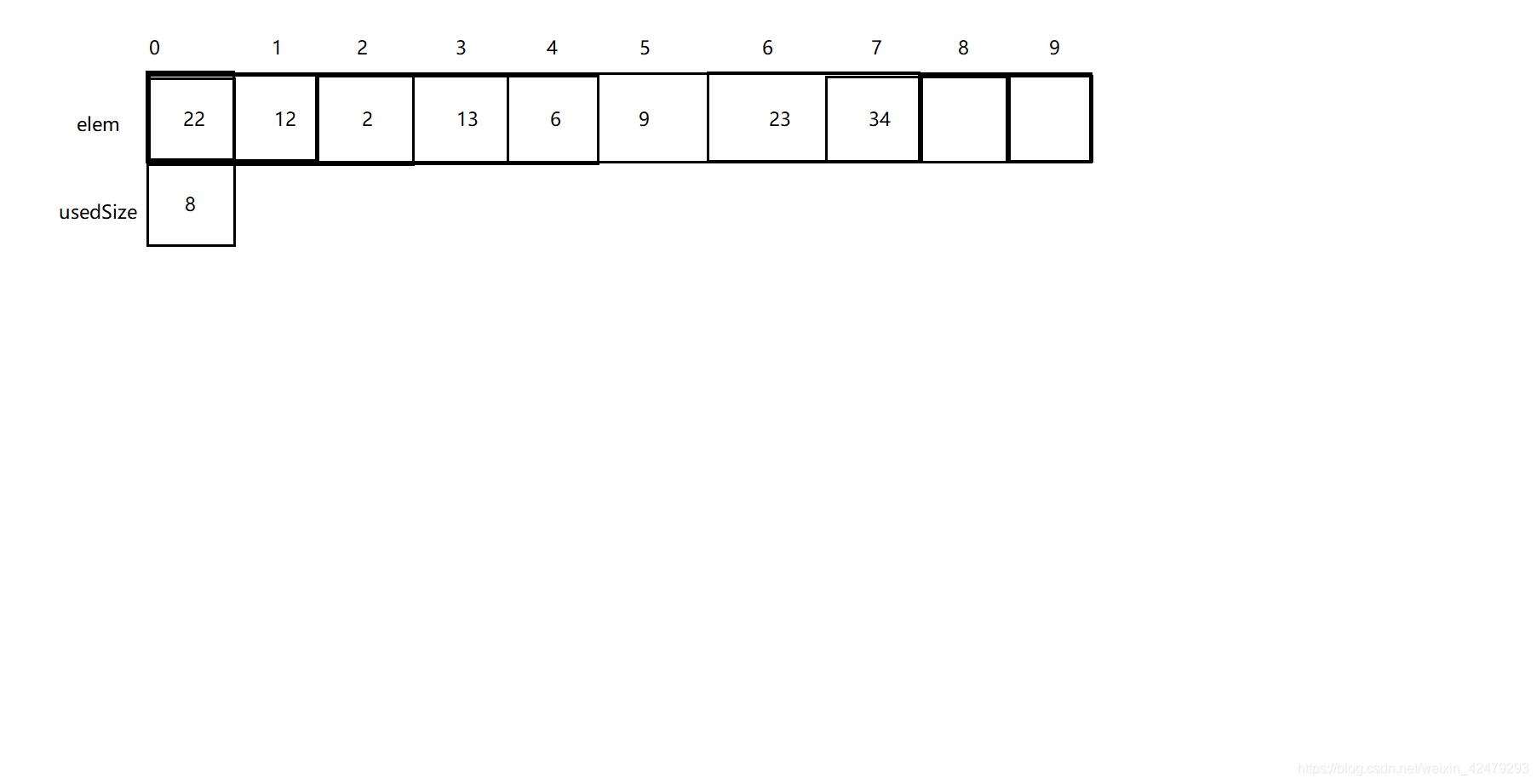
一、顺序存储结构
把数据放在地址连续的存储单元里,其数据间的逻辑关系和物理关系是一致的。
(一)
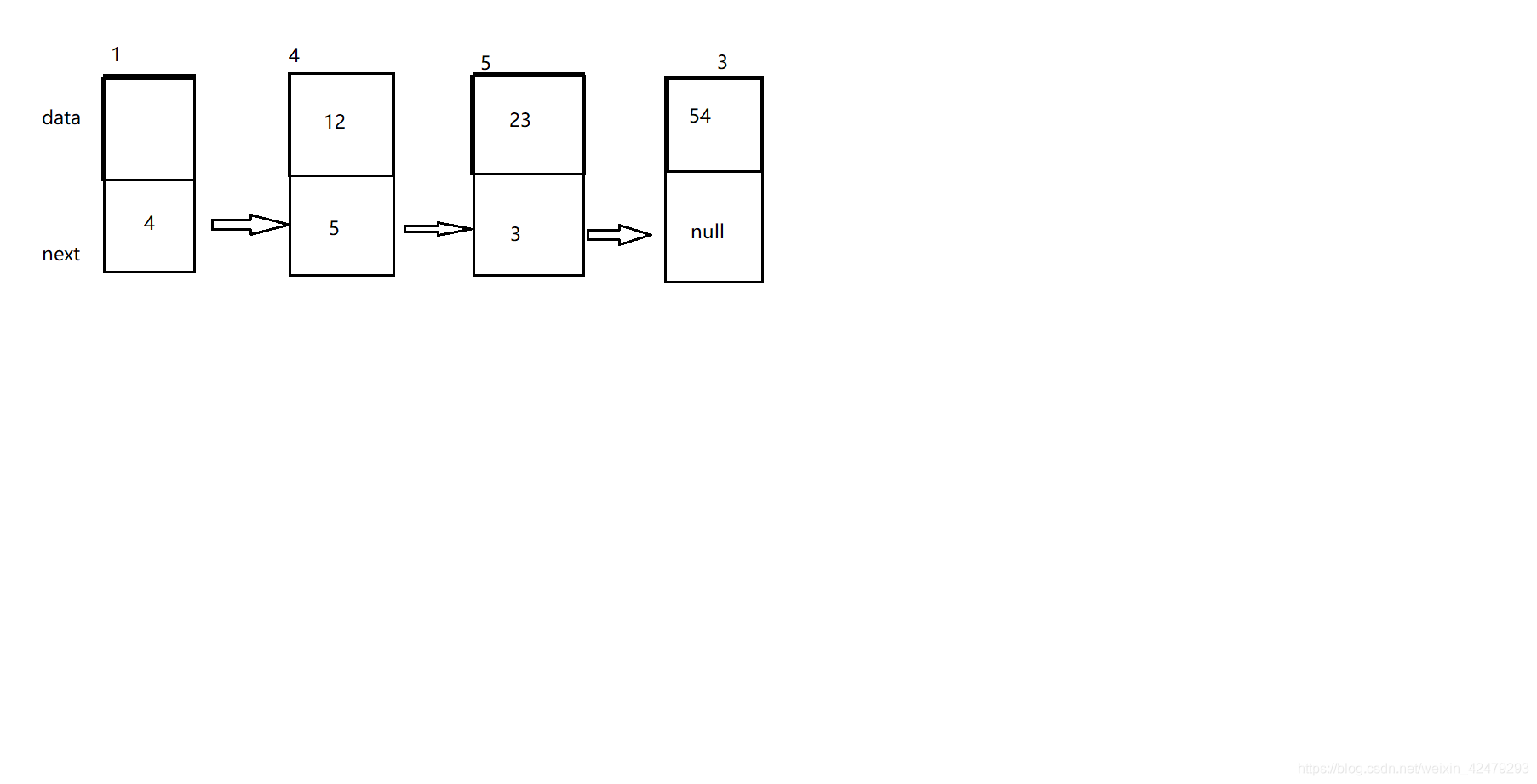
数据域:存储数据元素信息的域。
指针域:存储直接后继的域。指针域中存储的信息称为指针或链。
结点:由数据域和指针域组成数据元素的存储影像。
链表:n个结点链接成一个链表。
头指针:链表中第一个结点的存储位置。整个链表的存取必须是从头指针开始进行。
尾指针:线性链表的最后一个结点为“空”(NULL)。
头结点:在单链表的第一个结点前设置的一个结点。头结点的数据域可以不存储任何信息,也可以存储线性表的长度等附加信息,头结点的指针域存储指向第一个结点的指针。
(二)头指针和头结点的异同:
头指针:
(1)头指针是指链表指向第一个结点的指针,若链表有头结点,头指针则是指向头结点的指针。
(2)头指针具有标识作用,所以常用头指针冠以链表的名字。
(3)无论链表是否为空,头指针都不为空。头指针是链表的必要元素。
头结点:
(1)头结点是为了操作的统一和方便而设立的。
(2)有了头结点,对在大一元素结点前插入结点和删除第一结点的操作就和其他结点的操作就统一了。
(3)头结点不一定是链表的必须要素。
注:若线性表为空表,则头结点的指针域为“空”。
二、链式存储结构
把数据放在任意的存储单元里,这组数据可连续,也可以不连续。
单链表:每个结点中只包含一个指针域的链表。通过每个结点的指针域将线性表的数据元素按其逻辑次序链接在一起。
三、单链表的实现
class TestLink{
class Entry{
int data;
Entry next;
//构造函数
public Entry(){//头结点
this.data = -1;
this.next = null;
}
public Entry(int val){//数据节点
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
private Entry head;
//构造函数
public TestLink(){//头结点
this.head = new Entry();
}
}
四、单链表的基本操作
(一)插入
1、头插法
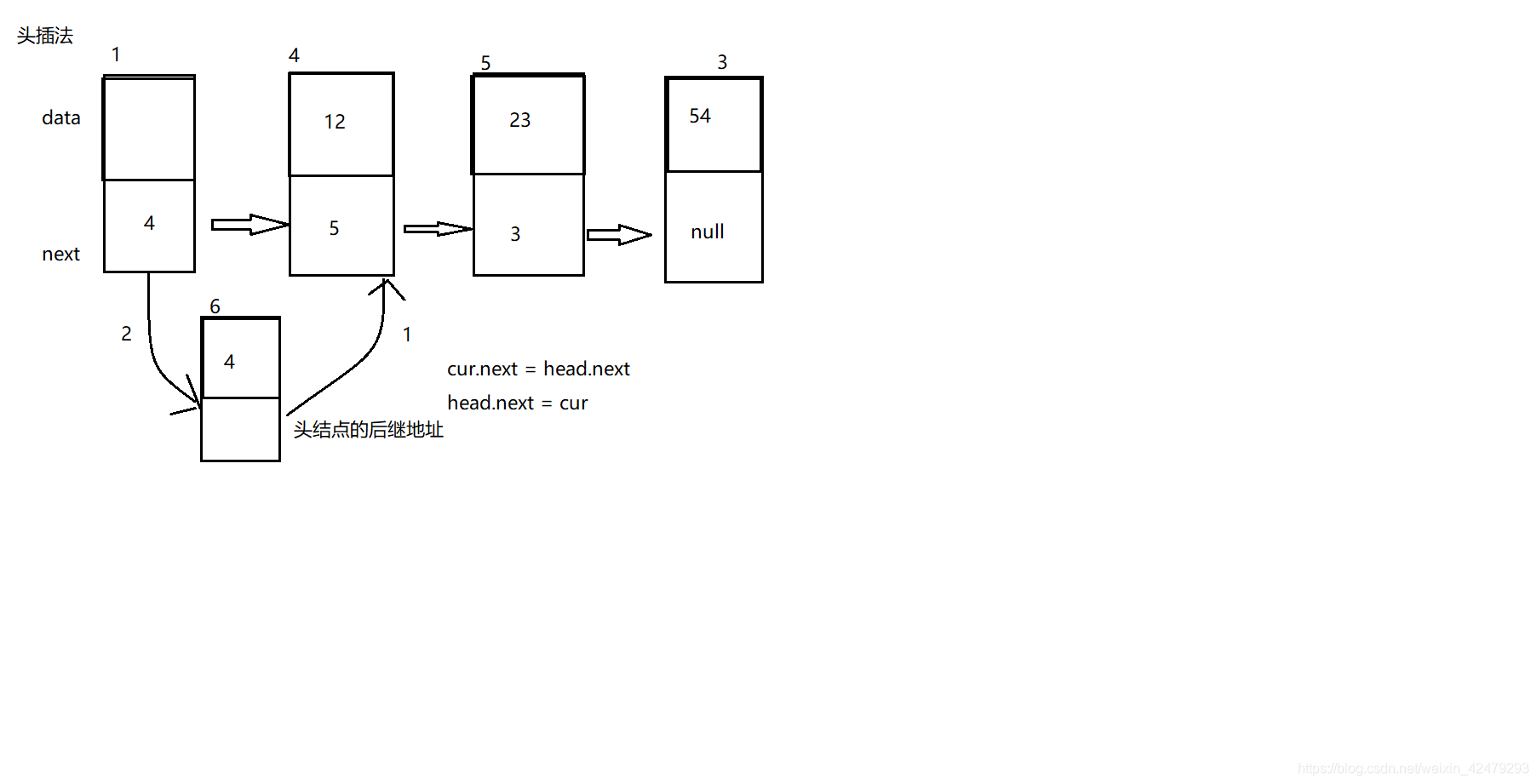
//头插法 插入数据
public void insertHead(int val){
Entry cur = new Entry(val);
cur.next = this.head.next;
this.head.next = cur;
}
2、尾插法
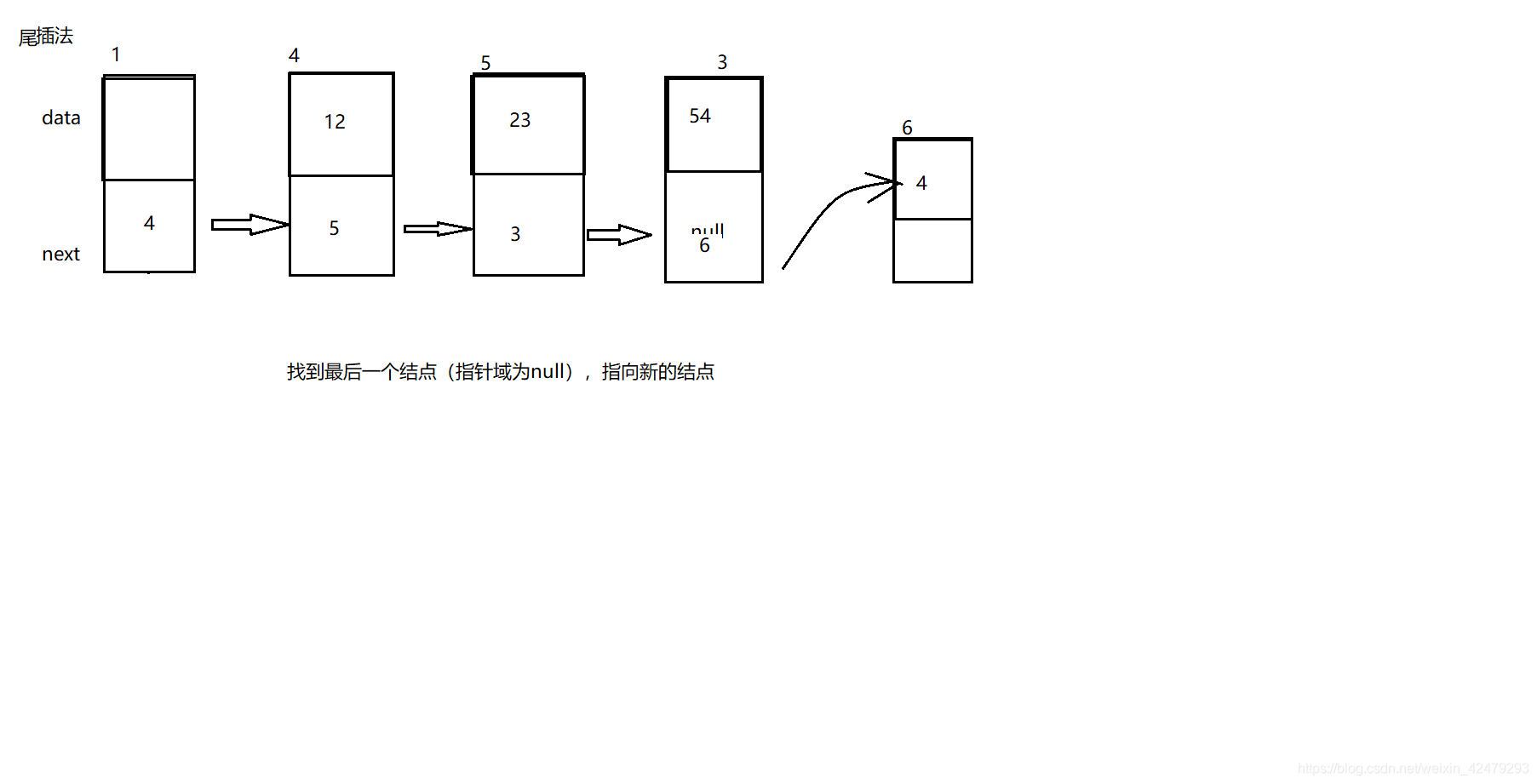
//尾插法
public void insertTial(int val){
Entry cur = new Entry(val);
Entry entry = this.head;
while(entry.next != null){
entry = entry.next;
}
entry.next = cur;
}
3、指定位置插入
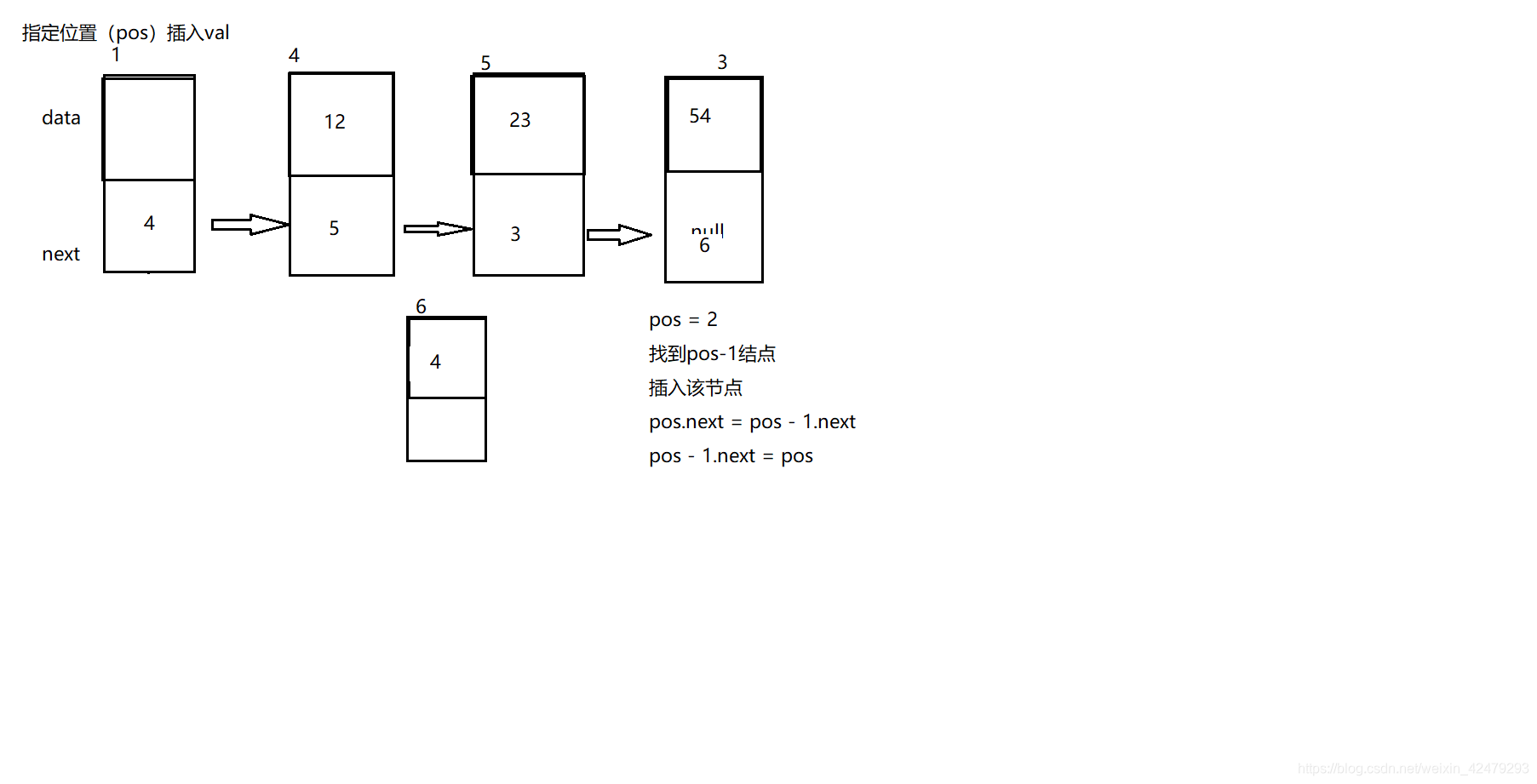
public void insertPos(int val,int pos){
if(pos < 0 || pos > getLength()){
return;
}
Entry cur = new Entry(val);
Entry entry = this.head;
for(int i = 0;i <= pos - 1;i ++){
entry = entry.next;
}
cur.next = entry.next;
entry.next = cur;
}
(二)得到单链表长度
public int getLength(){
int count = 0;
Entry entry = this.head.next;
while (entry != null){
count ++;
entry = entry.next;
}
return count;
}
(三)删除
1.删除指定位置的结点
//删除pos结点
public void deletePos(int pos){
if(pos < 0 || pos > getLength()) {
return;
}
Entry cur = this.head;
for(int i = 0;i <= pos - 1;i ++){
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}
2.删除单链表中所有值为val的节点
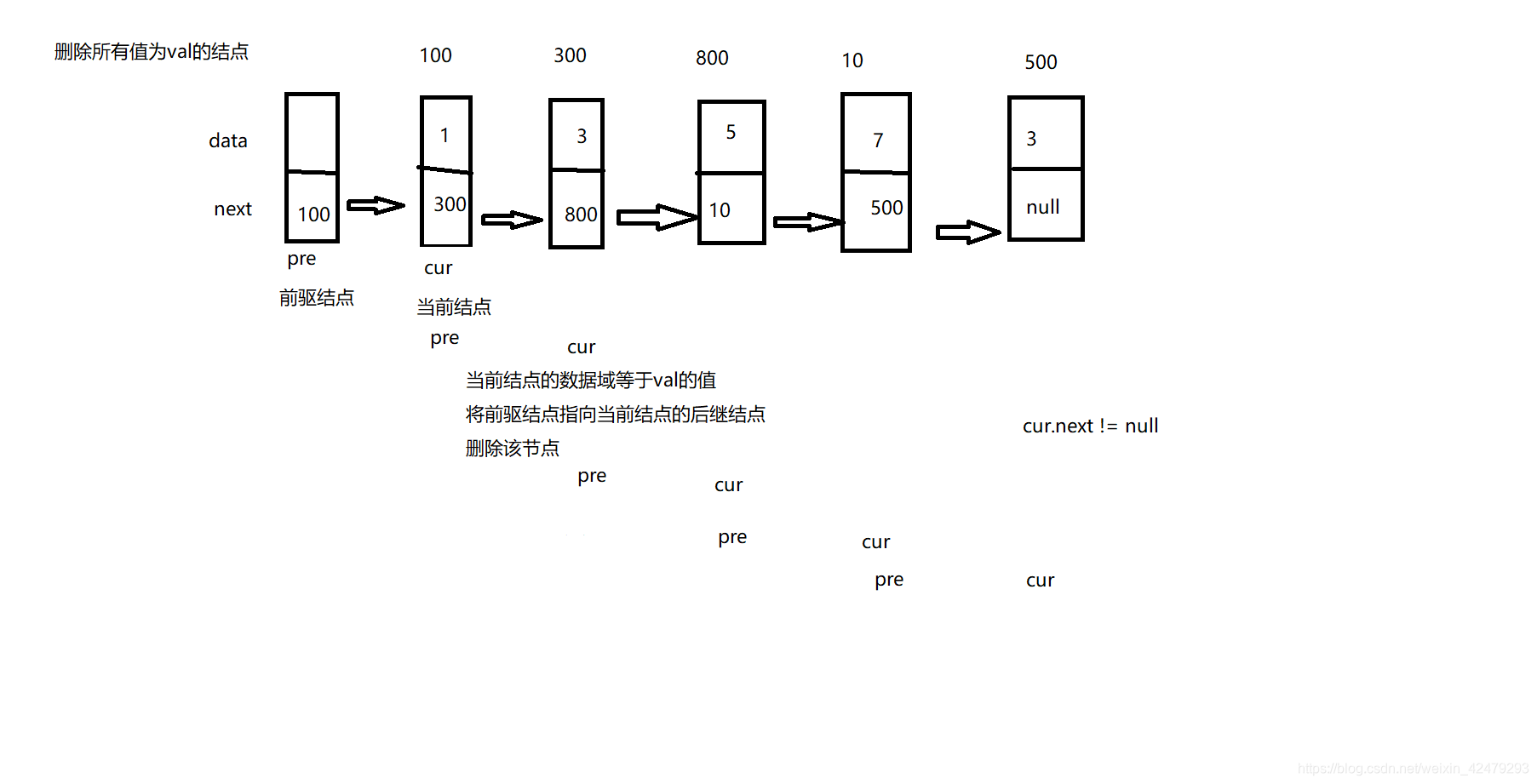
//删除单链表中所有值为val的节点 O(n)
public boolean deleteVal_1(int val) {
Entry pre = this.head;//前驱结点
Entry cur = this.head.next;//当前结点
while(cur != null){
if(cur.data == val){
pre.next = cur.next;
cur = pre.next;
}else{
pre = pre.next;
cur = pre.next;
}
}
return true;
}
3.最快时间内删除单链表的倒数第K个结点
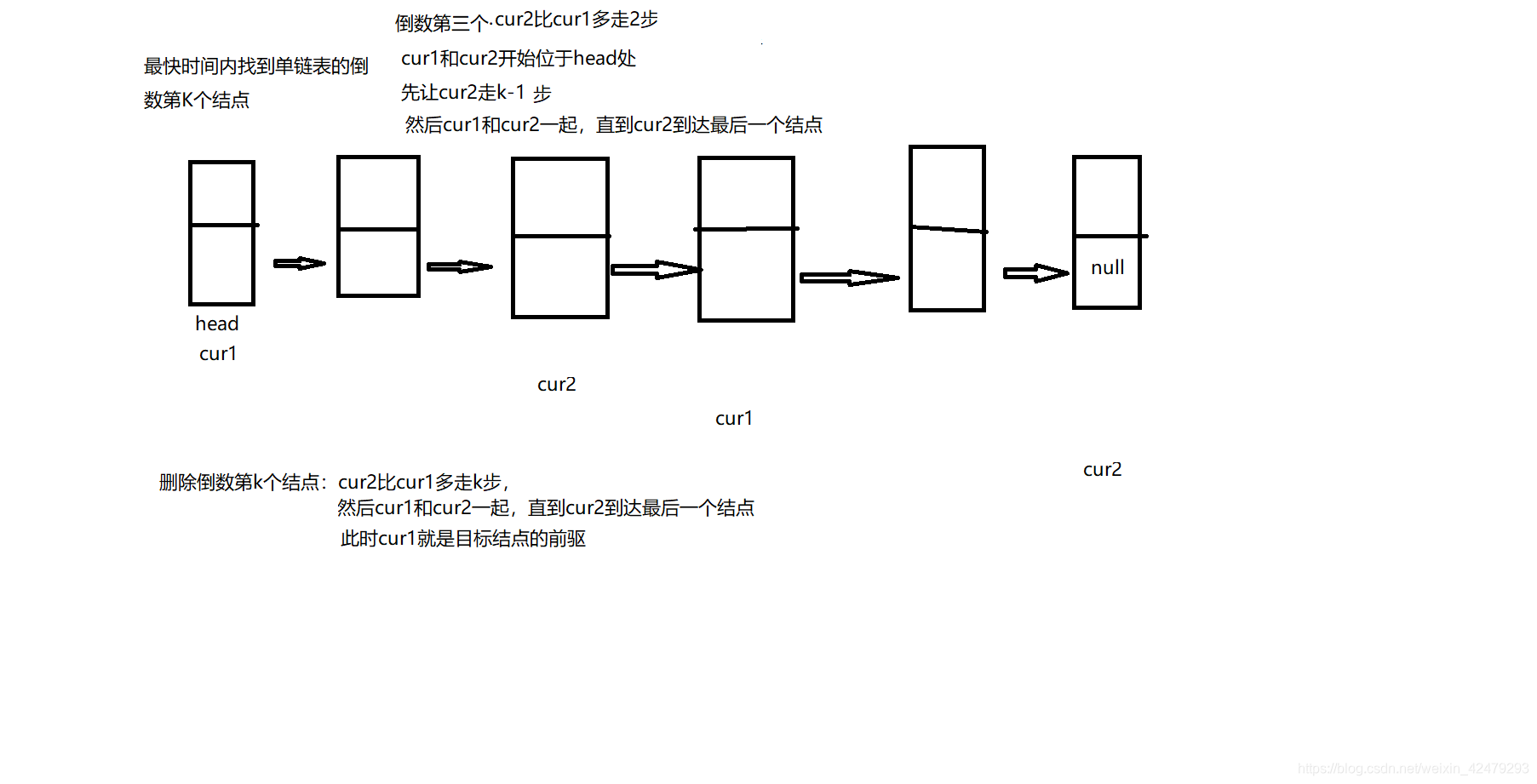
//最快时间内找到单链表的倒数第K个结点
public int lastK(int k) {
if(k < 0 || k > getLength()){
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("k不合法!");
}
Entry cur1 = this.head;
Entry cur2 = this.head;
while (k - 1 > 0){
cur2 = cur2.next;
-- k;
}
while (cur2.next != null) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1.data;
}
//最快时间内删除单链表的倒数第K个结点
public void deleteLastK(int k) {
if(k < 0 || k > getLength()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("k不合法!");
}
Entry cur1 = this.head;
Entry cur2 = this.head;
while(k > 0){
cur2 = cur2.next;
-- k;
}
while(cur2.next != null){
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
cur1.next = cur1.next.next;
}
(四)逆置
1.头插法
//头插法逆置
public void reverse(){
Entry cur = this.head;
if(cur == null || cur.next == null){
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("不可逆置!");
}
Entry cur2 = this.head;
while(cur2.next != null){
cur2 = cur2.next;
int val = cur2.data;
insertHead(val);//插入结点
}
//删除多余结点
int num = getLength() / 2;
for(int i = 0;i < num;i ++){
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = null;
show();
}





















 1491
1491

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








