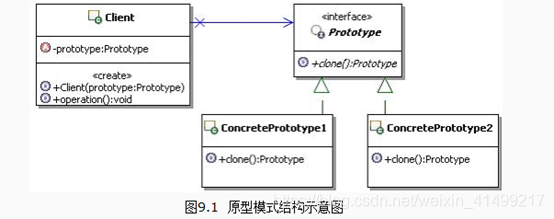
原型模式
public class ConcretePrototype1 implements Cloneable{
private String id;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public ConcretePrototype1(String id) {
super();
this.id = id;
}
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException{
return super.clone();
}
}
**********************
public class ConcretePrototype2 implements Cloneable{
private String id;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public ConcretePrototype2(String id) {
super();
this.id = id;
}
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException{
return super.clone();
}
}
***********************
public class client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ConcretePrototype1 p1=new ConcretePrototype1("I");
ConcretePrototype1 c1=(ConcretePrototype1)p1.clone();
System.out.println("p1"+p1.getId());
System.out.println("c1"+c1.getId());
}
}
优点
1.对客户端隐藏具体的实现类型
原型模式的客户端,只知道原型接口的类型,并不知道具体的实现类型,从而减少了客户端对这些具体实现类型的依赖。
2. 在运行时动态改变具体的实现类型
原型模式可以在运行期间,由客户来注册符合原型接口的实现类型,也可以动态的改变具体的实现类型,看起来接口没有任何变化,但其实运行的已经是另外一个类实例了。因为克隆一个原型就类似于实例化一个类。
缺点
1. 深度克隆方法实现会比较困难
原型模式最大的缺点就在于每个原型的子类都必须实现clone的操作,尤其在包含引用类型的对象时,clone方法会比较麻烦,必须要能够递归的让所有的相关对象都要正确的实现克隆。
本质
克隆生成对象 。
应用场景
建议在如下情况中,选用原型模式:
- 如果一个系统想要独立于它想要使用的对象时,可以使用原型模式,让系统只面向接口编程,在系统需要新的对象的时候,可以通过克隆原型来得到
- 如果需要实例化的类是在运行时刻动态指定时,可以使用原型模式,通过克隆原型来得到需要的实例
相关应用
原型模式和抽象工厂模式
功能上有些相似,都是用来获取一个新的对象实例的。
不同之处在于,原型模式的着眼点是在如何创造出实例对象来,最后选择的方案是通过克隆;而抽象工厂模式的着眼点则在于如何来创造产品簇,至于具体如何创建出产品簇中的每个对象实例,抽象工厂模式不是很关注。
正是因为它们的关注点不一样,所以它们也可以配合使用,比如在抽象工厂模式里面,具体创建每一种产品的时候就可以使用该种产品的原型,也就是抽象工厂管产品簇,具体的每种产品怎么创建则可以选择原型模式。
l 原型模式和生成器模式(建造者模式)
这两种模式可以配合使用。
生成器模式关注的是构建的过程,而在构建的过程中,很可能需要某个部件的实例,那么很自然地就可以应用上原型模式,通过原型模式来得到部件的实例。
简历问题
package com;
public class Resume implements Cloneable{
private String name;
private String sex;
private String age;
private Workexperience workExperience;
//设置个人信息
public void setPersonInfo(String name,String sex,String age){
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
}
public Resume() {
super();
workExperience=new Workexperience();
}
//两种初始化,根据名字,根据工作经历
public Resume(String name){
this.name=name;
workExperience=new Workexperience();
}
//实现深复制
private Resume(Workexperience workExperience) throws CloneNotSupportedException{
this.workExperience=(Workexperience)workExperience.clone();
}
public Workexperience getWorkExperience() {
return workExperience;
}
public void setWorkExperience(String workdate,String company) {
workExperience.setCompany(company);
workExperience.setWorkDate(workdate);
}
public void display(){
System.out.println(name+" "+sex+" "+age+" "+"工作经历:"+workExperience.getWorkDate()+" "+workExperience.getCompany());
}
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException{
Resume resume=new Resume(this.workExperience);
resume.name=this.name;
resume.sex=this.sex;
resume.age=this.age;
return resume;
}
}
************************************
package com;
public class Workexperience implements Cloneable{
private String workDate;
private String company;
public Workexperience() {
super();
}
public Workexperience(String workDate, String company) {
super();
this.workDate = workDate;
this.company = company;
}
public String getWorkDate() {
return workDate;
}
public void setWorkDate(String workDate) {
this.workDate = workDate;
}
public String getCompany() {
return company;
}
public void setCompany(String company) {
this.company = company;
}
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException{
return super.clone();
}
}
********************************
package com;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Resume a=new Resume();
a.setPersonInfo("大鸟", "男","29");
a.setWorkExperience("2009-2010", "百度");
Resume b=(Resume)a.clone();
b.setWorkExperience("2011-2014", "阿里巴巴");
Resume c=(Resume)a.clone();
c.setPersonInfo("菜鸟", "男","20");
a.display();
b.display();
c.display();
}
}
订单处理系统。拆分订单
/**
* 个人订单对象
*/
public class PersonalOrder implements OrderApi{
private String customerName;
private String productId;
private int orderProductNum = 0;
public int getOrderProductNum() {
return this.orderProductNum;
}
public void setOrderProductNum(int num) {
this.orderProductNum = num;
}
public String getCustomerName() {
return customerName;
}
public void setCustomerName(String customerName) {
this.customerName = customerName;
}
public String getProductId() {
return productId;
}
public void setProductId(String productId) {
this.productId = productId;
}
public String toString(){
return "本个人订单的订购人是="+this.customerName
+",订购产品是="+this.productId+",订购数量为="
+this.orderProductNum;
}
public OrderApi cloneOrder() {
//创建一个新的订单,然后把本实例的数据复制过去
PersonalOrder order = new PersonalOrder();
order.setCustomerName(this.customerName);
order.setProductId(this.productId);
order.setOrderProductNum(this.orderProductNum);
return order;
}
}
/**
* 企业订单对象
*/
public class EnterpriseOrder implements OrderApi{
private String enterpriseName;
private String productId;
private int orderProductNum = 0;
public int getOrderProductNum() {
return this.orderProductNum;
}
public void setOrderProductNum(int num) {
this.orderProductNum = num;
}
public String getEnterpriseName() {
return enterpriseName;
}
public void setEnterpriseName(String enterpriseName) {
this.enterpriseName = enterpriseName;
}
public String getProductId() {
return productId;
}
public void setProductId(String productId) {
this.productId = productId;
}
public String toString(){
return "本企业订单的订购企业是="+this.enterpriseName
+",订购产品是="+this.productId+",订购数量为="
+this.orderProductNum;
}
public OrderApi cloneOrder() {
//创建一个新的订单,然后把本实例的数据复制过去
EnterpriseOrder order = new EnterpriseOrder();
order.setEnterpriseName(this.enterpriseName);
order.setProductId(this.productId);
order.setOrderProductNum(this.orderProductNum);
return order;
}
}
public class OrderClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建订单对象,这里为了演示简单,直接new了
PersonalOrder op = new PersonalOrder();
//设置订单数据
op.setOrderProductNum(2925);
op.setCustomerName("张三");
op.setProductId("P0001");
//这里获取业务处理的类,也直接new了,为了简单,连业务接口都没有做
OrderBusiness ob = new OrderBusiness();
//调用业务来保存订单对象
ob.saveOrder(op);
}
}
public class OrderBusiness {
/**
* 创建订单的方法
* @param order 订单的接口对象
*/
public void saveOrder(OrderApi order){
//1:判断当前的预定产品数量是否大于1000
while(order.getOrderProductNum() > 1000){
//2:如果大于,还需要继续拆分
//2.1再新建一份订单,跟传入的订单除了数量不一样外,其它都相同
OrderApi newOrder = order.cloneOrder();
//然后进行赋值,产品数量为1000
newOrder.setOrderProductNum(1000);
//2.2原来的订单保留,把数量设置成减少1000
order.setOrderProductNum(
order.getOrderProductNum()-1000);
//然后是业务功能处理,省略了,打印输出,看一下
System.out.println("拆分生成订单=="+newOrder);
}
//3:不超过,那就直接业务功能处理,省略了,打印输出,看一下
System.out.println("订单=="+order);
}
}





















 169万+
169万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








