目录
- 一、Spring概述
- 二、Spring中基于XML的IOC配置
- 三、Spring中基于注解的IOC配置
- 四、Spring整合Junit
- 五、Spring中基于XML的AOP配置
- 六、Spring中基于注解的AOP配置
- 七、Spring中的JdbcTemplate
- 八、Spring事务控制【重点】
一、Spring概述
Spring官方网站:传送门
Spring配置文件约束:传送门,选择相应版本的 Reference Doc.
-
Spring 是分层的 Java SE/EE 应用 full-stack 轻量级开源框架,以 IoC(Inverse Of Control: 反转控制)和 AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming:面向切面编程)为内核,提供了展现层 Spring MVC 和持久层 Spring JDBC 以及业务层事务管理等众多的企业级应用技术,还能整合开源世界众多 著名的第三方框架和类库,逐渐成为使用最多的 Java EE 企业应用开源框架。
-
Spring的两大核心:IOC和AOP
- IOC:Inverse Of Control 控制反转
- AOP:Aspect Oriented Programming 面向切面编程
-
Spring的发展历程和优势
- 方便解耦,简化开发
- AOP 编程的支持
- 声明式事务的支持
- 方便程序的测试
- 方便集成各种优秀框架
- 降低 JavaEE API 的使用难度
- Java 源码是经典学习范例
-
Spring体系结构
-
程序的耦合及解耦
- 耦合:程序间的依赖
- 类之间的依赖
- 方法间的依赖
- 解耦:降低程序间的依赖关系
- 第一步:使用反射创建对象,避免使用new关键字
- 比如:注册驱动
- Class.forName(“com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver”); 即使没有导入jdbc的jar包,该方法编译器也不会报错。但是这种方式也带来了新的问题:驱动配置的字符串写死,切换数据库时,还是需要修改。解决办法看第二步。
- DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver()); 没有导入jdbc的jar包,该方法编译器会报错
- 第二步:读取配置文件来获取创建的对象全限定类名
- 第一步:使用反射创建对象,避免使用new关键字
- 实际开发中:编译器不依赖,运行时才依赖。
工厂模式解耦
- 耦合:程序间的依赖
二、Spring中基于XML的IOC配置
核心容器的两个接口:
1️⃣ApplicationContext
单例对象适用,实际开发中,更多的是采用此接口。
在创建核心容器时,创建对象采取的策略是采用立即加载的方式。也就是说,只要一读取完配置文件马上就创建配置文件中配置的所有对象。
2️⃣BeanFactory
多例对象适用
它在构建核心容器时,创建对象采取的策略是延迟加载的方式。也就是,只有在调用根据id获取对象的方法时,才会真正创建对象。
ApplicationContext三个常用实现类:
1️⃣ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:加载类路径下得配置文件。要求配置文件必须在类路径下,否则加载不了。
2️⃣FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:加载磁盘任意路径下的配置文件(必须具有访问权限)
3️⃣AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:读取注解创建容器。
bean标签的属性
bean标签中的属性:
- id:bean标签的唯一标识符,方便其他标签引用该标签
- class:全限定类名
- factory-bean:指定工厂bean
- factory-method:指定要使用工厂bean的哪个方法获取对象
- scope:用于指定bean的作用范围
- 取值
- singleton:单例(默认值)。多次调用getBean方法获取同一个bean标签,获取的对象地址值相同。
- prototype:多例的。多次调用getBean方法获取同一个bean标签,获取的对象地址值不同。
- request:作用于web应用的请求范围
- session:作用于web应用的会话范围
- global-session:作用于集群环境的会话范围(全局会话范围),当不是集群环境时,它就是session
- 取值
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="accountService" class="com.hxh.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl" scope="prototype"></bean>
</beans>
2.1 创建bean的三种方式
- 第一种方式:使用默认构造函数创建对象
在Spring的配置文件中,使用bean标签,指定id和class属性且没有其他属性和标签时,采用的就是默认构造函数创建bean对象。若该类中没有默认构造函数,则对象无法创建。Spring会抛出异常org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException
Spring的配置文件bean.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="accountService" class="com.hxh.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
</beans>
AccountServiceImpl.java:
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("AccountServiceImpl的saveAccount方法执行了。。。");
}
测试:
@Test
public void testByDefaultConstructor() {
// 获取核心容器对象
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
// 根据id获取bean对象
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("accountService", AccountServiceImpl.class);
// 关闭容器
applicationContext.close();
System.out.println(accountService);
}
输出结果:com.hxh.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl@80503
- 第二种方式:使用普通工厂中的方法创建对象(使用某个类中的方法创建对象,并存入spring容器)
Spring配置文件bean.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="instanceFactory" class="com.hxh.factory.InstanceFactory"></bean>
<bean id="accountService" factory-bean="instanceFactory" factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>
</beans>
InstanceFactory模拟一个jar包中的工厂类:我们无法通过修改源码的方式提供默认构造函数,但是可以使用Spring来实现使用工厂中的方法创建对象。
public class InstanceFactory {
public AccountService getAccountService() {
return new AccountServiceImpl();
}
}
测试:
@Test
public void testByInstanceFactory() {
// 获取核心容器对象
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
// 根据id获取bean对象
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("accountService", AccountServiceImpl.class);
// 关闭容器
applicationContext.close();
System.out.println(accountService);
}
输出结果:com.hxh.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl@27808f31
- 第三种方式:使用静态工厂中的静态方法创建对象(使用某个类中的静态方法创建对象,并存入spring容器)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="accountService" class="com.hxh.factory.StaticFactory" factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>
</beans>
静态工厂:
public class StaticFactory {
public static AccountService getAccountService() {
return new AccountServiceImpl();
}
}
测试方法同上。
总结:第二种和第三种方法,解决的问题:如何使用jar包中的类的方法获取某个对象,并存入spring容器!(jar包中的类,无法修改源码)
2.2 依赖注入 DI(Dependency Injection)
2.2.1 依赖注入的三类数据
- 第一类:基本类型和String
- 第二类:其他的Bean类型(在配置文件中或者注解配置过的bean)
- 第三类:复杂类型/集合类型
在依赖注入的三种方式中,我们将穿插讲解三种数据的注入。
2.2.2 依赖注入的三种方式
- 第一种:使用构造函数提供
使用的标签:<constructor-arg>
标签出现的位置:bean标签的内部
标签中的属性:
type:用于指定要注入的数据的数据类型,该数据类型也是构造函数中某个或某些参数的数据类型index:用于指定要注入的数据给构造函数中指定索引位置的参数赋值。从0开始name:用于指定给构造函数中指定名称的参数赋值【常用】
=以上三个用于指定给构造函数中哪个参数赋值==value:用于指定基本数据类型和String类型的数据ref:用于指定其他bean类型的数据。它指的就是spring的Ioc核心容器中出现过的bean对象(配置过的)
优势:在获取bean对象时,注入数据是必须的操作,否则对象无法创建成功
缺点:改变了bean对象的实例化方式,我们在创建对象时,如果用不到这些数据,也必须提供。
Spring配置文件bean.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="accountService" class="com.hxh.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="我是一个名称"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="18"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="birthday" ref="now"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="now" class="java.util.Date"></bean>
</beans>
配置的类 AccountServiceImpl.java:
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
// 如果是经常变化的数据,并不适用于注入的方式
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Date birthday;
public AccountServiceImpl(String name, Integer age, Date birthday) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("AccountServiceImpl的saveAccount方法执行了。"+name+"。"+age+"。"+birthday+"");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "AccountServiceImpl{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", birthday=" + birthday +
'}';
}
}
测试:
@Test
public void testWonstructorArg() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("accountService", AccountServiceImpl.class);
applicationContext.close();
System.out.println(accountService);
}
输出结果:AccountServiceImpl{name=‘Alex’, age=18, birthday=Tue Apr 09 09:20:47 CST 2019}
- 第二种:使用set方法提供【常用】
使用的标签:<property>
标签出现的位置:bean标签的内部
标签的属性:
name:用于指定注入时所调用的set方法名称value:用于指定基本数据类型和String类型的数据ref:用于指定其他bean类型的数据。它指的就是spring的Ioc核心容器中出现过的bean对象(配置过的)
优势:创建对象时没有明确的限制,可以直接使用默认构造函数
缺点:如果某个成员必须有值,那么set方法无法保证一定注入
Spring配置文件 bean.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="accountService2" class="com.hxh.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl2">
<property name="name" value="TEST"></property>
<property name="age" value="21"></property>
<property name="birthday" ref="now"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="now" class="java.util.Date"></bean>
</beans>
配置文件配置的类 AccountServiceImpl2.java:
public class AccountServiceImpl2 implements AccountService {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Date birthday;
// 实现成员变量的set方法
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("AccountServiceImpl2的saveAccount方法执行了。"+name+"。"+age+"。"+birthday+"");
}
}
测试:
@Test
public void test2() {
// 1.获取核心容器对象
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
// 2.根据id获取bean对象。如下两种方式
AccountService as = (AccountService)ac.getBean("accountService2");
as.saveAccount();
// 3.手动关闭容器
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) ac).close();
System.out.println(as);
}
输出结果:AccountServiceImpl2的saveAccount方法执行了。TEST。21。Tue Apr 09 09:25:39 CST 2019
四月 09, 2019 9:25:39 上午 org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext doClose
信息: Closing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@c39f790: startup date [Tue Apr 09 09:25:39 CST 2019]; root of context hierarchy
AccountServiceImpl2{name=‘TEST’, age=21, birthday=Tue Apr 09 09:25:39 CST 2019}
复杂类型/集合类型的注入
用于给list结构集合注入的标签:list、array、set
用于给map结构集合注入的标签:map、props
结论:结构相同,标签可以互换。
使用set注入方式,讲解如何实现复杂类型/集合类型的注入
Spring配置文件bean.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="accountService3" class="com.hxh.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl3">
<!--数组注入-->
<property name="strs">
<array>
<value>AAA</value>
<value>bbb</value>
<value>ccc</value>
</array>
</property>
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>xxx</value>
<value>rrr</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>qqqq</value>
<value>oooo</value>
</set>
</property>
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="key1" value="value1"></entry>
<entry key="key2" value="value2"></entry>
<entry key="key3">
<value>value3</value>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="keyA">AAA</prop>
<prop key="keyB">BBB</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
配置的类 AccountServiceImpl3.java:
需要注入的属性要实现set方法。
public class AccountServiceImpl3 implements AccountService {
private String[] strs;
private List<String> list;
private Set<String> set;
private Map<String, String> map;
private Properties properties;
public void setStrs(String[] strs) {
this.strs = strs;
}
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public void setSet(Set<String> set) {
this.set = set;
}
public void setMap(Map<String, String> map) {
this.map = map;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strs));
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(set);
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(properties);
}
}
测试:
@Test
public void testComplexType() {
// 1.获取核心容器对象
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
// 2.根据id获取bean对象。如下两种方式
AccountService as = (AccountService)ac.getBean("accountService3");
as.saveAccount();
// 3.手动关闭容器
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) ac).close();
}
输出结果:
[AAA, bbb, ccc]
[xxx, rrr]
[qqqq, oooo]
{key1=value1, key2=value2, key3=value3}
{keyB=BBB, keyA=AAA}
- 第三种:使用注解注入
我们将在注解篇章中讲解注解如何实现注入。
三、Spring中基于注解的IOC配置
使用注解配置IOC,需要在配置文件中告知Spring在创建容器时哪些包使用了注解配置,以便Spring扫描到包中的注解。使用 context 名称空间和约束中
注意此时配置文件的约束发生了变化:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.hxh"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
注解分类
3.1 用于创建对象的注解
@Component
属性 value:用于指定bean的id。当我们不写该属性时,它的默认值是当前类的类名,且首字母小写。
@Controller 和 @RestController
修饰表现层的类
@Controller和@RestController的区别:
1、如果只是使用@RestController注解Controller,则Controller中的方法无法返回jsp页面,或者html,配置的视图解析器 InternalResourceViewResolver不起作用,返回的内容就是Return 里的内容。
2、如果需要返回到指定页面,则需要用 @Controller配合视图解析器InternalResourceViewResolver才行。
如果需要返回JSON,XML或自定义mediaType内容到页面,则需要在对应的方法上加上@ResponseBody注解。
@Service
修饰业务层的类
@Respository
修饰持久层的类
@Controller、@Service、@Respository注解,他们的作用和属性与Component是一模一样的。如果当前类不属于三种中任何一个,使用@Component。
这三个注解是Spring框架为我们提供明确的三层使用的注解,使三层对象更加清晰。
示例:
使用注解@Service修饰Service层实现类AccountServiceImpl.java:
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("AccountServiceImpl执行了saveAccount方法");
}
}
使用注解@Repository(“accountDao”)修饰Dao层实现类AccountDaoImpl.java
@Repository("accountDao")
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
public AccountDaoImpl() {
System.out.println("AccountDaoImpl被创建了");
}
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("保存了账户");
}
}
测试:
@Test
public void testAnnotation() {
// 1.获取核心容器对象
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
// 2.根据id获取bean对象
AccountService accountService = ac.getBean("accountServiceImpl", AccountService.class);
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) ac).close();
System.out.println(accountService);
accountService.saveAccount();
}
输出结果
AccountDaoImpl被创建了
com.hxh.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl@6b419da
AccountServiceImpl执行了saveAccount方法
通过输出结果我们可以看到,核心容器对象一旦加载了xml配置文件,就会把配置的对象都会创建出来。
3.2 用于注入数据的注解
和在bean标签中的property标签功能一样
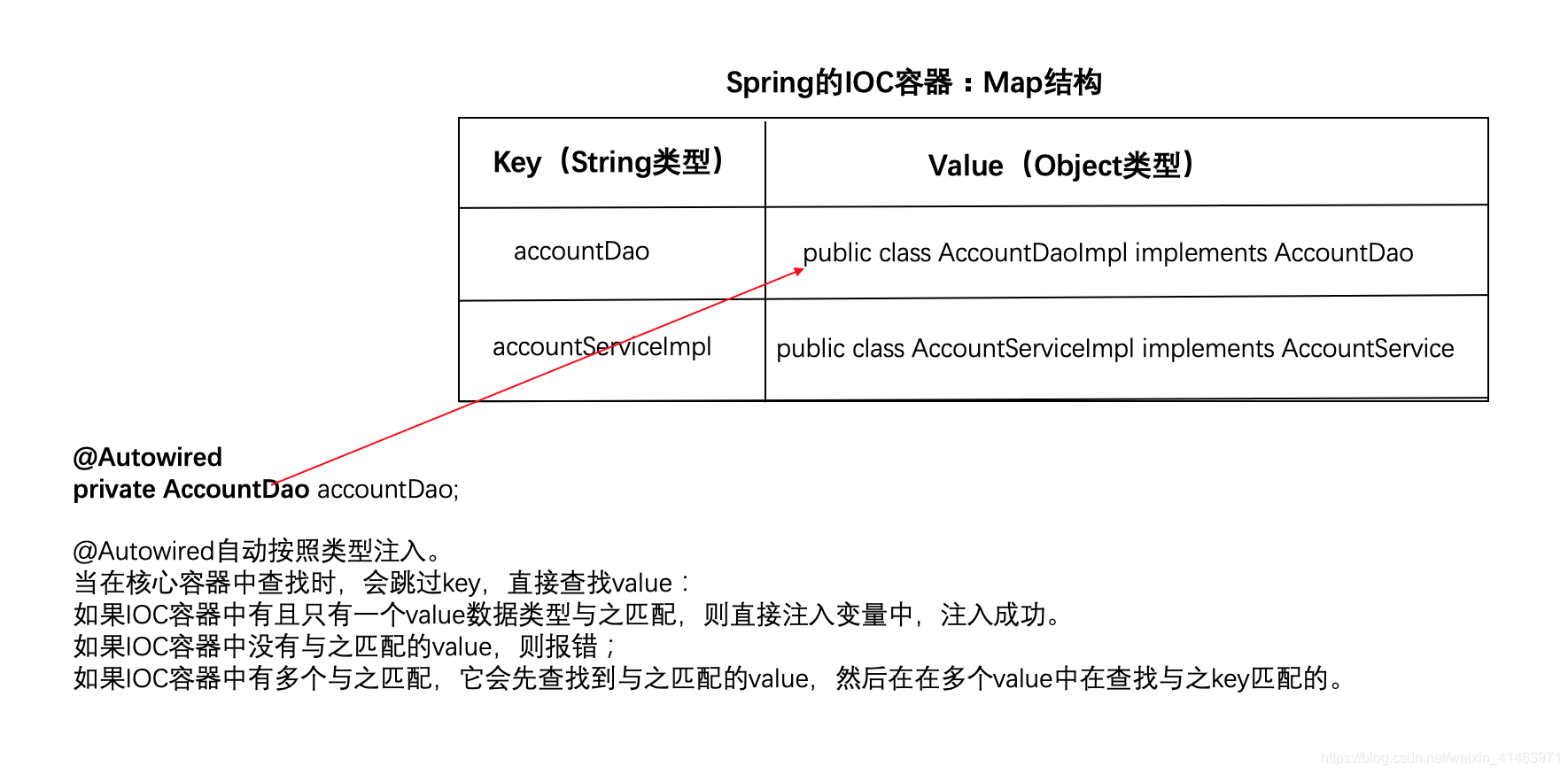
@Autowired
作用:自动按照类型注入。
位置:常用来修饰成员变量、方法
细节:在使用注解注入时,set方法可以不写。
注意:
- 如果容器中有唯一的一个bean对象类型和要注入变量的对象类型匹配,则注入成功;
- 如果IOC容器中没有任何bean的类型和要注入的变量类型匹配,则报错;
- 如果IOC容器中有多个与之匹配,它会先查找到与之匹配的value,然后在在多个value中在查找与之key匹配的。
示例代码:
AccountServiceImpl.java:
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void saveAccount() {
accountDao.saveAccount();
System.out.println("AccountServiceImpl执行了saveAccount方法");
}
}
AccountDaoImpl.java:
@Repository("accountDao")
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
public AccountDaoImpl() {
System.out.println("AccountDaoImpl被创建了");
}
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("保存了账户");
}
}
测试:
@Test
public void testAnnotation() {
// 1.获取核心容器对象
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
// 2.根据id获取bean对象
AccountService accountService = ac.getBean("accountServiceImpl", AccountService.class);
System.out.println(accountService);
accountService.saveAccount();
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) ac).close();
}
注意:如果不使用@Autowired修饰AccountServiceImpl.java的成员变量private AccountDao accountDao;,会出现空指针异常!因为该属性无论配置文件还是注解注入都未配置。使用@Autowired修饰之后:
关于@Autowired的图解:
@Qualifier
作用:在按照类型注入(@Autowired)的基础之上,再按照名称注入。在给类成员注入时,不能单独使用;但是在给方法参数注入时可以单独使用。
属性:value 用于指定注入bean的id。
@Autowired
@Qualifier("accountDao1")
private AccountDao accountDao1;
直接在IOC容器中查找key=accountDao1对应value注入。
@Resource
作用:直接按照bean的id注入,独立使用。
属性:name 用于注定bean的id
以上三个注解都只能注入其他bean类型的数据,而基本类型和String类型无法使用上述注解实现。
另外,集合类型的注入只能通过XML来实现。
@Resource
private AccountDao accountDao1;
@Value
作用:用于注入基本数据类型和String类型的数据
属性:value 用于指定数据的值。它可以使用Spring中的SpEL(也就是Spring中的EL表达式)
SpEL的写法:${表达式}
3.3 用于改变作用范围的注解
相当于bean标签的scope属性
@Scope
作用:用于指定bean的作用范围
属性:value 指定范围的取值。常用取值:singleton单例、prototype多例。默认单例。【具体可见bean标签的属性】
3.4 和生命周期相关的注解
bean标签的init-method destroy-method属性作用一样
@PreDestroy
用于指定销毁方法
@PostConstruct
用于指定初始化方法
示例代码:
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("初始化方法");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("销毁方法");
}
}
测试:
@Test
public void testAnnotation() {
// 1.获取核心容器对象
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
// 2.根据id获取bean对象
AccountService accountService = ac.getBean("accountServiceImpl", AccountService.class);
// 关闭容器
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) ac).close();
}
输出结果:
初始化方法
销毁方法
注意:关闭容器后才能执行销毁方法。
3.5 基于注解实现主配置类+子配置类
首先,介绍一下实现Spring配置类,需要使用的注解。@Configuration
作用:指定当前类是一个配置类
细节:当配置类是 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象创建的参数时,该注解可以不写。
比如:
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
那么,此时SpringConfig类可以不使用@Configuration注解:
@ComponentScan("com.hxh") // 告诉Spring创建容器时要扫描的package
@Import(JdbcConfig.class) // 导入子配置文件
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbcConfig.properties") // 告知Spring要加载的properties文件
public class SpringConfig {}
@ComponentScan
作用:用于通过注解指定Spring在创建容器时需要扫描的包
属性:value:它和basePackages的作用是一样的,都是用于指定创建容器时需要扫描的包。
等同于Spring配置文件中的:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.hxh"></context:component-scan>
@Bean
作用:用于把当前方法的返回值作为bean对象存入Spring的IOC容器中
属性:name:用于指定bean的id。默认值是当前方法的名称
细节:
- 当我们使用注解配置方法时,如果方法有参数,Spring框架回去容器中查找有没有可用的bean对象。
- 查找的方式和Autowired注解的作用是一样的。
比如:
@Bean(name = "runner")
@Scope("prototype")
public QueryRunner createQueryRunner(@Qualifier("dataSource1") DataSource dataSource2) {
return new QueryRunner(dataSource2);
}
表示:IOC容器存入key=runner,value=方法返回值。
@Import
作用:用于在主配置类中导入其他的子配置类。
属性:value 指定其他类的字节码。
当使用Import的注解后,有Import注解的类就是主配置类或父配置类,导入的都是子配置类(一般都这么认为。当然也可以是平级)
@PropertySource
作用:用于指定.properties文件的路径
属性:value:指定文件的名称。关键字:classpath:,表示类路径
比如:
// 加载类路径下的 jdbcConfig.properties 文件
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbcConfig.properties")
public class SpringConfig {}
3.6 如何使用注解完成配置类?
实现:1️⃣2️⃣3️⃣4️⃣
1️⃣主配置类
SpringConfig.java:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.hxh")
@Import(JdbcConfig.class)
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbcConfig.properties")
public class SpringConfig {}
2️⃣JDBC配置类,
注意:该配置类中有2个创建DataSource的方法。
public class JdbcConfig {
// 使用@PropertySource("classpath:jdbcConfig.properties")修饰主配置类,Spring就会加载jdbcConfig.properties文件
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
/**
* 用于创建一个QueryRunner对象。
* 使用@Qualifier("dataSource1") 告知spring我们查找数据源DataSource的key值
*/
@Bean(name = "runner")
@Scope("prototype")
public QueryRunner createQueryRunner(@Qualifier("dataSource1") DataSource dataSource2) {
return new QueryRunner(dataSource2);
}
/**
* 创建数据源对象:连接数据库spring。模拟IOC容器内有多个数据源对象
*/
@Bean(name = "dataSource1")
public DataSource createDataSource() {
try {
ComboPooledDataSource ds = new ComboPooledDataSource();
ds.setDriverClass(driver);
ds.setJdbcUrl(url);
ds.setUser(username);
ds.setPassword(password);
return ds;
} catch (PropertyVetoException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/**
* 创建数据源对象:连接数据库spring2。模拟IOC容器内有多个数据源对象
*/
@Bean(name = "dataSource2")
public DataSource createDataSource2() {
try {
ComboPooledDataSource ds = new ComboPooledDataSource();
ds.setDriverClass(driver);
ds.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring1");
ds.setUser(username);
ds.setPassword(password);
return ds;
} catch (PropertyVetoException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
3️⃣测试:
@Test
public void testFindAll() {
// 1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
// 2.获取业务层对象
AccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class);
// 3.执行方法
List<Account> accounts = as.findAll();
for (Account account : accounts) {
System.out.println(account);
}
}
4️⃣数据库配置文件 jdbcConfig.properties:
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=88888888
3.7 如果IOC容器的value中存在两个相同对象,那么如何获取指定的数据源对象?
分析 3.6 中的代码
首先,createDataSource、createDataSource1两个方法,都是用了注解@Bean修饰了,都会被存入IOC容器中,也就是说容器中存在两个DataSource。
如果没有注解```@Qualifier(“dataSource1”)
操作1,不能实现获取指定对象
@Bean(name = "runner")
@Scope("prototype")
public QueryRunner createQueryRunner(DataSource dataSource) {
return new QueryRunner(dataSource);
}
构造QueryRunner对象需要数据源参数,Spring会去IOC容器中的value中查找DataSource对象,因为出现了2个,Spring会抛出异常:org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException,要查找的对象不唯一。
操作2,能实现获取指定对象
让createQueryRunner参数与数据源的@Bean(name=“xxx”)的name一致,即使没有注解@Qualifier(“dataSource1”)修饰,也可以实现获取指定数据源对象的功能。
@Bean(name = "runner")
@Scope("prototype")
public QueryRunner createQueryRunner(DataSource dataSource1) {
return new QueryRunner(dataSource1);
}
如果使用注解@Qualifier("dataSource1")修饰参数
@Bean(name = "runner")
@Scope("prototype")
public QueryRunner createQueryRunner(@Qualifier("dataSource1") DataSource dataSource) {
return new QueryRunner(dataSource);
}
那么,构造DataSource对象时,Spring会直接去容器中查找key=dataSource1对应的value值。
四、Spring整合Junit
问题
在测试类中,每个测试方法都有以下两行代码:
// 1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
// 2.获取业务层对象
AccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class);
分析
针对上述问题,我们需要的是程序能自动帮我们创建容器。一旦程序能自动为我们创建 Spring 容器,我们就 无须手动创建了,问题也就解决了。
显然Junit 是无法实现的,因为它自 己都无法知晓我们是否使用了 Spring 框架,更不用说帮我们创建 Spring 容器了。不过好在,Junit 给我们暴露 了一个注解,可以让我们替换掉它的运行器。
这时,我们需要依靠 Spring 框架,因为它提供了一个运行器,可以读取配置文件(或注解)来创建容器。我 们只需要告诉它配置文件在哪就行了。
配置
- 导入Spring整合Junit的jar包或坐标(名称:spring-test)
- Junit提供了一个注解,可以替换成Spring的运行器:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) - 使用@Autowired 给测试类中的变量注入数据
@Autowired
private AccountService as;
- 告知Spring的运行器,Spring和ioc创建时基于xml还是注解的,并且说明位置。
使用注解注解:@ContextConfiguration
- locations:指定xml文件的位置,加上classpath关键字,表示在类路径下的xml文件
- classes:指定注解类所在的位置
注意:当使用Spring 5.x版本时,Spring要求Junit的jar包必须是4.12及以上。
实现:
注解配置类:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class)
public class AccountServiceTest {
@Autowired
private AccountService as = null;
@Test
public void testFindAll() {
List<Account> accounts = as.findAll();
for (Account account : accounts) {
System.out.println(account);
}
}
xml配置文件:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:bean.xml")
public class AccountServiceTest {
@Autowired
private AccountService as = null;
@Test
public void testFindAll() {
List<Account> accounts = as.findAll();
for (Account account : accounts) {
System.out.println(account);
}
}
五、Spring中基于XML的AOP配置
5.1 AOP 相关术语
Joinpoint(连接点 ):所谓连接点是指那些被拦截到的点。在 Spring 中,这些点指的是方法,因为 Spring 只支持方法类型的连接点。
Pointcut(切入点 ):所谓切入点是指我们要对哪些 Joinpoint 进行拦截的定义。比如,被动态代理增强的方法可以称之为切入点,拦截到但是未增强的方法不能称为切入点。
Advice(通知/增强):所谓通知是指拦截到 Joinpoint 之后所要做的事情就是通知。 通知的类型:前置通知,后置通知,异常通知,最终通知,环绕通知。
Introduction(引介 ):引介是一种特殊的通知在不修改类代码的前提下, Introduction 可以在运行期为类动态地添加一些方法或 Field。
Target(目标对象 ):代理的目标对象。
Weaving(织入 ):是指把增强应用到目标对象来创建新的代理对象的过程。Spring 采用动态代理织入,而 AspectJ 采用编译期织入和类装载期织入。
Proxy(代理):一个类被 AOP 织入增强后,就产生一个结果代理类
Aspect(切面 ):是切入点和通知(引介)的结合。
5.2 编写AOP代码
① 开发阶段
→ 编写核心业务代码
→ 抽取公共代码,制作成通知
→ 在配置文件中,配置切面:即声明切入点与通知间的关系
② 运行阶段(由 Spring 框架完成)
Spring 框架监控切入点方法的执行。一旦监控到切入点方法被运行,使用代理机制,动态创建目标对 象的代理对象,根据通知类别,在代理对象的对应位置,将通知对应的功能织入,完成完整的代码逻辑运行。
5.3 关于代理的选择
Spring 框架会根据目标类是否实现了接口来决定采用哪种动态代理的方。关于动态代理的分类可以查看这篇博客 :传送门。
5.4 环境搭建
第一步:业务层Service+持久层dao代码。此处仅是模拟,不在准备实体类。
目的:增强业务层方法的功能
第二步:Spring框架坐标和切入点表达式解析包aspectjweaver
pox.xml添加 Spring和 aspectjweaver坐标
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--aspectjweaver用于解析切入点表达式-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.8.7</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
第三步:导入约束
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
</beans>
第四步:配置 Spring 的 IOC
<bean id="accountService" class="com.hxh.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
第五步:配置AOP
参考这篇博客:传送门





 本文详细介绍了Spring框架的IOC(控制反转)配置,包括基于XML和注解的两种方式。XML配置中讲解了核心容器接口、bean标签属性、创建bean的三种方式以及依赖注入。注解配置部分涉及了@Component、@Service、@Repository、@Controller等注解,以及@Autowired、@Qualifier等用于数据注入的注解。此外,文章还提到了Spring的AOP配置和JdbcTemplate的使用。
本文详细介绍了Spring框架的IOC(控制反转)配置,包括基于XML和注解的两种方式。XML配置中讲解了核心容器接口、bean标签属性、创建bean的三种方式以及依赖注入。注解配置部分涉及了@Component、@Service、@Repository、@Controller等注解,以及@Autowired、@Qualifier等用于数据注入的注解。此外,文章还提到了Spring的AOP配置和JdbcTemplate的使用。
















 5万+
5万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








