目录
AnnotaionConfigApplicationContext
AnnotaionConfigApplicationContext
指定配置类生成IOC容器
@Test
public void test1(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class);
User user = applicationContext.getBean("user1", User.class);
System.out.println(user);
}@AliasFor
设置别名,用于为注解属性声明别名
spring-@AliasFor注解_Just-Today的博客-优快云博客
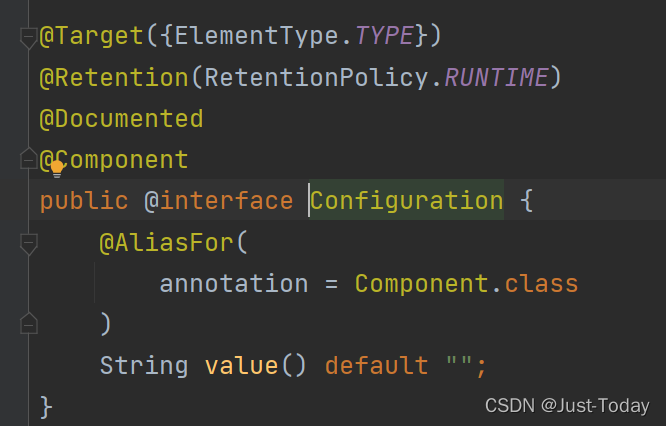
@Configuration
表示标记该注解的类是一个spring配置类,可代替xml配置文件
@ComponentScan
指定扫描组件所在的包
参考【Spring注解】@ComponentScan之includeFilters和excludeFilters_小白伐的博客-优快云博客
public enum FilterType {
//根据注解类型过滤
ANNOTATION,
//根据指定类的类型过滤
ASSIGNABLE_TYPE,
//ASPECTJ表达式
ASPECTJ,
//正则表达式
REGEX,
//自定义过滤规则,TypeFilter接口实现类
CUSTOM
}@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.mzp.component",useDefaultFilters = false,
includeFilters = {
//@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, classes = Controller.class),
//@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE, classes = {TestConfig.class}),
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM,classes = {TestCustomFilter.class})
})
public class Config {
@Bean()
public User getUser(){
return new User("user1", 11);
}
}public class TestCustomFilter implements TypeFilter {
@Override
public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) throws IOException {
ClassMetadata classMetadata = metadataReader.getClassMetadata();
System.out.println(classMetadata.getClassName());
return true;
}
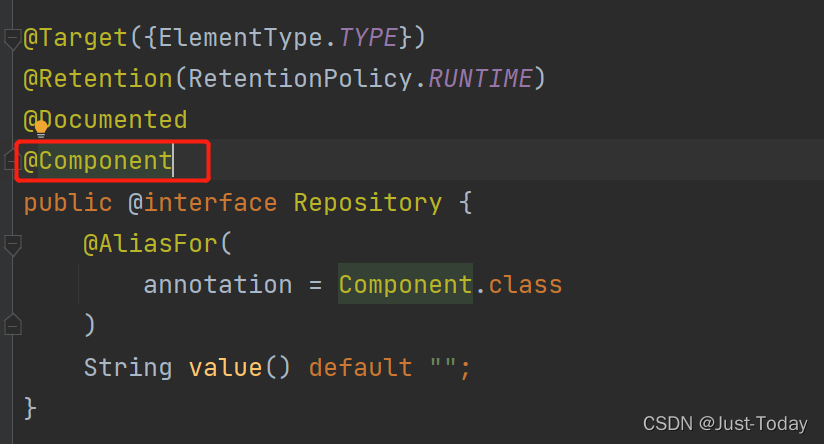
}@Component
标明某个类是Spring的Bean,需要Spring容器进行管理
指定id
@Component("id")
@Repository、@Controller、@Service与@Component作用一样,底层也使用了@Component注解
@Bean
在配置类中标记该注解的方法的返回值对象将会由spring容器进行管理,名称默认是方法名,类型是返回值类型,可通过@Bean的value指定名称
@Bean("beanUser")
public User getUser(){
return new User("jack");
}@Scope
设置bean作用域,默认是singleton(单例模式)
/*
singleton:单例,ioc容器创建时调用方法创建该对象放到ioc容器
prototype:多实例,ioc容器创建时不会创建该对象,每次获取该对象时才会调用方法创建对象
request:同一个request请求创建一个实例
session:同一个session请求创建一个实例
*/
@Scope("prototype")
@Bean()
public User getUser(){
return new User("user1", 11);
}@Lazy
懒加载,在单例模式下,ioc容器创建时并不会立刻调用方法创建对象,而是在第一次调用(获取)时调用方法创建对象并放到ioc容器中
@Lazy
@Bean()
public User getUser(){
System.out.println("创建user");
return new User("user1", 11);
}@Conditional
满足特定条件后,将bean注册到ioc容器中
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Conditional {
Class<? extends Condition>[] value();
}通过实现Condition接口来自定义条件
public class WindowCondition implements Condition {
/**
*
* @param context 上下文
* @param metadata 相关类或方法上的注解信息
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
Environment environment = context.getEnvironment();
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
if (property.contains("Window")){
return true;
}
//System.out.println(metadata);
return false;
}
}@Conditional(WindowCondition.class)//注解在类上,满足特定条件后,将该bean对象注册到ioc容器中
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.mzp.component.config")
public class TestConditional {
@Bean
public User getUser2(){
return new User("user2", 1);
}
@Bean("windowUser")
public User getUser(){
return new User("window", 1);
}
@Bean("linuxUser")
@Conditional(LinuxCondition.class)//注解在方法上,满足条件后,将方法返回值注册到ioc容器中
public User getUser1() {
return new User("linux", 1);
}
}@Import
快速给容器中导入组件
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Import {
/**
* {@link Configuration}, {@link ImportSelector}, {@link ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar}
* or regular component classes to import.
*/
//组件的class、ImportSelector、ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar的实现类
Class<?>[] value();
}
@Import({Blue.class, MyImportSelector.class, MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class})public class MyImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
/**
*
* @param importingClassMetadata 当前标识Import注解的类的所有注解信息
* @return 返回组件的全类名
*/
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
return new String[]{"com.mzp.component.service.Red"};
}
}public class MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
/**
*
* @param importingClassMetadata 标识Import注解的类的所有注解信息
* @param registry Bean定义的注册类
*/
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
//定义bean,例如该bean的作用域
RootBeanDefinition rootBeanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(RainRow.class);
registry.registerBeanDefinition("rain",rootBeanDefinition);
}
}@AutoWired
默认按照属性类型注入。
若是有多个相同类型,则以属性名称为id注入属性,若是以属性名称为id找不到相同名称id的bean组件,则报错。
可通过设置required属性为false,获取不到对应bean组件,不报错
@Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Autowired {
/**
* Declares whether the annotated dependency is required.
* <p>Defaults to {@code true}.
*/
boolean required() default true;
}@Autowired可使用在构造器、方法、参数、属性、注解定义类上
注意:注入规则跟在属性上一致,默认按照类型注入,多个相同类型则按参数id注入
1、构造器
标记在有参构造器上,则参数会从IOC容器中根据类型获取并赋值到对应参数。
若是只有一个有参构造器,则可省略@Autowird注解。
注意:
a)构造器上的参数需要从容器中获取,若是获取不到,则报错,可通过@Autowired里的required属性设置false,则获取不到,不报错。
b)参数需为引用类型
@Component
public class Color {
@Autowired
public Color(Red red){
this.red2 = red;
}
private Red red2;
public Red getRed2() {
return red2;
}
public void setRed2(Red red2) {
this.red2 = red2;
}
}
2、方法
package com.mzp.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Color {
private Red red2;
public Red getRed2() {
return red2;
}
@Autowired
@Qualifier("red")
public void setRed2(Red red1) {
this.red2 = red1;
}
}
标记@Bean的方法的参数,参数从容器中获取,@Autowired可省略
@Bean
public Red red(@Autowired Dog dog){
return new Red();
}3、参数
标记在参数上,只能标记在构造器或@Bean注解方法上才有效,若是只有一个有参构造器,也可省略注解
注意:
a)构造器上的参数需要从容器中获取,若是获取不到,则报错,可通过@Autowired里的required属性设置false,则获取不到,不报错。
b)参数需为引用类型
package com.mzp.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Color {
public Color(Red red, Red red1, @Autowired(required = false)@Qualifier("t")Red t){
System.out.println(red);
System.out.println(red1);
}
private Red red2;
public Red getRed2() {
return red2;
}
public void setRed2(Red red1) {
this.red2 = red1;
}
}
4、属性
package com.mzp.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Color {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("red1")
private Red red2;
public Red getRed2() {
return red2;
}
public void setRed2(Red red2) {
this.red2 = red2;
}
}
@Qualifier
与@AutoWired注解配合使用,可用该注解指定id
@Primary
可在对应bean加上该注解,则使用@Autowired进行自动装配时,若有多个相同类型的组件,则优先将标识@Primary注解的组件注入属性中(若使用@Qualifier则会注入指定名称id的组件)
注意:同一类型只能标识其中一个组件,否则报错
@Resource
该注解是Java注解。
默认根据属性类型注入属性,可通过指定name来指定id注入属性
package com.mzp.bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Component
public class Color {
@Resource(name = "red1")
private Red red;
public Red getRed() {
return red;
}
public void setRed(Red red) {
this.red = red;
}
}
@Inject
@inject注解是Java注解,使用需引入依赖。
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/javax.inject/javax.inject -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.inject</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.inject</artifactId>
<version>1</version>
</dependency>
功能与@Autowired功能一致,少了required属性功能。可与spring@Qualifier、@Primary注解配套使用。
package com.mzp.bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.inject.Inject;
@Component
public class Color {
@Inject
private Red red;
public Red getRed() {
return red;
}
public void setRed2(Red red) {
this.red = red;
}
}
@PropertySource
将指定配置文件加载到容器中
可通过IOC容器的environment属性获取对应配置文件key-value值或者@Value注解获取
SpringIOC容器中BeanPostProcessor后置处理器处理标识该注解,将配置文件解析配置到容器中。
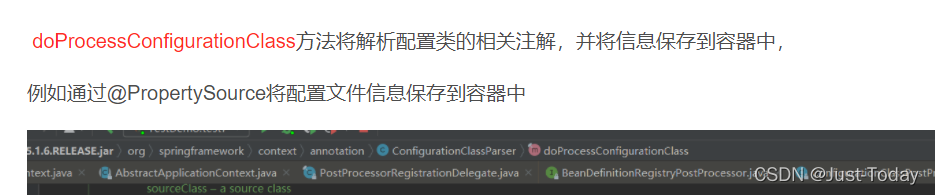
可参考:spring-bean生命周期_Just-Today的博客-优快云博客
package com.mzp.component.config;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.api.R;
import com.mzp.bean.Red;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.mzp.bean"})
@PropertySource(name="test",value = {"classpath:/test.properties"})
public class ConfigurationAutowired {
@Bean
public Red red(){
return new Red();
}
@Bean
public Red red1(){
return new Red();
}
}
@Test
public void test9(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConfigurationAutowired.class);
String property = applicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty("test.name");
System.out.println(property);
}@Value
单一属性注入值
1、普通类型
@Value("11")
private String value;2、SpEl表达式,通过@Value("#{表达式}")
@Value("#{11*11}")
private String value;3、从IOC配置文件中获取对应值,通过@Value("${key}"),若是找不到,则直接将${key}字符串返回
@Value("${test.name}")
private String value;@Profile
@Profile可根据当前环境,动态激活或切换一系列组件的功能,也就是根据@Profile的value参数判断当前环境是否符合并加载该组件到IOC容器中。
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(ProfileCondition.class)
public @interface Profile {
/**
* The set of profiles for which the annotated component should be registered.
*/
String[] value();
}例如在开发环境、测试环境、生产环境下加载不同组件。
若标记在类上,则符合环境后,该类组件和内部相关配置才会被加载到容器中。
若是不指定环境标识,默认是default环境,则default默认被加载到容器中。
没有指定@Profile环境标识的bean组件,任何环境都可被加载。
package com.mzp.component.config;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.api.R;
import com.mzp.bean.Dog;
import com.mzp.bean.Red;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.mzp.bean"})
@PropertySource(name="test",value = {"test.properties"})
public class ConfigurationAutowired {
@Bean("test")
@Profile({"test"})
public Red red(){
return new Red();
}
@Bean("dev")
@Profile("dev")
public Red red1(){
return new Red();
}
@Bean("default")
@Profile("default")//若是不指定环境标识,默认是default环境,则default默认被加载到容器中
public Red red2(){
return new Red();
}
}
1、在容器刷新之前设置好环境
@Test
public void test9(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
applicationContext.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("test");
applicationContext.register(ConfigurationAutowired.class);
applicationContext.refresh();
for (String s : applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(Red.class)) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
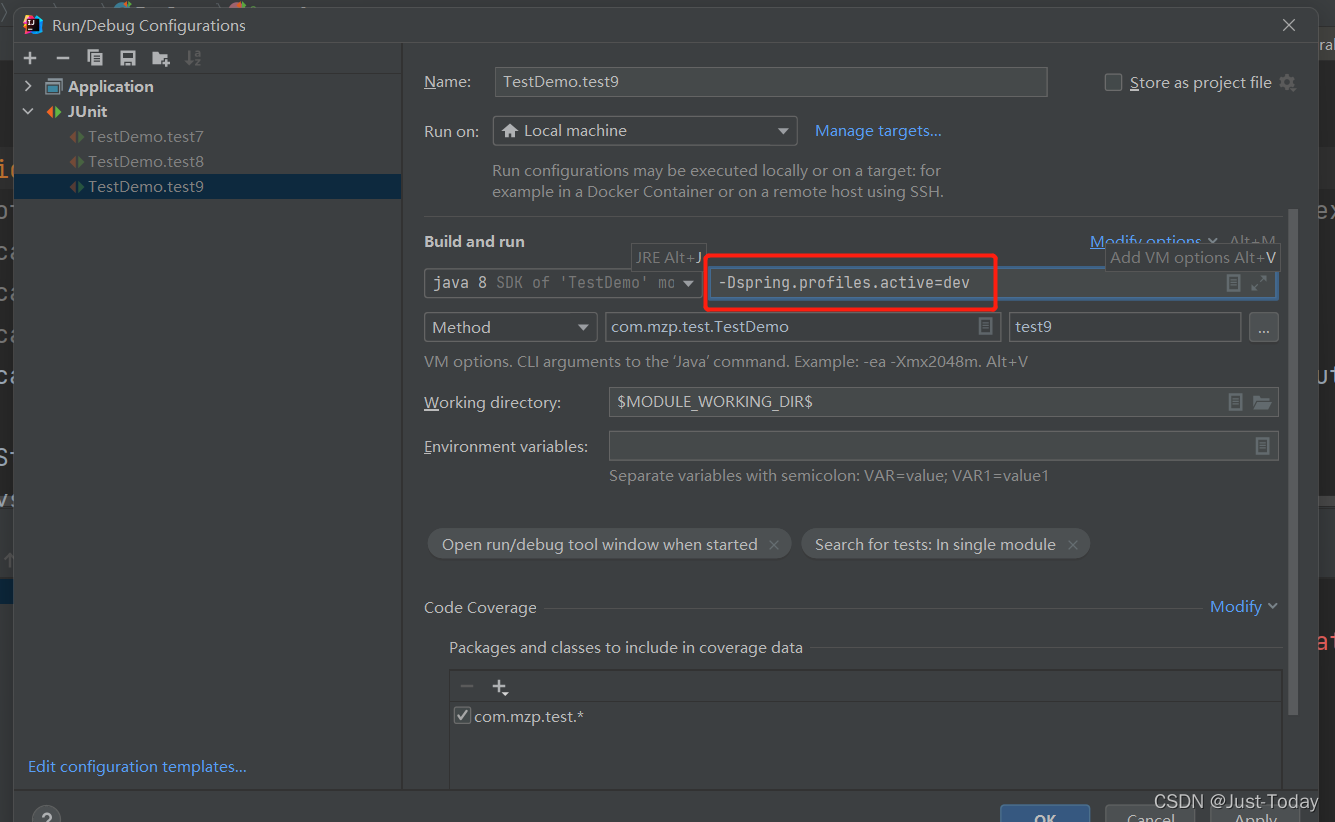
2、通过命令行参数设置环境
@Test
public void test9(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConfigurationAutowired.class);
for (String s : applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(Red.class)) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}-Dspring.profiles.active=dev
 Spring核心注解详解
Spring核心注解详解























 852
852

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








