VUEX的使用,就不用说了,具体的看文档,分state、getter、mutation、actions、map[state| getter| mutation| action] 五个细节,来实现一个我们几个的vuex。
vuex-state
new Vuex.Store({}) // vuex 中存在 store ,
// 在 vuex index.js中
export class Store {
constructor(){}
}
# install
vue.use(Vuex) 会自动调用 , 至于为啥需要 install函数 ,可参考vue-插件
// 在 vuex index.js中
class Store {
constructor(){}
}
function install() { //具体使用 后面继续介绍
}
export default {
Store,
install,
}
#$store.state
- vue实例 this.$store 的实现:
function install(_vue) {
// 通过mixin 给vue 实例 混入 $store
_vue.mixin({
beforeCreate(){
// console.log('install') 可以看到 打印 n个页面+n个组件 + mian.js 次数
const options = this.$options;
if(options.store) { // 判断是否是在跟组件中,即 mian.js 中的实例
this.$store = options.store;
} else {
if(this.$parent && this.$parent.$store) {
this.$store = this.$parent.$store;
}
}
}
}) // applyMixin 函数实现,我这边为方便讲解直接写在函数中
}
// 这时在vue实例中,可以获取到 this.$store
2. vue实例中 this.$store.state 及 其数据的双向绑定 的实现:
class Store {
constructor(option){
this.state = option.state; // 你发现 vue 中可以获取到 this.$store.state 的 ️
}
}
但 在改变数据时,页面并没有发生改变,即没有实现数据的双向绑定;在vue中data的数据可以实现页面的双向绑定,我们是否可以通过vue 来实现这一功能呢?
let vue;
class Store {
constructor(option){
// this.state = option.state;
const _vm = new vue({
data: option.state
})
this.state = _vm.$data;
}
}
function install(_vue) {
vue = _vue;
... // 只留 当前 目标的步骤
}
export default{
install,
Store,
}
这个时候会发现,当你改变count 的值,页面会发生改变,那就实现了vuex 数据的双向绑定。
3. vuex-modules 子模块 的state
3.1 将option中数据重新整理格式 , 整理后格式为:
root: {
state:{}, // 用于存储 状态
_rawModule:{}, // 当前模块
_children:[ // 当前模块的子模块
{state:{},_rawModule:{},_children:[]}
// ...
]
}
重点:之后每部分功能的实现都与新整理数据有关
export default class ModuleCollection {
constructor(rawModlue){
this.register([], rawModlue)
}
/**
* @desc 注册模块
* @param {Array} path []=> root ['student'] => root/student ['student','a'] => root/student/a
* @param {Object} rawModule 当前模块
*/
register(path,rawModlue) {
const newModule = new Module(rawModlue);
// 根路径
if (path.length === 0) {
this.root = newModule;
} else {
// 1. 获取父节点
const parenModule = this.get(path.slice(0,-1));
// 2. 当前模块的名字
const rawModlueName = path[path.length - 1];
// 3. 挂载到父模块
parenModule._chidren[rawModlueName] = newModule;
}
// 判断当前模块是否存在子模块
if (rawModlue.modules) {
Object.keys(rawModlue.modules).forEach(moduleName => {
const childModule = rawModlue.modules[moduleName];
this.register(path.concat(moduleName), childModule);
});
}
}
get(path) {
return path.reduce((module, key)=>{
return module.getChild(key);
},this.root)
}
}
class Module {
constructor(rawModlue) {
this.state = rawModlue.state || {};
this._rawModule = rawModlue;
this._chidren = rawModlue.modules || {};
}
getChild(key) {
return this._chidren[key];
}
}
3.2 整理 state 数据
数据最终整理为:
// 注意:这里是namespaced:false 的情况下
state: {
count: 0;
student: {
count: 222
}
}
class Store {
constructor(option){
// 将 option重新整理
....
installModule(this, option.state, [], this._modules.root) // ⚠️ this._modules.root 不是 this._modules
// ...
}
}
function installModule(Store,rootState, path, module) {
// 判断是否为根状态
const isRoot = path.length === 0;
if (!isRoot) {
// 1. 父模块状态
const parentState = getNestedState(path.slice(0, -1), rootState);
// 2. 当前模块名
const moduleName = path[path.length - 1];
// 3. 给父模块放置 该子模块
parentState[moduleName] = module.state;
}
// 循环遍历 module (这个可以给之前的Module 上直接绑定该方法)
module.forEachChild((childModule, childName) => {
installModule(Store, rootState, path.concat(childName), childModule);
})
}
function getNestedState(path, rootState) {
return path.reduce((moduleState, path)=>{
return moduleState[path];
},rootState)
}
到这个时候,vuex 中的 state 功能就结束了!
主要思路,整理下:
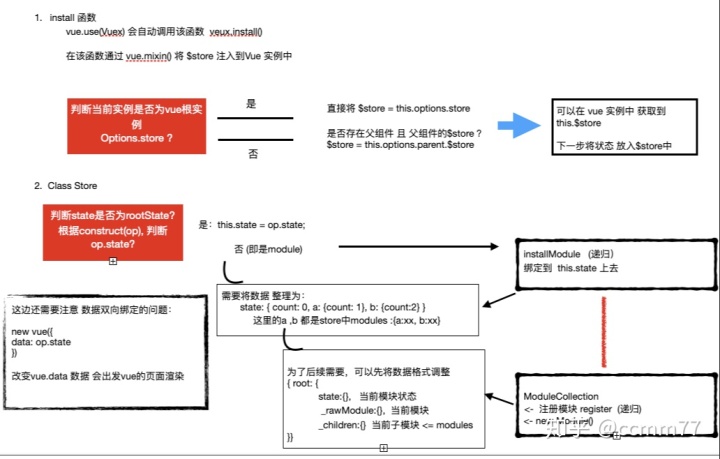
补充:
// vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<p>
{{ $store.state.count}}
</p>
<hr />
<!-- {{ $store.state.student.count }} 子模块不存在命名空间 -->
<!-- {{ $store.state['student/count'] }} 子模块student 存在命名空间-->
<button @click="handleClick"> click </button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
created() {
console.log(this.$store);
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
this.$store.state.count ++;
// this.$store.state.student.count ++ ;
}
}
}
</script>
// store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from '../vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0,
},
modules: {
student: {
// namespaced: true,
state: {
count: 1111,
},
},
},
})
源码中会对提取些公共方法,方便后续使用,具体代码可以查看 :
myVuex state分支github.com



 本文深入解析了Vuex的使用方法,包括状态管理、数据双向绑定及子模块管理等核心功能,并详细介绍了如何通过Vue实例实现对Vuex状态的访问。
本文深入解析了Vuex的使用方法,包括状态管理、数据双向绑定及子模块管理等核心功能,并详细介绍了如何通过Vue实例实现对Vuex状态的访问。

















 624
624

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








