之前一直对spring中bean的初始化顺序模糊不清,感觉作用都一样,也没去认真的去看看它的源码,直到遇到问题才想着去认真看下,这拖延症真的是太可怕了。
首先说下结论再去跟着结论去看源码。
bean的构造方法-----》属性赋值-----》BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法-----》@PostConstruct注解修饰的方法-----》InitializingBean接口afterPropertiesSet方法---》Init-method方法----》BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法。
跟着这个结论来一起看下源码是怎么实现的。
1.首先看下这个容器入口。
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringDemo.class);
2.查看该构造方法 可以看到初始化方法refresh()
3.进入refresh()方法,可以看到在BeanFactory初始化完成后进去finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法加载所有的单例对象。
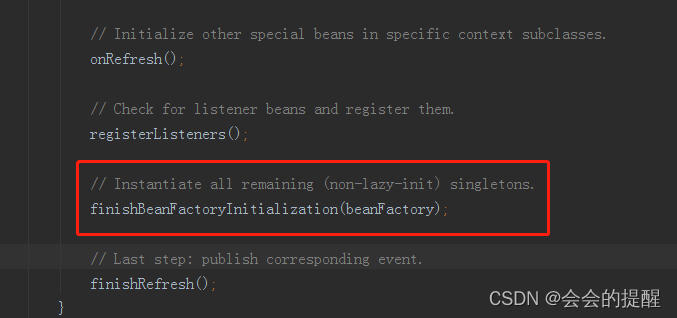
4.通过 beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons()实例化所有的单例对象
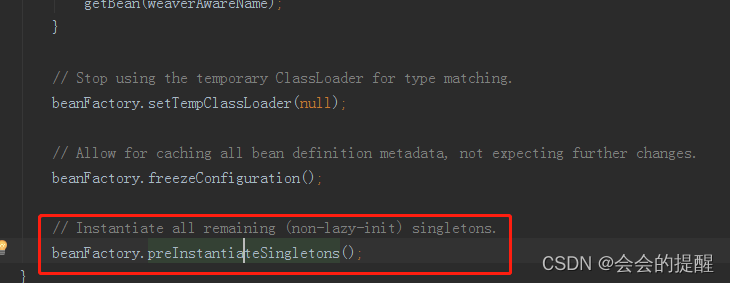
5.在该方法中通过bean名称来获取该bean的元数据,调用getBean()方法获取bean实例。
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
List<String> beanNames;
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
beanNames = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
}
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() {
public Boolean run() {
return ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit();
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
}
6.进去doGetBean方法。该方法前面是从容器中去获取bean,获取不到走底下的创建这个bean实例逻辑。
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() {
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
7.进去 createBean方法,首先会初始化bean实例
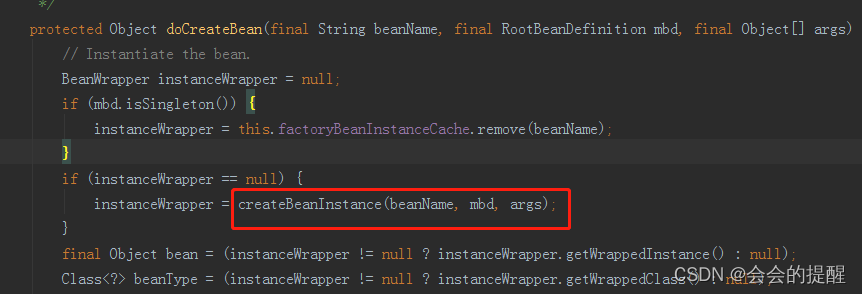
下面会通过 populateBean方法给实例的属性赋值。接着会执行初始化动作。
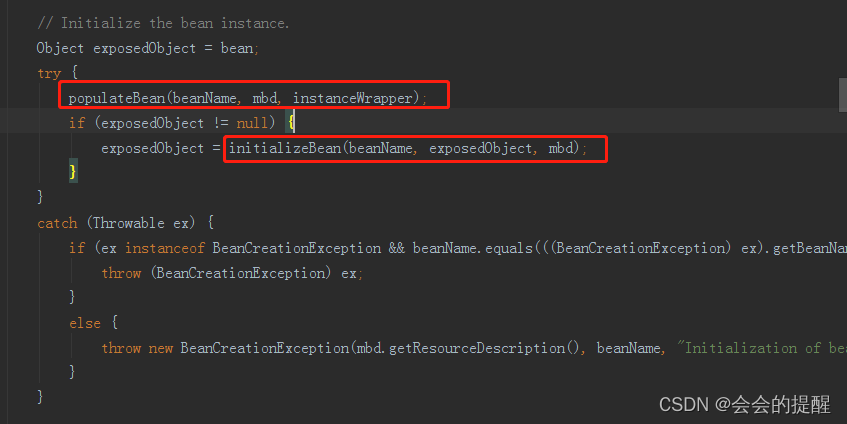
8.来看下初始化方法initializeBean。从方法名称上可以清楚的看到后置处理器的before先执行,中间是initMethod方法,最后是后置处理器的After方法。
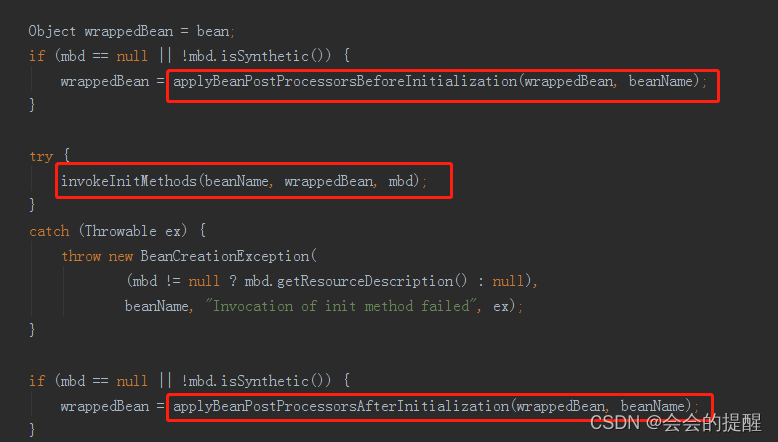
9.进去applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization方法。获取所有的BeanPostProcessor接口实现类来进行匹配,这是Spring的一个扩展点,而我们的@PostConstruct就是通过这种扩展机制实现的,它对应的类是InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor。
可以看到有该注解的存在
10.现在我们进入下面的方法invokeInitMethods,该方法逻辑简单,判断是否实现了InitializingBean接口下面再判断了是否有自定义初始化方法。
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() {
public Object run() throws Exception {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw pae.getException();
}
}
else {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
}
if (mbd != null) {
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
if (initMethodName != null && !(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
}
}
10.最后是后置处理器的after方法。




 这篇博客详细解析了Spring中Bean的初始化过程,从构造方法开始,经过属性赋值,到BeanPostProcessor的前后处理方法,再到@PostConstruct注解的方法和InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet方法,最后是Init-method指定的初始化方法。博主通过跟踪源码,逐步揭示了Bean初始化的整个流程,强调了理解和掌握这一过程对于解决实际问题的重要性。
这篇博客详细解析了Spring中Bean的初始化过程,从构造方法开始,经过属性赋值,到BeanPostProcessor的前后处理方法,再到@PostConstruct注解的方法和InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet方法,最后是Init-method指定的初始化方法。博主通过跟踪源码,逐步揭示了Bean初始化的整个流程,强调了理解和掌握这一过程对于解决实际问题的重要性。
















 2284
2284










