volatile概念:主要作用是使变量在多个线程间可见
我们使用synchronized或者lock,可以对某个变量和方法加锁来保证一致性,但是这样性能很低,因为只有一个线程进来操作此加锁方法。
在jdk1.5以后,对每一个Thread加了优化,对每一个线程加了一块引用,线程在取值的时候去这块副本中取。
示例代码:
public class RunThread extends Thread {
private volatile boolean isRunning = true;
private void setRunning(boolean isRunning) {
this.isRunning = isRunning;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("进入run方法。。");
while (isRunning == true) {
}
System.out.println("线程停止");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
RunThread rt = new RunThread();
rt.start();
Thread.sleep(3000);
rt.setRunning(false);
System.out.println("isRunning的值已经被设置了false");
//Thread.sleep(1000);
//System.out.println(rt.isRunning);
}
}
其中定义了isRunning=true。
1.在不加volatile关键字时,当修改了isRunning变量时是修改了主内存中的变量,线程的独立内存空间里面的变量没有修改,我们找变量不能每次都去主内存中取。所以加volatile关键字,
加volatile关键字:
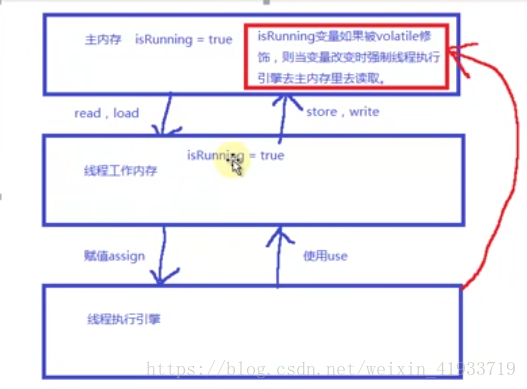
当主内存中变量修改了,发现变化了会去线程的独立内存中读取





 本文深入讲解了Java中Volatile关键字的作用及其对多线程中变量可见性的影响,并通过示例代码展示了如何正确使用Volatile来避免线程间的可见性问题。
本文深入讲解了Java中Volatile关键字的作用及其对多线程中变量可见性的影响,并通过示例代码展示了如何正确使用Volatile来避免线程间的可见性问题。
















 867
867

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








