JS继承
继承,类与类之间的关系,面向对象的语言的继承是为了多态服务的,js不是面向对象的语言,但是可以模拟面向对象.模拟继承.为了节省内存空间
Js实现继承的方式
1)原型继承:改变原型的指向
2)借用构造函数继承:主要解决属性的问题
3)组合继承(原型继承+借用构造函数继承):既能解决属性问题,又能解决方法问题
注意原型作用: 数据共享,达到继承的效果 ,目的是:为了节省内存空间
原型实现继承
为了数据共享,改变原型指向,做到了继承---通过改变原型指向实现的继承
缺陷:因为改变原型指向的同时实现继承,直接初始化了属性,继承过来的属性的值都是一样的了,所以,这就是问题只能重新调用对象的属性进行重新赋值
function Person(name, age, sex, weight) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
this.weight = weight;
}
Person.prototype.sayHi = function () {
console.log("您好");
};
function Student(score) {
this.score = score;
}
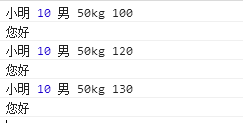
【1】改变原型指向,而且传值,说明继承了Person的属性和方法
希望人的类别中的数据可以共享给学生---继承
Student.prototype = new Person("小明", 10, "男", "50kg");
var stu1 = new Student("100");
stu1.sayHi();
console.log(stu1.name, stu1.age, stu1.sex, stu1.weight, stu1.score);
var stu2 = new Student("120");
console.log(stu2.name, stu2.age, stu2.sex, stu2.weight, stu2.score);
stu2.sayHi();
var stu3 = new Student("130");
console.log(stu3.name, stu3.age, stu3.sex, stu3.weight, stu3.score);
stu3.sayHi();
借用构造函数实现继承
解决方案:继承的时候,不用改变原型的指向,直接调用父级的构造函数的方式来为属性赋值就可以了------借用构造函数:把要继承的父级的构造函数拿过来,使用一下就可以了
//借用构造函数:构造函数名字.call(当前对象,属性,属性,属性....);
//解决了属性继承,并且值不重复的问题
//缺陷:父级类别中的方法不能继承
function Person(name, age, sex, weight) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
this.weight = weight;
}
Person.prototype.sayHi = function () {
console.log("您好");
};
function Student(name,age,sex,weight,score) {
//借用构造函数 //this:当前学生的实例对象
//this呼叫Person构造函数,把Person需要的对象传过去
Person.call(this,name,age,sex,weight);
this.score = score;
}
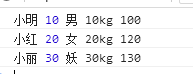
var stu1 = new Student("小明",10,"男","10kg","100");
console.log(stu1.name, stu1.age, stu1.sex, stu1.weight, stu1.score);
var stu2 = new Student("小红",20,"女","20kg","120");
console.log(stu2.name, stu2.age, stu2.sex, stu2.weight, stu2.score);
var stu3 = new Student("小丽",30,"妖","30kg","130");
console.log(stu3.name, stu3.age, stu3.sex, stu3.weight, stu3.score);
组合继承:原型继承+借用构造函数继承
//属性和方法都被继承了
//【1】组合继承:原型继承+借用构造函数继承
function Person(name, age, sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
Person.prototype.sayHi = function () {
console.log("阿涅哈斯诶呦");
};
function Student(name, age, sex, score) {
//【2】借用构造函数:属性值重复的问题
Person.call(this, name, age, sex);
this.score = score;
}
//改变原型指向----继承
//【3】不传值避免属性重复,意味只继承了Person的方法
Student.prototype = new Person();
Student.prototype.eat = function () {
console.log("吃东西");
};
var stu = new Student("小黑", 20, "男", "100分");
console.log(stu.name, stu.age, stu.sex, stu.score);
stu.sayHi();
stu.eat();
var stu2 = new Student("小黑黑", 200, "男人", "1010分");
console.log(stu2.name, stu2.age, stu2.sex, stu2.score);
stu2.sayHi();
stu2.eat();

拷贝继承
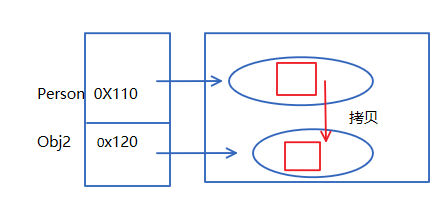
拷贝继承:就是把对象中需要共享的属性或者方法,直接遍历的方式复制到另一个对象中
//浅拷贝
function Person() {
}
Person.prototype.age=10;
Person.prototype.sex="男";
Person.prototype.height=100;
Person.prototype.play=function () {
console.log("玩的好开心");
};
var obj2={};
//Person的构造中有原型prototype,prototype就是一个对象,那么里面,age,sex,height,play都是该对象中的属性或者方法
//注意并非是完全拷贝原型prototype,因为原型prototype有些东西是不让拷贝的
for(var key in Person.prototype){
obj2[key]=Person.prototype[key];
}
console.dir(obj2);
obj2.play();





 本文深入探讨JavaScript中的继承方式,包括原型继承、借用构造函数继承及组合继承等,解析各种继承方式的特点与应用场景,帮助读者理解JS如何模拟面向对象的继承。
本文深入探讨JavaScript中的继承方式,包括原型继承、借用构造函数继承及组合继承等,解析各种继承方式的特点与应用场景,帮助读者理解JS如何模拟面向对象的继承。
















 561
561

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








