一,直方图概念深入:
先看一副官方图片:
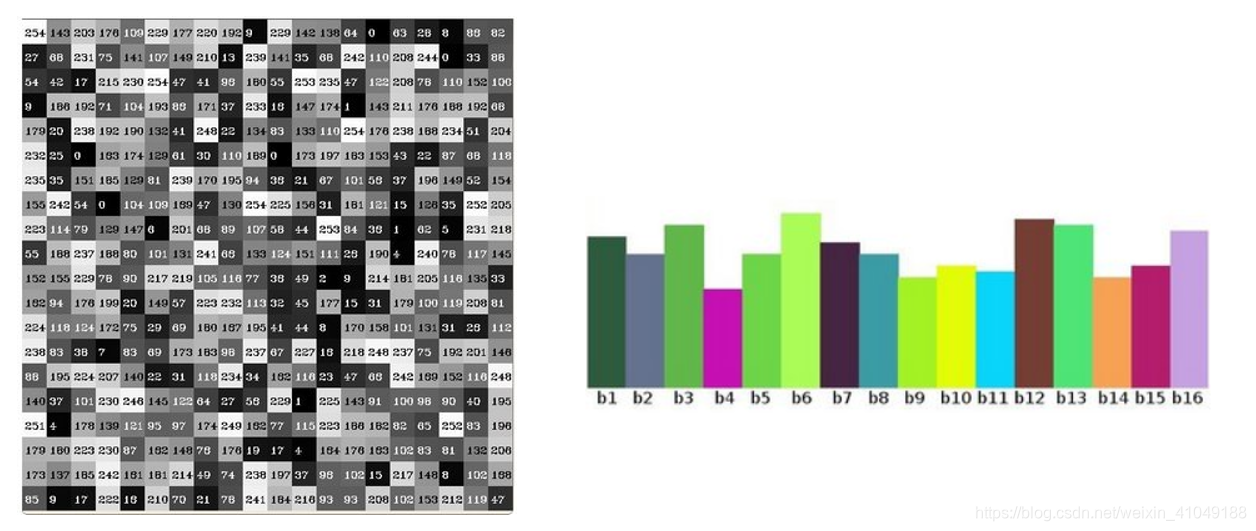
假设有一副图片,以及像素值(上图左)。把像素值分为不同的等级,每个等级称为bin。如图把直方图分为16个等级。每个等级包含不同的像素值范围(像素值最大255)。然后统计每个bin中像素出现的频率。
一副灰度图像的像素范围按照上面的划分如下:
[ 0 ~ 255]=[0 ~ 15] ⋃\bigcup⋃ [16 ~ 31] ⋃\bigcup⋃ [ 32 ~ 47] ⋃\bigcup⋃ … …⋃\bigcup⋃ [240 ~ 255]
range=bin1⋃bin2⋃bin3......⋃bin16range=bin_1\bigcup bin_2\bigcup bin_3 ... ...\bigcup bin_{16}range=bin1⋃bin2⋃bin3......⋃bin16
- 上述直方图概念是基于图像像素值,其实我们对图像的梯度,每个像素的角度等一切图像的属性值,我们都可以建立直方图。这个才是直方图的概念的真正意义。不过基于图像像素值灰度直方图是最长见的。
- 直方图常见的属性:
1:dims:表示维度,对于灰度图像(单通道)来说只有一个通道值 (dims=1)
2:bins:表示在维度中子区域大小划分,bins=255,划分为 255 个等级。
3:range:表示像素值的范围,灰度值范围在 0 ~ 255 之间。
二,API:
Cv2.Split() 将多通道阵列的每个平面复制到专用阵列 (如:分割图像(把三通道分割为3个单通道))
返回值为:Mat[] (数组的数量必须与mtx.channels()匹配。如果需要,将重新分配数组本身)
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Mat src | The source multi-channel array(源多通道阵列) |
Cv2.CalcHist(): 计算一组图像的联合密集直方图。有一个重载方法
方法1:
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Mat[] images | 输入单通道图像集合 |
| int[] channels | 图像在集合中对应的通道 : 0 ~ 2 之间 (0,1,2) |
| InputArray mask | 掩膜 输入的InputArray 对象,可以为空,或者输入对应 images[i],要与通道对应 |
| OutputArray hist | 输出计算后的直方图 OutputArray对象。 |
| int dims | 维度 ,单通道为 1 |
| int[] histSize | 直方图的级数,就是把像素分为几个等级。像素大小在 0 ~ 255之间,如果全部输出就是 256个等级。 |
| float[][] ranges | 值域的范围。 |
| bool uniform = true | 是否规范化。(每个bins大小取值等级一致,默认为true) |
| bool accumulate = false | 是否累加(多通道的需要,默认值为 false) |
方法2:
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Mat[] images | 输入单通道图像集合 |
| int[] channels | 图像在集合中对应的通道 : 0 ~ 2 之间 (0,1,2) |
| InputArray mask | 掩膜对象 输入的InputArray 对象,可以为空,或者输入对应 images[i],要与通道对应 |
| OutputArray hist | 输出计算后的直方图 OutputArray对象。 |
| int dims | 维度 ,单通道为 1 |
| int[] histSize | 直方图的级数,就是把像素分为几个等级。像素大小在 0 ~ 255之间,如果全部输出就是 256个等级。 |
| Rangef[] ranges | 值域的范围。 |
| bool uniform = true | 是否规范化。(每个bins大小取值等级一致,默认为true) |
| bool accumulate = false | 是否累加(多通道的需要,默认值为 false) |
三,代码:
/// <summary>
/// 直方图计算
/// </summary>
/// <param name="path"></param>
private static void HistogramCalculation(string path)
{
using (Mat src = new Mat(path, ImreadModes.AnyColor | ImreadModes.AnyDepth))
using (Mat histogram = new Mat())
{
//计算直方图
Mat[] mats = Cv2.Split(src); //分割图像(把三通道分割为3个单通道)
Mat hist_B = new Mat();
Mat hist_G = new Mat();
Mat hist_R = new Mat();
int[] channels0 = { 0 };
int[] channels1 = { 1 };
int[] channels2 = { 2 };
int[] histSize = { 256 };
Rangef[] rangefs = new Rangef[]
{
new Rangef(0, 256),
};
//
// 摘要:
// computes the joint dense histogram for a set of images.
// 计算一组图像的联合密集直方图。
// 参数:
// images: 输入单通道图像集合,
//
// channels: 图像在集合中对应的通道 : 0 ~ 2 之间
//
// mask: 输入的InputArray 对象,可以为空,或者输入对应 images[i],要与通道对应
//
// hist: 输出计算后的直方图 OutputArray对象。
//
// dims: 维度 ,单通道为 1
//
// histSize: 直方图的级数,就是把像素分为几个等级。像素大小在 0 ~ 255之间,如果全部输出就是 256个等级。
//
// ranges: 值域的范围。
//
// uniform: 布尔值
//
// accumulate: 布尔值
Cv2.CalcHist(mats, channels0, new Mat(), hist_B, 1, histSize, rangefs, true, false);
Cv2.CalcHist(mats, channels1, new Mat(), hist_G, 1, histSize, rangefs, true, false);
Cv2.CalcHist(mats, channels2, new Mat(), hist_R, 1, histSize, rangefs, true, false);
int high = 400;
int width = 512;
int bin_w = width / 256;//每个bins的宽度 画布的宽度除以bins的个数
Mat histImage = new Mat(width, high, MatType.CV_8UC3, new Scalar(0, 0, 0)); //定义一个Mat对象,相当于一个画布
//归一化,像素值有可能数据量很大,压缩一下。是范围在定义画布的范围内。
//
// 摘要:
// scales and shifts array elements so that either the specified norm (alpha) or
// the minimum (alpha) and maximum (beta) array values get the specified values
// 缩放和移动数组元素,使指定的范数(alpha)或最小(alpha)和最大(beta)数组值得到指定的值
// 参数:
// src:
// The source array 源数据
//
// dst:
// The destination array; will have the same size as src 目标数组;会和src一样大
//
// alpha:
// The norm value to normalize to or the lower range boundary in the case of range
// normalization
// 在范围的情况下,要规格化到或较低范围边界的范数值归一化
// beta:
// The upper range boundary in the case of range normalization; not used for norm
// normalization
// 距离归一化情况下的上范围边界;不用于规范标准化
// normType:
// The normalization type 归一化类型
//
// dtype:
// When the parameter is negative, the destination array will have the same type
// as src, otherwise it will have the same number of channels as src and the depth
// =CV_MAT_DEPTH(rtype)
// 当参数为负时,目标数组将具有与src相同的类型,否则它将具有与src相同的通道数量,并且depth =CV_MAT_DEPTH(rtype)
// mask:
// The optional operation mask 可选操作掩码
Cv2.Normalize(hist_B, hist_B, 0, histImage.Rows, NormTypes.MinMax, -1, null);
Cv2.Normalize(hist_G, hist_G, 0, histImage.Rows, NormTypes.MinMax, -1, null);
Cv2.Normalize(hist_R, hist_R, 0, histImage.Rows, NormTypes.MinMax, -1, null);
//绘制直方图
for (int i = 1; i < 256; i++)//遍历直方图的级数
{
//B 画线,一条线有两个点组成。首先确定每个点的坐标(x,y) .遍历从1开始。0 ~ 1 两个点组成一条线,依次类推。
Cv2.Line(histImage, new Point(bin_w * (i - 1), high - Math.Round(hist_B.At<float>(i - 1))), new Point(bin_w * (i - 1), high - Math.Round(hist_B.At<float>(i))), new Scalar(255, 0, 0), 1, LineTypes.AntiAlias);
//G
Cv2.Line(histImage, new Point(bin_w * (i - 1), high - Math.Round(hist_G.At<float>(i - 1))), new Point(bin_w * (i - 1), high - Math.Round(hist_G.At<float>(i))), new Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1, LineTypes.AntiAlias);
//R
Cv2.Line(histImage, new Point(bin_w * (i - 1), high - Math.Round(hist_R.At<float>(i - 1))), new Point(bin_w * (i - 1), high - Math.Round(hist_R.At<float>(i))), new Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1, LineTypes.AntiAlias);
}
using (new Window("SRC", WindowMode.Normal, src))
using (new Window("histImage", WindowMode.Normal, histImage))
{
Cv2.WaitKey(0);
}
}
}
输出结果图:
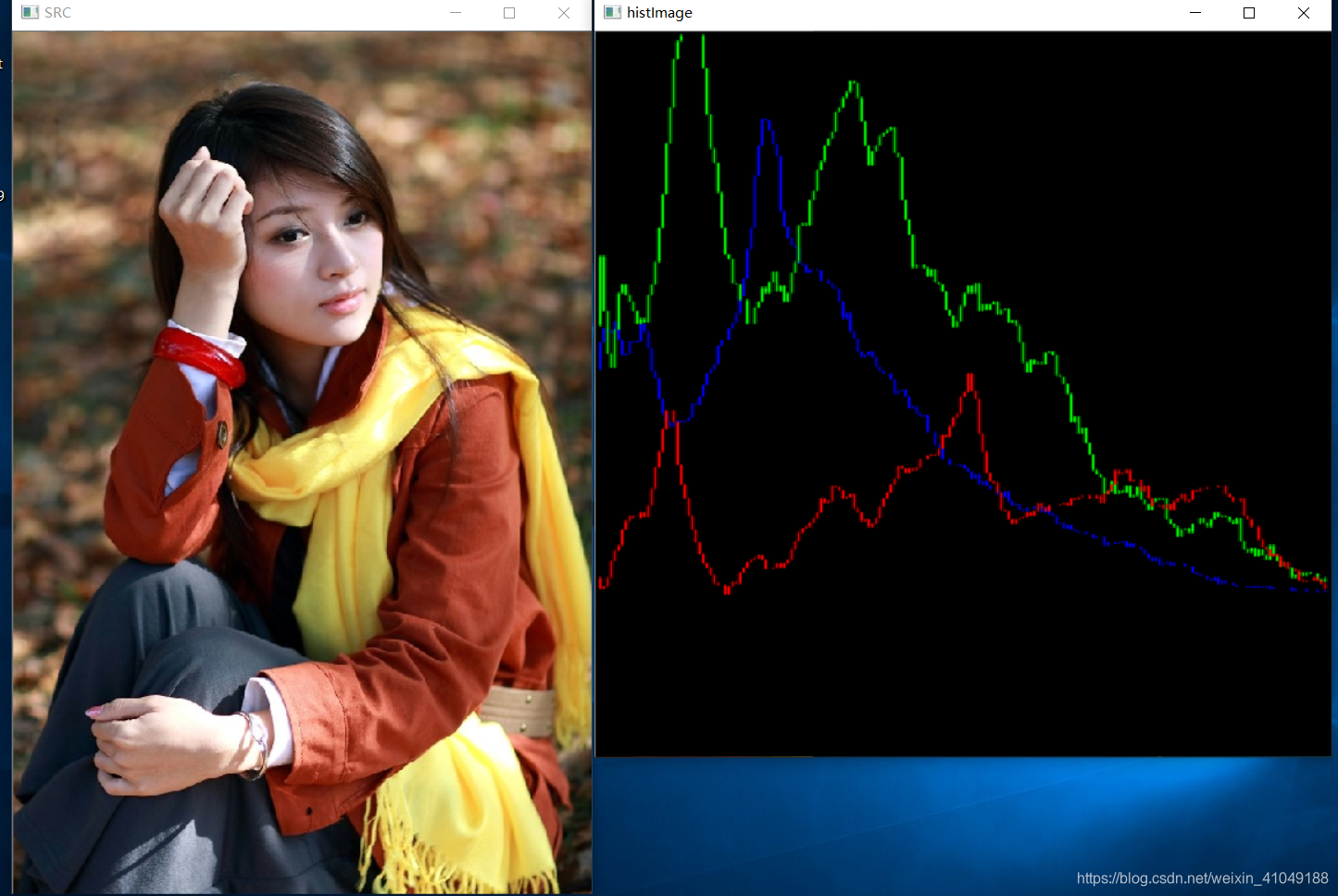





 博客深入介绍图像直方图概念,基于图像像素值、梯度等属性值均可建立直方图,常见属性有dims、bins、range。还介绍了Cv2.Split()和Cv2.CalcHist()两个API,前者用于分割多通道阵列,后者用于计算联合密集直方图,最后给出代码及输出结果图。
博客深入介绍图像直方图概念,基于图像像素值、梯度等属性值均可建立直方图,常见属性有dims、bins、range。还介绍了Cv2.Split()和Cv2.CalcHist()两个API,前者用于分割多通道阵列,后者用于计算联合密集直方图,最后给出代码及输出结果图。
















 2075
2075

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








