ORB 原理参考
FAST 算法原理
BRIEF 特征描述子
此示例演示了如何使用稀疏ORB特征对应来稳健地估计两个视图之间的极线几何。
基本矩阵涉及一对未校准图像之间的对应点。 矩阵将一个图像中的均匀图像点变换为另一个图像中的极线。
未校准意味着两个摄像机的固有校准(焦距,像素偏斜,主点)未知。 因此,基本矩阵能够实现捕获的场景的投影3D重建。 如果校准已知,则估计基本矩阵使得能够对捕获的场景进行度量3D重建。
import numpy as np
from skimage import data
from skimage.color import rgb2gray
from skimage.feature import match_descriptors, ORB, plot_matches
from skimage.measure import ransac
from skimage.transform import FundamentalMatrixTransform
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
np.random.seed(0)
img_left, img_right, groundtruth_disp = data.stereo_motorcycle()
img_left, img_right = map(rgb2gray, (img_left, img_right))
# Find sparse feature correspondences between left and right image.
descriptor_extractor = ORB()
descriptor_extractor.detect_and_extract(img_left)
keypoints_left = descriptor_extractor.keypoints #关键点左图
descriptors_left = descriptor_extractor.descriptors
descriptor_extractor.detect_and_extract(img_right)
keypoints_right = descriptor_extractor.keypoints#关键点位置右图 500X2
descriptors_right = descriptor_extractor.descriptors #每个关键点1X256维 总共500X256
matches = match_descriptors(descriptors_left, descriptors_right,
cross_check=True) #相匹配关键点的返回坐标值 【1~500】,有223个匹配,(223, 2)
# Estimate the epipolar geometry between the left and right image.
model, inliers = ransac((keypoints_left[matches[:, 0]], #model为模型参数 ,inliners 相匹配的坐标值 163X1
keypoints_right[matches[:, 1]]),
FundamentalMatrixTransform, min_samples=8,
residual_threshold=1, max_trials=5000)
#第一和第二组描述符中相应匹配的索引,其中匹配[:,0]表示第一组中的索引,并匹配第二组描述符中的索引[:,1]。model:具有最大共识集的最佳模型。inliers:数组分类为True的内部的布尔掩码
inlier_keypoints_left = keypoints_left[matches[inliers, 0]]
inlier_keypoints_right = keypoints_right[matches[inliers, 1]]
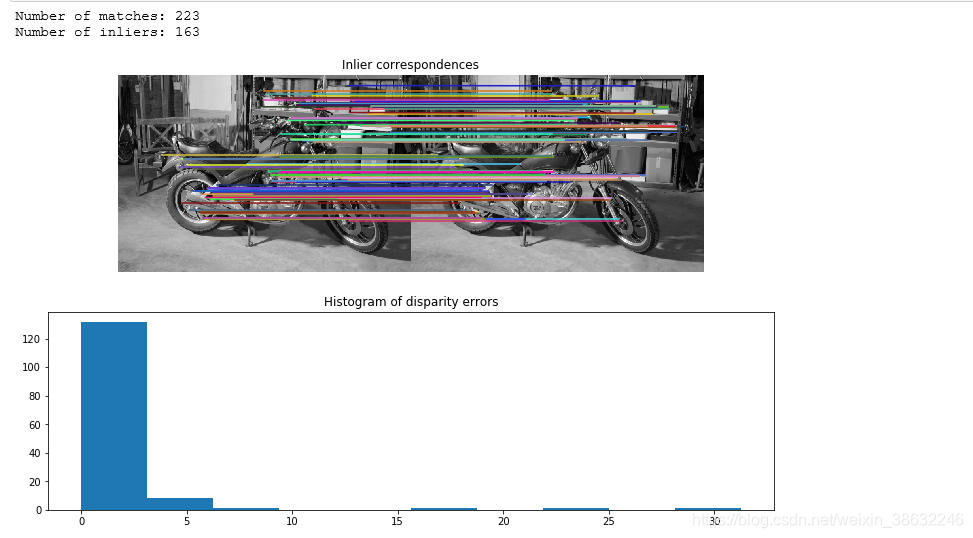
print("Number of matches:", matches.shape[0])
print("Number of inliers:", inliers.sum())
# Compare estimated sparse disparities to the dense ground-truth disparities.
disp = inlier_keypoints_left[:, 1] - inlier_keypoints_right[:, 1]
disp_coords = np.round(inlier_keypoints_left).astype(np.int64) #浮点转整形
disp_idxs = np.ravel_multi_index(disp_coords.T, groundtruth_disp.shape)
disp_error = np.abs(groundtruth_disp.ravel()[disp_idxs] - disp)
disp_error = disp_error[np.isfinite(disp_error)]
# Visualize the results.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=1,figsize=(13,8))
plt.gray()
plot_matches(ax[0], img_left, img_right, keypoints_left, keypoints_right,
matches[inliers], only_matches=True)
ax[0].axis("off")
ax[0].set_title("Inlier correspondences")
ax[1].hist(disp_error)
ax[1].set_title("Histogram of disparity errors")
plt.show()







 本文介绍如何使用ORB特征匹配算法进行图像对应点检测,通过RANSAC算法稳健估计两视图间的极线几何关系,实现场景的3D重建。文章详细展示了使用Python的skimage库进行特征提取、匹配及基本矩阵估计的过程。
本文介绍如何使用ORB特征匹配算法进行图像对应点检测,通过RANSAC算法稳健估计两视图间的极线几何关系,实现场景的3D重建。文章详细展示了使用Python的skimage库进行特征提取、匹配及基本矩阵估计的过程。
















 1234
1234

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








