SpringMVC(二)
- SpringMVC_如何确定目标方法POJO类型参数
- SpringMVC_ModelAttribute注解修饰POJO类型的入参
- SpringMVC_SessionAttributes注解引发的异常
- SpringMVC_视图解析流程分析
- SpringMVC_JstlView
- SpringMVC_mvc_view-controller标签
- SpringMVC_自定义视图
- SpringMVC_重定向
- SpringMVC_RESTRUL_CRUD_需求
- SpringMVC_RESTRUL_CRUD_显示所有员工信息
- SpringMVC_RESTRUL_CRUD_添加操作&表单标签
- SpringMVC_RESTRUL_CRUD_删除操作&处理静态资源
- SpringMVC_RESTRUL_CRUD_修改操作
- SpringMVC_数据绑定流程分析
- SpringMVC_自定义类型转换器
- SpringMVC_annotation-driven配置
- SpringMVC_InitBinder注解
- SpringMVC_数据的格式化
- SpringMVC_JSR303数据校验
- SpringMVC_错误消息的显示及国际化
SpringMVC_如何确定目标方法POJO类型参数
SpringMVC 确定目标方法 POJO 类型入参的过程
1. 确定一个 key:
1). 若目标方法的 POJO 类型的参数木有使用 @ModelAttribute 作为修饰, 则 key 为 POJO 类名第一个字母的小写
2). 若使用了 @ModelAttribute 来修饰, 则 key 为 @ModelAttribute 注解的 value 属性值.
2. 在 implicitModel 中查找 key 对应的对象, 若存在, 则作为入参传入
1). 若在 @ModelAttribute 标记的方法中在 Map 中保存过, 且 key 和 1 确定的 key 一致, 则会获取到.
3. 若 implicitModel 中不存在 key 对应的对象, 则检查当前的 Handler 是否使用 @SessionAttributes 注解修饰,
若使用了该注解, 且 @SessionAttributes 注解的 value 属性值中包含了 key, 则会从 HttpSession 中来获取 key 所
对应的 value 值, 若存在则直接传入到目标方法的入参中. 若不存在则将抛出异常.
4. 若 Handler 没有标识 @SessionAttributes 注解或 @SessionAttributes 注解的 value 值中不包含 key, 则
会通过反射来创建 POJO 类型的参数, 传入为目标方法的参数
5. SpringMVC 会把 key 和 POJO 类型的对象保存到 implicitModel 中, 进而会保存到 request
SpringMVC_ModelAttribute注解修饰POJO类型的入参
1. 有 @ModelAttribute 标记的方法, 会在每个目标方法执行之前被 SpringMVC 调用!
2. @ModelAttribute 注解也可以来修饰目标方法 POJO 类型的入参, 其 value 属性值有如下的作用:
1). SpringMVC 会使用 value 属性值在 implicitModel 中查找对应的对象, 若存在则会直接传入到目标方法的入参中.
2). SpringMVC 会以 value 为 key, POJO 类型的对象为 value, 存入到 request 中.
SpringMVC_SessionAttributes注解引发的异常
上面我们分析原理,我们就知道这个异常是怎么产生的:SpringMVC会先从标注 @ModelAttribute 注解的方法里面去找,查找是否有对应的值,如果没有 ,则会强制从@SessionAttributes里面去找,如果还没有找到,那么就会抛出异常;
SpringMVC 确定目标方法 POJO 类型入参的过程
1. 确定一个 key:
1). 若目标方法的 POJO 类型的参数木有使用 @ModelAttribute 作为修饰, 则 key 为 POJO 类名第一个字母的小写
2). 若使用了 @ModelAttribute 来修饰, 则 key 为 @ModelAttribute 注解的 value 属性值.
2. 在 implicitModel 中查找 key 对应的对象, 若存在, 则作为入参传入
1). 若在 @ModelAttribute 标记的方法中在 Map 中保存过, 且 key 和 1 确定的 key 一致, 则会获取到.
3. 若 implicitModel 中不存在 key 对应的对象, 则检查当前的 Handler 是否使用 @SessionAttributes 注解修饰,
若使用了该注解, 且 @SessionAttributes 注解的 value 属性值中包含了 key, 则会从 HttpSession 中来获取 key 所
对应的 value 值, 若存在则直接传入到目标方法的入参中. 若不存在则将抛出异常.
4. 若 Handler 没有标识 @SessionAttributes 注解或 @SessionAttributes 注解的 value 值中不包含 key, 则
会通过反射来创建 POJO 类型的参数, 传入为目标方法的参数
5. SpringMVC 会把 key 和 POJO 类型的对象保存到 implicitModel 中, 进而会保存到 request
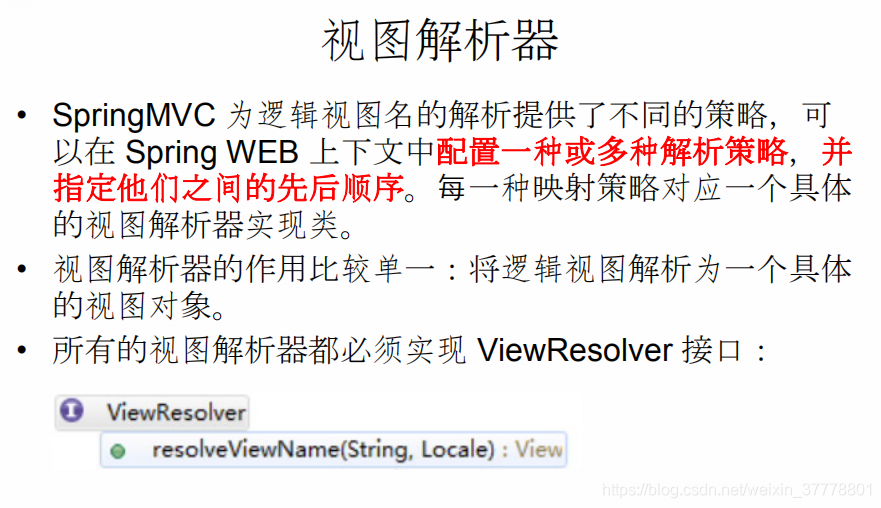
SpringMVC_视图解析流程分析



SpringMVC_JstlView

我们来配置一个国际化资源文件:
i18n.properties:
i18n.username=Username
i18n.password=Password
i18n_en_US.properties:
i18n.username=Username
i18n.password=Password
i18n_zh_CN.properties:
i18n.username=\u7528\u6237\u540D
i18n.password=\u5BC6\u7801
我们需要在SpringMVC的配置文件里面来进行配置国际化资源文件:
<!-- 配置国际化资源文件 -->
<bean id="messageSource"
class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource">
<property name="basename" value="i18n"></property>
</bean>
在页面就是可以这样来用 :
<fmt:message key="i18n.username"></fmt:message>
<br><br>
<fmt:message key="i18n.password"></fmt:message>
<br><br>
这个时候,我们切换浏览器的语言,就有国际化的效果了;
SpringMVC_mvc_view-controller标签
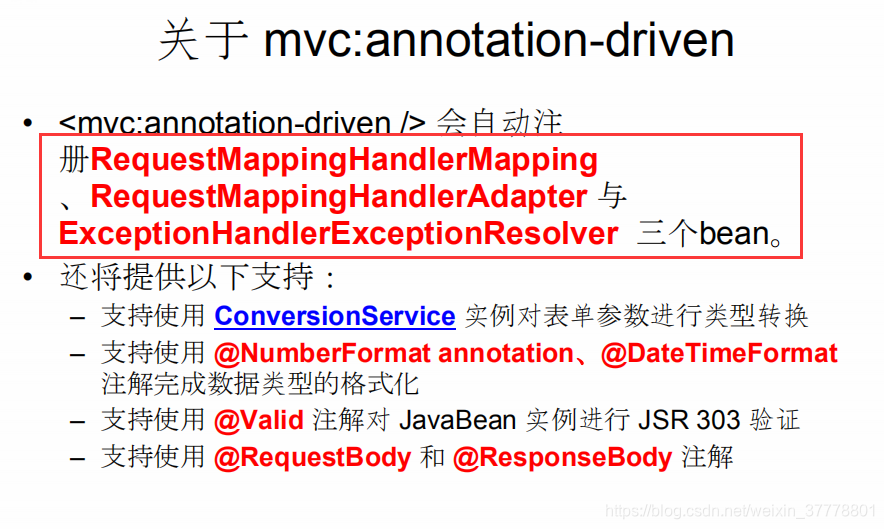
这样配置的话,就直接输入url就可以到指定的页面,而不需要经过Controller的映射:如果不加<mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven>这个配置,那么以前通过@RequestMapping("/success")映射的就不好使了
通常这两个是需要一起来用的:
<!-- 配置直接转发的页面 -->
<!-- 可以直接相应转发的页面, 而无需再经过 Handler 的方法. -->
<mvc:view-controller path="/success" view-name="success"/>
<!-- 在实际开发中通常都需配置 mvc:annotation-driven 标签 -->
<mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven>
SpringMVC_自定义视图
@Component
public class HelloView implements View{
@Override
public String getContentType() {
return "text/html";
}
@Override
public void render(Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
response.getWriter().print("hello view, time: " + new Date());
}
}
并且还要在SpringMVC的配置文件里面配置这个:
<!-- 配置视图 BeanNameViewResolver 解析器: 使用视图的名字来解析视图 -->
<!-- 通过 order 属性来定义视图解析器的优先级, order 值越小优先级越高 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.BeanNameViewResolver">
<property name="order" value="100"></property>
</bean>
SpringMVC_重定向

@RequestMapping("/testRedirect")
public String testRedirect(){
System.out.println("testRedirect");
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
}
SpringMVC_RESTRUL_CRUD_需求

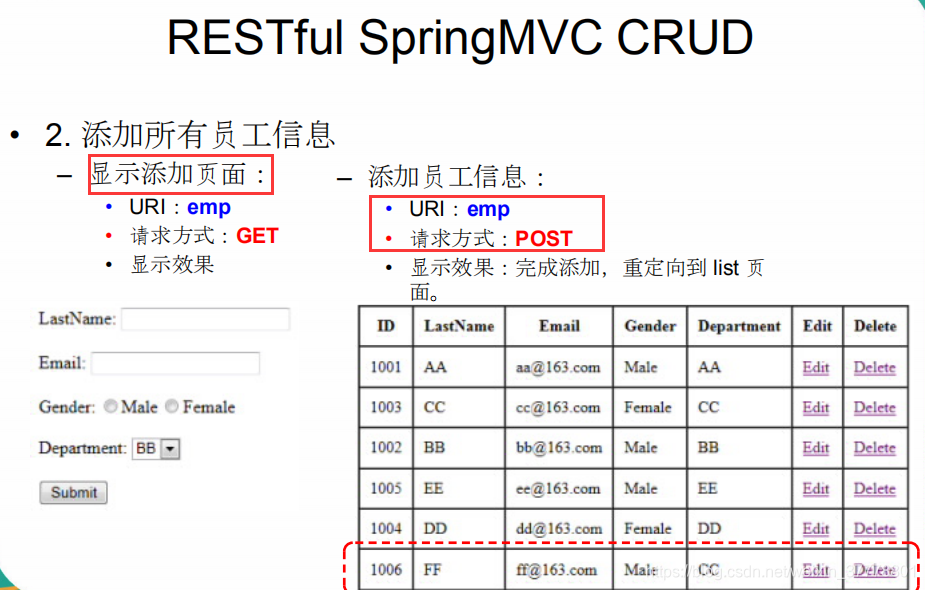

SpringMVC_RESTRUL_CRUD_显示所有员工信息
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"
id="WebApp_ID" version="2.5">
<!-- 配置 SpringMVC 的 DispatcherServlet -->
<!-- The front controller of this Spring Web application, responsible for handling all application requests -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springDispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<!-- Map all requests to the DispatcherServlet for handling -->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springDispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!-- 配置 HiddenHttpMethodFilter: 把 POST 请求转为 DELETE、PUT 请求 -->
<filter>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
</web-app>
Controller:
@Controller
public class EmployeeHandler {
@Autowired
private EmployeeDao employeeDao;
@Autowired
private DepartmentDao departmentDao;
@RequestMapping("/emps")
public String list(Map<String, Object> map){
map.put("employees", employeeDao.getAll());
return "list";
}
}
list.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<!--
SpringMVC 处理静态资源:
1. 为什么会有这样的问题:
优雅的 REST 风格的资源URL 不希望带 .html 或 .do 等后缀
若将 DispatcherServlet 请求映射配置为 /,
则 Spring MVC 将捕获 WEB 容器的所有请求, 包括静态资源的请求, SpringMVC 会将他们当成一个普通请求处理,
因找不到对应处理器将导致错误。
2. 解决: 在 SpringMVC 的配置文件中配置 <mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
-->
<script type="text/javascript" src="scripts/jquery-1.9.1.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function(){
$(".delete").click(function(){
var href = $(this).attr("href");
$("form").attr("action", href).submit();
return false;
});
})
</script>
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="POST">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="DELETE"/>
</form>
<c:if test="${empty requestScope.employees }">
没有任何员工信息.
</c:if>
<c:if test="${!empty requestScope.employees }">
<table border="1" cellpadding="10" cellspacing="0">
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>LastName</th>
<th>Email</th>
<th>Gender</th>
<th>Department</th>
<th>Edit</th>
<th>Delete</th>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="${requestScope.employees }" var="emp">
<tr>
<td>${emp.id }</td>
<td>${emp.lastName }</td>
<td>${emp.email }</td>
<td>${emp.gender == 0 ? 'Female' : 'Male' }</td>
<td>${emp.department.departmentName }</td>
<td><a href="emp/${emp.id}">Edit</a></td>
<td><a class="delete" href="emp/${emp.id}">Delete</a></td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
</c:if>
<br><br>
<a href="emp">Add New Employee</a>
</body>
</html>
SpringMVC_RESTRUL_CRUD_添加操作&表单标签
<%@page import="java.util.HashMap"%>
<%@page import="java.util.Map"%>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="testConversionServiceConverer" method="POST">
<!-- lastname-email-gender-department.id 例如: GG-gg@atguigu.com-0-105 -->
Employee: <input type="text" name="employee"/>
<input type="submit" value="Submit"/>
</form>
<br><br>
<!--
1. WHY 使用 form 标签呢 ?
可以更快速的开发出表单页面, 而且可以更方便的进行表单值的回显
2. 注意:
可以通过 modelAttribute 属性指定绑定的模型属性,
若没有指定该属性,则默认从 request 域对象中读取 command 的表单 bean
如果该属性值也不存在,则会发生错误。
-->
<br><br>
<form:form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/emp" method="POST"
modelAttribute="employee">
<form:errors path="*"></form:errors>
<br>
<c:if test="${employee.id == null }">
<!-- path 属性对应 html 表单标签的 name 属性值 -->
LastName: <form:input path="lastName"/>
<form:errors path="lastName"></form:errors>
</c:if>
<c:if test="${employee.id != null }">
<form:hidden path="id"/>
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="PUT"/>
<%-- 对于 _method 不能使用 form:hidden 标签, 因为 modelAttribute 对应的 bean 中没有 _method 这个属性 --%>
<%--
<form:hidden path="_method" value="PUT"/>
--%>
</c:if>
<br>
Email: <form:input path="email"/>
<form:errors path="email"></form:errors>
<br>
<%
Map<String, String> genders = new HashMap();
genders.put("1", "Male");
genders.put("0", "Female");
request.setAttribute("genders", genders);
%>
Gender:
<br>
<form:radiobuttons path="gender" items="${genders }" delimiter="<br>"/>
<br>
Department: <form:select path="department.id"
items="${departments }" itemLabel="departmentName" itemValue="id"></form:select>
<br>
<!--
1. 数据类型转换
2. 数据类型格式化
3. 数据校验.
1). 如何校验 ? 注解 ?
①. 使用 JSR 303 验证标准
②. 加入 hibernate validator 验证框架的 jar 包
③. 在 SpringMVC 配置文件中添加 <mvc:annotation-driven />
④. 需要在 bean 的属性上添加对应的注解
⑤. 在目标方法 bean 类型的前面添加 @Valid 注解
2). 验证出错转向到哪一个页面 ?
注意: 需校验的 Bean 对象和其绑定结果对象或错误对象时成对出现的,它们之间不允许声明其他的入参
3). 错误消息 ? 如何显示, 如何把错误消息进行国际化
-->
Birth: <form:input path="birth"/>
<form:errors path="birth"></form:errors>
<br>
Salary: <form:input path="salary"/>
<br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit"/>
</form:form>
</body>
</html>
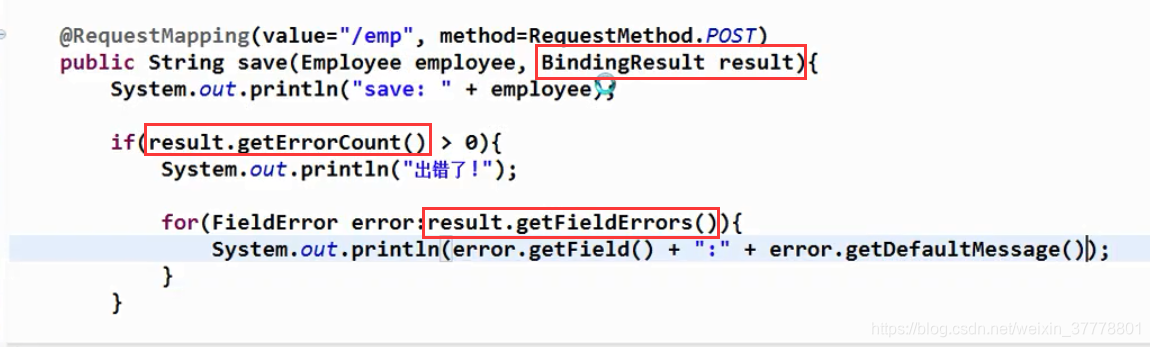
@RequestMapping(value="/emp", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public String save(@Valid Employee employee, Errors result,
Map<String, Object> map){
System.out.println("save: " + employee);
if(result.getErrorCount() > 0){
System.out.println("出错了!");
for(FieldError error:result.getFieldErrors()){
System.out.println(error.getField() + ":" + error.getDefaultMessage());
}
//若验证出错, 则转向定制的页面
map.put("departments", departmentDao.getDepartments());
return "input";
}
employeeDao.save(employee);
return "redirect:/emps";
}
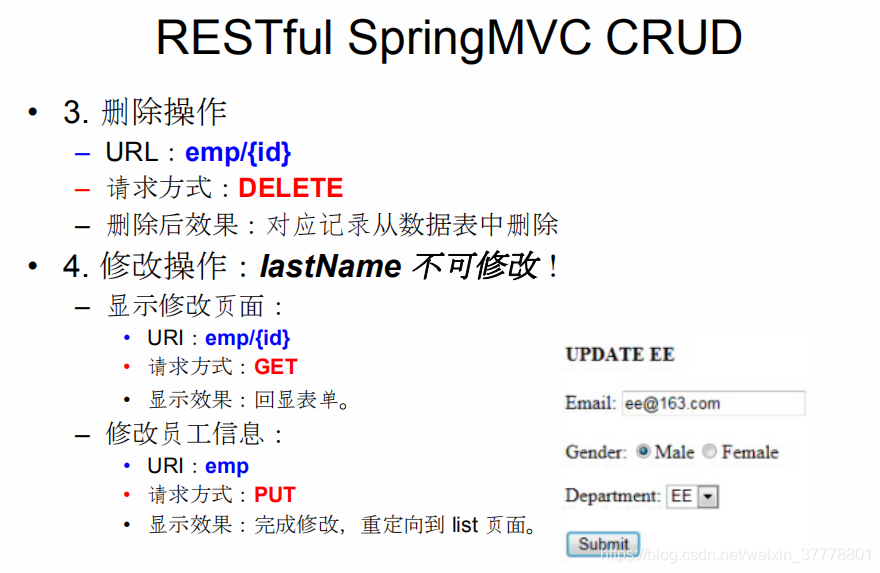
SpringMVC_RESTRUL_CRUD_删除操作&处理静态资源
@RequestMapping(value="/emp/{id}", method=RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String delete(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
employeeDao.delete(id);
return "redirect:/emps";
}

<!--
default-servlet-handler 将在 SpringMVC 上下文中定义一个 DefaultServletHttpRequestHandler,
它会对进入 DispatcherServlet 的请求进行筛查, 如果发现是没有经过映射的请求, 就将该请求交由 WEB 应用服务器默认的
Servlet 处理. 如果不是静态资源的请求,才由 DispatcherServlet 继续处理
一般 WEB 应用服务器默认的 Servlet 的名称都是 default.
若所使用的 WEB 服务器的默认 Servlet 名称不是 default,则需要通过 default-servlet-name 属性显式指定
-->
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService"></mvc:annotation-driven>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function(){
$(".delete").click(function(){
var href = $(this).attr("href");
$("form").attr("action", href).submit();
return false;
});
})
</script>
<form action="" method="POST">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="DELETE"/>
</form>
SpringMVC_RESTRUL_CRUD_修改操作
@RequestMapping(value="/emp", method=RequestMethod.PUT)
public String update(Employee employee){
employeeDao.save(employee);
return "redirect:/emps";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/emp/{id}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String input(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, Map<String, Object> map){
map.put("employee", employeeDao.get(id));
map.put("departments", departmentDao.getDepartments());
return "input";
}
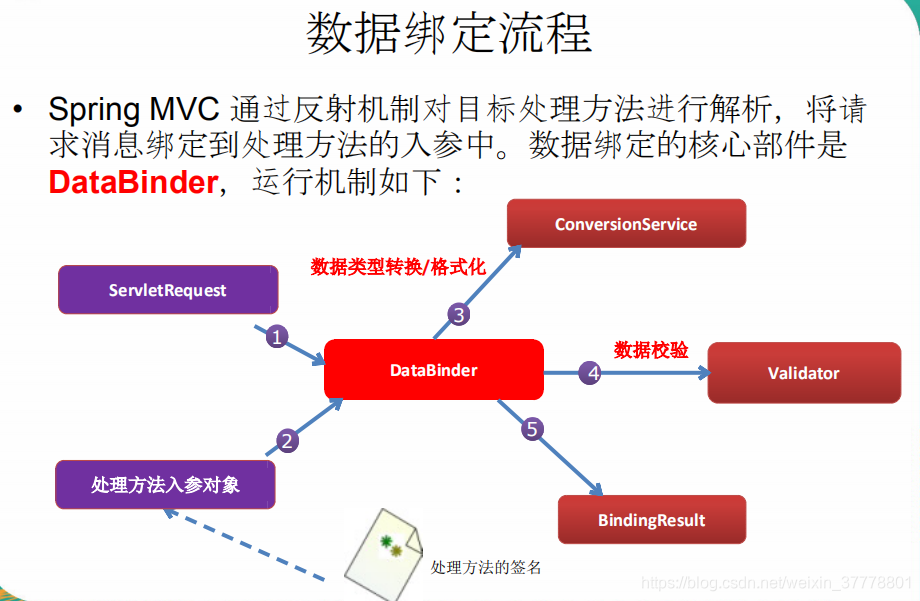
SpringMVC_数据绑定流程分析



<!--
1. 数据类型转换
2. 数据类型格式化
3. 数据校验.
1). 如何校验 ? 注解 ?
①. 使用 JSR 303 验证标准
②. 加入 hibernate validator 验证框架的 jar 包
③. 在 SpringMVC 配置文件中添加 <mvc:annotation-driven />
④. 需要在 bean 的属性上添加对应的注解
⑤. 在目标方法 bean 类型的前面添加 @Valid 注解
2). 验证出错转向到哪一个页面 ?
注意: 需校验的 Bean 对象和其绑定结果对象或错误对象时成对出现的,它们之间不允许声明其他的入参
3). 错误消息 ? 如何显示, 如何把错误消息进行国际化
-->
Birth: <form:input path="birth"/>
<form:errors path="birth"></form:errors>
SpringMVC_自定义类型转换器


<form action="testConversionServiceConverer" method="POST">
<!-- lastname-email-gender-department.id 例如: GG-gg@atguigu.com-0-105 -->
Employee: <input type="text" name="employee"/>
<input type="submit" value="Submit"/>
</form>
前端传的是一个字符串:
@RequestMapping("/testConversionServiceConverer")
public String testConverter(@RequestParam("employee") Employee employee){
System.out.println("save: " + employee);
employeeDao.save(employee);
return "redirect:/emps";
}
这个时候,我们就来写一个Converter:
@Component
public class EmployeeConverter implements Converter<String, Employee> {
@Override
public Employee convert(String source) {
if(source != null){
String [] vals = source.split("-");
//GG-gg@atguigu.com-0-105
if(vals != null && vals.length == 4){
String lastName = vals[0];
String email = vals[1];
Integer gender = Integer.parseInt(vals[2]);
Department department = new Department();
department.setId(Integer.parseInt(vals[3]));
Employee employee = new Employee(null, lastName, email, gender, department);
System.out.println(source + "--convert--" + employee);
return employee;
}
}
return null;
}
}
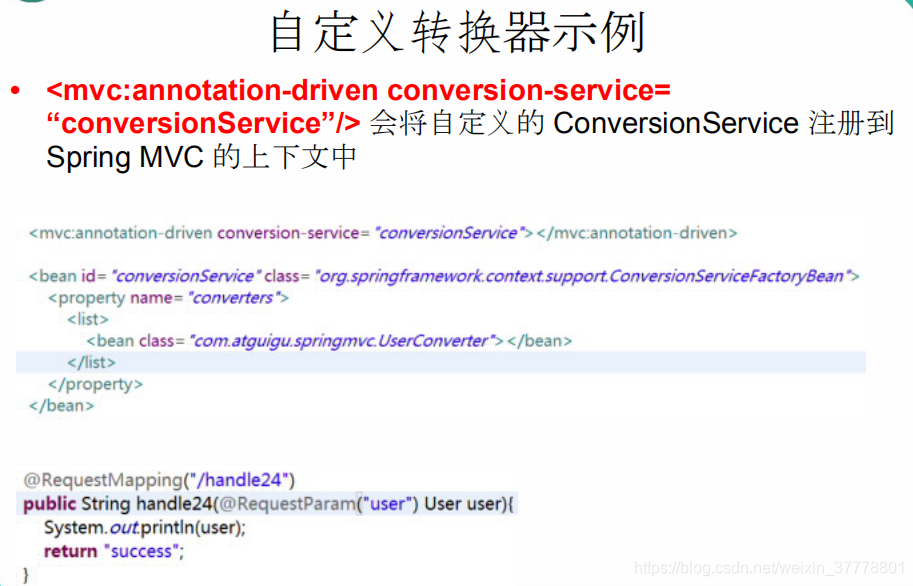
我们还要在SpringMVC的配置文件里面进行注册:
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService"></mvc:annotation-driven>
<!-- 配置 ConversionService -->
<bean id="conversionService"
class="org.springframework.format.support.FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<property name="converters">
<set>
<ref bean="employeeConverter"/>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
这个时候,我们再来试,就已经把字符串转成了Employee对象了;
SpringMVC_annotation-driven配置
SpringMVC_InitBinder注解
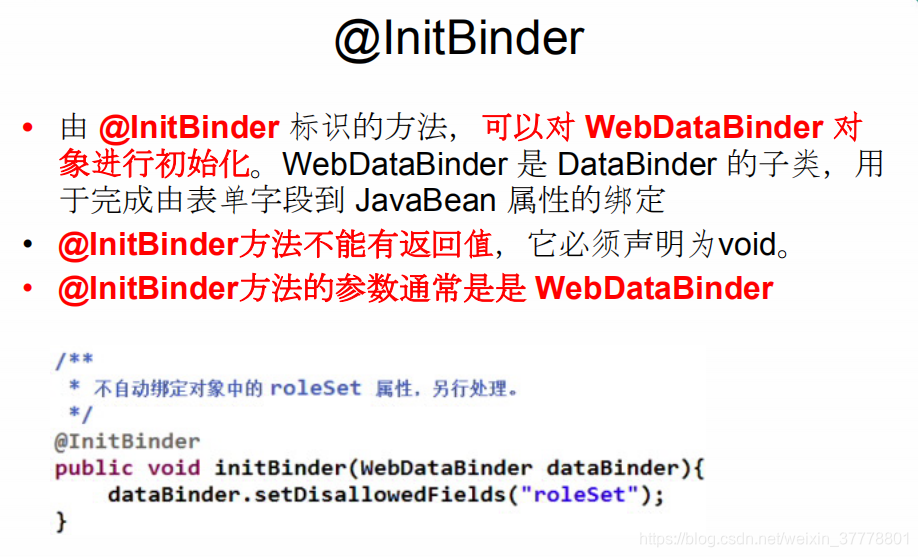
这个时候,lastName是不进行赋值的:
@InitBinder
public void initBinder(WebDataBinder binder){
binder.setDisallowedFields("lastName");
}
SpringMVC_数据的格式化
- 配置
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService"></mvc:annotation-driven> - 在目标属性上加上注解:
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
@NotEmpty
private String lastName;
@Email
private String email;
//1 male, 0 female
private Integer gender;
private Department department;
@Past
@DateTimeFormat(pattern="yyyy-MM-dd")
private Date birth;
@NumberFormat(pattern="#,###,###.#")
private Float salary;
}




<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService"></mvc:annotation-driven>
<!-- 配置 ConversionService -->
<bean id="conversionService"
class="org.springframework.format.support.FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<property name="converters">
<set>
<ref bean="employeeConverter"/>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
这样写的话,我们即能使用自己定义的类型转换器,又能使用@DateTimeFormat和@NumberFormat这两个注解;
如果类型转换失败,可以在这个对象里面进行获取:
SpringMVC_JSR303数据校验
1. 数据类型转换
2. 数据类型格式化
3. 数据校验.
1). 如何校验 ? 注解 ?
①. 使用 JSR 303 验证标准
②. 加入 hibernate validator 验证框架的 jar 包
③. 在 SpringMVC 配置文件中添加 <mvc:annotation-driven />
④. 需要在 bean 的属性上添加对应的注解
⑤. 在目标方法 bean 类型的前面添加 @Valid 注解
2). 验证出错转向到哪一个页面 ?
注意: 需校验的 Bean 对象和其绑定结果对象或错误对象时成对出现的,它们之间不允许声明其他的入参
3). 错误消息 ? 如何显示, 如何把错误消息进行国际化





public class Employee {
private Integer id;
@NotEmpty
private String lastName;
@Email
private String email;
//1 male, 0 female
private Integer gender;
private Department department;
@Past
@DateTimeFormat(pattern="yyyy-MM-dd")
private Date birth;
@NumberFormat(pattern="#,###,###.#")
private Float salary;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Integer getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(Integer gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public Department getDepartment() {
return department;
}
public void setDepartment(Department department) {
this.department = department;
}
public Date getBirth() {
return birth;
}
public void setBirth(Date birth) {
this.birth = birth;
}
public Float getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(Float salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [id=" + id + ", lastName=" + lastName + ", email="
+ email + ", gender=" + gender + ", department=" + department
+ ", birth=" + birth + ", salary=" + salary + "]";
}
public Employee(Integer id, String lastName, String email, Integer gender,
Department department) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.email = email;
this.gender = gender;
this.department = department;
}
public Employee() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
}
SpringMVC_错误消息的显示及国际化
显示的话 ,我们只需要加上这样的标签就可以了:


配置国际化资源文件:
<!-- 配置国际化资源文件 -->
<bean id="messageSource"
class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource">
<property name="basename" value="i18n"></property>
</bean>







 本文深入探讨SpringMVC框架的高级特性,包括数据绑定流程、自定义类型转换器、数据格式化、JSR303数据校验、错误消息国际化及RESTful CRUD操作。详细分析了@ModelAttribute、@SessionAttributes、@InitBinder等注解的使用场景,以及如何通过配置实现国际化资源文件、自定义视图、重定向和静态资源处理。
本文深入探讨SpringMVC框架的高级特性,包括数据绑定流程、自定义类型转换器、数据格式化、JSR303数据校验、错误消息国际化及RESTful CRUD操作。详细分析了@ModelAttribute、@SessionAttributes、@InitBinder等注解的使用场景,以及如何通过配置实现国际化资源文件、自定义视图、重定向和静态资源处理。
















 232
232

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








