1 简介
2 原则
3 工具
4 应用
4.1 在 4G/5G 拨号中的应用
1 简介
AT 命令是 TE (Terminal Equipment)(如 PC 等用户终端)和 MT(Mobile Terminal)(如移动台等移动终端)之间的通信命令协议
如图:

「AT 命令有的区分大小写,有的不区分」
2 原则
AT 命令是以 AT 作首, 字符结束的 字符串
❝对字符串的定义:由双引号包括起来的,不含引号或逗号的字节流
❞
每个接口功能内聚
数据包大小有限制:发送不大于
2+260个,上报不大于688个每一行只包含一条命令或者响应
不要有多余的冗余的空格
第一条命令发送后必须等到响应才能发第二条命令,否则第二条命令将不被执行
耗时较长的命令采用异步方式
要能处理字符
@
3 工具
「microcom」
一般嵌入式系统中会自带 microcom,可以用来操作 AT 串口,用法如下:
~ # microcom -h
microcom: invalid option -- 'h'
BusyBox v1.26.2 (2019-12-24 10:35:33 CST) multi-call binary.
Usage: microcom [-d DELAY] [-t TIMEOUT] [-s SPEED] [-X] TTY
Copy bytes for stdin to TTY and from TTY to stdout
-d Wait up to DELAY ms for TTY output before sending every
next byte to it
-t Exit if both stdin and TTY are silent for TIMEOUT ms
-s Set serial line to SPEED
-X Disable special meaning of NUL and Ctrl-X from stdin
~ #
## 注意:退出 microcom 程序使用 ctrl+x 而不是 ctrl+c
「你也可以自己写一个操作串口的程序」
4 应用
4.1 在 4G/5G 拨号中的应用
4.1.1 移植驱动
❝每个 4G 或者 5G 模块都有一个专门用于 AT 命令通讯的串口,我们首先要找到它才能进行后面的操作。同时,要想模块正常工作,必须移植正确的「网卡驱动」和「串口驱动」
❞
如图所示:
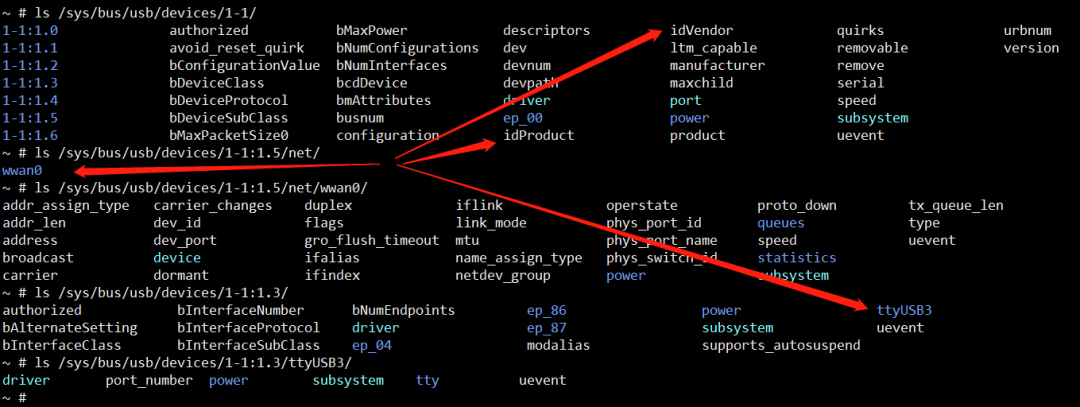
网口:wwan0 AT 串口:ttyUSB3
idVendor 和 idProduct 会在移植驱动的时候添加进去。
我们通过 idVendor 和 idProduct 遍历得到自己的模块设备,从而获取 NET 网口名称和 AT 串口名称。
4.1.2 获取网口名称和串口名称
「opendir」
NAME
opendir, fdopendir - open a directory
SYNOPSIS
#include
#include
DIR *opendir(const char *name);
DIR *fdopendir(int fd);
「readdir」
NAME
readdir - read a directory
SYNOPSIS
#include
struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp);
「示例代码片段」
DIR *pDir;
struct dirent *ent = NULL;
char dir[255] = "/sys/bus/usb/devices";
pDir = opendir(dir);
if (pDir)
{
while ((ent = readdir(pDir)) != NULL)
{
struct dirent *subent = NULL;
DIR *psubDir;
char subdir[255];
char subdir2[255 * 2];
char idVendor[4 + 1] = {0};
char idProduct[4 + 1] = {0};
int fd = 0;
char netcard[32] = "\0";
char qmifile[32] = "\0";
snprintf(subdir, sizeof(subdir), "%s/%s/idVendor", dir, ent->d_name);
fd = open(subdir, O_RDONLY);
if (fd > 0)
{
read(fd, idVendor, 4);
close(fd);
}
snprintf(subdir, sizeof(subdir), "%s/%s/idProduct", dir, ent->d_name);
fd = open(subdir, O_RDONLY);
if (fd > 0)
{
read(fd, idProduct, 4);
close(fd);
}
if (!strncasecmp(idVendor, "05c6", 4) || !strncasecmp(idVendor, "2c7c", 4) || !strncasecmp(idVendor, "1e0e", 4))
;
else
continue;
printf("Find %s/%s idVendor=%s idProduct=%s\n", dir, ent->d_name, idVendor, idProduct);
snprintf(tmpdir, sizeof(tmpdir), "%s/%s", dir, ent->d_name);
snprintf(subdir, sizeof(subdir), "%s/%s:1.5/net", dir, ent->d_name);
psubDir = opendir(subdir);
if (psubDir == NULL)
{
printf("Cannot open directory: %s, errno: %d (%s)", subdir, errno, strerror(errno));
continue;
}
while ((subent = readdir(psubDir)) != NULL)
{
if (subent->d_name[0] == '.')
continue;
printf("Find %s/%s\n", subdir, subent->d_name);
printf("Find usbnet_adapter = %s\n", subent->d_name);
strcpy(netcard, subent->d_name);
break;
}
closedir(psubDir);
}
closedir(pDir);
}
4.1.3 常用指令
at+cpin?
~ # microcom /dev/ttyUSB3
at+cpin?
+CME ERROR: SIM not inserted
~ # microcom /dev/ttyUSB7
at+cpin?
+CPIN: READY
OK
#############################
可以使用此命令判断卡是否插入或者接触是否良好
at+cereg?
~ # microcom /dev/ttyUSB7
at+cereg?
+CEREG: 0,1
OK
#############################
0 未注册,未进行附着或搜网操作
1 在本地网注册
2 未注册,正在进行附着或搜网操作
3 注册被拒绝
4 未知
5 已注册, 漫游状态
注意: 只有 modem 上报 1 或者 5 时,才是正常入网状态。
0 一般表示模块坏了或者模块配置有问题
2 一般表示模块信号不好,可以检查一下模块天线
3 一般情况是卡没有开户或者开户信息异常,联系运营商开户或者自己在基站上开户
at+csq
~ # microcom /dev/ttyUSB7
at+csq
+CSQ: 31,99
OK
#############################
接收信号强度指示
0 等于或小于-113 dBm
1 -111dBm
2...30 取整(-109… -53) dBm
31 等于或大于-51 dBm
99 未知或不可测
返回的是 RSSI 值
99 一般表示不在服务区或者没插天线或者卡接触不好没有认到
at+fcun
at+cfun=0 模块最少功能,可看作飞行模式,离线
at+cfun=1 模块全部功能,可看作默认值,上线
其他常用
A/重复上一条指令ATI查询制造商信息AT+CGMI查询制造商名称AT+CIMI获取 IMSIAT+CGSN查询 IMEIAT+CGMR查询软件版本AT+CGMM查询模块型号AT^SYSINFO查询系统信息
4.1.4 根据 IMSI 判断运营商
/*
AT+CIMI
check "China Mobile" or "China Telecom" or "China Unicom"
*/
if (mnc==0||mnc==2||mnc==4||mnc==7)
{
printf("SIM Card is China Mobile!\n");
}
else if (mnc==1||mnc==6||mnc==9)
{
printf("SIM Card is China Unicom!\n");
}
else if (mnc==3||mnc==5||mnc==11)
{
printf("SIM Card is China Telecom!\n");
}
else
{
printf("SIM Card is Unknown!\n");
}
4.1.5 IMEI 定义规则
合法的 IMEI 示例: 867530040102632, 867530040102640
- 由 15 位数字组成
- 前 6 位(TAC)是型号核准号码,代表手机类型。
- 接着 2 位(FAC)是最后装配号,代表产地。
- 后 6 位(SNR)是串号,代表生产顺序号。
- 最后 1 位(SP)是检验码
86 中国 01 美国
「IMEI 校验码算法」
- 将偶数位数字分别乘以 2,分别计算个位数和十位数之和
- 将奇数位数字相加,再加上上一步算得的值
- 如果得出的数个位是 0 则校验位为 0,否则为 10 减去个位数
如:35 89 01 80 69 72 41 偶数位乘以 2 得到 5*2=10 9*2=18 1*2=02 0*2=00 9*2=18 2*2=04 1*2=02, 计算奇数位数字之和和偶数位个位十位之和,得到 3+(1+0)+8+(1+8)+0+(0+2)+8+(0+0)+6+(1+8)+7+(0+4)+4+(0+2)=63 => 校验位 10-3 = 7




 本文介绍了在STM32F030上使用AT指令与4G/5G模块进行通信的基础知识,包括AT命令的使用原则、常用指令,以及如何在拨号应用中进行驱动移植、获取网口和串口名称。通过示例代码展示了如何遍历设备找到4G/5G模块,并提供了IMEI的定义规则和校验算法。
本文介绍了在STM32F030上使用AT指令与4G/5G模块进行通信的基础知识,包括AT命令的使用原则、常用指令,以及如何在拨号应用中进行驱动移植、获取网口和串口名称。通过示例代码展示了如何遍历设备找到4G/5G模块,并提供了IMEI的定义规则和校验算法。
















 8193
8193

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








