集合的概述
集合的概念
我们知道数据多了,使用数组存放,并且数组是定长的。但是若要存储的数据是不定长的话,可以使用集合。集合和数组区别是数组的长度是固定的;集合的长度是可变的集合中存储的元素必须是引用类型数据。注:集合本身是一个工具,它存放在java.util包中。
常用的集合接口有:Collecton、List、Set、Map、Iterator、Map.Entry。
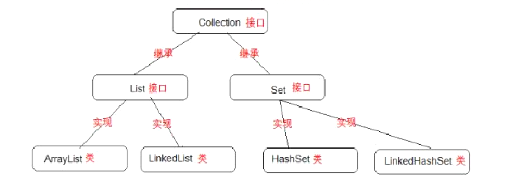
Collection接口概述
上图我们可以看到Collection接口是集合中的顶层接口,所以它中定义的所有功能子类都可以使用。
Collection接口中定义的方法:
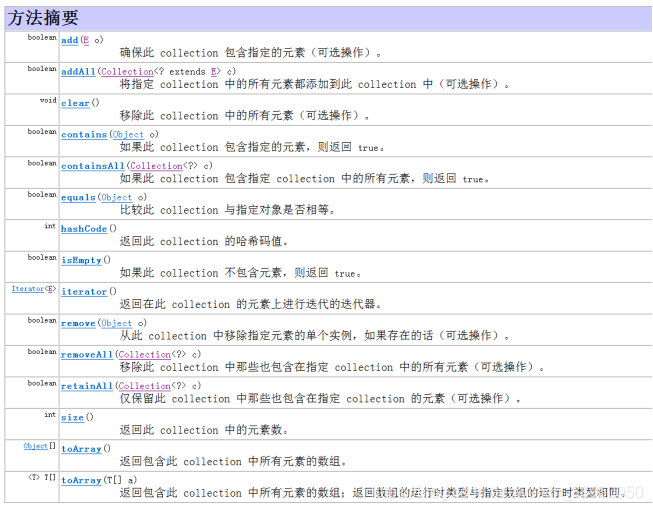
Collection 表示一组对象,这些对象也称为 collection 的元素。一些 collection 允许有重复的元素,而另一些则不允许。一些 collection 是有序的,而另一些则是无序的。JDK 不提供此接口的任何直接 实现:它提供更具体的子接口(如 Set 和 List)实现。此接口通常用来传递 collection,并在需要最大普遍性的地方操作这些 collection。
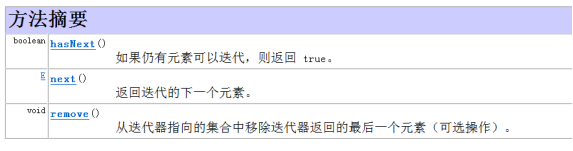
Iterator迭代器
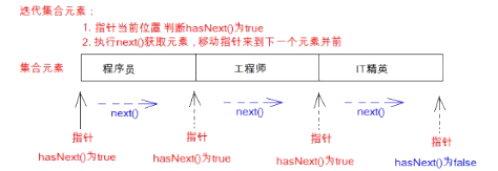
Java中提供了很多个集合,它们在存储元素时,采用的存储方式不同。我们要取出这些集合中的元素,可以通过一种通用的获取方式来完成。
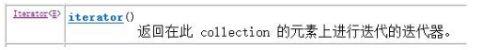
Collection集合元素的通用获取方式:在元素之前先要判断集合中有没有元素,如果有,就把这个元素取出来,继续再判断,如果还有就再取出来,没有就跳出循环。一直把集合中的所有元素全部取出。这种取出方式专业术语称为迭代。集合中把这种取元素的方式描述在Iterator接口中。Iterator接口的常用方法如下:
迭代集合元素图解:
在Collection接口描述了一个抽象方法Iterator方法,所有Collection子类都实现了这个方法,且有自己的迭代形式。
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<String>(); //1,创建集合对象
coll.add("abc1");
coll.add("abc2");
coll.add("abc3");
coll.add("abc4");
Iterator it = coll.iterator(); //2,获取容器的迭代器对象。通过iterator方法
while(it.hasNext()){//3,使用具体的迭代器对象获取集合中的元素。参阅迭代器的方法
System.out.println(it.next());
}
/*
迭代器for循环的形式的使用
for(Iterator it = coll.iterator();it.hasNext();){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
*/
List接口
List接口的概念
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> {}
List接口是有序的collection(也称为序列)。此接口的用户可以对列表中每个元素的插入位置进行精确地控制。用户可以根据元素的整数索引(在列表中的位置)访问元素,并搜索列表中的元素。
与set不同,列表通常允许重复的元素。更正式地说,列表通常允许满足e1.equals(e2)的元素对e1和e2,并且如果列表本身允许null元素的话,通常它们允许多个null元素。难免有人希望通过在用户尝试插入重复元素时抛出运行时异常的方法来禁止重复的列表,但我们希望这种用法越少越好。
List接口中定义的方法:
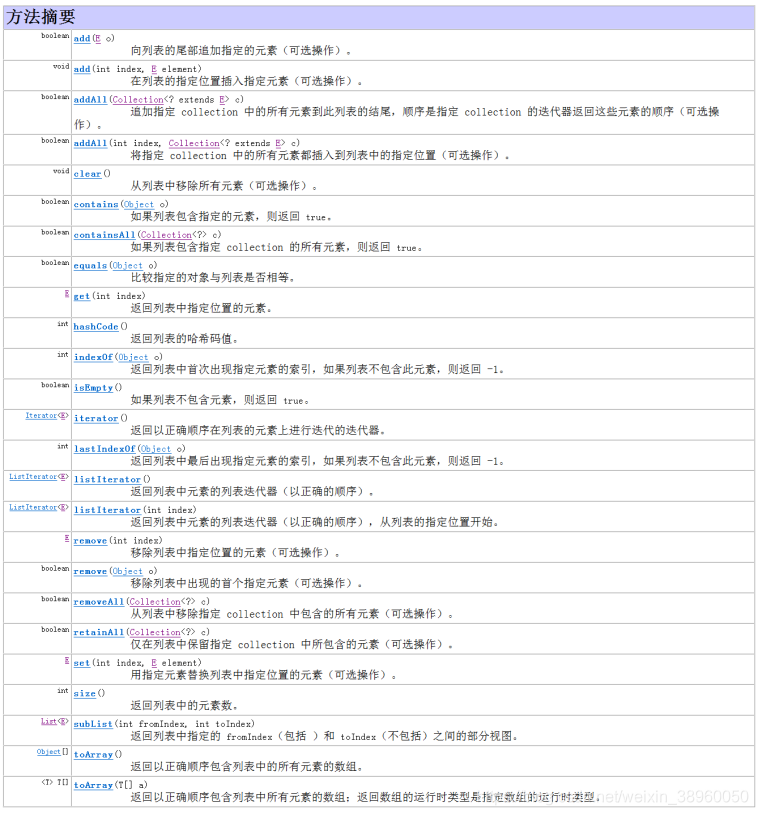
List接口比Collection接口扩充了更多的方法,而且这些方法操作起来更加方便。但是要想使用此接口,则需要通过其子类来进行实例化。
ArrayList集合
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{}
ArrayList集合数据存储的结构是数组结构。元素增删慢,查找快,由于日常开发中使用最多的功能为查询数据、遍历数据,所以ArrayList是最常用的集合。
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
Collection<String> collection = new ArrayList<String>();
//向集合中增加元素, addAll:在指定的位置添加元素;add:只是在集合的最后进行追加
list.add("one");
list.add(0,"zero");
System.out.println(list);
collection.add("Hello");
collection.add("World");
list.addAll(collection);
list.addAll(0,collection);
System.out.println(list);
//查询和遍历
int length = list.size();
for(int i = 0; i < length ; i++){
System.out.print(list.get(i)+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
//将集合变为对象数组
Object[] objects = list.toArray();
length = objects.length;
for(int i = 0; i < length ; i++){
System.out.print(objects[i]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
String[] strings = list.toArray(new String[]{});
length = strings.length;
for(int i = length - 1; i >= 0 ; i--){
System.out.print(strings[i]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
//删除元素
list.remove("one");
System.out.println(list);
list.remove(2);
System.out.println(list);
list.removeAll(collection);
System.out.println(list);
Vector集合
public class Vector<E> extends AbstractList<E>implements List<E>,RandomAccess, Cloneable, Serializable
Vector类可以实现可增长的对象数组。与数组一样,它包含可以使用整数索引进行访问的组件。但是Vector的大小可以根据需要增大或缩小,以适应创建Vector后进行添加或移除项的操作。
Vector集合数据存储的结构是数组结构,为JDK中最早提供的集合。Vector中提供了一个独特的取出方式,就是枚举Enumeration,它其实就是早期的迭代器。此接口Enumeration的功能与 Iterator 接口的功能是类似的。Vector集合已被ArrayList替代。枚举Enumeration已被迭代器Iterator替代。
Vector常见的方法:
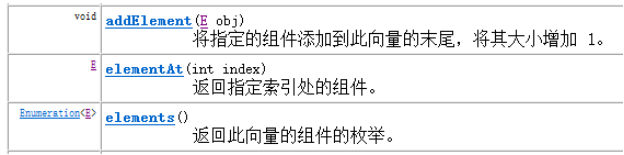
Vector集合对ArrayList集合使用的对比:

LinkedList集合
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Queue<E>, loneable, Serializable {}
LinkedList集合数据存储的结构是链表结构。方便元素添加、删除的集合。实际开发中对一个集合元素的添加与删除经常涉及到首尾操作,而LinkedList提供了大量首尾操作的方法。
LinkedList实现了Queue接口(此接口表示队列操作接口)。所以LinkedList集合可以作为堆栈,队列的结构使用。
Queue接口的方法:
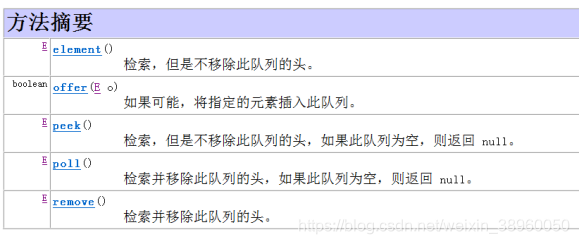
除了上述的方法,LinkedList还提供了大量首尾操作的方法:

LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.add("one");
linkedList.add("two");
linkedList.add("three");
System.out.println(linkedList);
//在链表的开头和结尾增加数据
linkedList.addFirst("zero");
linkedList.addLast("four");
System.out.println(linkedList);
//找到链表头
//1、public E element(); 检索,不移除此队列的头。若此队列为空,抛出异常NoSuchElementException。
//2、public E peek(); 检索,不移除此队列的头,若此队列为空,则返回 null。
//3、public E poll(); 检索并且移除此队列的头,若此队列为空,则返回 null。
//4、public E remove(); 检索并且移除此队列的头。若此队列为空,抛出异常NoSuchElementException。
System.out.println("element()方法找到表头:" + linkedList.element());
System.out.println("执行element()方法后:" + linkedList);
System.out.println("peek()方法找到表头:" + linkedList.peek());
System.out.println("peek()方法后:" + linkedList);
System.out.println("poll()方法找到表头:" + linkedList.poll());
System.out.println("poll()方法后:" + linkedList);
System.out.println("remove()方法找到表头:" + linkedList.remove());
System.out.println("remove()方法后:" + linkedList);
//以FIFO(先进先出)的方式取数
System.out.print("以FIFO的方式输出:");
int length = linkedList.size();
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++){
System.out.print(linkedList.poll()+"\t");
}
Set接口
Set接口的概念
前面说过Collection接口可以存放重复元素,也可以不存放重复元素,而List接口中是可以存放重复元素的。这里的Set接口是存放不重复元素的。注Set集合是通过元素的equals方法,来判断是否为重复元素,
public interface Set<E>extends Collection<E>
从上面的定义上看Set接口和List的接口并没有很大的不同,但Set接口的主要与Collection一致,没有对Collection接口进行扩展,只是不能存放重复的数据。并且没有提供像List接口定义的get(int index)方法。
HashSet集合
HashSet是Set接口的一个实现类,主要特点是:里面不能存放重复元素,而且采用散列的存储方式,故没有顺序。
给HashSet中存储JavaAPI中提供的类型元素时,不需要重写元素的hashCode和equals方法,因为这两个方法,在JavaAPI的每个类中已经重写完毕,如String类、Integer类等。
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add(1);
hashSet.add("two");
hashSet.add(1);
hashSet.add(true);
hashSet.add("two");
System.out.println(hashSet);
给HashSet中存放自定义类型元素时,需要重写对象中的hashCode和equals方法,建立自己的比较方式,才能保证HashSet集合中的对象唯一。否则就会直接根据地址来判断是否重复。
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
Person person = (Person) o;
if (age != person.age) {
return false;
}
return name != null ? name.equals(person.name) : person.name == null;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;
return 31 * result + age;
}
}
测试代码:
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add(new Person("张三",18));
hashSet.add(new Person("李四",19));
hashSet.add(new Person("王五",17));
hashSet.add(new Person("马六",20));
hashSet.add(new Person("张三",18));
System.out.println(hashSet);
HashSet保证元素唯一,可是元素存放进去是没有顺序的,若要保证保证元素的存入和取出的顺序时,可以使用LinkedHashSet类,它是HashSet类的一个子类,是链表和哈希表组合的一个数据存储结构。
Set<String> set = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
set.add("one");
set.add("two");
set.add("three");
set.add("four");
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
TreeSet集合
LinkedHashSet类保证存入和取出时顺序相同,但若要保证按特定的顺序排列数据(无须按照存入的先后顺序)时,可以使用TreeSet类。TreeSet类实现Set接口,该接口由TreeMap实例支持。此类保证排序后的set按照升序排列元素,根据使用的构造方法不同,可能会按照元素的自然顺序进行排序,或按照在创建set时所提供的比较器进行排序。
public class TreeSet<E> extends AbstractSet<E> implements SortedSet<E>, Cloneable, Serializable
验证TreeSet类
TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet();
treeSet.add("B");
treeSet.add("C");
treeSet.add("A");
treeSet.add("E");
treeSet.add("D");
treeSet.add("A");
treeSet.add("B");
System.out.println(treeSet);
给TreeSet中存放自定义类型元素时,需要实现Comparable接口,使用compareTo方法来排序。
public class User implements Comparable<User>{
private String name;
private int age;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public int compareTo(User user) {
if (this.age > user.age){
return 1;
}else if (this.age < user.age){
return -1;
}else {
return this.name.compareTo(user.name);
}
}
}
注:在重写compareTo方法时,比如若只写age的比较时,则age相同时,就会默认是同一对象,不会去比较其他的属性。
TreeSet<User> treeSet = new TreeSet<User>();
treeSet.add(new User("张三",18));
treeSet.add(new User("张三1",19));
treeSet.add(new User("张三2",18));
treeSet.add(new User("张三3",17));
treeSet.add(new User("张三4",18));
treeSet.add(new User("张三",18));
System.out.println(treeSet);
在开发中若碰到要区别同一对象时,最好是覆写Object类的hashCode()、equals()、toString()3个方法。
Map接口
Map接口的概念
Map接口是将键映射到值的对象。一个映射不能包含重复的键;每个键最多只能映射一个值。
public interface Map<K,V>
Map接口下的集合与Collection接口下的集合,它们存储数据的形式不同。Collection中的集合,元素是孤立存在的(理解为单身),向集合中存储元素采用一个个元素的方式存储。Map中的集合,元素是成对存在的。每个元素由键与值两部分组成,通过键可以找对所对应的值。即Collection中的集合称为单列集合,Map中的集合称为双列集合。
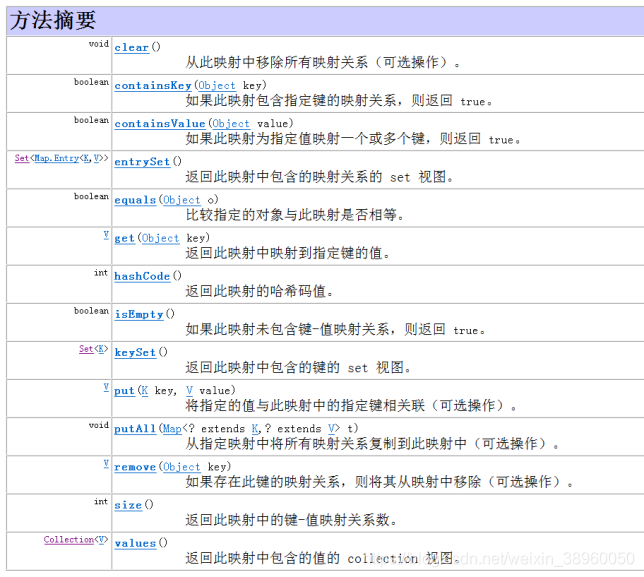
Map中常用的集合为HashMap集合、LinkedHashMap集合。
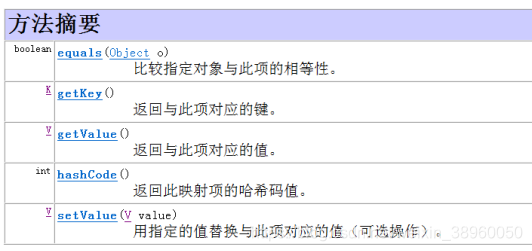
Map.Entry<K,V>接口简介
Map.Entry接口是Map内部定义的一个接口,专门用来存储key→value内容。
public static interface Map.Entry<K,V>
该接口使用static关键字声明的内部接口,所以可以由外部通过“外部类.内部类”的形式直接调用。
HashMap集合
HashMap本身是Map的一个实现类,可以直接使用此类为Map接口实例化。
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>,Cloneable, Serializable
当向map添加数据时,key已经存在,则会将此key上values值覆盖。
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
//向map集合中添加\取出数据
map.put("1","one");
map.put("2","two");
map.put("3","three");
map.put("4","four");
map.put("5","five");
map.put("壹","one");
map.put("1","one");
System.out.println(map.get("1"));
//判断指定的内容是否存在
if (map.containsKey("1")){
System.out.println("搜索的key为1存在");
}else {
System.out.println("搜索的key为1不存在");
}
if (map.containsValue("one")){
System.out.println("搜索的value为one存在");
}else {
System.out.println("搜索的value为one不存在");
}
//输出全部的key和value
Set keys = map.keySet();
Iterator iterator = keys.iterator();
System.out.println("全部的key:");
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.print(iterator.next()+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
Collection values = map.values();
Iterator iter = values.iterator();
System.out.println("全部的value:");
while (iter.hasNext()){
System.out.print(iter.next()+"\t");
}
Map接口的使用注意事项
不能直接使用迭代器输出Map中的全部
Iterator每次只能找到一个值,而Map是存放一对值(key→value),所以不能直接使用迭代器进行输出。
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
//向map集合中添加\取出数据
map.put("1","one");
map.put("2","two");
map.put("3","three");
map.put("4","four");
map.put("5","five");
//使用Iterator输出
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = map.entrySet();
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> iterator = entries.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<String,String> entry = iterator.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"-------->"+entry.getValue());
}
//使用foreach输出
for (Map.Entry<String,String> entry:map.entrySet()){
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"-------->"+entry.getValue());
}
使用自定义的类作为key
在使用自定义的类作为key时,需要重写Object类的hashCode()和equals()的方法,来区分是否是同一对象。
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
if (age != student.age) return false;
return name != null ? name.equals(student.name) : student.name == null;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;
result = 31 * result + age;
return result;
}
}
测试代码:
Map<Student,String> map = new HashMap<Student, String>();
map.put(new Student("李四",18),"李四");
System.out.println(map.get(new Student("李四",18)));
LinkedHashMap集合
HashMap能够保证成对元素唯一,并且查询速度很快,可是成对元素存放进去是没有顺序的,那么若要保证有序,还要速度快的话,可以使用LinkedHashMap类,是HashMap下面的一个子类,它是链表和哈希表组合的一个数据存储结构。
LinkedHashMap<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<String,String>();
map.put("1", "one");
map.put("2", "two");
map.put("3", "three");
Set<Map.Entry<String,String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : entrySet) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+" "+entry.getValue());
}
其他的集合
工具类Collections
此类完全由在collection 上进行操作或返回collection 的静态方法组成。它包含在collection 上操作的多态算法,即“包装器”,包装器返回由指定collection 支持的新collection,以及少数其他内容。
可以通过Collections类方便地操作集合。

//返回不可变的集合
List emptyList = Collections.emptyList();
Set emptySet = Collections.emptySet();
Map emptyMap = Collections.emptyMap();
emptyList.add(“one”); //报错,生成的集合是不可变的
//为集合增加内容
List list = new ArrayList();
Collections.addAll(list,"one","two","three","four");
System.out.println(list);
//反转集合中的内容
Collections.reverse(list);
System.out.println(list);
//检索内容
int i = Collections.binarySearch(list,"two");
int j = Collections.binarySearch(list,"four");
System.out.println(i+"\t"+j);
//替换集合中的内容
Collections.replaceAll(list,"one","1");
System.out.println(list);
//集合排序
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
//交换指定位置的内容
Collections.swap(list,0,2);
System.out.println(list);
属性类Properties
Properties类表示了一个持久的属性集。Properties 可保存在流中或从流中加载。属性列表中每个键及其对应值都是一个字符串。
public class Properties extends Hashtable<Object,Object>
特点:
1、Hashtable的子类,map集合中的方法都可以用。
2、该集合没有泛型。键值都是字符串。
3、它是一个可以持久化的属性集。键值可以存储到集合中,也可以存储到持久化的设备(硬盘、U盘、光盘)上。键值的来源也可以是持久化的设备。

因为Properties继承于Hashtable,所以可对Properties对象应用put和putAll方法。但强烈反对使用这两个方法,因为它们允许调用方插入其键或值不是 Strings的项。相反应该使用setProperty方法。
Properties properties = new Properties();
//设置和取得属性
properties.setProperty("1","one");
properties.setProperty("2","two");
System.out.println("key为1,value为"+properties.getProperty("1"));
System.out.println("key为3,value不存在,是"+
properties.getProperty("3"));
System.out.println("key为3,value不存在,设置默认值是"+
properties.getProperty("3","我是默认值"));
//将属性保存到properties文件中
File file = new File("demo.properties");
properties.store(new FileOutputStream(file),"demo info");
properties.clear();
//从properties文件读取内容
properties.load(new FileInputStream(file));
System.out.println(properties);
双向迭代输出接口ListIterator
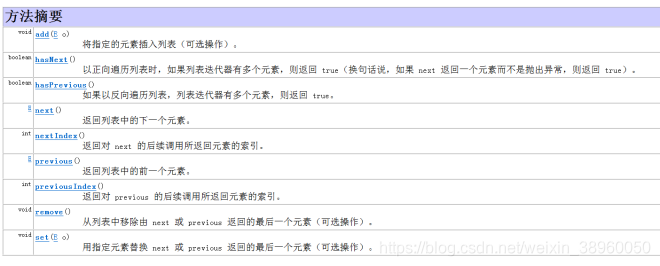
双向迭代输出接口ListIterator允许程序员按任一方向遍历列表、迭代期间修改列表,并获得迭代器在列表中的当前位置。ListIterator没有当前元素;它的光标位置始终位于调用previous()所返回的元素和调用next()所返回的元素之间。需要注意的是ListIterator接口只能通过List接口实例化,即只能输出List接口中的内容。
public interface ListIteratorextends Iterator
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("one");
list.add("two");
list.add("three");
list.add("four");
list.add("five");
ListIterator<String> listIterator = list.listIterator();
System.out.println("由前向后输出:");
while (listIterator.hasNext()){
System.out.print(listIterator.next()+"\t");
}
System.out.println("\n由后向前输出:");
while (listIterator.hasPrevious()){
System.out.print(listIterator.previous()+"\t");
}
//增加及替换元素
System.out.println("\n由前向后输出:");
while (listIterator.hasNext()){
String str =listIterator.next();
System.out.print(str+"\t");
listIterator.set("替换:"+str); //替换
}
listIterator.add("six"); //增加
listIterator.add("seven");
System.out.println("\n由后向前输出:");
while (listIterator.hasPrevious()){
System.out.print(listIterator.previous()+"\t");
}





















 6561
6561

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








