Hive有三种复合数据类型:
数组(array):基于数据(列表)的数据结构形式,array访问通过下标访问对应的值,从0开始
字典(map):基于key-value的数据结构形式,map可以通过["指定key名称"]访问对应的value值
结构体(struct):基于对象的数据结构形式,struct内部的数据可以通过(.)来存取
1、数据类型定义
三种复合结构的定义如下:
数组使用array
字典使用map
结构体使用struct
三种复杂数据类型允许任意层次的嵌套。
下例中用户信息表(dw.dws_user_info_d)使用三种复合结构:
create table if not existsdw.dws_user_info_d
(
uid bigint
,active_days array
,follow_user map
,test_info array>
)
PARTITIONED BY (dt STRING)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\t' --字段分隔符
COLLECTION ITEMS TERMINATED BY',' --元素之间分割符
MAP KEYS TERMINATED BY ':' --map K-V对分割符号
LINES TERMINATED BY '\n' --记录之间分隔符
STORED AS TEXTFILE --文件存储格式,parquet、orc等其它格式
;
其中分隔符部分可以使用hive默认的分隔符,如果需要从文件中导入数据,需要指定分隔符才能得到正确的数据内容。
其中:
active_days 使用array类型,值是bigint类型,可存储任意个bigint类型的元素;
follow_user使用map类型,其中key和value都是string类型,可存储任意对string类型的K-V对;
test_info使用array的嵌套方式,其中单个struct必须包含字段中定义的字段个数,字段名称,字段类型;由于可以直接把struct的字段拆分成多个字段来存储,使用struct来存储几个字段的集合比较少,而使用array的嵌套方式是比较常见的使用方式,形成表中表。
2、数据生成
Array数据生成:通过collect_set或collect_list函数将多行的数据聚合成一个array
日活表存储的是每天活跃的用户信息,每个用户活跃的日期和天数是不固定的,可以使用array来存储用户的活跃日期。
日活表(dw.dwf_user_active_d)的定义如下:
create table if not exists dw.dwf_user_active_d
(
uid bigint
,active bigint
);
表中数据如下图所示:

使用collect_set、collect_list函数将每个用户对应的活跃日期聚合成一个array,SQL如下所示:
select uid
,collect_set(active) as active_set
,collect_list(active) as active_list
from dw.dwf_user_active_d
group by uid;

其中2个函数的区别在于collect_set会对元素去重,而collect_list不对元素去重;
Map数据生成:通过concat函数将任意个K-V对拼接成字符串,再通过str_to_map函数将字符串转换成Map类型
用户关注关系表存储用户和粉丝及关注时间信息,需要保存用户的关注列表及关注时间信息,可以使用map类型来存储。
用户关注关系表(dw.dwv_user_follow_d)定义如下:
create table if not exists dw.dwv_user_follow_d
(
uid bigint
,follow_uid bigint
,follow_time timestamp
);
表中数据如下图所示:
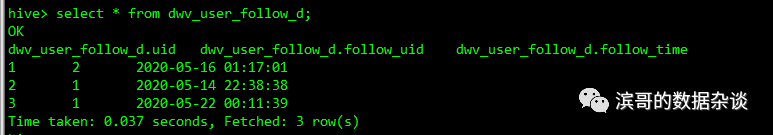
以下语句将生成用户的关注用户及关注时间信息,其中key是关注的用户,value是关注的时间,SQL如下所示:
select follow_uid
,str_to_map(concat_ws(',',collect_set(concat(uid,'|',follow_time))),',','\\|') as follow_info
from dw.dwv_user_follow_d
group by follow_uid;
首先使用concat(uid,'|',follow_time)将2个字段和字段分隔符拼接成K-V对字符串,
其次使用collect_set()将多行关注用户转换成array数组,
再次使用concat_ws(',',array)将数组拼接成以','分隔的字符串
最后使用str_to_map(str, ',','\\|')将字符串转换成map,其中','是多个K-V对之间的分隔符,'|'是每个K-V对内的分隔符。
struct数据生成:通过named_struct函数按照顺序将字段名称,字段值生成结构体
实验表存储的是用户归属于某个实验的某个分组,1个用户可能同时会有多个实验,而对于实验组之间,用户实验信息是固定的,可以使用struct来存储每个实验的具体信息,嵌套array来存储多个实验的信息,形成类似表中表的数据存储。
实验表(dw.dwv_user_test_d)定义如下:
create table if not exists dw.dwv_user_test_d
(
uid bigint
,test_id bigint
,test_name string
,group_id string
,group_name string
);
实验表存储的是用户归属于某个实验的某个分组,1个用户可能同时会有多个实验,而对于实验组之间,用户实验信息是固定的,可以使用struct来存储每个实验的具体信息,嵌套array来存储多个实验的信息,形成类似表中表的数据存储。
用户实验表是dwv_user_test_d,有用户,实验id和名称,分组id和名称等信息。
表中数据如下图所示:
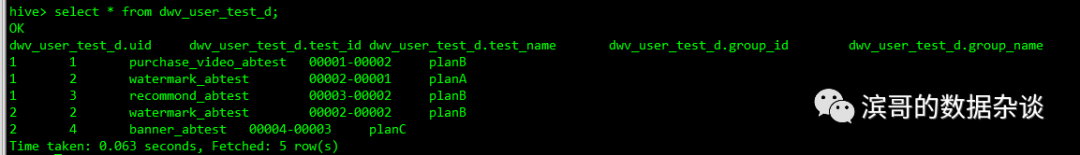
以下语句生成用户的实验结构体数组,SQL如下:
select uid
,collect_list(test) as tests
from (select uid
,named_struct('test_id',test_id,'test_name',test_name,'group_id',group_id,'group_name',group_name) as test
from dwv_user_test_d
)as t
group by uid;
先使用named_struct函数把多个字段拼接成结构体,
再使用collect_list或者collect_set函数将多个结构体拼接是array。
合并数据写入结果表
with tmp_dau as
(
select uid
,collect_set(active) as active_days
fromdw.dwf_user_active_d
groupby uid
)
,tmp_follow as
(
select follow_uid as uid
,str_to_map(cast(concat_ws(',',collect_set(concat(uid,'|',follow_time)))as string),',','|') as follow_info
fromdw.dwv_user_follow_d
groupby follow_uid
)
,tmp_test as
(
select uid
,collect_list(test) as test_info
from(select uid
,named_struct('test_id',test_id,'test_name',test_name,'group_id',group_id,'group_name',group_name)as test
from dwv_user_test_d
) as t
groupby uid
)
,tmp_test_dafaulte as
(
select collect_set(test) as test_default
from(
select named_struct('test_id',cast(-999 asbigint),'test_name','none','group_id','none','group_name','none') as test) as t
)
insert overwrite table dw.dws_user_info_dpartition(dt='2020-05-25')
select t1.uid
,t1.active_days
,t2.follow_info
,if(t3.uid is not null,t3.test_info,t4.test_default) as test_info
from tmp_dau as t1
left join tmp_follow as t2 on t1.uid=t2.uid
left join tmp_test as t3 on t1.uid=t3.uid
left join tmp_test_dafaulte as t4
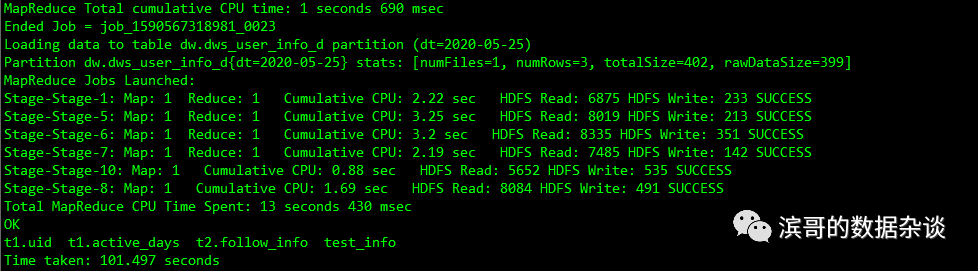
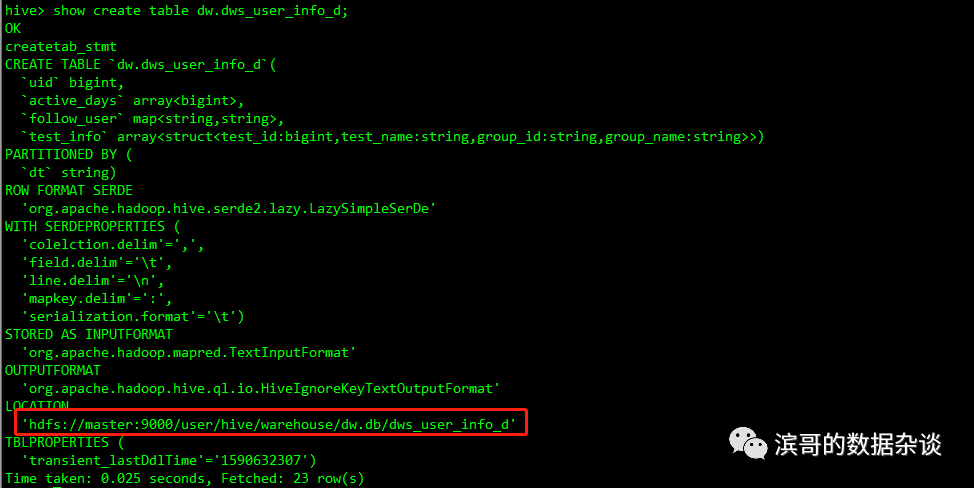
Show create table dw.dws_user_info_d;
看下表的信息,获取表数据的存储路径;
hadoop dfs -ls hdfs://master:9000/user/hive/warehouse/dw.db/dws_user_info_d/dt=2020-05-25

hadoop dfs -cat hdfs://master:9000/user/hive/warehouse/dw.db/dws_user_info_d/dt=2020-05-25/000000_0

从存储文件上可以看出:
字段之间以\t分隔
字符串之间以逗号分隔,如2|2020-05-14 22:38:38,3|2020-05-22 00:11:39
Map的K-V对以|分隔

select *
from dw.dws_user_info_d
order by uid;

3、数据访问
单个元素访问
select active_days[0] --下标访问array单个元素,以0开始
,active_days[100] --超过数据元素个数,返回null
,follow_user['3'] --以key值访问对于value
,follow_user['4'] --访问不存在的key值,返回null
,test_info[0].test_name --通过结构体的字段名查询字段值
,test_info[0].group_name
from dw.dws_user_info_d
where uid=1;
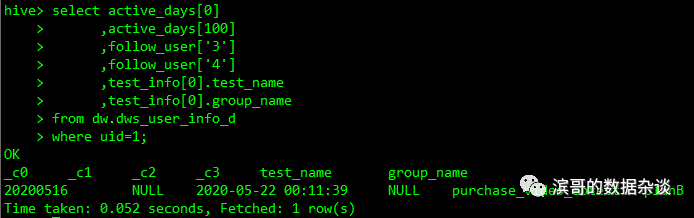
使用array[n]访问数据对应值,从0开始访问array的第1个元素,如果超过最大的数量,返回NULL;
使用Map['Key']访问Key对应的Value值,如果Key不存在则返回NULL,key可以填任意值,只要符合定义的类型就可以。
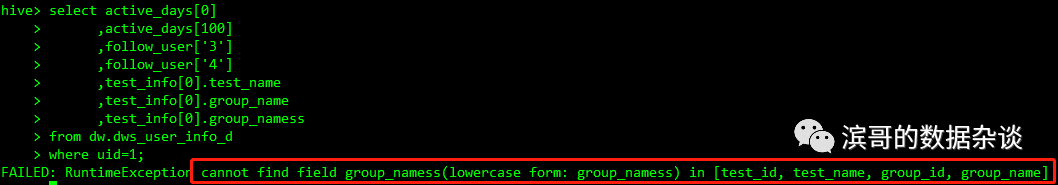
使用struct.column_name访问对应字段的值,如果struct不存在对应的column_name则报错,struct是固定的,字段名必须按照建表时定义的命名,字段值类型必须是定义的类型。
所有元素遍历
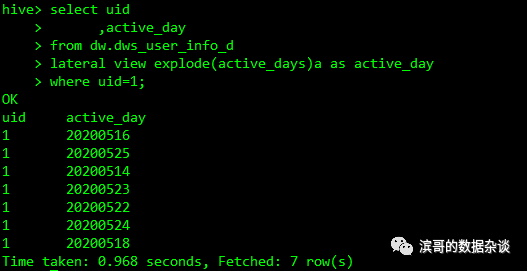
使用explode(array)访问array中所有元素的值
select uid
,active_day
from dw.dws_user_info_d
lateral view explode(active_days)a as active_day
where uid=1
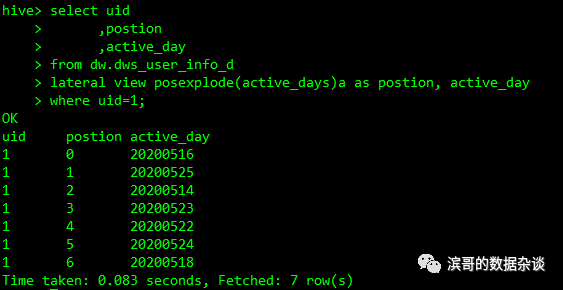
使用posexplode(array)访问array中所有元素的位置以及对应的值
select uid
,postion
,active_day
from dw.dws_user_info_d
lateral view posexplode(active_days)a as postion, active_day
where uid=1
使用explode(map)访问map中所有Key和Value
select uid
,map_key
,map_value
from dw.dws_user_info_d
lateral view explode(follow_user)a as map_key,map_value
where uid=1
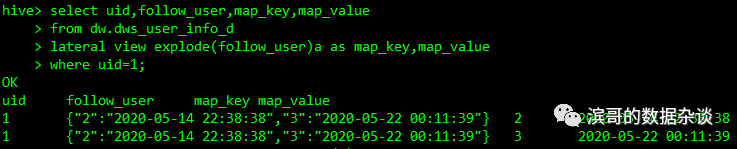
使用struct.column_name来访问结构体内对应的字段
select uid
,test_infos.test_id
,test_infos.test_name
,test_infos.group_id
,test_infos.group_name
from dw.dws_user_info_d
lateral view explode(test_info)a as test_infos
where uid=1
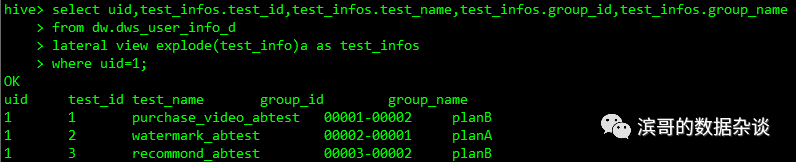
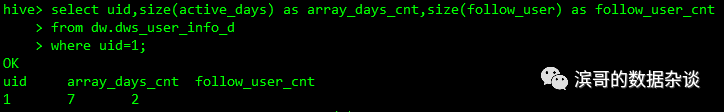
其它数据访问
使用size()函数获取array元素的个数,获取map的K-V数量
select uid,size(active_days) asarray_days_cnt,size(follow_user) as follow_user_cnt
from dw.dws_user_info_d
where uid=1
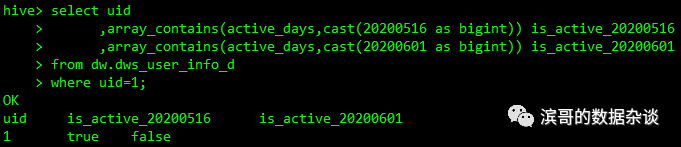
使用array_contains(array,value)判断value是否存在array,存在返回true,不存在返回false
select uid
,array_contains(active_days,cast(20200516 as bigint)) is_active_20200516
,array_contains(active_days,cast(20200601 as bigint)) is_active_20200601
from dw.dws_user_info_d
where uid=1
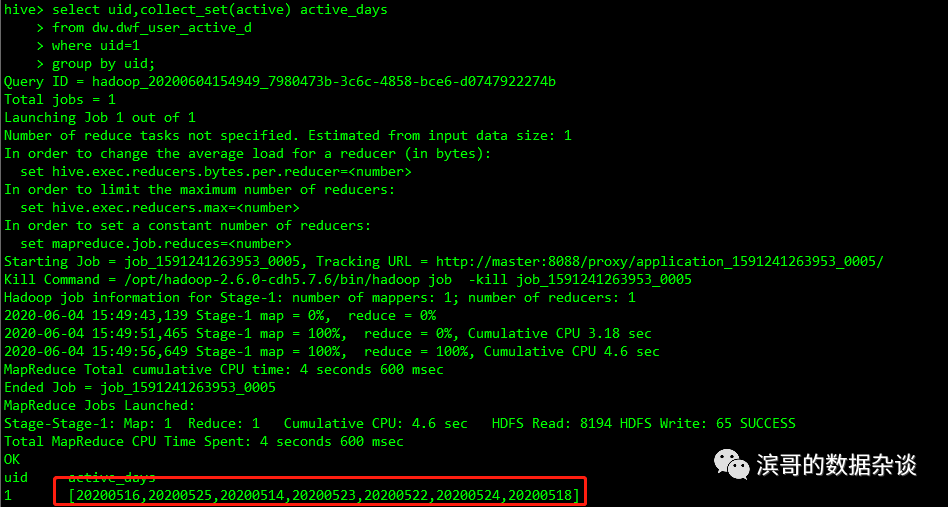
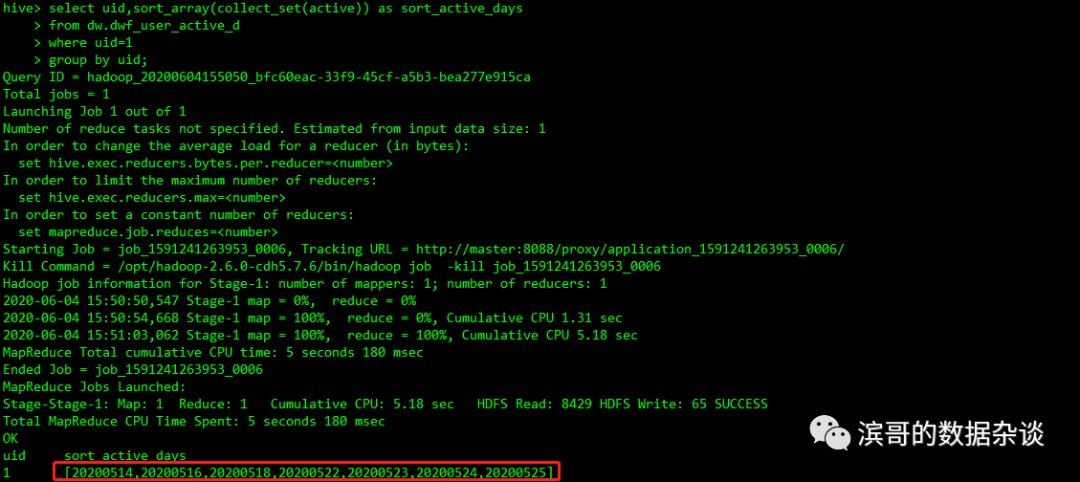
使用sort_array()来对array进行排序,这个函数在解决collect_set()无序的问题可能会派上用场。
select uid,sort_array(collect_set(active)) assort_active_days
from dw.dwf_user_active_d
where uid=1
group by uid;
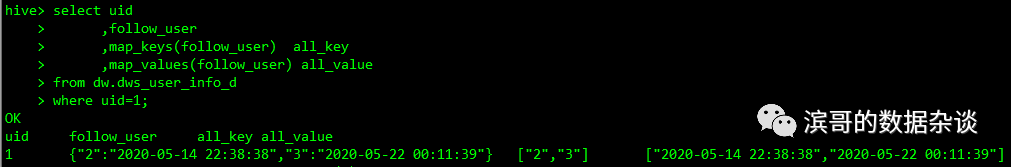
使用map_keys(Map), map_values(Map)返回map所有的key/value,返回数据类型是array
select uid
,follow_user
,map_keys(follow_user) all_key
,map_values(follow_user) all_value
fromdw.dws_user_info_d
where uid=1
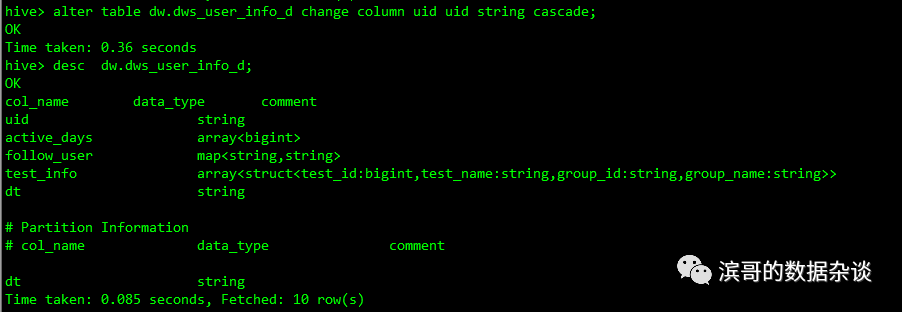
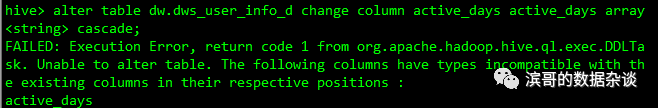
4、数据类型修改
有时候需要修改hive表的数据类型,修改的语句是
Alter table table_name changecolumn old_column_name new_column_name new_type cascade;
下面把uid的类型从bigint修改成string,
alter table dw.dws_user_info_dchange column uid uid string cascade;
但是对于特殊类型就会报错,需要添加以下参数才可以修改特殊类型
set hive.metastore.disallow.incompatible.col.type.changes=false;

5、适用场景
数组(Array) 适用存储数量不定,类型相同的数据,例如用户的活跃日期,做出一个array,存储用户所有的日期,使用时再遍历所有元素进行统计。
字典(Map) 适用存储数量不定、Key不确定的数据,例如将多个相关的埋点事件做到同一张表中,公用部分使用单独的字段来存储,个性部分使用map来存储;第二个适用场景将某个维度值作为key,统计值作为value,使用map来存储,如用户的关注用户作为key,关注时间作为value使用map来存储。
结构体(Struct) 适用存储多组结构固定的数据,如果只有一组完全可以把struct拆成多个字段存储,如用户多个实验信息,用户的多级标签信息等。






 本文介绍了Hive中的三种复合数据类型:数组、字典和结构体,包括它们的定义、数据生成方法、数据访问以及适用场景。通过示例展示了如何创建和操作这些复合类型,如使用collect_set、collect_list、str_to_map等函数,以及如何遍历和修改数据类型。
本文介绍了Hive中的三种复合数据类型:数组、字典和结构体,包括它们的定义、数据生成方法、数据访问以及适用场景。通过示例展示了如何创建和操作这些复合类型,如使用collect_set、collect_list、str_to_map等函数,以及如何遍历和修改数据类型。
















 1427
1427

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








