Java Programming中的Point2D类
课本上的内容是这样的
import java.util.Scanner;
import javafx.geometry.Point2D;
public class TestPoint2D {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter point1's x-, y-coordinates:");
double x1 = input.nextDouble();
double y1 = input.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Enter point2' s x-, y-coordinates:");
double x2 = input.nextDouble();
double y2 = input.nextDouble();
Point2D p1 = new Point2D(x1, y1);
Point2D p2 = new Point2D(x2, y2);
System.out.println("p1 is " + p1.toString());
System.out.println("p2 is " + p2.toString());
System.out.println("The distance between pi and p2 is" + p1.distance(p1);
}
}
在eclipse中编译报错,

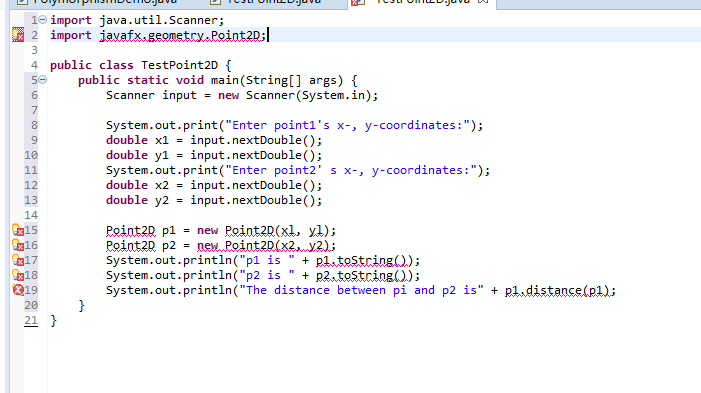
不仅Point2D类不能实例化,声明都不可以
这是怎么回事呢,经过多次试验,终于发现了问题所在,将上面的导入类javafx.geometry.Point2D换成java.awt.geom.Point2D;
此时便解决了声明问题,但是还是无法实例化。
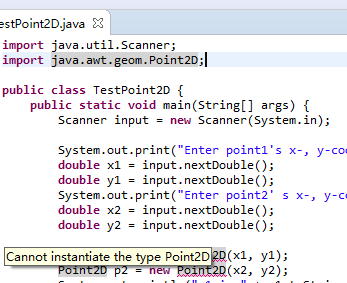
我找到了java的jdk中的文件
package java.awt.geom;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* The <code>Point2D</code> class defines a point representing a location
* in {@code (x,y)} coordinate space.
* <p>
* This class is only the abstract superclass for all objects that
* store a 2D coordinate.
* The actual storage representation of the coordinates is left to
* the subclass.
*
* @author Jim Graham
* @since 1.2
*/
public abstract class Point2D implements Cloneable {
/**
* The <code>Float</code> class defines a point specified in float
* precision.
* @since 1.2
*/
public static class Float extends Point2D implements Serializable {
/**
* The X coordinate of this <code>Point2D</code>.
* @since 1.2
* @serial
*/
public float x;
/**
* The Y coordinate of this <code>Point2D</code>.
* @since 1.2
* @serial
*/
public float y;
/**
* Constructs and initializes a <code>Point2D</code> with
* coordinates (0, 0).
* @since 1.2
*/
public Float() {
}
/**
* Constructs and initializes a <code>Point2D</code> with
* the specified coordinates.
*
* @param x the X coordinate of the newly
* constructed <code>Point2D</code>
* @param y the Y coordinate of the newly
* constructed <code>Point2D</code>
* @since 1.2
*/
public Float(float x, float y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
它的构造函数中有Double, Float,使用的时候只需要用相应的构造函数。。
/** Float type */
System.out.print("Enter point1's x-, y-coordinates:");
float x1 = input.nextFloat();
float y1 = input.nextFloat();
System.out.print("Enter point2' s x-, y-coordinates:");
float x2 = input.nextFloat();
float y2 = input.nextFloat();
Point2D p1 = new Point2D.Float(x1,y1);
Point2D p2 = new Point2D.Float(x2, y2);
/** Double type */
System.out.print("Enter point1's x-, y-coordinates:");
double x1 = input.nextDouble();
double y1 = input.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Enter point2' s x-, y-coordinates:");
double x2 = input.nextDouble();
double y2 = input.nextDouble();
Point2D p1 = new Point2D.Double(x1,y1);
Point2D p2 = new Point2D.Double(x2, y2);
这样就解决了问题,TestPoint2D类就搞定了,以下是完整代码
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.awt.geom.Point2D;
public class TestPoint2D {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Scanner
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter point1's x-, y-coordinates:");
double x1 = input.nextDouble();
double y1 = input.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Enter point2' s x-, y-coordinates:");
double x2 = input.nextDouble();
double y2 = input.nextDouble();
Point2D p1 = new Point2D.Double(x1,y1);
Point2D p2 = new Point2D.Double(x2, y2);
System.out.println("p1 is " + p1.toString());
System.out.println("p2 is " + p2.toString());
System.out.println("The distance between pi and p2 is" + p1.distance(p1));
}
}
运行结果如下
Enter point1’s x-, y-coordinates: 2.5 7
Enter point2’ s x-, y-coordinates:3.5 12
p1 is Point2D.Double[2.5, 7.0]
p2 is Point2D.Double[3.5, 12.0]
The distance between p1 and p2 is 5.0990195135927845
以上就是解决问题的全部过程,如果有幸被您看到,非常感谢指正(qiaoguangtong_1@126.com)







 博客围绕Java Programming中的Point2D类展开。在eclipse编译时,该类声明和实例化均报错。经试验,将导入类换成java.awt.geom.Point2D解决了声明问题,通过使用jdk文件中构造函数含Double、Float的相应构造函数,解决了实例化问题,并给出运行结果。
博客围绕Java Programming中的Point2D类展开。在eclipse编译时,该类声明和实例化均报错。经试验,将导入类换成java.awt.geom.Point2D解决了声明问题,通过使用jdk文件中构造函数含Double、Float的相应构造函数,解决了实例化问题,并给出运行结果。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








