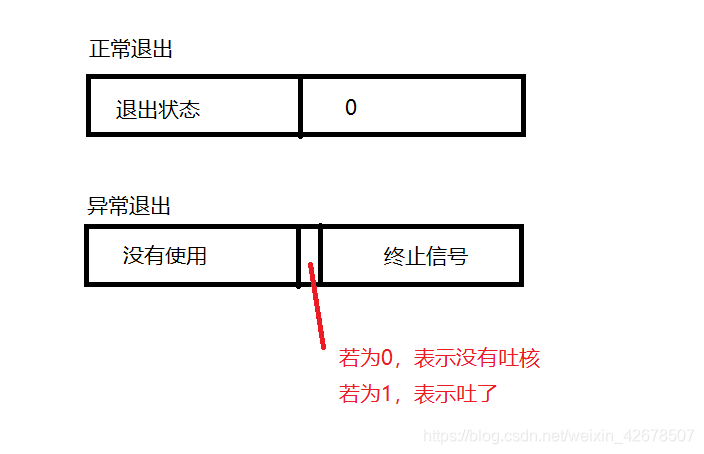
如果子进程正常退出,也就是说第八位为0时,这个时候才会用到次八位表示子进程的退出状态。
如果子进程异常退出,那么次八位就不需要了,因为异常退出退出码是多少就没人关心了,就看看是什么信号终止的它。
正常退出:
#include <iostream> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <unistd.h> int main(void) { std::cout << "Process Wait Test" << std::endl; pid_t ret = fork(); if (ret == 0)//child { std::cout << "I am child, And my id is : " << getpid() << std::endl; sleep(1); exit(1); } int status; int ret1 = wait(&status); std::cout << "I am parent, And my id is : " << getpid() << std::endl; std::cout << "Waited for " << ret1 << " process." << std::endl; if ((status & 0xff) == 0) { status >>= 8; std::cout << ret1 << " process exit code is :" << (status & 0xff) << std::endl; } else { std::cout << ret1 << " process exit exception, and the signal is : " << (status & 0x7f) << std::endl; } return 0; }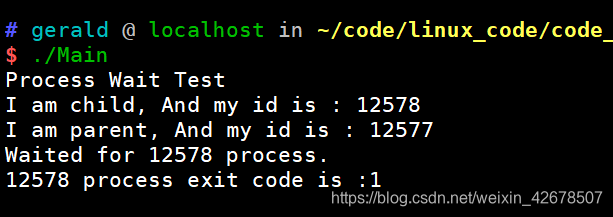
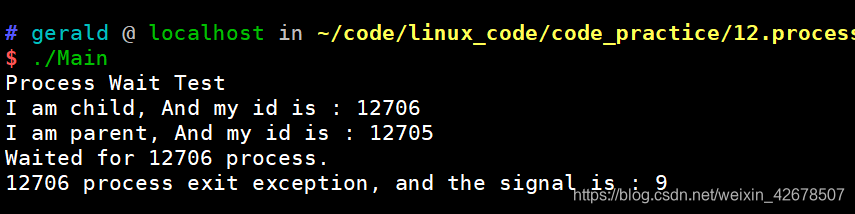
异常退出:(手动 kill 掉子进程)
#include <iostream> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <unistd.h> int main(void) { std::cout << "Process Wait Test" << std::endl; pid_t ret = fork(); if (ret == 0)//child { std::cout << "I am child, And my id is : " << getpid() << std::endl; sleep(100); exit(1); } int status; int ret1 = wait(&status); std::cout << "I am parent, And my id is : " << getpid() << std::endl; std::cout << "Waited for " << ret1 << " process." << std::endl; if ((status & 0xff) == 0) { status >>= 8; std::cout << ret1 << " process exit code is :" << (status & 0xff) << std::endl; } else { std::cout << ret1 << " process exit exception, and the signal is : " << (status & 0x7f) << std::endl; } return 0; }
-
总结:
进程等待是一件非常重要且非常必要的事情,一定要正确的使用进程等待的系统调用。
叮~?





 本文深入解析了进程等待的概念,包括父进程为何需要等待子进程、如何避免僵尸进程的产生,以及如何正确使用wait和waitpid系统调用来回收子进程资源和获取其退出信息。通过实例演示了阻塞和非阻塞等待的区别。
本文深入解析了进程等待的概念,包括父进程为何需要等待子进程、如何避免僵尸进程的产生,以及如何正确使用wait和waitpid系统调用来回收子进程资源和获取其退出信息。通过实例演示了阻塞和非阻塞等待的区别。
















 134
134

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








