Cache<String, Map<String, String>> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumSize(CACHR_MAX_SIZE)
.expireAfterWrite(CACHE_EXPIRE_TIME, TimeUnit.HOURS)
.removalListener()
.recordStats().build();
.newBuilder() //创建缓存对象
public static CacheBuilder<Object, Object> newBuilder() {
return new CacheBuilder<Object, Object>();
}
.maximumSize(CACHR_MAX_SIZE)//设置缓存大小
这里会有几个参数的校验,初始化时都是通过的,设置完之后如果再次设置则会抛异常
public CacheBuilder<K, V> maximumSize(long size) {
checkState(this.maximumSize == UNSET_INT, "maximum size was already set to %s",
this.maximumSize);
checkState(this.maximumWeight == UNSET_INT, "maximum weight was already set to %s",
this.maximumWeight);
checkState(this.weigher == null, "maximum size can not be combined with weigher");
checkArgument(size >= 0, "maximum size must not be negative");
this.maximumSize = size;
return this;
}
.expireAfterWrite(CACHE_EXPIRE_TIME, TimeUnit.HOURS)//设置缓存失效时间
这里也会有校验,底层通过纳秒存储
public CacheBuilder<K, V> expireAfterWrite(long duration, TimeUnit unit) {
checkState(expireAfterWriteNanos == UNSET_INT, "expireAfterWrite was already set to %s ns",
expireAfterWriteNanos);
checkArgument(duration >= 0, "duration cannot be negative: %s %s", duration, unit);
this.expireAfterWriteNanos = unit.toNanos(duration);//时间转成纳秒
return this;
}
.removalListener() //移除监听,在key从缓存中remove时会调用
自定义实现RemovalListener中的onRemoval方法在key移除时会调用
public <K1 extends K, V1 extends V> CacheBuilder<K1, V1> removalListener(
RemovalListener<? super K1, ? super V1> listener) {
checkState(this.removalListener == null);
// safely limiting the kinds of caches this can produce
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
CacheBuilder<K1, V1> me = (CacheBuilder<K1, V1>) this;
me.removalListener = checkNotNull(listener);
return me;
}
.recordStats()//主要记录cache的状态,包括hit命中数量,miss数量,加载成功数量,加载异常数量,总加载时间,驱逐数量
public CacheBuilder<K, V> recordStats() {
statsCounterSupplier = CACHE_STATS_COUNTER;
return this;
}
static final Supplier<StatsCounter> CACHE_STATS_COUNTER =
new Supplier<StatsCounter>() {
@Override
public StatsCounter get() {
return new SimpleStatsCounter();
}
public static final class SimpleStatsCounter implements StatsCounter {
private final LongAddable hitCount = LongAddables.create();
private final LongAddable missCount = LongAddables.create();
private final LongAddable loadSuccessCount = LongAddables.create();
private final LongAddable loadExceptionCount = LongAddables.create();
private final LongAddable totalLoadTime = LongAddables.create();
private final LongAddable evictionCount = LongAddables.create();
};
}
guava cache底层使用类似ConcurrentHashMap的实现,加上了失效时间、状态信息的管理。结构图如下
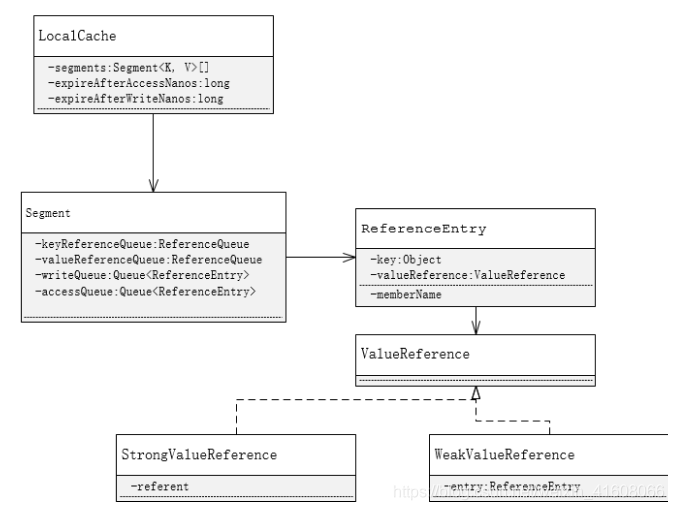
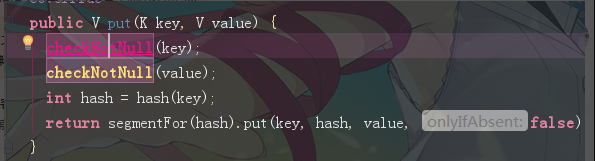
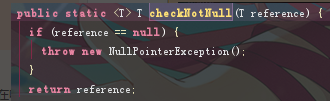
注意:cache的key和value不可以为null




 本文介绍了如何使用Guava Cache,包括通过 `.newBuilder()` 创建缓存对象,设置 `.maximumSize()` 缓存大小,`.expireAfterWrite()` 缓存失效时间,以及添加 `.removalListener()` 移除监听器。自定义`RemovalListener`可以在键被移除时进行操作,`.recordStats()` 用于记录缓存状态。Guava Cache内部基于类似`ConcurrentHashMap`的数据结构,并管理失效时间和状态信息,注意键值均不能为null。
本文介绍了如何使用Guava Cache,包括通过 `.newBuilder()` 创建缓存对象,设置 `.maximumSize()` 缓存大小,`.expireAfterWrite()` 缓存失效时间,以及添加 `.removalListener()` 移除监听器。自定义`RemovalListener`可以在键被移除时进行操作,`.recordStats()` 用于记录缓存状态。Guava Cache内部基于类似`ConcurrentHashMap`的数据结构,并管理失效时间和状态信息,注意键值均不能为null。
















 1165
1165

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








