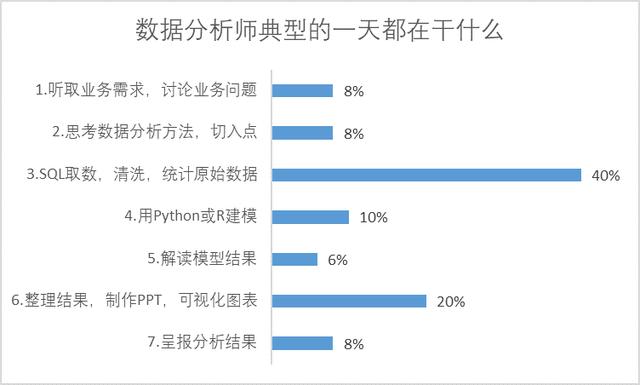
数据分析师的一天
作为一名数据分析师,目前而言是以业务为中心,取数,清洗整理数据,取数与清洗数据会消耗大量的工作时间,毕竟代码需要跟着业务节奏变化。
其中文本数据相比数值数据更具复杂性,本文就pandas处理文本数据的几个常用点展开讲解。
文本数据是指不能参与算术运算的任何字符,也称为字符型数据。如英文字母、汉字、不作为数值使用的数字(以单引号开头)和其他可输入的字符。
文本数据具有数据维度高、数据量大且语义复杂等特点,是一种较为复杂的数据类型。今天,我们就来一起看看如何使用Pandas对文本数据进行数据处理。
一、string类型的性质
1. 1 string与object的区别
string类型和object不同之处有三点:
① 字符存取方法(string accessor methods,如str.count)会返回相应数据的Nullable类型,而object会随缺失值的存再而改变返回类型;
② 某些Series方法不能在string上使用,例如:Series.str.decode(),因为存储的是字符串而不是字节;
③ string类型在缺失值存储或运算时,类型会广播为pd.NA,而不是浮点型np.nan
其余全部内容在当前版本下完全一致,但迎合Pandas的发展模式,我们仍然全部用string来操作字符串。
1.2 string类型的转换
#导入所需要的包import pandas as pdimport numpy as np#如果将一个其他类型的容器直接转换string类型可能会出错:#pd.Series([1,'1.']).astype('string') #报错#pd.Series([1,2]).astype('string') #报错#pd.Series([True,False]).astype('string') #报错#当下正确的方法是分两部转换,先转为str型object,在转为string类型:pd.Series([1,'1.']).astype('str').astype('string')pd.Series([1,2]).astype('str').astype('string')pd.Series([True,False]).astype('str').astype('string')二、拆分与拼接
2.1 str.split方法
(1)分割符与str的位置元素选取
s = pd.Series(['a_b_c', 'c_d_e', np.nan, 'f_g_h'], dtype="string")s0 a_b_c1 c_d_e2 3 f_g_hdtype: string根据某一个元素分割,默认为空格
s.str.split('_')
0 [a, b, c]1 [c, d, e]2 3 [f, g, h]dtype: object这里需要注意split后的类型是object,因为现在Series中的元素已经不是string,而包含了list,且string类型只能含有字符串。
对于str方法可以进行元素的选择,如果该单元格元素是列表,那么str[i]表示取出第i个元素,如果是单个元素,则先把元素转为列表再取出。

(2)其他参数
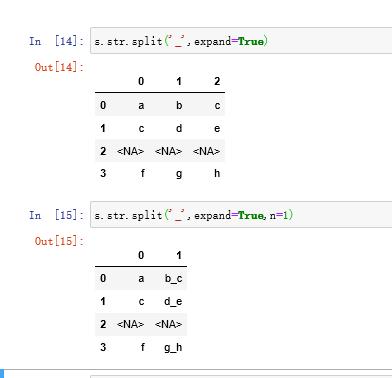
expand参数控制了是否将列拆开,n参数代表最多分割多少次
s.str.split('_',expand=True)
2.2 str.cat方法
(1)不同对象的拼接模式
cat方法对于不同对象的作用结果并不相同,其中的对象包括:单列、双列、多列
#单列s = pd.Series(['ab',None,'d'],dtype='string')s.str.cat()'abd'#其中可选sep分隔符参数,和缺失值替代字符na_rep参数s.str.cat(sep=',',na_rep='*')'ab,*,d'#对于两个Series合并而言,是对应索引的元素进行合并s2 = pd.Series(['24',None,None],dtype='string')s.str.cat(s2)0 ab241 2 dtype: string#同样也有相应参数,需要注意的是两个缺失值会被同时替换s.str.cat(s2,sep=',',na_rep='*')0 ab,241 *,*2 d,*dtype: string #多列拼接可以分为表的拼接和多Series拼接#表的拼接s.str.cat(pd.DataFrame({0:['1','3','5'],1:['5','b',None]},dtype='string'),na_rep='*')0 ab151 *3b2 d5*dtype: string#多个Series拼接s.str.cat([s+'0',s*2])0 abab0abab1 2 dd0dddtype: string三、替换
广义上的替换,就是指str.replace函数的应用,fillna是针对缺失值的替换,提到替换,就不可避免地接触到正则表达式。
s = pd.Series(['A', 'B', 'C', 'Aaba', 'Baca','', np.nan, 'CABA', 'dog', 'cat'],dtype="string")0 A1 B2 C3 Aaba4 Baca56 7 CABA8 dog9 catdtype: string#第一个值写r开头的正则表达式,后一个写替换的字符串s.str.replace(r'^[AB]','***')0 ***1 ***2 C3 ***aba4 ***aca56 7 CABA8 dog9 catdtype: string3.2 子组与函数替换#通过正整数调用子组(0返回字符本身,从1开始才是子组)s.str.replace(r'([ABC])(w+)',lambda x:x.group(2)[1:]+'*')0 A1 B2 C3 ba*4 ca*56 7 BA*8 dog9 catdtype: string关于str.replace的注意事项
首先,要明确str.replace和replace并不是一个东西:
- str.replace针对的是object类型或string类型,默认是以正则表达式为操作,目前暂时不支持DataFrame上使用;
- replace针对的是任意类型的序列或数据框,如果要以正则表达式替换,需要设置regex=True,该方法通过字典可支持多列替换。
(a)str.replace赋值参数不得为pd.NA
这听上去非常不合理,例如对满足某些正则条件的字符串替换为缺失值,直接更改为缺失值在当下版本就会报错
#pd.Series(['A','B'],dtype='string').str.replace(r'[A]',pd.NA) #报错#pd.Series(['A','B'],dtype='O').str.replace(r'[A]',pd.NA) #报错此时,可以先转为object类型再转换回来,曲线救国:pd.Series(['A','B'],dtype='string').astype('O').replace(r'[A]',pd.NA,regex=True).astype('string')至于为什么不用replace函数的regex替换(但string类型replace的非正则替换是可以的),原因在下面一条。
(b)对于string类型Series在使用replace函数时不能使用正则表达式替换,该bug现在还未修复pd.Series(['A','B'],dtype='string').replace(r'[A]','C',regex=True)pd.Series(['A','B'],dtype='O').replace(r'[A]','C',regex=True)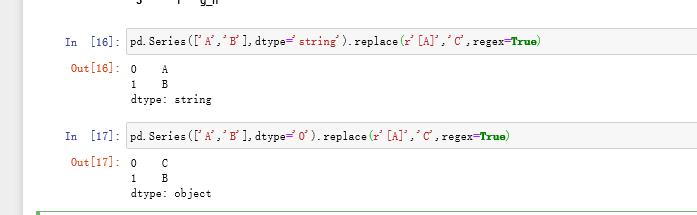
(c)string类型序列如果存在缺失值,不能使用replace替换
#pd.Series(['A',np.nan],dtype='string').replace('A','B') #报错pd.Series(['A',np.nan],dtype='string').str.replace('A','B')综上,概括的说,除非需要赋值元素为缺失值(转为object再转回来),否则请使用str.replace方法
四、子串匹配与提取
4.1 str.extract方法
pd.Series(['10-87', '10-88', '10-89'],dtype="string").str.extract(r'([d]{2})-([d]{2})')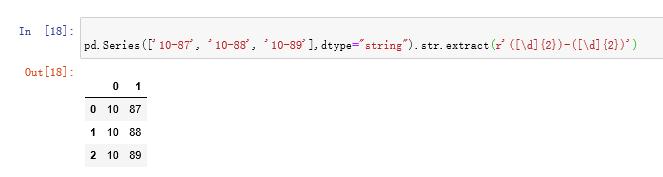
使用子组名作为列名pd.Series(['10-87', '10-88', '-89'],dtype="string").str.extract(r'(?P[d]{2})-(?P[d]{2})')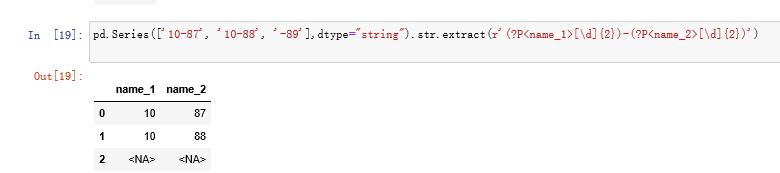
利用?正则标记选择部分提取
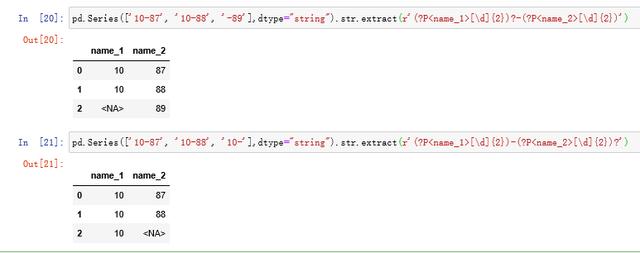
(b)expand参数(默认为True)
对于一个子组的Series,如果expand设置为False,则返回Series,若大于一个子组,则expand参数无效,全部返回DataFrame。
对于一个子组的Index,如果expand设置为False,则返回提取后的Index,若大于一个子组且expand为False,报错。
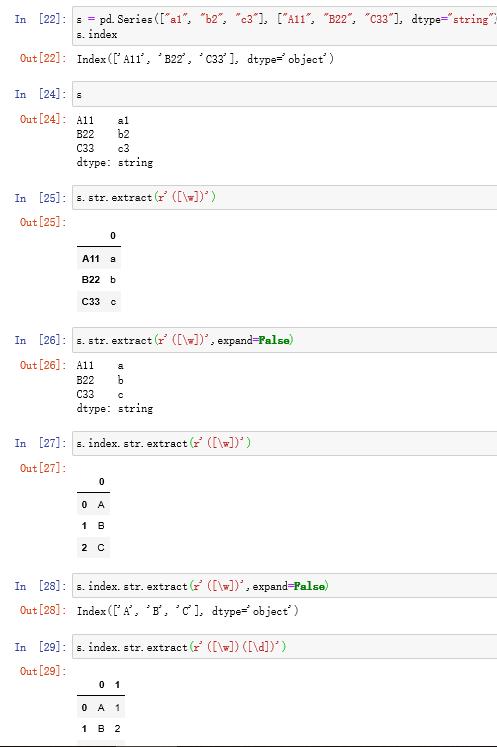
4.2 str.extractall方法
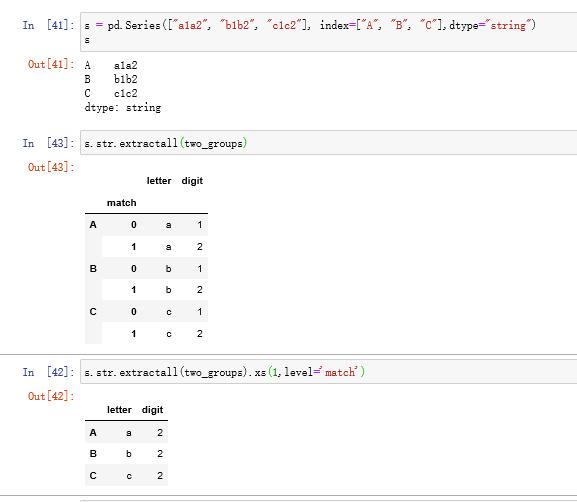
与extract只匹配第一个符合条件的表达式不同,extractall会找出所有符合条件的字符串,并建立多级索引(即使只找到一个)
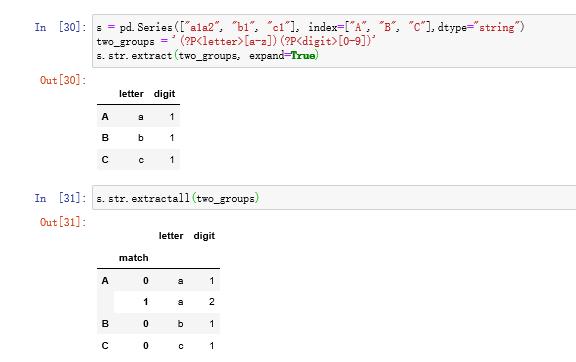

如果想查看第i层匹配,可使用xs方法
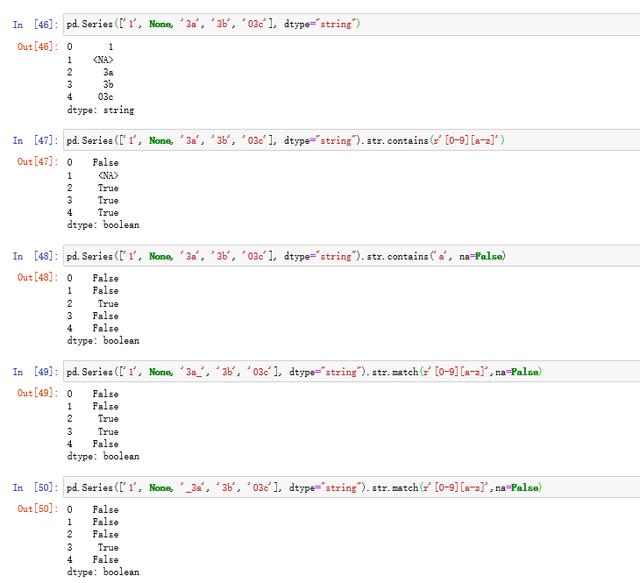
4.3 str.contains和str.match
前者的作用为检测是否包含某种正则模式,str.match与其区别在于,match依赖于python的re.match,检测内容为是否从头开始包含该正则模式
五、常用字符串方法
5.1 过滤型方法
(a)str.strip
常用于过滤空格

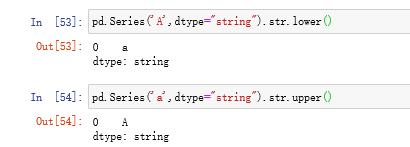
(b)str.lower和str.upper
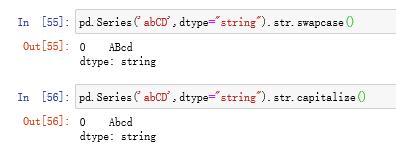
(c)str.swapcase和str.capitalize
分别表示交换字母大小写和大写首字母
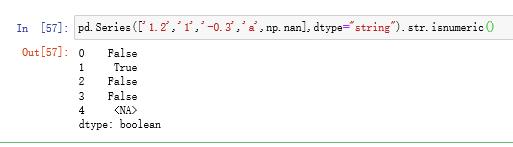
5.2 isnumeric方法
检查每一位是否都是数字,请问如何判断是否是数值?




 本文详细介绍使用Pandas处理文本数据的方法,包括string类型的性质、拆分与拼接、替换、子串匹配与提取及常见字符串操作等。适用于数据分析师和技术人员提升数据处理效率。
本文详细介绍使用Pandas处理文本数据的方法,包括string类型的性质、拆分与拼接、替换、子串匹配与提取及常见字符串操作等。适用于数据分析师和技术人员提升数据处理效率。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








