流程图
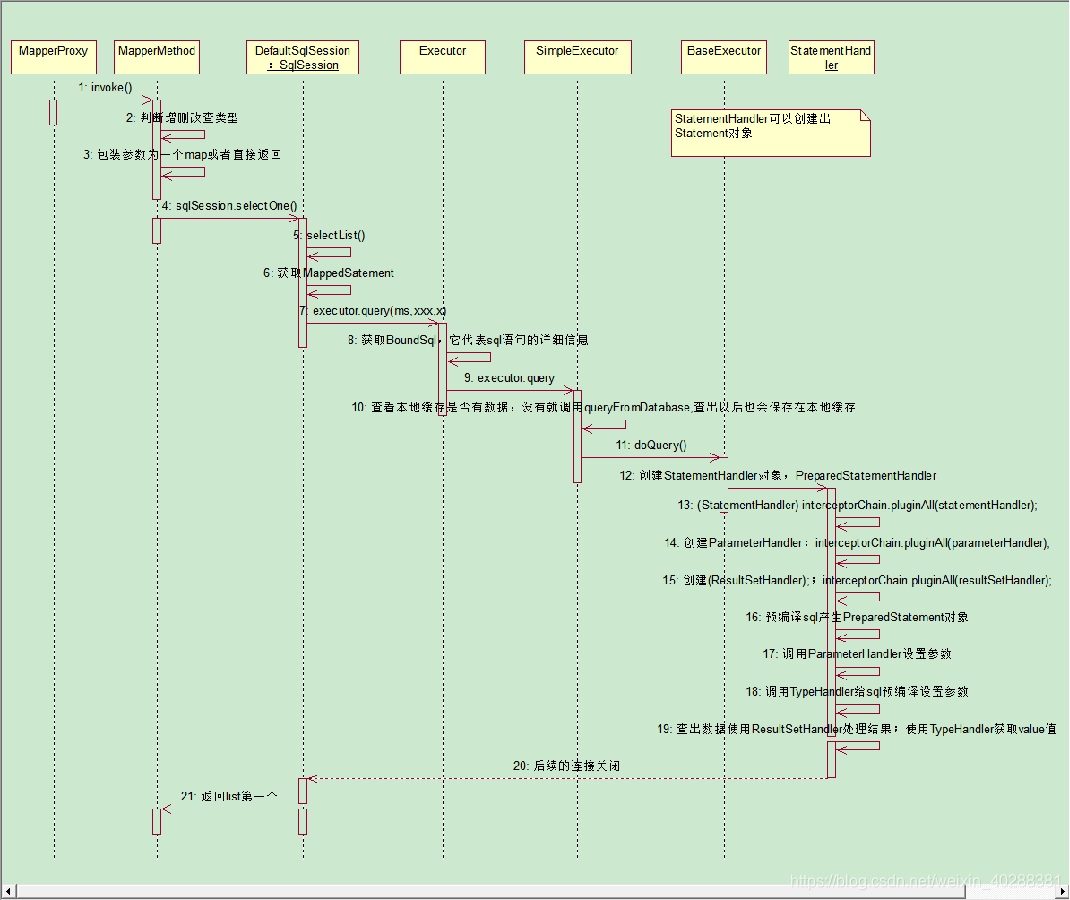
- 创建代理对象
- 代理对象调用DefaultSqlSession
- 使用Executor调用StatementHandler,创建ParammeterHandler和ResultHandler
- 利用ParameterHandler设置参数,ResultSetHandler处理结果
- ParameterHandler和ResultHandler底层都是调用TypeHandler,而TypeHandler是调用JDBC下的Statement和Preparement
源码剖析
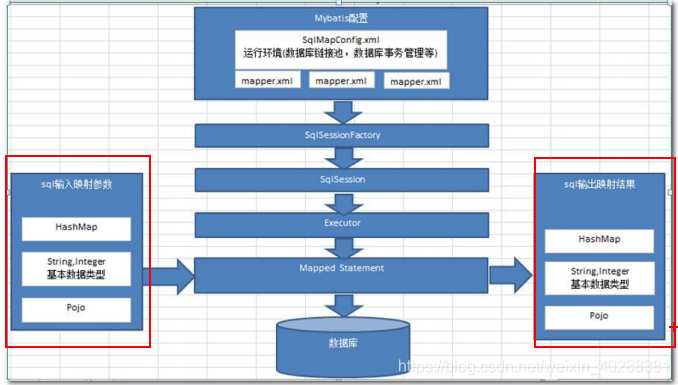
Mybatis的Xml映射文件和Mybatis内部数据结构之间的映射关系
Mybatis将所有Xml配置信息都封装到All-In-One重量级对象Configuration内部。在Xml映射文件中,标签会被解析为ParameterMap对象,其每个子元素会被解析为ParameterMapping对象。标签会被解析为ResultMap对象,其每个子元素会被解析为ResultMapping对象。每一个< select>、< insert>、< update>、< delete>标签均会被解析为MappedStatement对象,标签内的sql会被解析为BoundSql对象
1.SqlSession传入接口,创建MapperProxy代理类,调用invoke方法
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//如果是Objcct下的方法,如toString或hashCode等,则直接执行
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
//将方法包装成MapperMethod,包装参数为Map或直接返回
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
//此处调用Executor
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
//包装方法
//返回Map或者直接返回
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
2.MapperMethod执行execute,使用Executor
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
//判断传入Sql类型
if (SqlCommandType.INSERT == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.UPDATE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.DELETE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.SELECT == command.getType()) {
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else {
//我们只分析查询实现中单参数传递
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
} else if (SqlCommandType.FLUSH == command.getType()) {
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
} else {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
3.执行selectOne下的selectList方法
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// 执行selectList方法
List<T> list = this.<T>selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
//获取MapperStatement,即得到Mapper中增删改查的详细信息
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
//执行executor下的query方法并返回Lisy
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
4.执行selectList下Executor的query方法
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
//获取BoundSql,代表Sql的详细信息
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
//调用SimpleExecutor的query方法
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
5.执行SimpleExecutor下doQuery方法,创建PrepareStatement
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
//获取configuation信息
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
//创建StatementHandler
//此处开始调用StatementHandler
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
//调用PrepareStatement,底层是TypeHandler
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
//调用ResultSetHandler,底层是TypeHandler
//最终返回查询结果给调用者
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
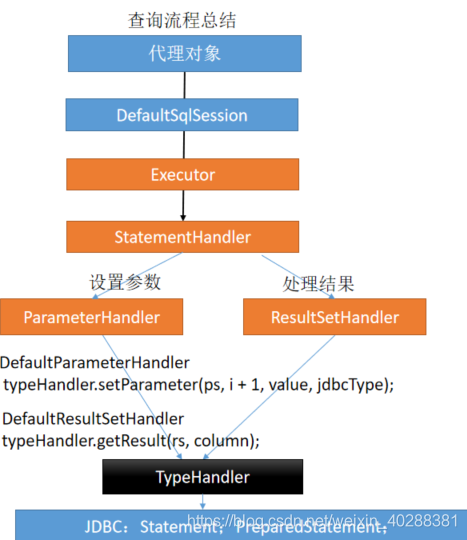
- StatementHandler:处理sql语句预编译,设置参数等相关工作
- ParameterHandler:设置预编译参数用的
- ResultHandler:处理结果集
- TypeHandler:在整个过程中,进行数据库类型和javaBean类型的映射
小结
MyBatis为映射接口创建代理对象,通过代理对象执行invoke方法进行对原方法的增强,执行DefaultSqlSession下的Executor,获取查询语句的详细信息。通过StatementHandler下的ParameterHandler和ResultSetHandler为TypeHandler下Statement设置参数和处理结果,最终使用Statement的PreparedStatement查询相关信息,并返回查询结果给调用者。
MyBatis整体运行原理小结
- 根据配置文件初始化Configuration对象
- 创建一个DefaultSqlSession对象,里面包含Configuration以及Executor(根据全局配置文件中的defaultExecutorType创建出对应的Executor)
- DefaultSqlSession.getMapper(),创建Mapper接口对应的MapperProxy
- MapperProxy内有DefaultSqlSession,执行增删查改方法:
- 调用DefaultSqlSession的增删查改(Executor)
- 创建一个StatementHandler对象,同时也会创建出ParameterHandler和ResultSetHandler
- 调用StatementHandler预编译参数以及设置参数值,使用ParameterHandler设置参数值
- 调用StatementHandler的增删改查方法
- ResultSetHandler封装结果
注意
四大对象(即Executor,StatementHandler,ParameterHandler,ResultSetHandler)创建的时候都有interceptorChain.pluginAll方法





 本文详细解析了MyBatis的运行原理,从创建代理对象开始,阐述了SqlSession如何通过MapperProxy调用Executor执行查询。深入剖析了MapperMethod的execute方法,以及Executor的query过程,包括SimpleExecutor的doQuery方法。文中还介绍了StatementHandler、ParameterHandler和ResultHandler的角色,以及它们在TypeHandler协助下处理数据库交互的过程。最后总结了MyBatis的整体运行流程,强调了Configuration对象和四大对象在执行过程中的关键作用。
本文详细解析了MyBatis的运行原理,从创建代理对象开始,阐述了SqlSession如何通过MapperProxy调用Executor执行查询。深入剖析了MapperMethod的execute方法,以及Executor的query过程,包括SimpleExecutor的doQuery方法。文中还介绍了StatementHandler、ParameterHandler和ResultHandler的角色,以及它们在TypeHandler协助下处理数据库交互的过程。最后总结了MyBatis的整体运行流程,强调了Configuration对象和四大对象在执行过程中的关键作用。
















 228
228

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








