单链表
本篇博客主要整理了带头指针的单链表的,初始化,头插,尾插,头删,尾删,在指定位置之后插入数据,查找数据位置,删除指定位置之后的结点,删除指定位置之后的所有结点等功能,并在代码的注释附上了详细的解释,希望可以对读者有所帮助。
链表
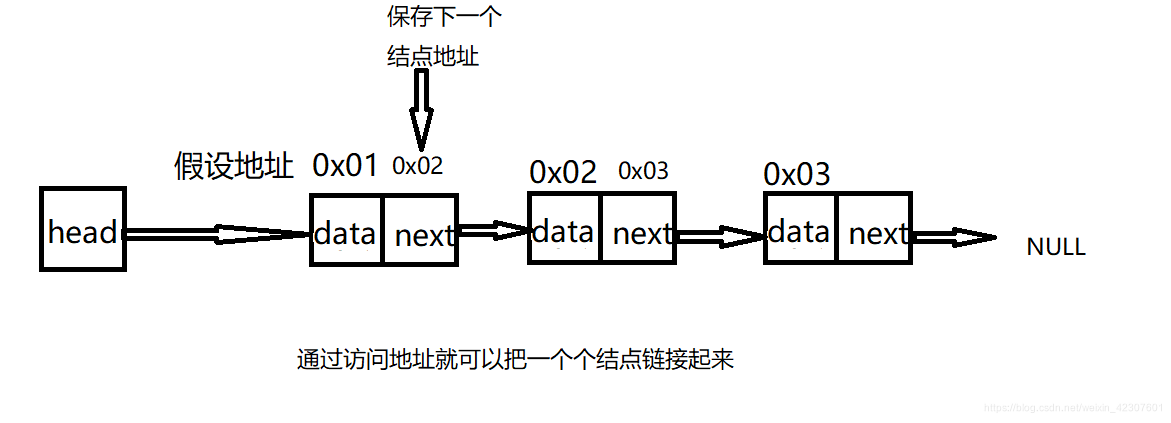
概念:链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的
实际中链表的结构非常多样,以下情况组合起来就有8种链表结构:
- 单向、双向
- 带头、不带头
- 循环、非循环
今天我们主要讲一下单链表:
先来看一下单链表的基本构图:
头文件
#pragma once
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int SDataType;//类型重定义
typedef struct SListNode//定义单链表节点结构体
{
SDataType _data;//存放节点的数据
struct SListNode* _next;//存放下一个节点的指针,指向下一个结构体 因此是struct SListNode*类型
}SListNode;
typedef struct Slist//定义单链表
{
SListNode* head;//定义指向单链表的头指针
}Slist;
void InitSlist(Slist* plt);//初始化单链表
void SLTPushBack (Slist*plt, SDataType value);//尾插
void SLTPushFront (Slist*plt, SDataType value);//头插
void SLTPopBack(Slist* plt);//尾删
void SLTPopFront(Slist* plt);//头删
SDataType SLTFind(Slist* plt, SDataType x);//查找节点
void SListInsertAfter(Slist*plt,SDataType pos, SDataType x);//在给定位置之后插入一个新节点
void SListEraseAfter(Slist*plt,SDataType pos);//在删除指定位置之后的节点
void SListPrintf(Slist*plt);//打印数据
void SListEraseAfterAll(Slist*plt,SDataType pos);//在删除指定位置后的所有节点
子函数
#include"SList.h"
Slist lt;//定义一个Slist 的变量 lt;
void InitSlist(Slist* plt)//初始化单链表
{
assert(plt);
plt->head=NULL;
if(plt->head==NULL)
{
printf("初始化成功!\n");
}
else
{
printf("初始化失败!");
}
}
void SLTPushBack (Slist*plt, SDataType value)//尾插
{ //尾插的基本思想是,先把数据存放到新节点的数据域并把next置空
//然后找到尾节点插入即可
SListNode* newnode=(SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));//为新结点开辟空间
SListNode*cur=plt->head;
newnode->_data=value;
newnode->_next=NULL;
if(plt->head==NULL)//如果链表为空,直接将头指针指向新结点
{
plt->head=newnode;
}
else//找到单链表的尾
{
while(cur->_next!=NULL)
{
cur=cur->_next;
}
cur->_next=newnode;//
}
}
void SLTPushFront (Slist*plt, SDataType value)//头插
{ //和尾插做法一致
//不过这里要考虑插入的顺序,先将要插入的新结点和原来的头结点链上,
//再和头指针链上
SListNode*newnode=(SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));
assert(plt);
newnode->_data=value;
newnode->_next=NULL;
newnode->_next=plt->head;
plt->head=newnode;
}
void SLTPopBack(Slist* plt)//尾删
{
//首先要找到尾然后进行删除,不过这里有几种特殊的情况
SListNode* cur=plt->head;
assert(plt);
if(cur==NULL)//如果链表为空
{
return;
}
else if((cur->_next)==NULL)//只有一个数据
{
free(cur);
plt->head=NULL;
}
else {
while((cur->_next->_next)!=NULL)//正常情况找到尾结点的前一个
{
cur=cur->_next;
}
//将前一个结点的next 释放掉,然后再置空
//若果直接释放最后一个导致倒数第二个的next既找不到下一个结点也不为空
//因此是释放倒数第二个的next,将倒数第二个的next置空
free(cur->_next);
cur->_next=NULL;
}
}
void SLTPopFront(Slist* plt)//头删
{
//头删也就是把头指针和第一个结点的next链起来,并且释放掉第一个结点
//但要注意的是先链起来再释放否则找不到第一个结点的next
assert(plt);
if(plt->head==NULL)
{
return ;
}
else
{
SListNode*cur=plt->head;
plt->head=cur->_next;
free(cur);
cur=NULL;
}
}
SDataType SLTFind(Slist* plt, SDataType x)//查找数据返回位置
{
int count=1;//定义一个计数器用作位置的返回值
SListNode*cur=plt->head;
assert(plt&&x);
if(plt->head==NULL)
{
return -1;
}
if(cur->_data==x&&cur->_next!=NULL)
{
return 1;//如果第一个就是返回位置1
}
else
{
while(cur->_next!=NULL)
{
if(cur->_data!=x)//不相等计数器就++,并且继续向后走遍历一遍
{
count++;
cur=cur->_next;
}
}
if(cur->_data==x)
{
return count;//找到就返回位置
}
else
return -1;//都没有找到返回-1
}
}
void SListInsertAfter(Slist*plt,SDataType pos, SDataType x)//在给定位置之后插入一个新结点
{
SDataType count=1;//设置计数器
SListNode*cur=plt->head;
SListNode*newnode=(SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));
newnode->_data=x;
newnode->_next=NULL;
while(count!=pos&&cur->_next!=NULL)//找到pos位置的结点
{
count++;
cur=cur->_next;
}
if(count==pos)//找到时插入
{
newnode->_next=cur->_next;//先将新结点的next链上前面结点的next
cur->_next=newnode;
}
}
void SListEraseAfter(Slist*plt,SDataType pos)//在删除指定位置之后的节点
{
SDataType count=1;
SListNode*cur1=plt->head;
if(pos==1)//相当于头删
{
SListNode*cur=plt->head;
plt->head=cur->_next;
free(cur);
cur=NULL;
}
while(count!=pos&&cur1->_next!=NULL)//找到pos位置的结点
{
count++;
cur1=cur1->_next;
}
if((pos)==count&&pos!=1)//找到的时候
{
SListNode*Next=cur1->_next->_next;//先保存要删除的结点的下一个结点
free(cur1->_next);//释放要删除的结点
cur1->_next=NULL;//置空
cur1->_next=Next;//再将前后链接起来
}
}
void SListEraseAfterAll(Slist*plt,SDataType pos)//在删除指定位置之后所有的结点
{ //和上一个子函数类似,只不过是将指定位置之后置空
SDataType count=1;
SListNode*cur=plt->head;
assert(plt);
if(pos==1)
{
free(cur->_next);
cur->_next=NULL;
}
while(count!=pos&&cur->_next!=NULL)//找到pos位置的结点
{
count++;
cur=cur->_next;
}
if((pos)==count&&pos!=1)
{
free(cur->_next);
cur->_next=NULL;
}
}
void SListPrintf(Slist*plt)//打印数据
{
SListNode*cur=plt->head;
assert(plt);
while(cur!=NULL)
{
printf("%d ",cur->_data);
cur=cur->_next;
}
printf("\n");
}
主函数
#include"SList.h"
void SListTest1()
{
Slist lt;//定义一个Slist 的变量 lt;
//SDataType ret;
InitSlist(<);//初始化单链表//注意需要传地址过来
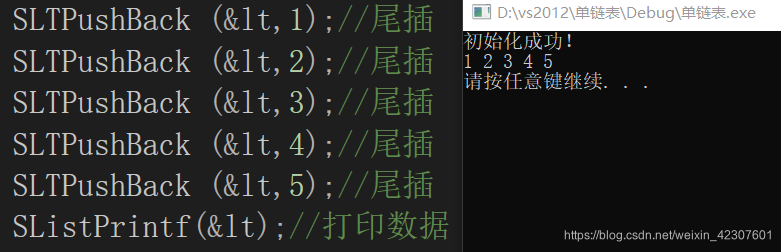
SLTPushBack (<,1);//尾插
SLTPushBack (<,2);//尾插
SLTPushBack (<,3);//尾插
SLTPushBack (<,4);//尾插
SLTPushBack (<,5);//尾插
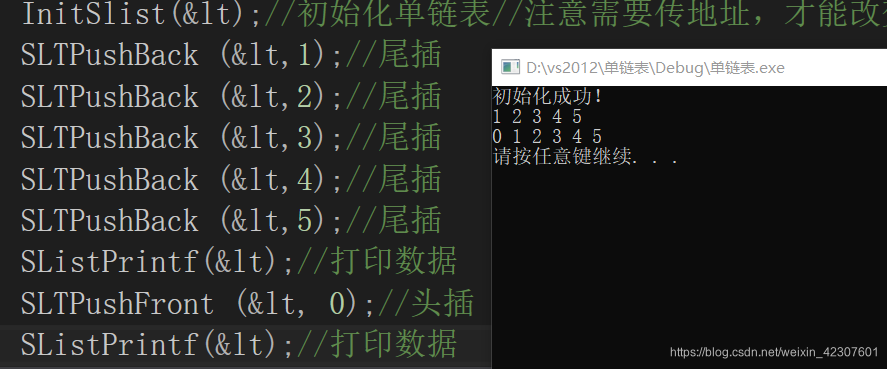
SLTPushFront (<, 0);//头插
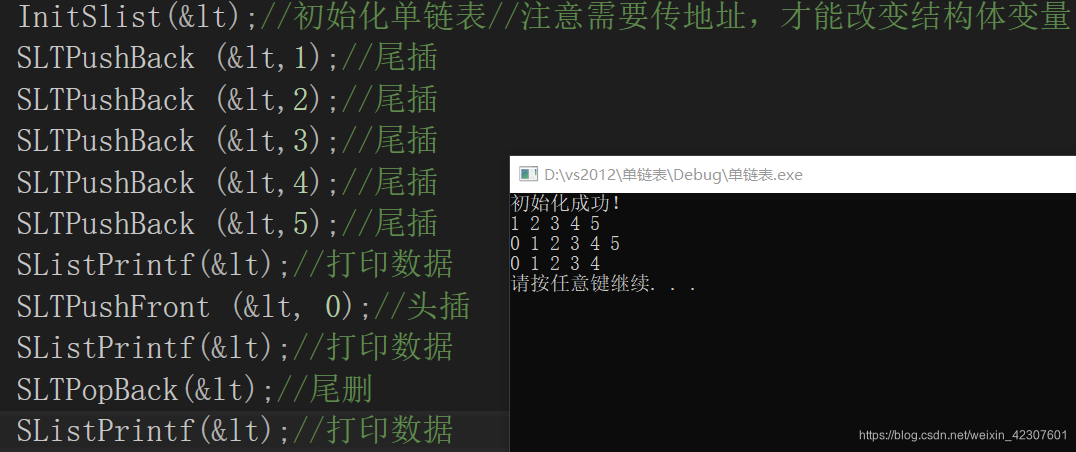
//SLTPopBack(<);//尾删
SListPrintf(<);//打印数据
//printf("\n");
//SLTPopFront(<);//头删
//SListPrintf(<);//打印数据
//ret=SLTFind(<, 7);//查找数据返回位置
//if(ret>0)
//{
// printf("找到了,位置是:%d\n",ret);
//}
//else
//{
// printf("找不到\n");
//}
//
//SListInsertAfter(<,1 ,9);//在给定位置之后插入一个新结点
SListPrintf(<);//打印数据
//SListEraseAfter(<,3);//在删除指定位置之后的结点
SListEraseAfterAll(<,2);//删除指定位置的所有结点
SListPrintf(<);//打印数据
}
int main()
{
SListTest1();//测试函数
system("pause");
}
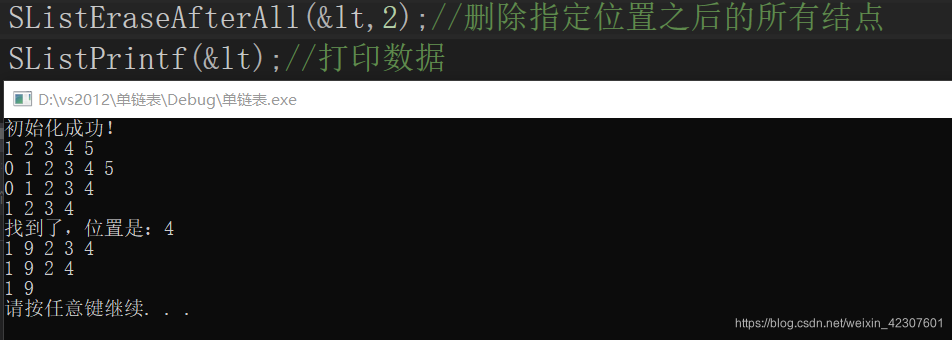
测试
尾插
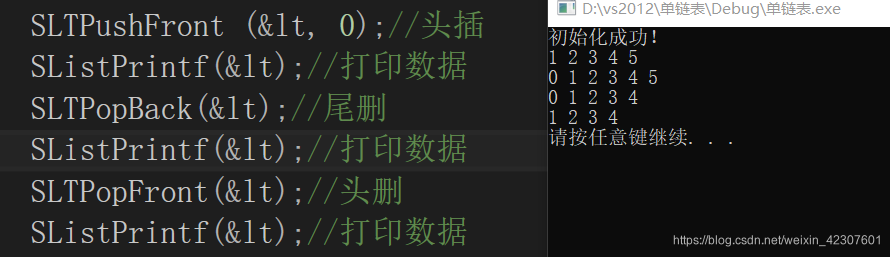
头插
尾删
头删
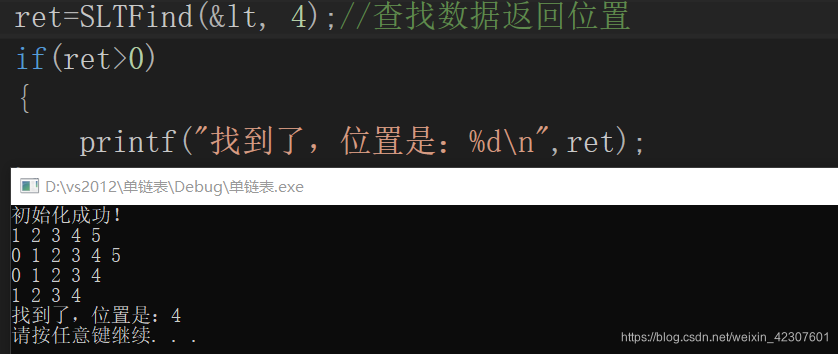
查找位置
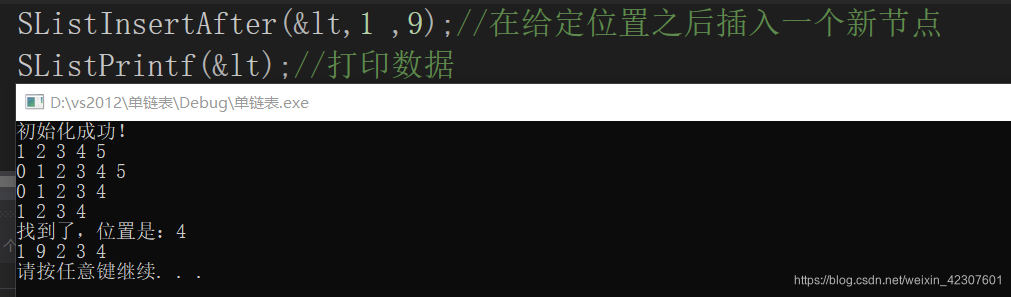
在给定位置之后插入一个新节点
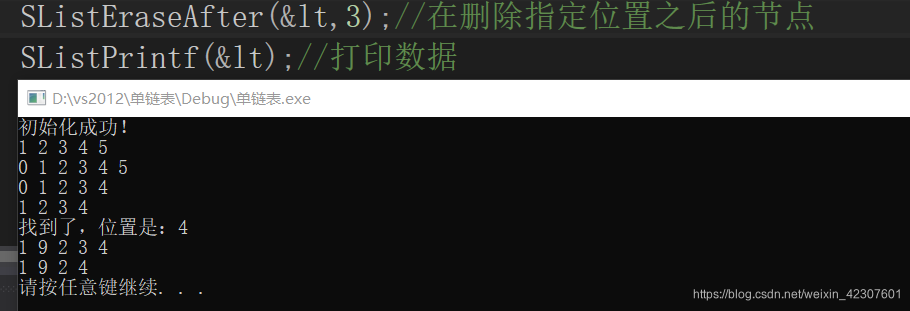
删除指定位置之后的结点
删除指定结点之后的所有结点























 581
581

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








